An Iterative Learning Control Strategy for Traffic Signals Considering NonlinearCharacteristics of Traffic Flow
-
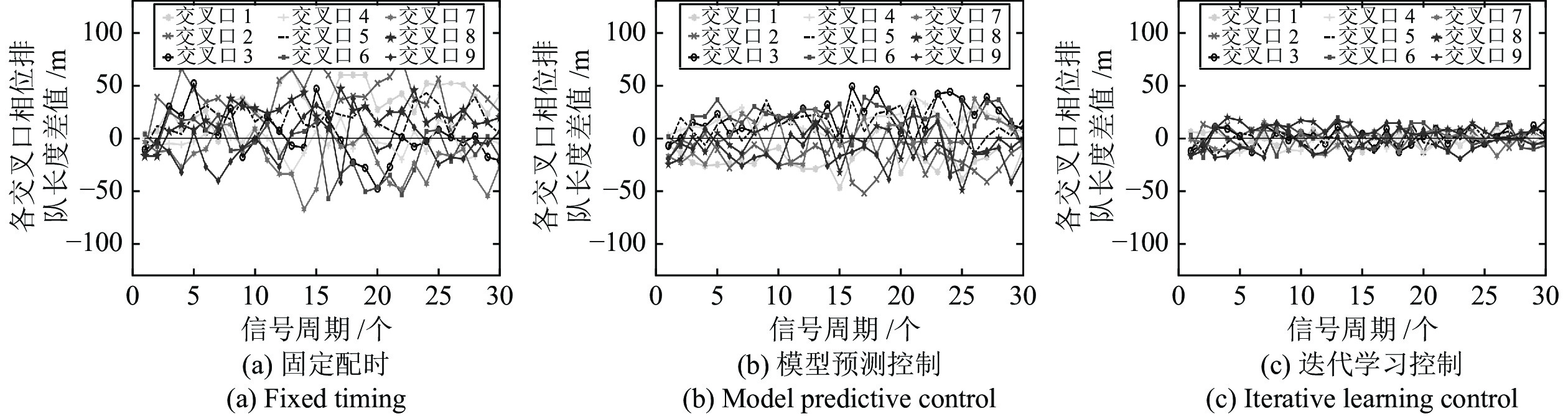
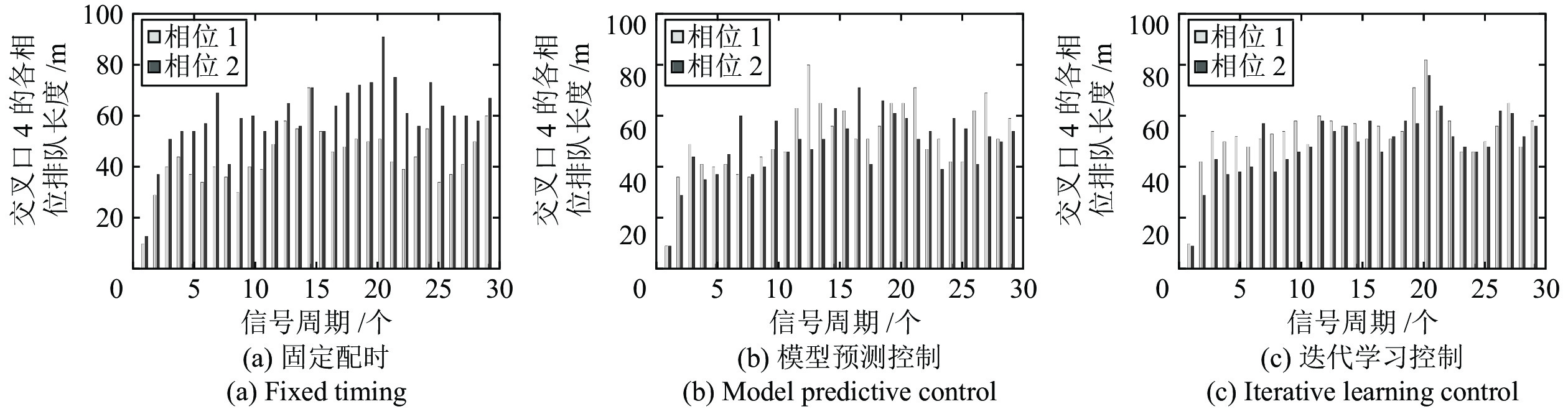
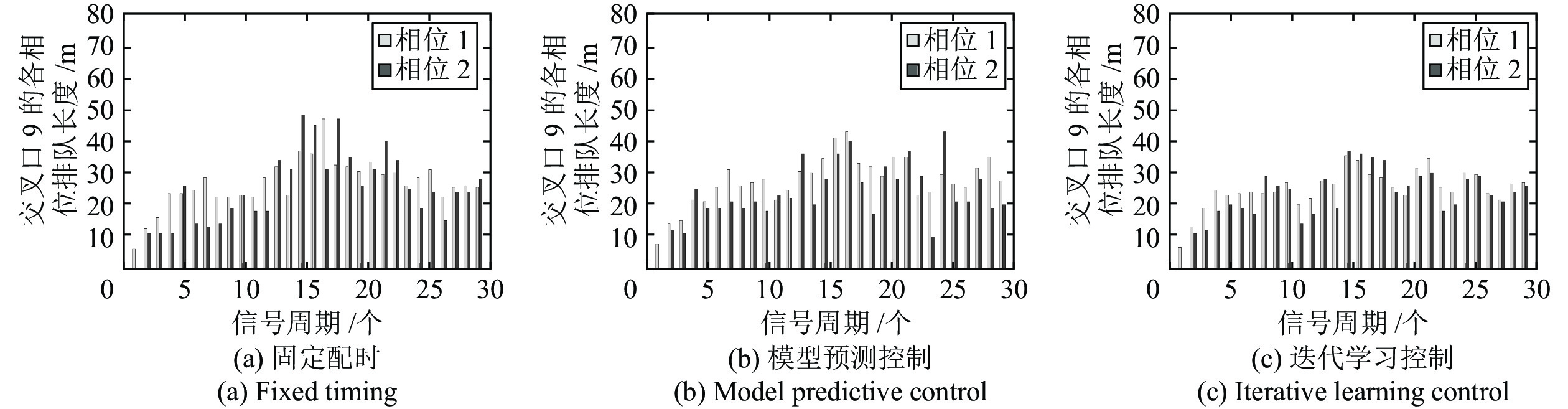
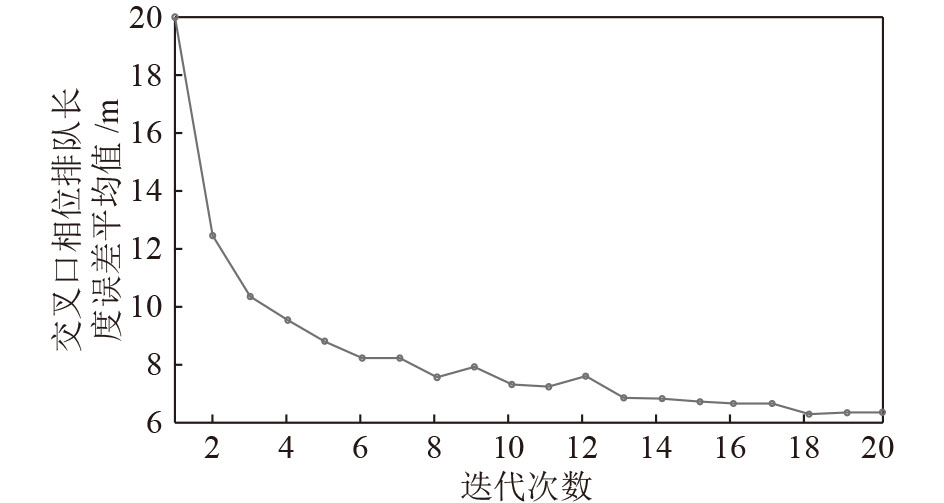
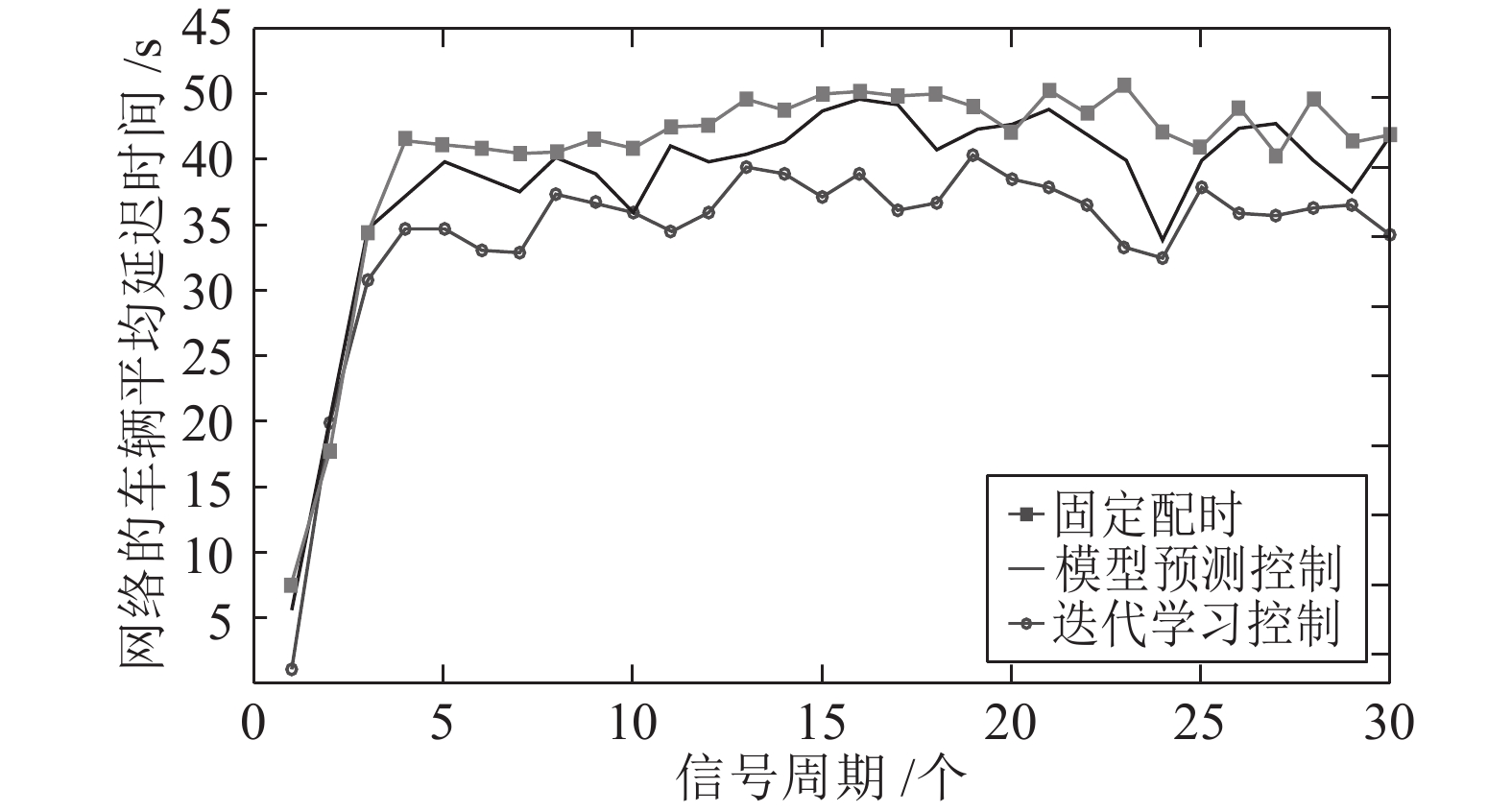
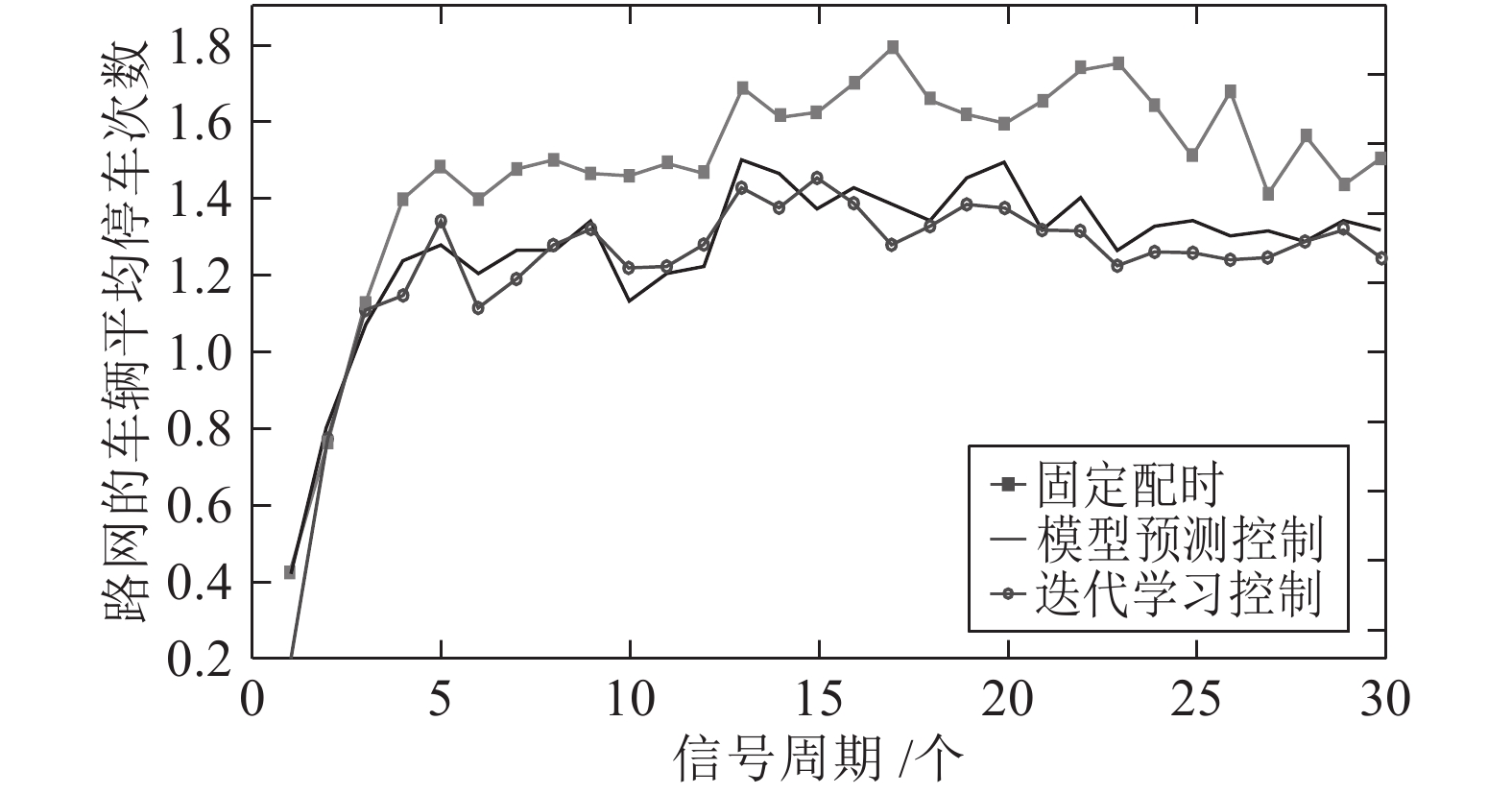
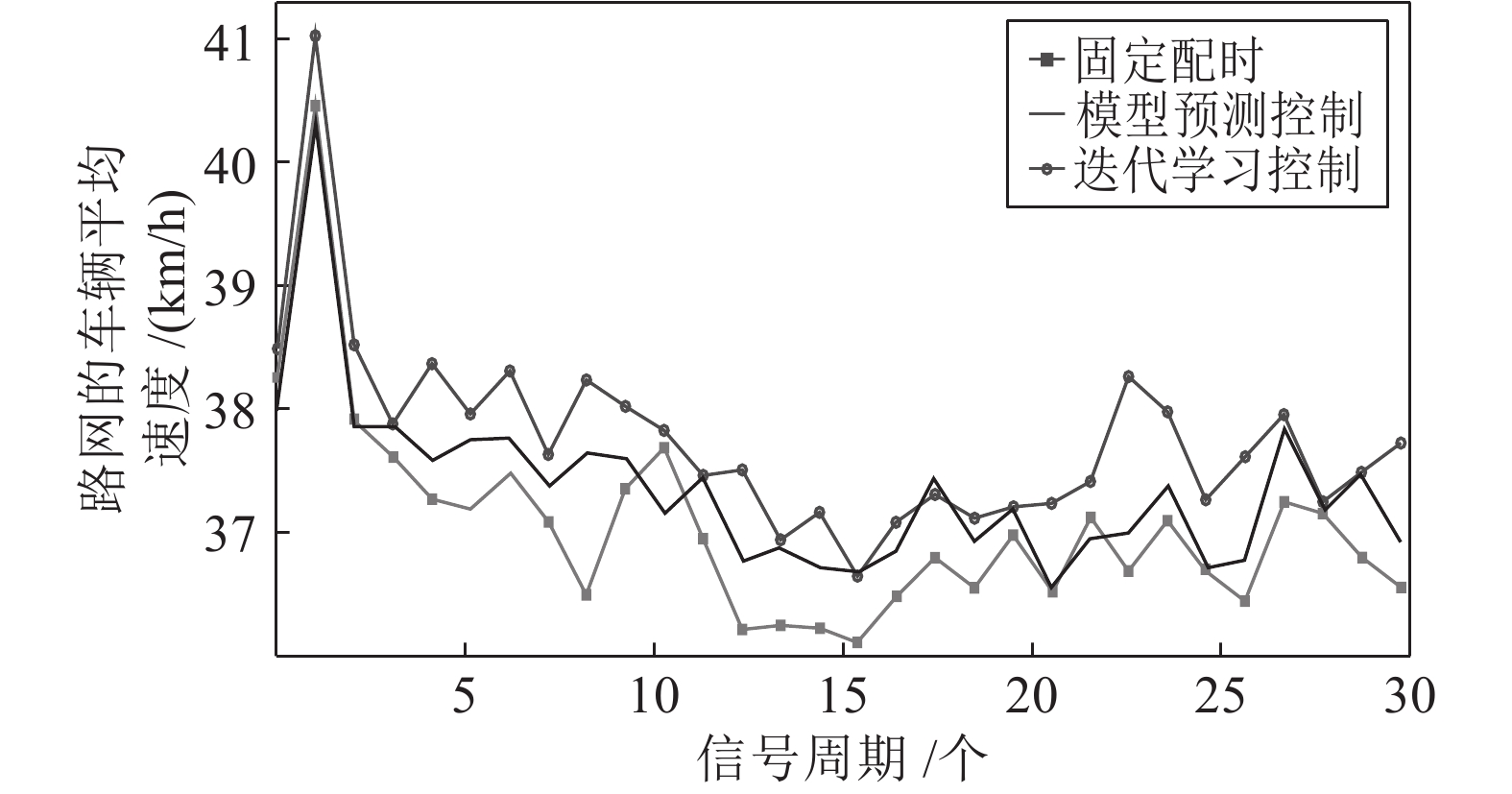
摘要: 现实中城市交通流的运行具有很强的非线性特性, 采用简单的线性模型难以全面描述交通流的实际运行过程. 本文在考虑城市交通流非线性动态特性的基础上, 提出了一种非线性交通流排队模型, 并基于宏观交通流固有的周期性特征, 设计了交叉口信号的迭代学习控制策略. 通过对交叉口信号的迭代学习控制, 使交叉口各进口道的车辆排队长度尽可能趋于均衡, 提高交叉口信号有效绿灯时间的利用率, 从而提高路网的通行效率. 最后通过严格的数学推导证明了该方法的收敛性, 仿真研究及实验结果验证了所提方法的有效性.Abstract: The operation of urban traffic flow has strong non-linear characteristics in real traffic situation, so it is difficult to describe the actual operation process of traffic flow comprehensively by using simple linear model. Considering the nonlinear dynamic characteristics of urban traffic flow, a nonlinear traffic flow queuing model is proposed, and an iterative learning control strategy for intersection signals is designed based on the inherent periodic characteristics of macroscopic traffic flow. By the iterative learning control of intersection signals, the vehicle queue lengths in the import way are balanced as far as possible, thus the utilization rate of effective green light time at intersections and the efficiency of road network are effectively improved. Finally, the convergence of the method is proved by strict mathematical deduction, and the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by the simulation research and experimental results.
-
表 1 各路段车道数
Table 1 The number of lanes in each link
道路情况 道路编号 双向 3 车道道路 $x_{1},x_{2},x_{3},x_{4},x_{9},x_{10},x_{11},x_{14},x_{17},x_{20},x_{23}$ 双向 4 车道道路 $x_{12},x_{13},x_{15},x_{16},x_{18},x_{19},x_{21},x_{22}$ 双向 7 车道道路 $x_{5},x_{6},x_{7},x_{8}$ 表 2 路网的输入流量(veh/h)
Table 2 The inflows of the road network (veh/h)
时段/min $x_{1},x_{4},x_{9},x_{12},x_{14},x_{21},x_{23}$ $x_{13},x_{22}$ $x_{5},x_{8}$ $0\sim20$ 1 600 3 000 2 000 $20\sim40$ 2 000 3 400 2 400 $40\sim60$ 1 800 3 200 2 200 表 3 交叉口的迭代学习增益
Table 3 The iterative learning gains at different intersections
交叉口编号 学习增益值 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 0.1 -
[1] Genders W, Razavi S. Asynchronous n-step Q-learning adaptive traffic signal control. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 23(4): 319-331 doi: 10.1080/15472450.2018.1491003 [2] van de Weg G S, Vu H L, Hegyi A, Hoogendoorn S P. A hierarchical control framework for coordination of intersection signal timings in all traffic regimes. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(5): 1815-1827 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2837162 [3] Zhang Y N, Zhou Y H. Distributed coordination control of traffic network flow using adaptive genetic algorithm based on cloud computing. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 119: 110-120 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2018.07.001 [4] 赵欢. 单信号交叉口绿灯时间无模型自适应控制 [硕士学位论文]. 北京交通大学, 中国, 2009.Zhao Huan. Model-free adaptive control of green light time at single signalized intersection [Master thesis], Beijing Jiaotong University, China, 2009. [5] Hao J G, Hou Z S, Bu X H. The iterative learning approach for vehicle queuing length balanced-control of the signalized isolated intersection. In: Proceedings of the 30th Chinese Control Conference. Yantan, China: IEEE, 2011. 5556−5561 [6] 齐驰, 侯忠生, 贾琰. 基于排队长度均衡的交叉口信号配时优化策略. 控制于决策, 2012, 27(8): 1191-1194Qi Chi, Hou Zhong-Sheng, Jia Yan. Optimal signal timing strategy based on the equilibrium of queue length. Control and Decision, 2012, 27(8): 1191-1194 [7] Hou Z S, Xu J X, Yan J W. An iterative learning approach for density control of freeway traffic flow via ramp metering. Transportation Research Part C, 2008, 16(1): 71-97 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2007.06.007 [8] Arimoto S, Kawamura S, Miyazaki F. Bet-tering operation of robots by learning. Journal of Robotic Systems, 1984, 1(2): 123-140 doi: 10.1002/rob.4620010203 [9] 池荣虎, 侯忠生, 黄彪. 间歇过程最优迭代学习控制的发展: 从基于模型到数据驱动. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(6): 917-932Chi Rong-Hu, Hou Zhong-Sheng, Huang Biao. Optimal iterative learning control of batch processes: from model-based to data-driven. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(6): 917-932 [10] Hou Z S, Xu J X. Freeway traffic density control using iterative learning control approach. In: Proceedings of the 6th International conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2003. 1081−1086 [11] 侯忠生, 宴静文. 带有迭代学习前馈的快速路无模型自适应入口匝道控制. 自动化学报, 2009, 35(5): 588-595Hou Zhong-Sheng, Yan Jing-Wen. Model free adaptive control based freeway ramp metering with feedforward iterative learning controller. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(5): 588-595 [12] Hou Z S, Xu X, Yan J W, Xu J W, Xiong G. A complementary modularized ramp metering approach based on iterative learning control and ALINE. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2011, 12(4): 1305-1318 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2011.2157969 [13] Hou Z S, Xu X, Yan J W, Xu J W, Li Z J. Modified iterative-learning-control-based ramp metering strategies for freeway traffic control with iteration-dependent factors. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(3): 606-618 [14] 郑一辰, 张毅, 胡坚明. 一种基于迭代学习的自适应交通信号控制方法. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2010, 10(6): 34-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2010.06.005Zheng Yi-Chen, Zhang Yi, Hu Jian-Ming. Iterative learning based adaptive traffic signal contral. Journal of Transporation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2010, 10(6): 34-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2010.06.005 [15] Huang W, Viti F, Tampère C. An iterative learning approach for signal control in urban traffic networks. In: Proceedings of the 16th Internaing conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Hague, the Netherland: IEEE, 2013. 468−473 [16] Yan F, Tian F L, Shi Z K. An iterative learning approach for traffic signal control of urban road networks. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 11(4): 466-475 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2016.0376 [17] Yan F, Tian F L, Shi Z K. An extended signal control strategy for urban network traffic flow. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2016, 445: 117-127 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2015.10.047 [18] Yan F, Tian F L, Shi Z K. Effects of iterative learning based signal control strategies on macroscopic fundamental diagrams of urban road networks. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 2016, 27(4): 1650045 doi: 10.1142/S0129183116500455 [19] Yan F, Yan G W, Ren M F, Tian J Y, Shi Z K. A novel control strategy for balancing traffic flow in urban traffic network based on iterative learning control. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 508: 519-531 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.05.134 [20] Gazis D C, Potts R B. The oversaturated intersection. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on the Theory of Road Traffic Flow. London, UK: 1963: 231−237 [21] Liu Y, Chang G L. An arterial signal optimization model for intersections experiencing queue spillback and lane blockage. Transportation Research Part C, 2011, 19(1): 130-144 [22] Sun M X, Wang D W. Initial shift issues on discrete-time iterative learning control with system relative degree. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(1): 144-148. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2002.806668 [23] 严求真, 孙明轩, 蔡建平. 迭代学习控制的参考信号初始修正方法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1470-1477Yan Qiu-Zhen, Sun Ming-Xuan, Cai Jian-Ping. Reference-signal rectifying method of iterative learning control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1470-1477 [24] Shim J, Yeo J, Lee S, Hamdar S H, Jang K. Empirical evaluation of influential factors on bifurcation in macroscopic fundamental diagrams. Transportation Research Part C, 2019, 102: 509-520 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2019.03.005 -




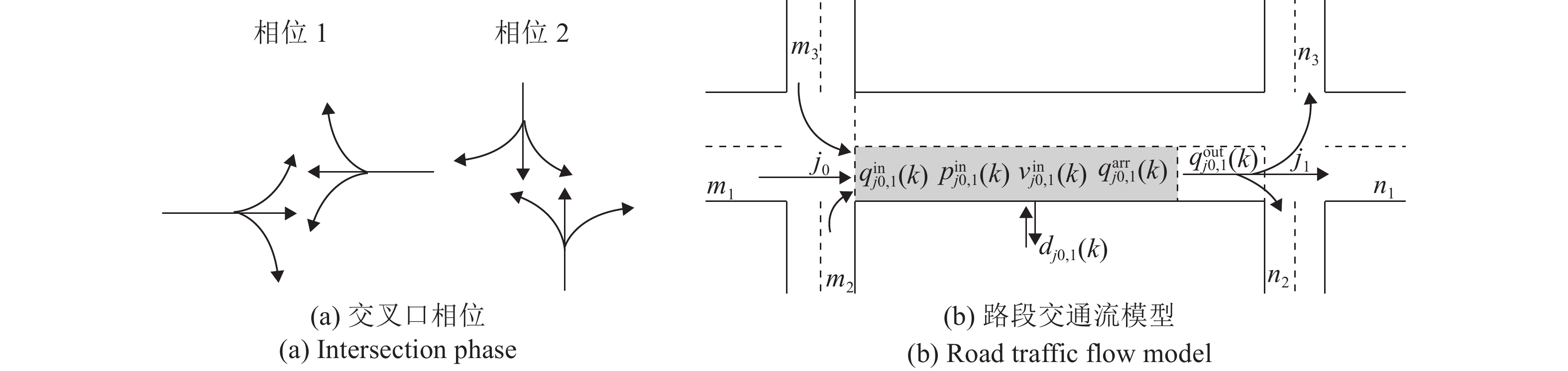
 下载:
下载: