Medical Image Non-rigid Registration Based on Adaptive Fractional Order
-
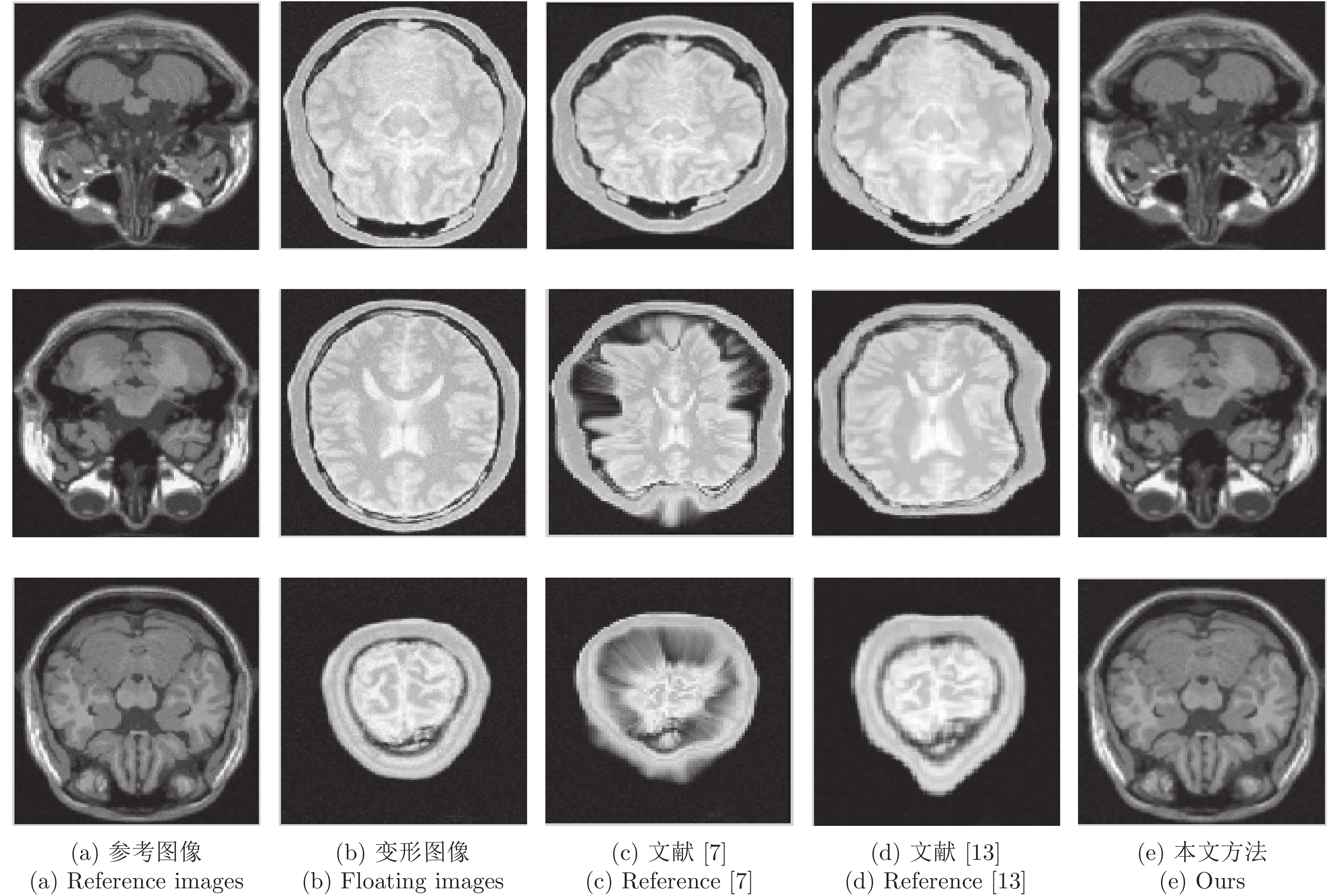
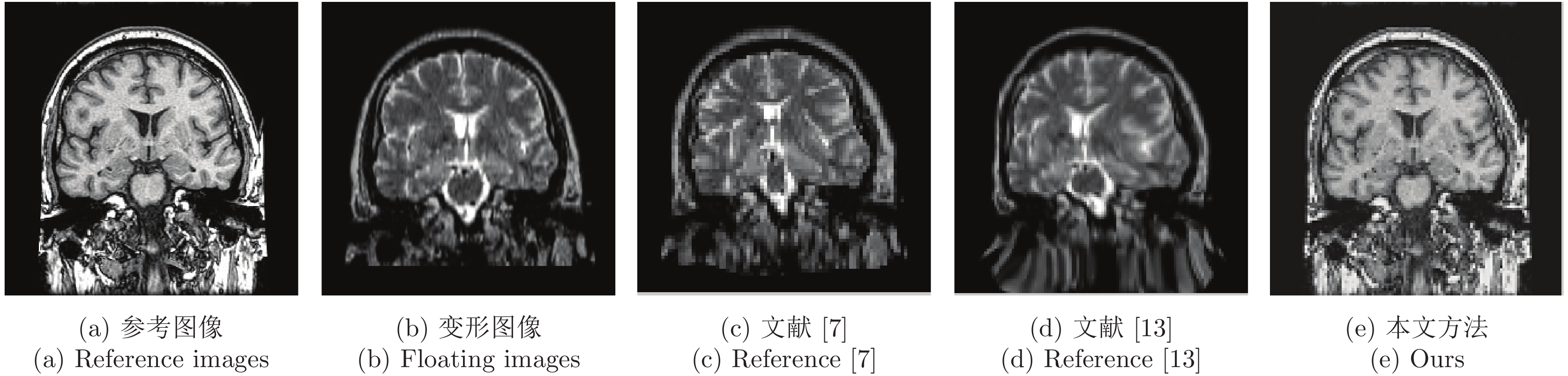
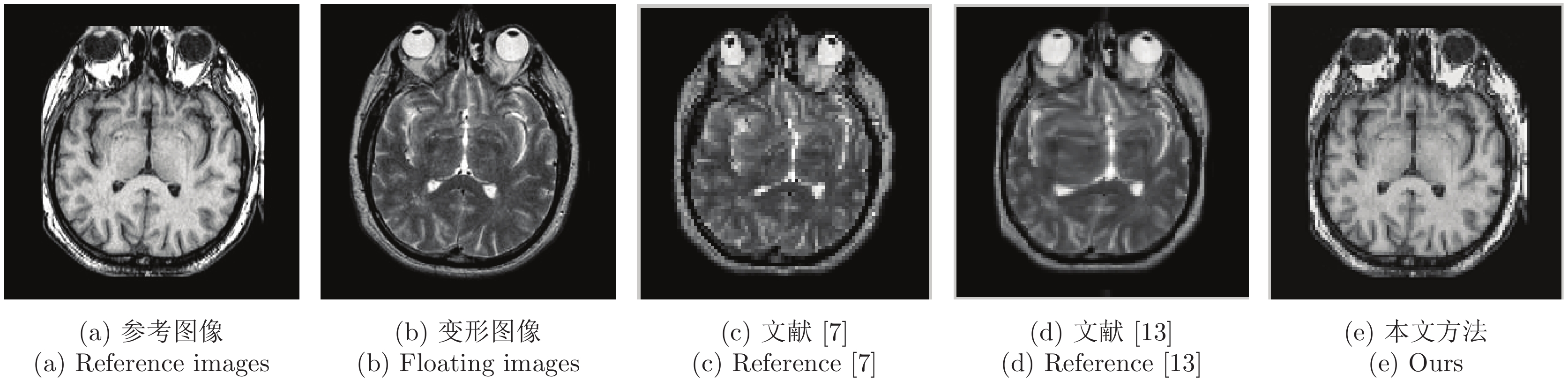
摘要: 现有的医学图像配准算法对于灰度均匀、弱边缘以及弱纹理图像易陷入局部最优从而导致配准精度低下、收敛速度缓慢. 分数阶主动Demons (Fractional active Demons, FAD)算法是解决该问题的有效方法, 并且适用于图像的非刚性配准. 但FAD中的最佳分数阶阶次是人工交互选取, 并且对整幅图像都是固定不变的. 为了解决该问题, 提出一种阶次自适应的主动Demons算法并将其应用到医学图像的非刚性配准中. 算法首先根据图像的局部特征建立分数阶阶次自适应的数学模型, 并逐像素计算最优阶次, 基于该阶次构造Riemann-Liouvill (R-L)分数阶微分动态模板; 然后将自适应R-L分数阶微分引入到Active Demons算法, 在一定程度上缓解了图像配准在弱边缘和弱纹理区域易陷入局部最优问题, 从而提高了配准精度. 通过在两个医学图像库上进行实验验证, 实验结果表明该方法可以处理灰度均匀、弱纹理和弱边缘的医学图像非刚性配准, 配准精度得到较大提升.
-
关键词:
- 自适应分数阶 /
- 主动Demons算法 /
- 自适应模型 /
- 非刚性配准 /
- 医学图像
Abstract: The existing medical image registration methods have limitation in registration images with intensity uniformity, weak edges and weak texture, troubled by inclining to local minimum, which always result in low registration accuracy and efficiency. Active Demons algorithm with fractional differential has been proved to be effective for non-rigid image registration. However, it searches the optimal order of fractional differential manually, lack of order adaptive in images registration. To address the problem, this paper applies multi-resolution and adaptive fractional differential to active Demons, and proposes a novel images registration method for 3D medical images registration. Firstly, a mathematical model of adaptive order for fractional differential is constructed, which adopts local image features such as gradient magnitude and information entropy, therefore the optimal order and differential dynamic template are adjusted adaptively; Secondly, multi-resolution strategy is introduced to adaptive fractional differential active Demons algorithm, optimization falling into local minimum is avoided, therefore the registration accuracy is improved once more. Lastly, extensive experiments show that the proposed algorithm is capable of registration images with intensity uniformity and weak texture. And the optimal order of fractional differential can be calculated adaptively. Furthermore, the presented methods is capable of avoiding falling into local optimum, thus the registration accuracy can be improved greatly. -
表 1 均方误差比较
Table 1 Mean square error comparison
表 2 Dice ratio比较
Table 2 Dice ratio comparison
表 3 冠状面配准精度对比
Table 3 Comparison of registration accuracy of coronal plane
表 4 矢状面配准精度对比
Table 4 Comparison of registration accuracy of sagittal plane
表 5 横切面配准精度对比
Table 5 Comparison of registration accuracy of transverse plane
表 6 不同算法的时间对比(s)
Table 6 Time comparison of two methods (s)
不同切片层的图像 文献 [13] 的方法 (不同的阶次) 本文方法 $ \alpha $ = 0.1$ \alpha $ = 0.2$ \alpha $ = 0.3$ \alpha $ = 0.4$ \alpha $ = 0.5$ \alpha $ = 0.6$ \alpha $ = 0.7$ \alpha $ = 0.8$ \alpha $ = 0.9总计时间 I 3.21 3.14 2.98 2.76 3.03 2.89 2.92 2.67 2.58 26.18 17.69 II 3.72 3.65 3.37 3.54 3.68 3.03 3.29 3.21 3.16 30.65 19.08 III 4.64 4.61 4.53 4.57 4.65 4.06 4.52 4.18 4.49 40.25 26.83 表 7 两种策略的时间对比(s)
Table 7 Time comparison of two strategies (s)
图像 不采用多分辨率 采用多分辨率 I 30.25 17.69 II 28.04 19.08 III 40.63 26.83 -
[1] 申艳平. 医学图像配准技术. 中国医学物理杂志, 2013, 30(1): 3385−3389Shen Yan-Ping. Review of image registration methods for medical images. Chinese Journal of Medical Physics, 2013, 30(1): 3385−3389 [2] Thirion J P. Image matching as a diffusion process: An analogy with Maxwell's demons. Medical Image Analysis, 1998, 2(3): 243−260 doi: 10.1016/S1361-8415(98)80022-4 [3] Wang H, Dong L, O′Daniel J, Mohan R, Garden A S, Ang K K, et al. Validation of an accelerated “demons” algorithm fordeformable image registration in radiation therapy. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2005, 50(12): 2887−2905 doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/12/011 [4] Ying S H, Li D, Xiao B, Peng Y X, Do S Y, Xu M F. Nonlinear image registration with bidirectional metric and reciprocal regularization. PloS One, 2017, 12(2): e0172432 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172432 [5] Du S Y, Guo Y R, Sanroma G, Ni D, Wu G R, Shen D G. Building dynamic population graph for accurate correspondence detection. Medical Image Analysis, 2015, 26(1): 256−267 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.10.001 [6] Du S Y, Zhang C J, Wu Z Z, Liu J, Xue J R. Robust isotropic sffigcaling ICP algorithm with bidirectional distance and bounded rotation angle. Neurocomputing, 2016, 215: 160−168 [7] Vercauteren T, Pennec X, Perchant A, Ayache N. Symmetric log-domain diffeomorphic registration: A demons-based approach. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv, 2008, 11(Pt1): 754−761 [8] 郝培博, 陈震, 江少锋, 汪洋. 基于Demons算法的多模态医学图像非刚性配准研究. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2014, 1: 161−165Hao P B, Chen Z, Jiang S F, Wang Y. Research on non-rigid registration of multi-modal medical image based on demons algorithm. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 1: 161−165 [9] Lu X Q, Yu H F, Zhao Y, Hou H, Li Y H. Three-dimensional lung medical image registration based on improved demons algorithm. Optik–International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2015, 127(4): 1893−1899 [10] 闫德勤, 刘彩凤, 刘胜蓝, 刘德山. 大形变微分同胚图像配准快速算法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(8): 1461−1470Yan De-Qin, Liu Cai-Feng, Liu Sheng-Lan, Liu De-Shan. A fast image registration algorithm for diffeomorphic image with large deformation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(8): 1461−1470 [11] 薛鹏, 杨佩, 曹祝楼, 贾大宇, 董恩清. 基于平衡系数的 Active demons非刚性配准算法. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(9): 1389−1400Xue Peng, Yang Pei, Cao Zhu-Lou, Jia Da-Yu, Dong En-Qing. Active demons non-rigid registration algorithm based on balance coefficient. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(9): 1389−1400 [12] 路玉昆, 巩贯忠, 虞刚, 李登旺, 尹勇. 基于微分同胚Demons形变配准算法获取肺通气图. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2017, 34(7): 666−670Lu Y K, Gong G Z, Yu G, Li D W, Yin Y. Diffeomorphic demons registration algorithm for obtaining lung ventilation image. Chinese Journal of Medical Physics, 2017, 34(7): 666−670 [13] 张桂梅, 曹红洋, 陈阳泉, 刘建新. 基于分数阶梯度驱动的主动Demons算法研究. 电子学报, 2016, 44(12): 2834−2841 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.12.004Zhang Gui-Mei, Cao Hong-Yang, Chen Yang-Quan, Liu Jian-Xin. Research on active demons based on fractional differentiation gradient driving. Acta Eletronica Sinica, 2016, 44(12): 2834−2841 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.12.004 [14] Hu Y P, Modat M, Gibson E, Ghavami N, Bonmati E, Moore C M, Emberton M, Noble J A, Barratt D C, Vercauteren T. Label-driven weakly-supervised learning for multimodal deformable image registration. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, 2018. 1070–1074 [15] Balakrishnan G, Zhao A, Sabuncu M R, Guttag J, Dalca A V. An unsupervised learning model for deformable medical image registration. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 235–242 [16] Pu Y F, Siarry P, Zhou J L, Zhang N. A fractional partial differential equation based multiscale denoising model for texture image. Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2014, 37(12): 1784−1806 doi: 10.1002/mma.2935 [17] Chen D L, Chen Y Q, Xue D Y. Fractional-order total variation image denoising based on proximity algorithm. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2015, 257: 537−545 [18] Mathieu B, Melchior P, Oustaloup A, Ceyral C. Fractional differentiation for edge detection. Signal Processing, 2003, 83(11): 2421−2432 doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(03)00194-4 [19] Ren Z M. Adaptive active contour model driven by fractional order fitting energy. Signal Processing, 2015, 117: 138−150 [20] 张桂梅, 徐继元, 刘建新. 一种新的基于自适应分数阶的活动轮廓模型. 计算机研究与发展, 2017, 54(5): 1045−1056 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2017.20160301Zhang Gui-Mei, Xu Ji-Yuan, Liu Jian-Xin. A new active contour model based on adaptive fractional order. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2017, 54(5): 1045−1056 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2017.20160301 [21] Yu J M, Tan L J, Zhou S B, Wang L P, Siddique M A. Image denoising algorithm based on entropy and adaptive fractional order calculus operator. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 12275−12285 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2718558 [22] 张桂梅, 郭黎娟, 熊邦书, 储珺. 基于多分辨率和自适应分数阶的Active Demons算法. 计算机研究与发展, 2018, 55(12): 2753−2763 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170523Zhang Gui-Mei, Guo Li-Juan, Xiong Bang-Shu, Chu Jun. Active demons algorithm based on multi-resolution and adaptive fractional differential. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(12): 2753−2763 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170523 [23] Du S Y, Xu G L, Zhang S R, Zhang X T, Gao Y, Chen B D. Robust rigid registration algorithm based on pointwise correspondence and correntropy. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 132: 91−98 -




 下载:
下载: