Industrial Operation Performance Evaluation of Industrial Processes Based on Modified Random Forest
-
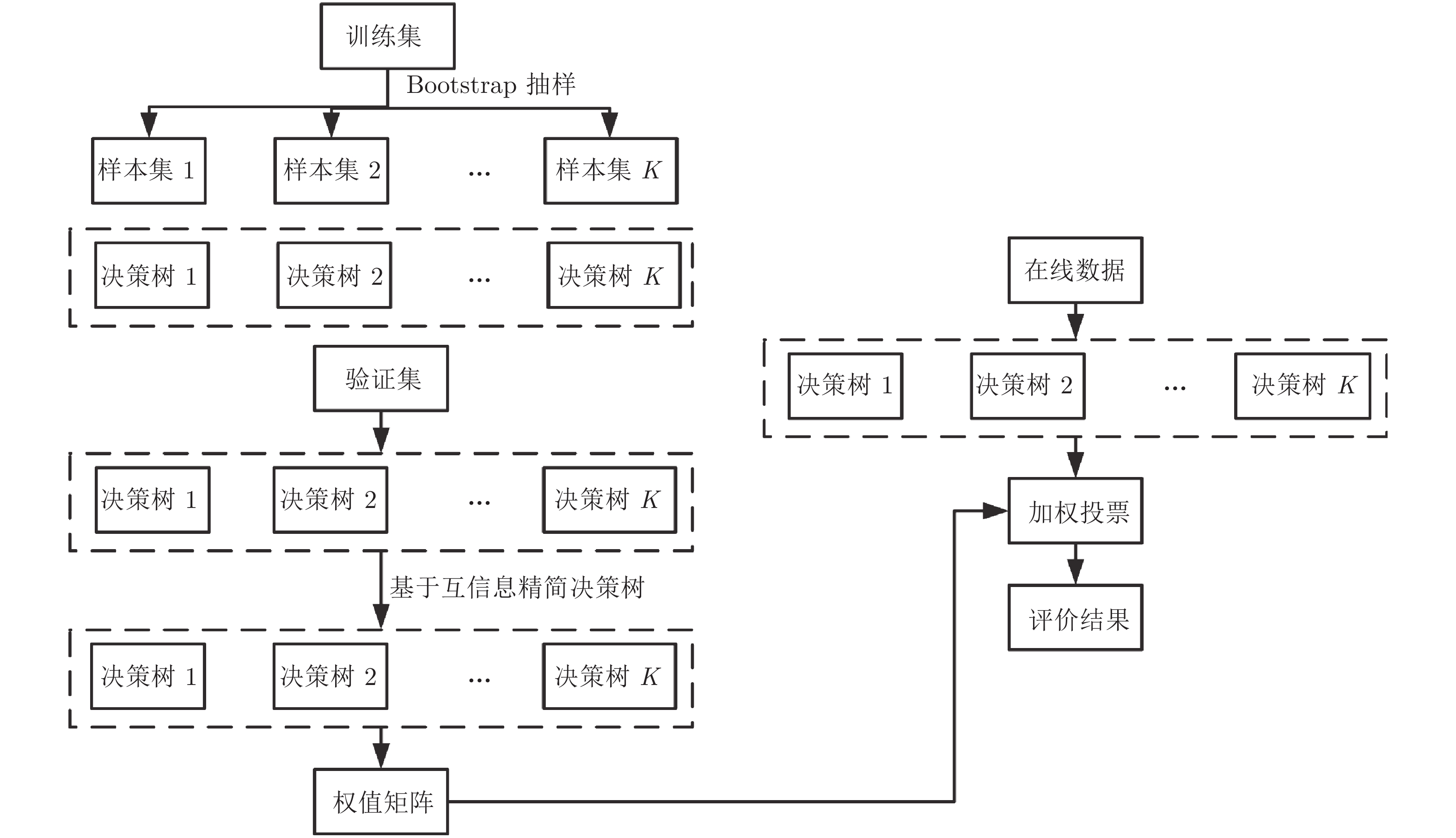
摘要: 运行状态评价是指在过程正常生产的前提下, 进一步判断生产过程运行状态的优劣. 针对复杂工业过程定量信息与定性信息共存的情况, 本文提出了一种基于随机森林的工业过程运行状态评价方法. 针对随机森林中决策树信息存在冗余的问题, 基于互信息将传统随机森林中的决策树进行分组, 并选出每组中最优的决策树组成新的随机森林. 同时为了强化评价精度高的决策树和弱化评价精度低的决策树对最终评价结果的影响, 使用加权投票机制取代传统众数投票方法, 最终构成一种基于互信息的加权随机森林算法(Mutual information weighted random forest, MIWRF). 对于在线评价, 本文通过计算在线数据处于各个等级的概率, 并且结合提出的在线评价策略, 判定当前样本运行状态等级. 为了验证所提算法的有效性, 将所提方法应用于湿法冶金浸出过程, 实验结果表明, 相对于传统随机森林算法, MIWRF 降低了模型的复杂度, 同时提高了运行状态评价精度.Abstract: Operation performance evaluation refers to further judging the operation performance of process on the premise of normal production. In the view of coexistence of qualitative information and quantitation information during the industrial processes, a method of industrial operation performance evaluation of industrial processes based on modified random forest is proposed. In order to solve the problem of redundancy of decision trees information in random forest, decision trees are grouped based on mutual information, and the optimal decision tree in each group is selected to form a new random forest. Meanwhile, in order to strengthen the decision tree with high evaluation accuracy and weaken the decision tree with low evaluation accuracy, weighted voting mechanism are proposed to replace the traditional mode voting, and finally a mutual information weighted random forest (MIWRF) based on mutual information is formed. To verify the proposed method, the method is applied to hydrometallurgical leaching process. The result shows that MIWRF reduces the complexity of the model and improves the accuracy of operation performance evaluation compared with the traditional random forest algorithm.1) 收稿日期 2019-01-27 录用日期 2019-09-09 Manuscript received January 27, 2019; accepted September 9,2019 国家自然科学基金 (61673092, 61533007, 61304121, 61973057, 61873053), 创新研究群体科学基金 (61621004), 中央高校基础科研业务费 (N150404017), 矿冶过程自动控制技术国家重点实验室开放基金 (BGRIMM-KZSKL-2018-08) 资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61673092, 61533007, 61304121, 61973057, 61873053), Science Fou-ndation for Innovative Research Groups (61621004), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N150404017), andOpen Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Process Automationin Mining and Metallurgy (BGRIMM-KZSKL-2018-08) 本文责任编委 伍洲 Recommended by Associate Editor WU Zhou 1. 东北大学信息科学与工程学院 沈阳 110819 2. 流程工业综合自动化国家重点实验室 (东北大学) 沈阳 110819 1. College of Information Science and Engineering, Northeast-2) ern University, Shenyang 110819 2. State Key Laboratory ofSynthetical Automation for Process Industries (NortheasternUniversity), Shenyang 110819
-
表 1 浸出过程变量列表
Table 1 Key variables affecting leaching efficiency
分割方法 单位 属性 矿石初始来料量 ${\rm{kg}}$ 定量 浸出调浆后矿浆浓度 % 定量 矿石初始金品位 ${\rm{g/t}}$ 定性 一浸浸出槽1氰化钠添加量 ${\rm{kg/ h}}$ 定量 一浸浸出槽2氰化钠添加量 ${\rm{kg/ h}}$ 定量 一浸浸出槽4氰化钠添加量 ${\rm{kg/ h}}$ 定量 一浸浸出槽1槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 一浸浸出槽2槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 一浸浸出槽3槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 一浸浸出槽4槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 二浸前矿浆浓度 % 定量 一浸后金品位 ${\rm{g/ t}}$ 定性 二浸浸出槽1氰化钠添加量 ${\rm{kg/ h}}$ 定量 二浸浸出槽2氰化钠添加量 ${\rm{kg/ h}}$ 定量 二浸浸出槽4氰化钠添加量 ${\rm{kg/ h}}$ 定量 二浸浸出槽1槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 二浸浸出槽2槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 二浸浸出槽3槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 二浸浸出槽4槽空气流量 ${\rm{m^3/ h}}$ 定量 表 2 浸出过程实验设计
Table 2 Experiment of leaching process
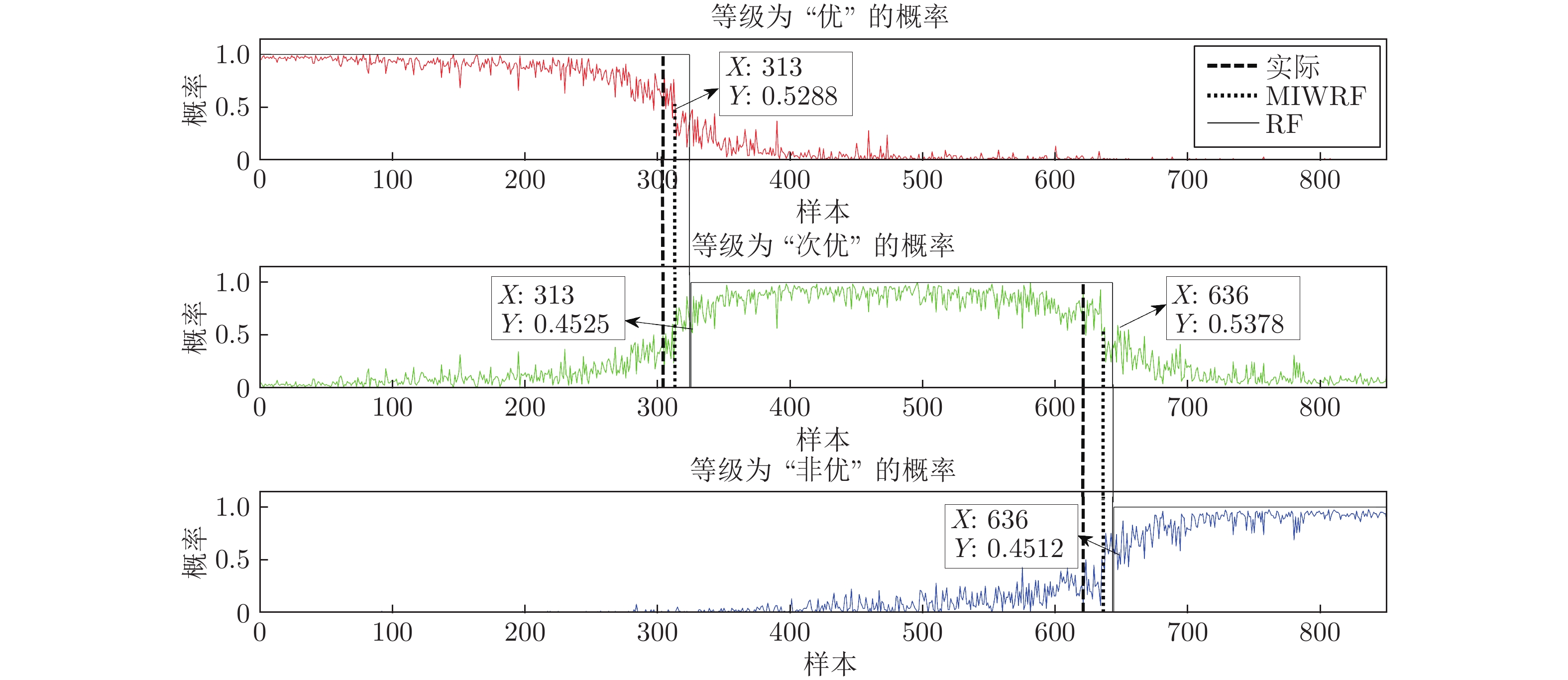
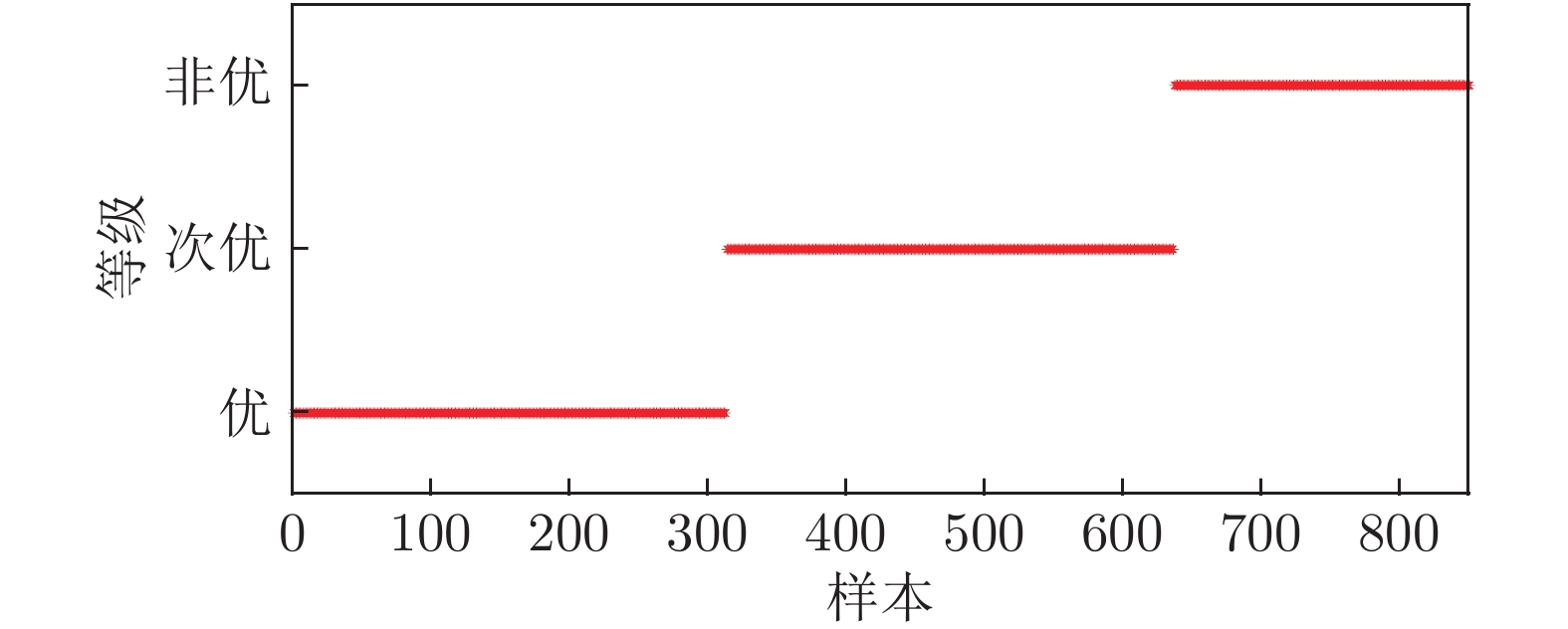
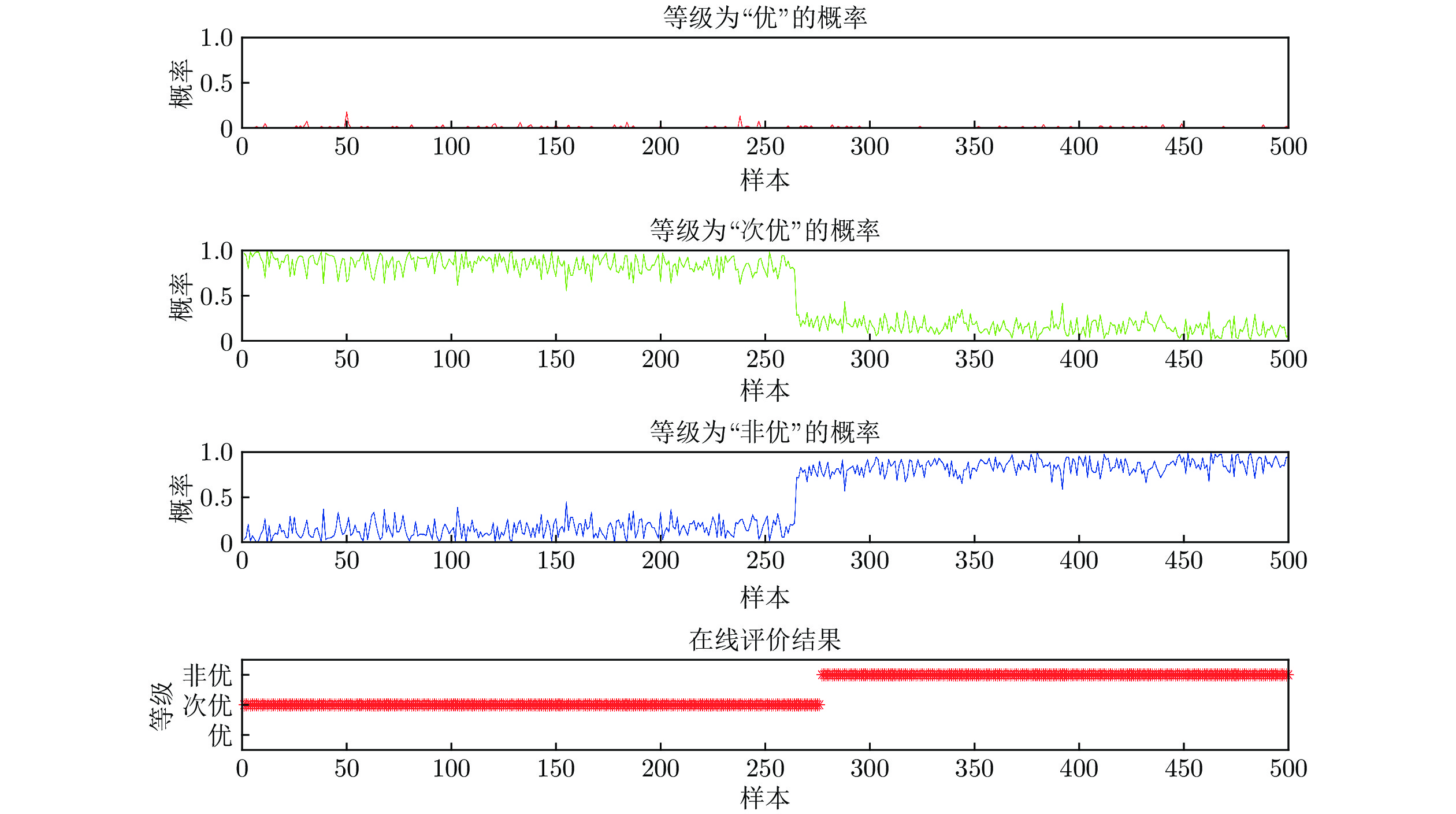
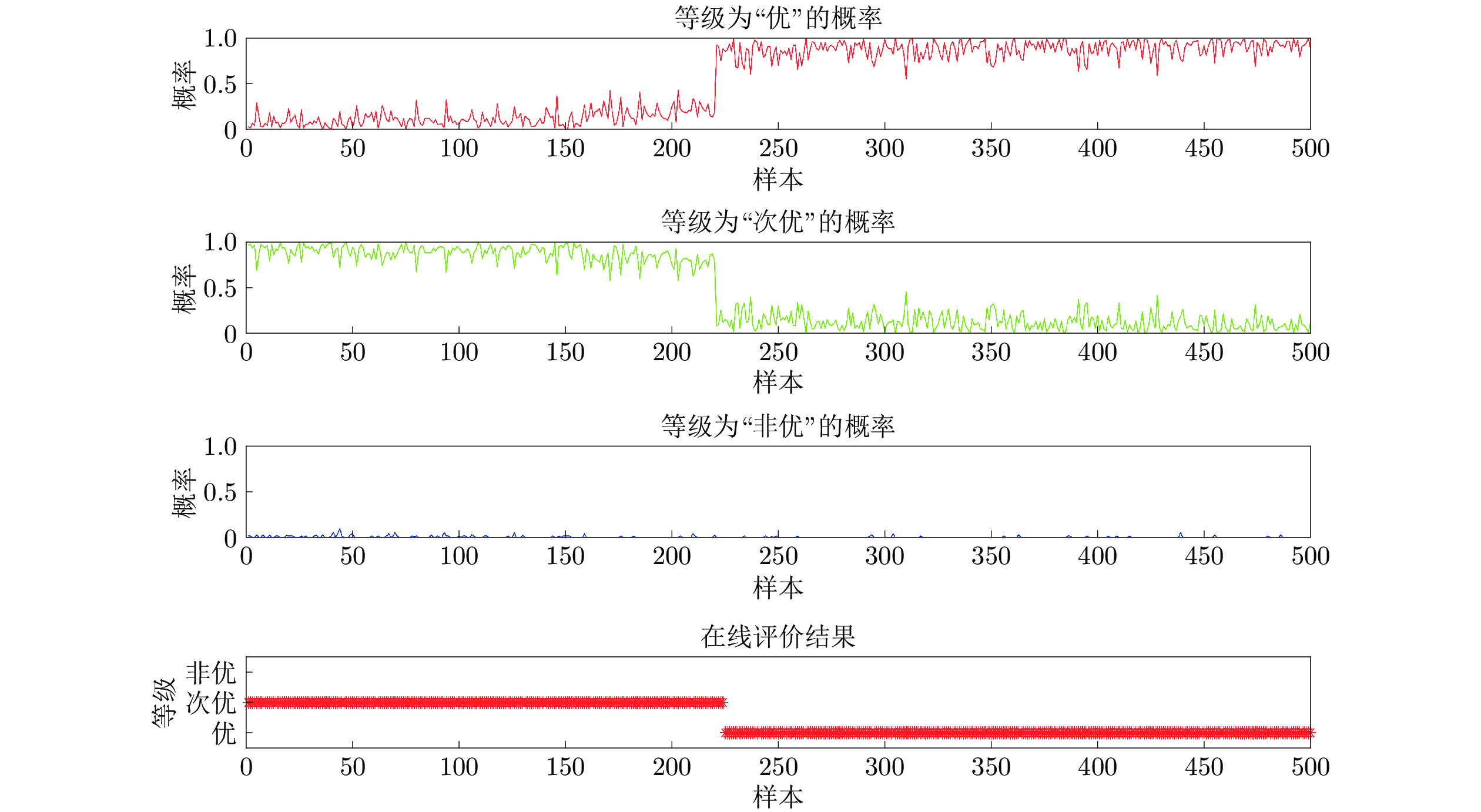
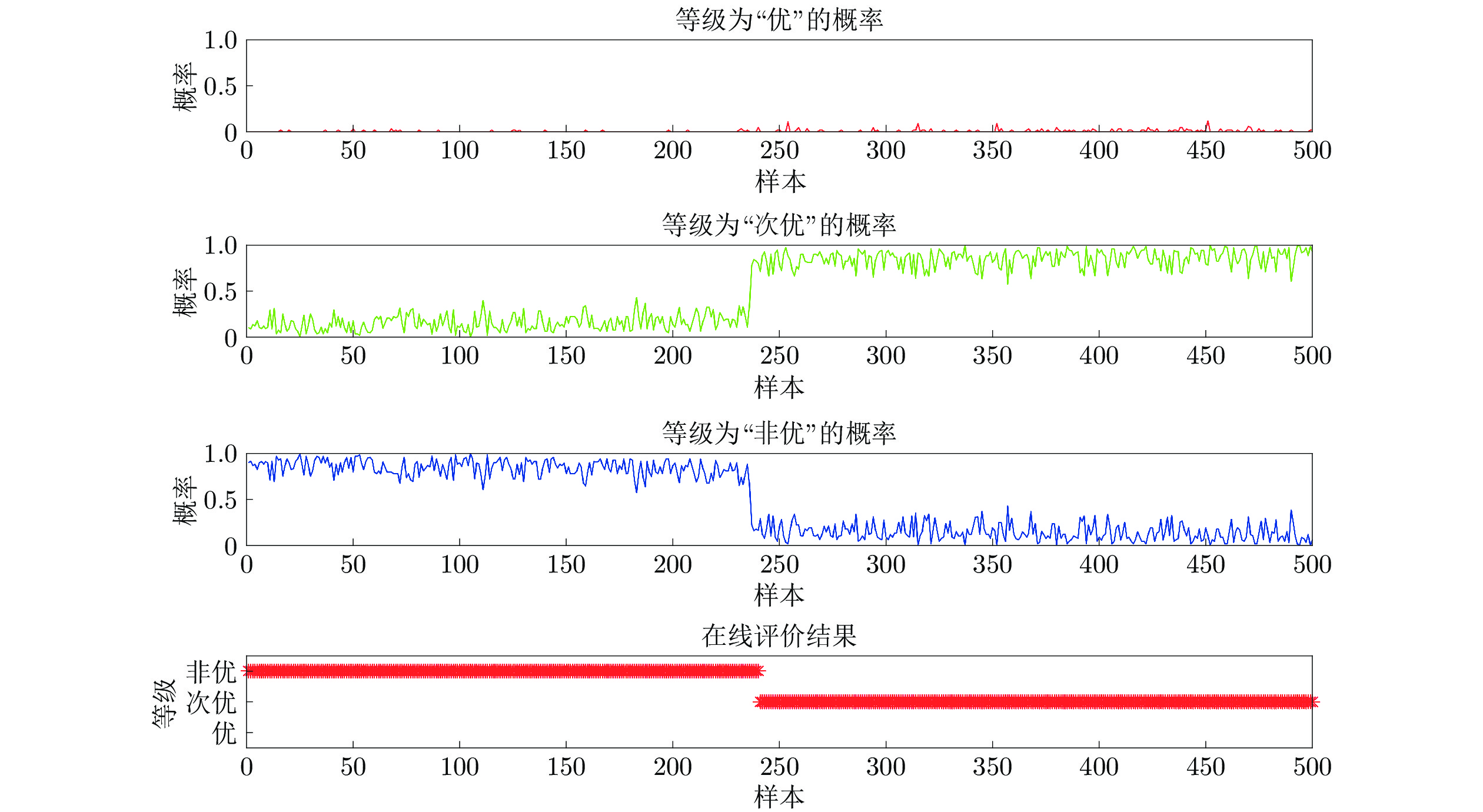
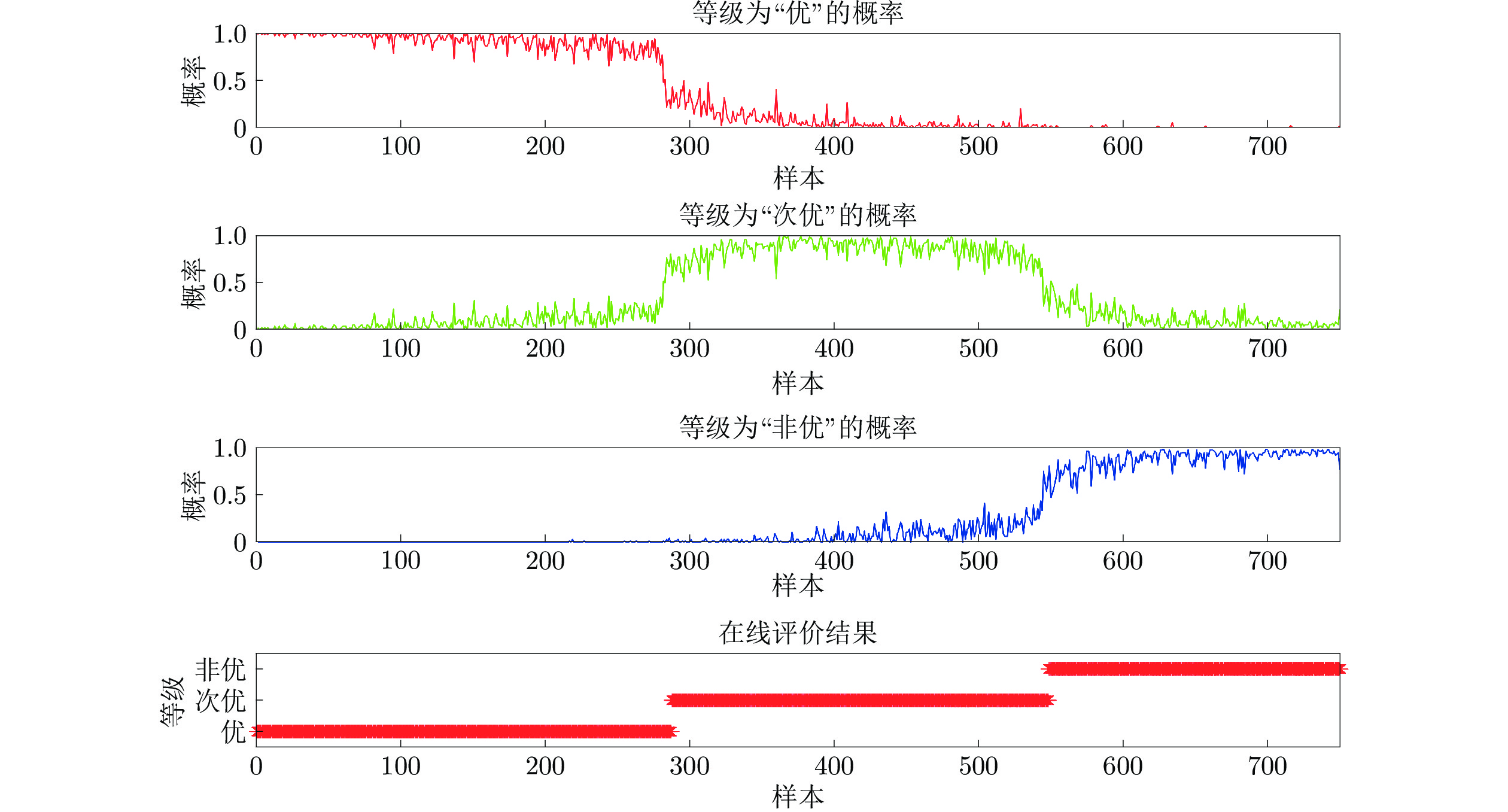
数据 等级 描述 1~304 优 1~160个样本点, 过程运行状态等级为“优”; 自第161个样本点, 一浸槽4氰化钠添加量逐渐减少, 运行状态等级优性逐渐减弱, 但始终保持“优”等级, 直到第304个样本点. 305~621 次优 314~479个样本点, 保持一浸槽4氰化钠添加量不变, 过程稳定运行于等级“次优”; 480~621个样本点, 持续减少槽4 氰化钠添加量, 运行状态等级优性再次减弱. 622~850 非优 保持一浸槽4氰化钠添加量不再变化, 过程稳定运行于等级“非优” 表 3 RF与MIWRF实验结果对比
Table 3 Comparison of experimental results of RF and MIWRF
实验编号 RF决策树数量 MIWRF决策树数量 RF评价精度 (%) MIWRF评价精度 (%) 决策树减少量 (%) 1 50 19 92.9 94.9 62.0 2 60 24 93.0 95.0 60.0 3 70 31 93.0 95.1 55.8 4 80 32 93.9 95.3 60.0 5 90 36 93.5 95.7 60.0 6 100 39 93.6 96.2 61.0 7 110 43 93.6 95.9 60.9 8 120 46 93.5 95.7 61.7 9 130 51 93.5 96.0 60.8 10 140 54 93.6 95.9 61.4 11 150 58 93.5 95.7 61.3 12 160 62 93.6 95.8 60.6 13 170 63 93.6 96.1 62.9 14 180 65 93.5 96.2 63.9 15 190 69 93.6 96.1 63.7 16 200 71 93.7 96.2 64.5 表 4 6种评价方法的运行状态评价性能
Table 4 Performances of 6 evaluation methods
方法 KNN ANN RF MIRF MIWRF FDbD 精度 (%) 88.8 91.2 93.6 95.2 96.2 93.3 建模时间 (s) 0 51.1519 27.4507 23.0871 23.6831 28.7613 测试时间 (s) 0.69011 0.11933 1.3123 0.9062 0.9639 1.1534 -
[1] Ye L, Liu Y, Fei Z. Online Probabilistic Assessment of Operating Performance Based on Safety and Optimality Indices for Multimode Industrial Processes. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009.48(24): 10912−10923 doi: 10.1021/ie801870g [2] Zou X, Wang F, Chang Y. Process operating performance optimality assessment and non-optimal cause identification under uncertainties. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2017, 120(Complete): 348−359 [3] Chang Y Q, Zou X Y, Wang F, Zhao L, Zheng W. Multimode plant-wide process operating performance assessment based on two-level multi-block hybrid model. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2018, 136: 721−733 doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2018.05.023 [4] 王东, 刘怀亮, 徐国华. 案例推理在故障诊断系统中的应用. 计算机工程, 2003, 29(12): 10−12 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2003.12.004Wang Dong, Liu Huai-Liang, Xu Guo-Hua. Application of case-based reasoning in faulty dignoses system. Computer Engineering, 2003, 29(12): 10−12 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2003.12.004 [5] 姜涛, 韩富春, 范卫星. 基于粗糙集理论的架空输电线路运行状态评估. 电气技术, 2007(12): 58−60Jiang Tao, Han Fu-Chun, Fan Wei-Xing. Evaluating the condition of overhead transmission lines based on rough sets theory. Computer Engineering, 2007(12): 58−60 [6] Guo L, Gao J, Yang J, et al. Criticality evaluation of petrochemical equipment based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and a BP neural network. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2009, 22(4): 469−476 doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2009.03.003 [7] Xu G, Yang Y P, Lu S Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of coal-fired power plants based on grey relational analysis and analytic hierarchy process. Energy Policy, 2011, 39(5): 2343−2351 doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2011.01.054 [8] Liu Y, Wang F, Chang Y. Online Fuzzy Assessment of Operating Performance and Cause Identification of Nonoptimal Grades for Industrial Processes. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(50): 18022−18030 doi: 10.1021/ie402243s [9] 邹筱瑜, 常玉清, 王福利, 周阳. 基于 GMM 和贝叶斯推理的多模态过程运行状态评价. 自动化学报, 2016, 33(2): 164−171Zou Xiao-Yu, Chang Yu-Qing, Wang Fu-Li, Zhou Yang. Operation performance assessment for multimode processes based on GMM and Bayesian inference. Control Theory and Applications, 2016, 33(2): 164−171 [10] Liu Y, Wang F, Chang Y. Operating optimality assessment and nonoptimal cause identification for multimode industrial process with transitions. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 94(7): 1342−1353 doi: 10.1002/cjce.22513 [11] Breiman Leo. Bagging predictors. Machine Learning, 1996, 24(2): 123−140 [12] Tuv E, Borisov A, Runger G, Torkkola K. Feature Selection with Ensembles, Artificial Variables, and Redundancy Elimination. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2009, 10(3): 1341−1366 [13] Paul A, Mukherjee D P, Das P, et al. Improved Random Forest for Classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processin, 2018, 27(8): 4012−4024 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2834830 [14] Schulter S, Wohlhart P, Leistner C, Saffari A, Roth P M, Bischof H. Alternating decision forests. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, Oregon, USA: IEEE, 2013. 508−515 [15] Liu Y, Ge Z. Weighted random forests for fault classification in industrial processes with hierarchical clustering model selection. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 64: 62−70 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2018.02.005 [16] Breiman L. Random Forests. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5−32 doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [17] Tao S. Steve H. Unsupervised learning with random forest predictors. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2006, 15(1): 118-138 [18] Ho T K. The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(8): 832−844 doi: 10.1109/34.709601 [19] 王丽婷, 丁晓青, 方驰. 一种鲁棒的全自动人脸特征点定位方法. 自动化学报, 2006, 35(1): 9−16Wang Li-Ting, Ding Xiao-Qing, Fang Chi. A novel method for robust and automatic facial features localization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 35(1): 9−16 [20] 方匡南, 吴见彬, 朱建平. 随机森林方法研究综述. 统计与信息论坛, 2011, 26(3): 32−38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2011.03.006Fang Kuang-Nan, Wu Jian-Bin, Zhu Jian-Ping. A review of technologies random forests. Statistics and Information Forum, 2011, 26(3): 32−38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2011.03.006 [21] Krogh A, Vedelsby J. Neural network ensembles, cross validation and active learning. In: Proceedings of the 1995 International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. MIT Press: 1995. 231−238 [22] Cover T, Thomas J, Wiley J. Elements of Information Theory. Tsinghua University Press, 2003. [23] Robnik-Šikonja M. Improving random forests. In: Proceedings of the 2004 European Conference on Machine Learning (ECML 2004). Berlin, Germemy: Springer Press, 2004. 359−370 [24] 陈家镛. 湿法冶金的研究与发展. 冶金工业出版社, 1998.Chen Jia-Yong. Research and Development of Hydrometallurgy. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press. 1998. [25] 刘维平, 邱定蕃, 卢惠民. 湿法冶金新技术进展. 矿冶工程, 2003, 23(5): 39−42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2003.05.014Liu Wei-Ping, Qiu Ding-Fan, Lu Hui-Min. New advances in hydrometallurgical technology. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2003, 23(5): 39−42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2003.05.014 [26] 马荣骏. 湿法冶金新发展. 湿法冶金, 2007, 26(1): 1−12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2617.2007.01.001Ma Rong-Jun. New development of hydrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2007, 26(1): 1−12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2617.2007.01.001 [27] 常玉清, 许弟伍. 含不确定信息的湿法冶金金泥品位软测量. 仪器仪表学报, 2018, 39(10): 18−26Chang Yu-Qing, Xu Di-Wu. New development of hydrometallurgy. Chinese Journal of Scientific Intrument, 2018, 39(10): 18−26 [28] 黄礼煌. 金银提取技术. 冶金工业出版社, 2001.Huang Li-Huang. Gold and Silver Extraction Technology. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press. 2001. -




 下载:
下载: