Fingerprint Template Protection Algorithm Based on Bit String XOR and Scrambling Transformation
-
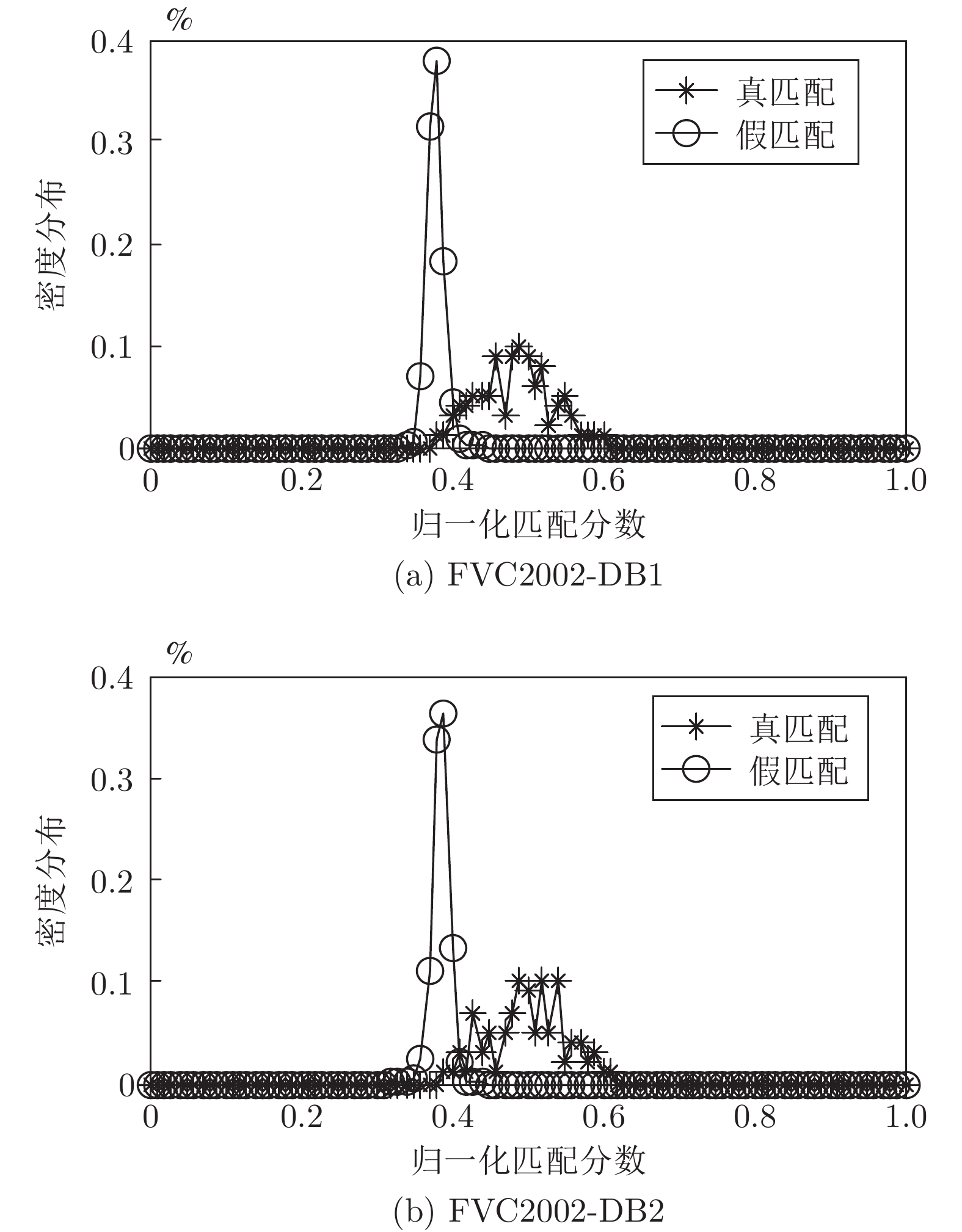
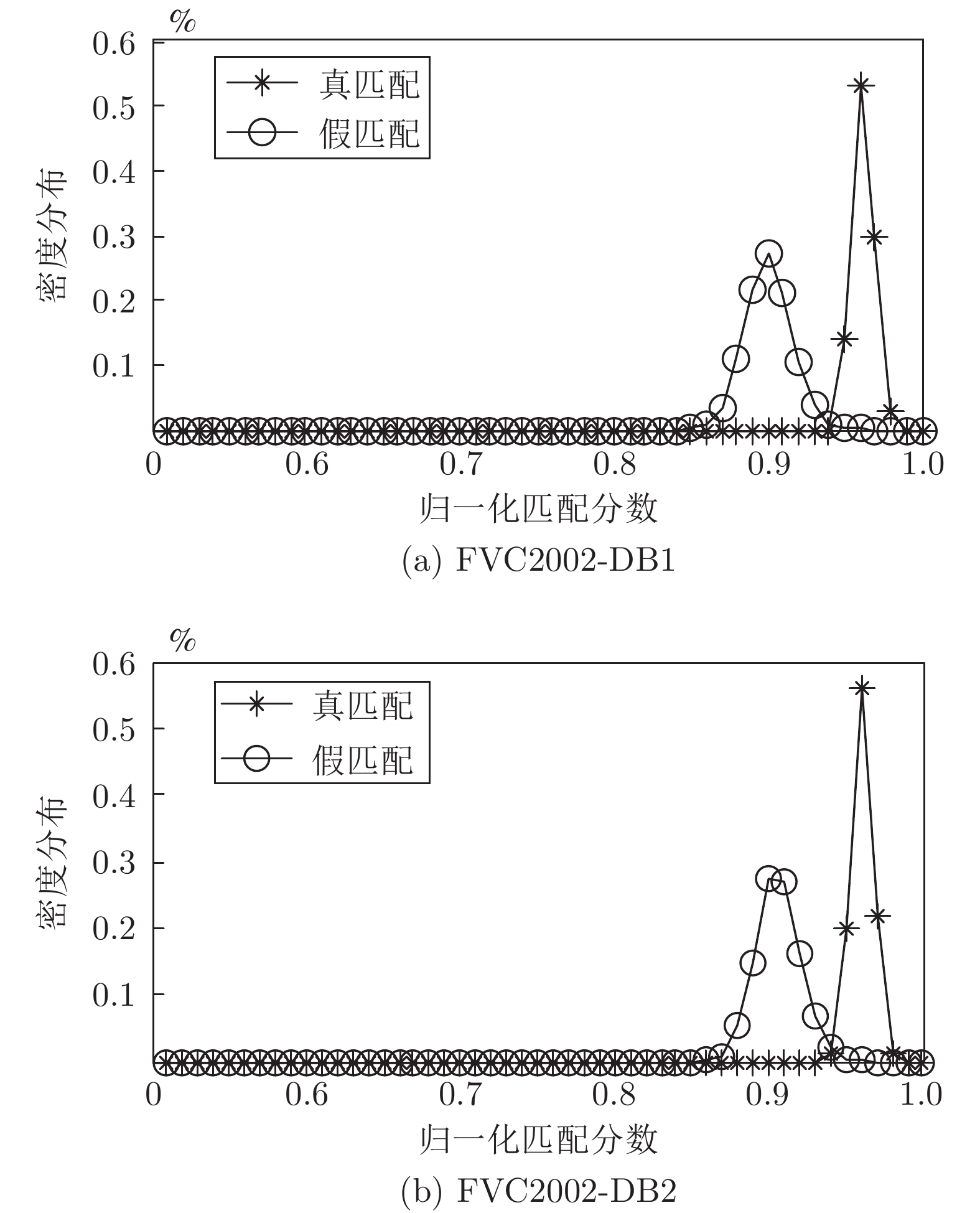
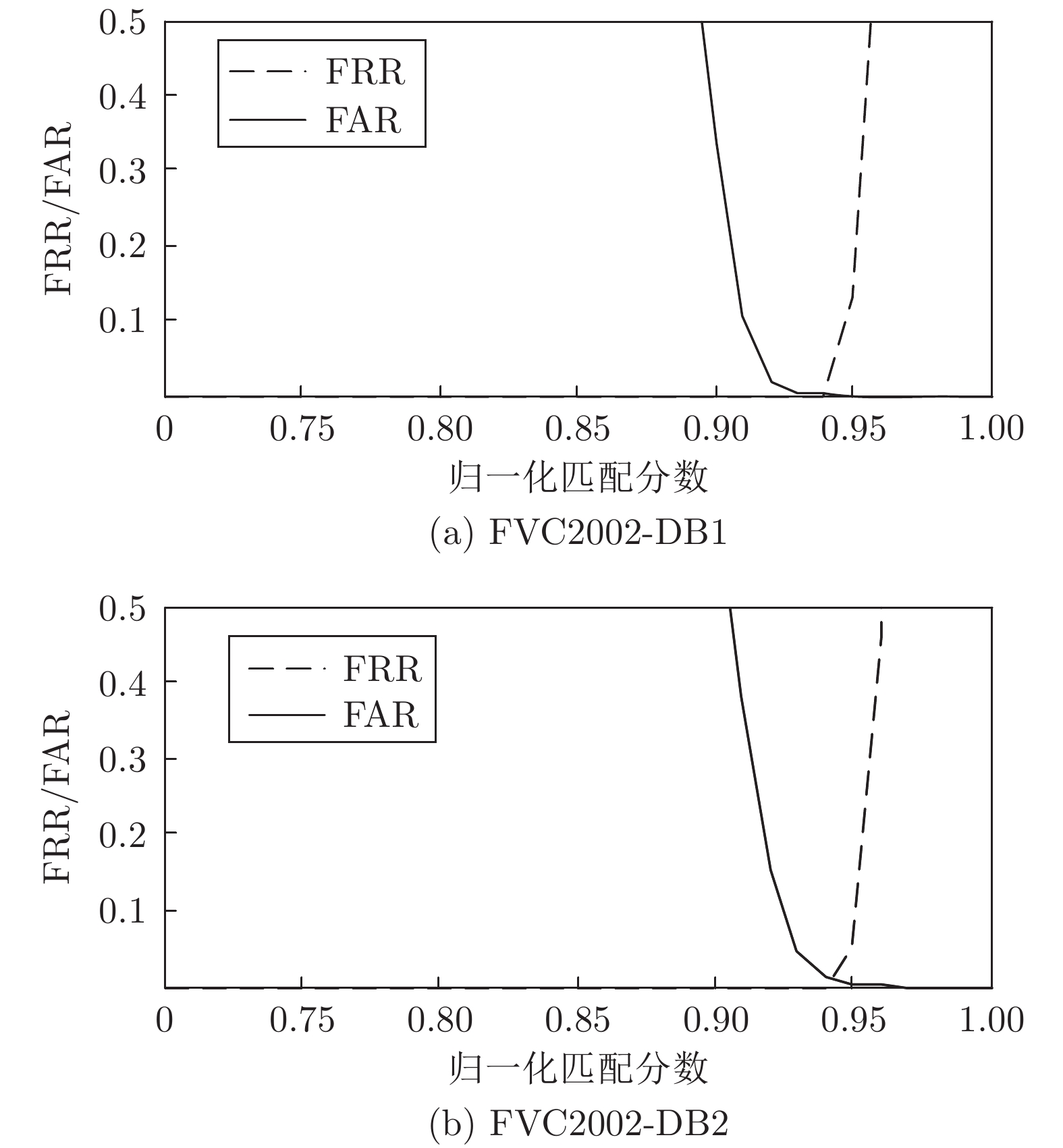
摘要: 针对现有指纹模板保护算法存在的准确性较低、安全性能较差的问题, 提出一种基于比特串异或和置乱变换的指纹模板保护算法. 该算法在已有二维映射算法的基础上, 对得到的比特串进行异或和随机索引置乱变换, 有效地将线性和非线性变换相结合, 扩展了密钥空间, 增强了指纹模板的安全性. 理论分析和仿真结果表明, 对于密钥泄露场景, 该算法在数据库FVC2002 DB1和DB2中的等错误率(Equal error rate, EER)分别为0.08 %和0.75 %, 与现有算法相比, 具有较好的准确性和安全性.Abstract: Aiming at the problems of low accuracy and poor security performance of the existing fingerprint template protection algorithm, A fingerprint template protection algorithm based on bit string XOR and scrambling transformation is proposed. Based on the existing two-dimensional mapping algorithm, the algorithm performs XOR and random index scrambling transformation on the obtained bit string, the algorithm effectively combines linear and nonlinear transformations, thereby expanding the key space and enhancing the security of the fingerprint template. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that for the key leakage scenario, the equal error rate (EER) of the algorithm in the database FVC2002 DB1, DB2 is 0.08 % and 0.75 %, respectively, compared with existing methods, it has better accuracy and security.
-
Key words:
- Fingerprint template /
- security /
- bit string /
- XOR /
- scrambling
-
表 1 数据库FVC2002 DB1、DB2和DB3的参数
Table 1 Parameters of the FVC2002 DB1, DB2 and DB3
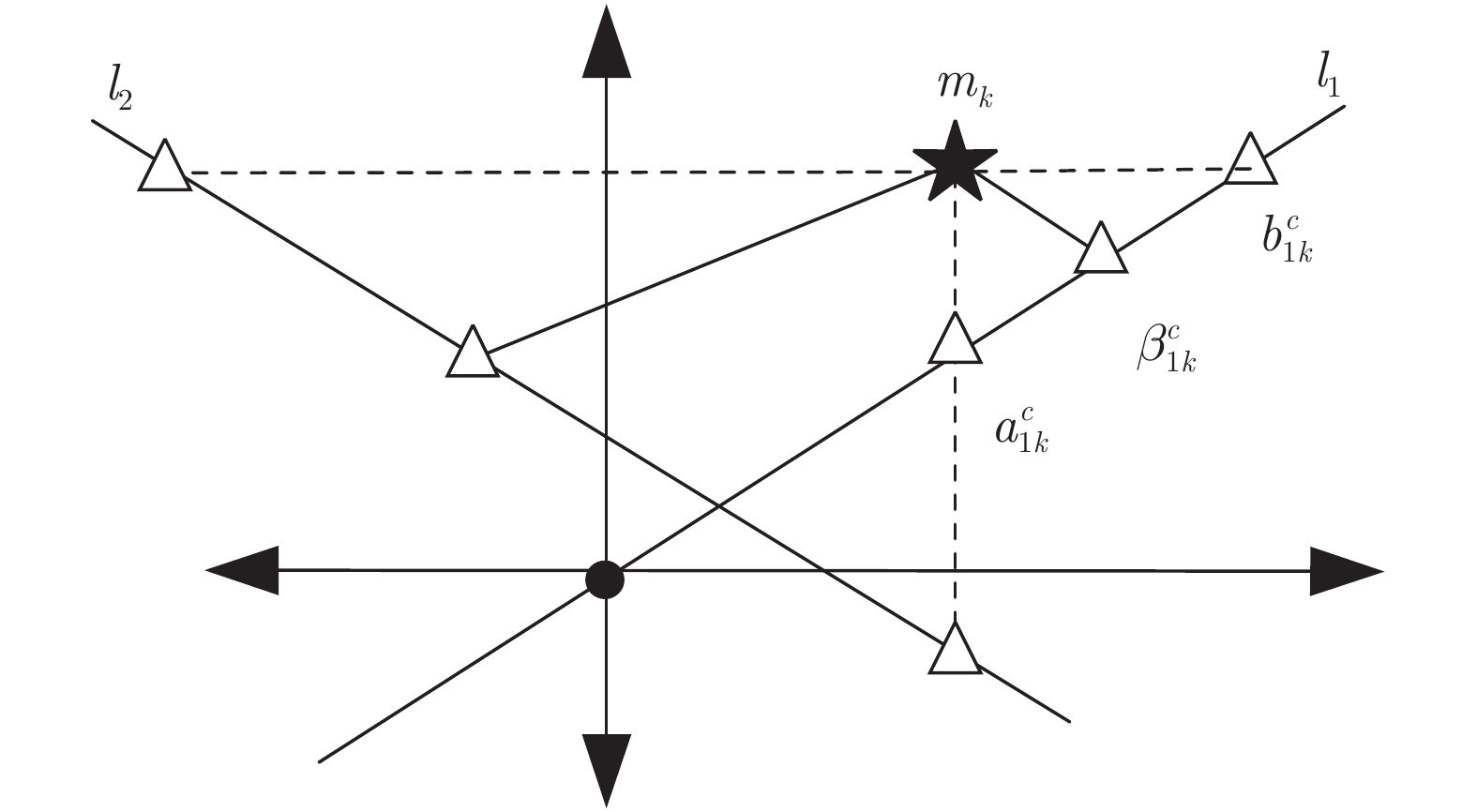
指纹数据库 DB1 DB2 DB3 传感器类型 光纤 光纤 电容 手指数量 $100$ $100$ $100$ 每枚手指样本个数 $8$ $8$ $8$ 分辨率 (dpi) $500$ $569$ $500$ 图像尺寸 $388\times374$ $296\times560$ $300\times300$ 图像质量 高 中 低 表 2 不同参数的取值范围
Table 2 Range of different parameters
参数 参数描述 参数范围 $r_{\rm{\min}}$ 环形区域最小半径 $\{ 15,16,17 \}$ $r_{\rm{\max}}$ 环形区域最大半径 $\{ 100,240 \}$ $G_{x}$ 二维网格的长 $\{13, 14,15, 16 \}$ $G_{y}$ 二维网格的宽 $\{ 7,14 \}$ $\rho_{1,2}$ 投影直线斜率 $[-2,4]$ $w$ 步长 $[2,4]$ 表 3 密钥泄露时不同参数的EER (%)
Table 3 EER of different parameters (%)
$r_{\rm{\min}}$ $r_{\rm{\max}}$ $G_{x}$ $G_{y}$ $\rho_{1}$ $\rho_{2}$ $w$ DB1 DB2 $16$ 100 $13$ $7$ $0.577$ $-1.73$ $2$ $0.25$ $2.02$ $16$ 110 $14$ $8$ $0.839$ $-1$ $2$ $0.17$ $1.67$ $16$ 120 $14$ $9$ $1$ $-0.84$ $2$ $0.22$ $1.82$ ${\bf 16}$ ${\bf 140}$ ${\bf 14}$ ${\bf 9}$ ${\bf 1.192}$ ${\bf -0.58}$ ${\bf 3}$ ${\bf 0.08}$ ${\bf 0.75}$ $16$ 160 $14$ $9$ $1.192$ $-0.58$ $4$ $0.12$ $1.46$ $16$ 180 $14$ $9$ $1.192$ $-0.36$ $4$ $0.15$ $1.66$ $16$ 200 $14$ $10$ $1.732$ $-0.26$ $4$ $0.42$ $2.30$ $16$ 220 $15$ $12$ $2.144$ $-0.18$ $4$ $1.12$ $3.11$ $16$ 240 $16$ $14$ $2.747$ $-0.14$ $4$ $0.68$ $1.81$ $16$ 260 $17$ $15$ $3.732$ $-0.09$ $4$ $0.98$ $2.64$ 表 4 SCFT算法和本文算法的EER比较(%)
Table 4 EER comparison between the SCFT algorithms and proposed algorithms (%)
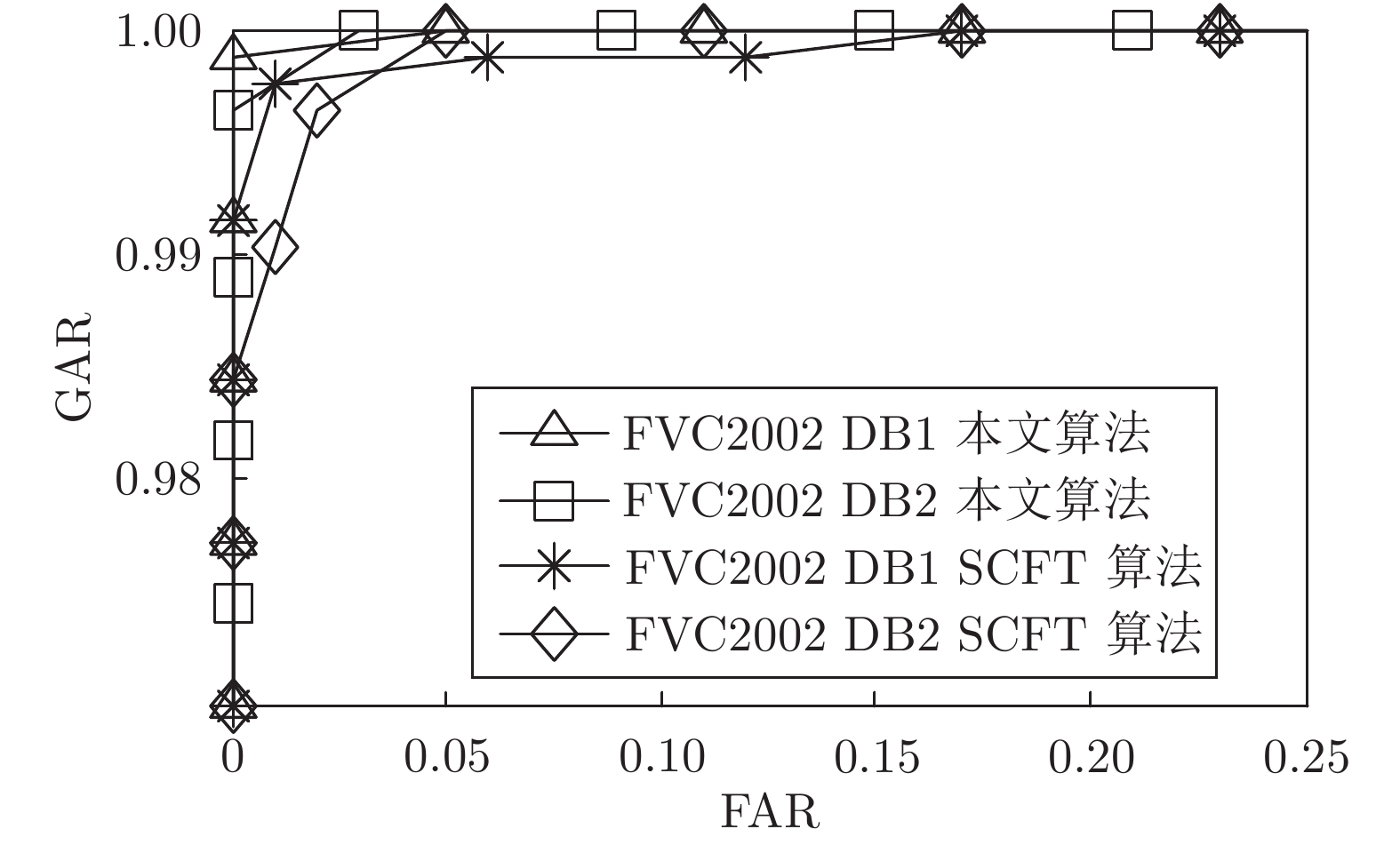
算法 密钥安全 密钥泄露 DB1 DB2 DB3 DB1 DB2 DB3 SCFT 算法 − − − 5.12 − 16.99 本文算法 0 0 0 0.08 0.75 3.26 表 5 不同算法的EER比较(%)
Table 5 EER comparison of different algorithms (%)
表 6 依次增加不同改进算法的EER (%)
Table 6 EER of add different improved algorithms (%)
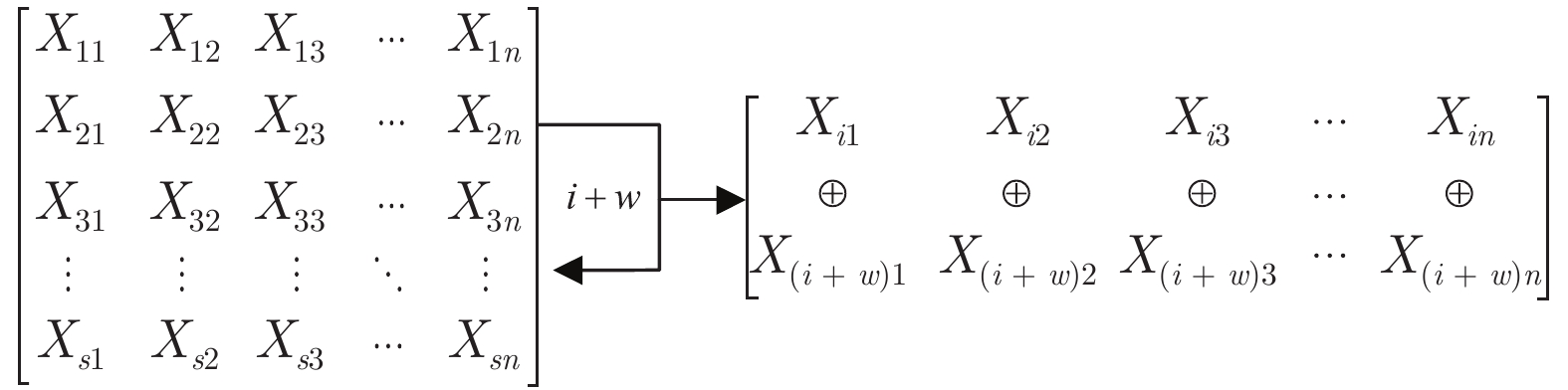
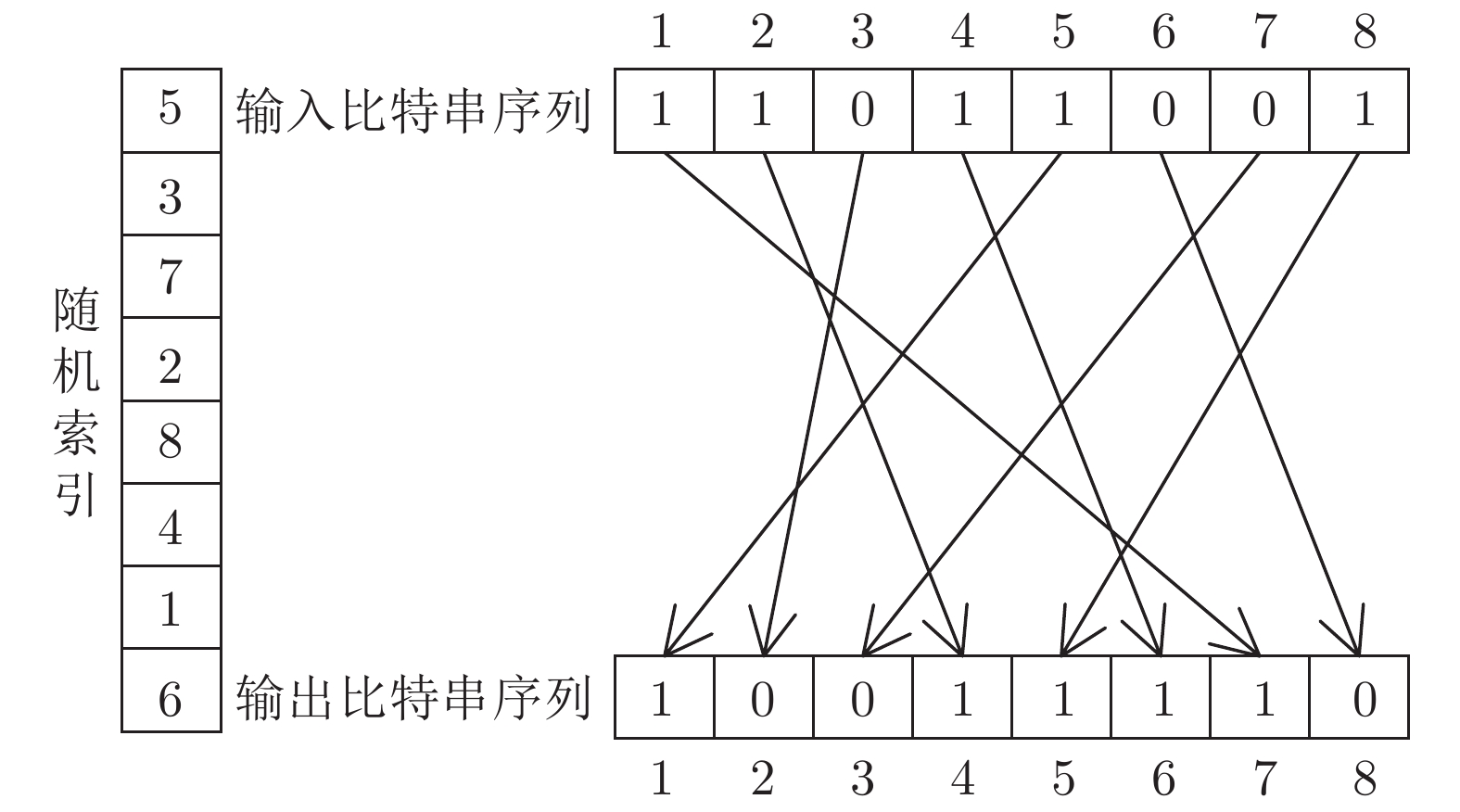
算法 DB1 DB2 密钥安全 密钥泄露 密钥安全 密钥泄露 改进前算法 0 3.26 0 2.915 随机异或 0 1.05 0 1.58 行间异或 0 0.44 0 1.24 随机索引置乱 0 0.08 0 0.75 -
[1] Nagar A. Biometric template security. Eurasip Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2008, 2008(1): 1−17 [2] Yue F, Zuo W M, Zhang D P. Survey of palmprint recognition algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(3): 353−365 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00353 [3] Jin Z, Teoh A B J, Ong T S, Tee C. Fingerprint template protection with minutiae-based bit-string for security and privacy preserving. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(6): 6157−6167 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.11.091 [4] Juels A, Wattenberg M. A fuzzy commitment scheme. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, New York, USA: ACM Press, 1999. 28−36 [5] Dodis Y, Reyzin L, Smith A. Fuzzy extractors: How to generate strong keys from biometrics and other noisy data. In: Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Technique, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2004. 523−540 [6] Juels A, Sudan M. A fuzzy vault scheme. Designs Codes and Cryptography, 2006, 38(2): 237−257 doi: 10.1007/s10623-005-6343-z [7] Ratha N K, Connell J H, Bolle R M. Enhancing security and privacy in biometrics-based authentication systems. IBM Systems Journal, 2001, 40(3): 614−634 doi: 10.1147/sj.403.0614 [8] Ratha N K, Chikkerur S, Connell J H, Bolle R M. Generating cancelable fingerprint templates. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(4): 561−572 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1004 [9] Tulyakov S, Farooq F, Mansukhani P, Govindaraju V. Symmetric hash functions for secure fingerprint biometric systems. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2007, 28(16): 2427−2436 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2007.08.008 [10] Lee C, Kim J. Cancelable fingerprint templates using minutiae-based bit-strings. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2010, 33(3): 236−246 [11] Ahmad T, Hu J K. Generating cancelable biometric templates using a projection line. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Control Automation Robotics and Vision, Singapore: IEEE 2011. 7−12 [12] Li S, Kot A C. Fingerprint combination for privacy protection. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2013, 8(2): 350−360 [13] Sandhya M, Prasad M V N K. K-nearest neighborhood structure (k-NNS) based alignment-free method for fingerprint template protection. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Biometrics, Phuket, Thailand: IEEE, 2015. 386−393 [14] Wang S, Hu J K. A blind system identification approach to cancelable fingerprint templates. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 54(1): 14−22 [15] 许秋旺, 张雪锋. 基于细节点邻域信息的可撤销指纹模板生成算法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(4): 645−652Xu Qiu-Wang, Zhang Xue-Feng. Generating cancelable fingerprint templates using minutiae local information. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(4): 645−652 [16] Ahmad T, Rasyid B. SCFT: Sector-based cancelable fingeprint template. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), 2017. 156−160 [17] Alam B, Jin Z, Yap W S, Goi B M. An alignment-free cancelable fingerprint template for bio-cryptosystems. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 115: 20−32 [18] Wang S, Yang W C, Hu J K. Design of alignment-free cancelable fingerprint templates with zoned minutia pairs. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 66: 295−301 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.01.019 [19] Pambudi D S, Ahmad T, Usagawa T. Improving the performance of projection-based cancelable fingerprint template method. In: Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition, Fukuoka, Japan: IEEE, 2016. 84−88 [20] Ahmad T, Hu J K. Generating cancelable biometric templates using a projection line. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Control Automation Robotics and Vision, Singapore: IEEE, 2010. 7−12 [21] Prasad M V N K, Kumar C S. Fingerprint template protection using multiline neighboring relation. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41(14): 6114−6122 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.04.020 [22] Ahmad T, Hu J K, Wang S. Pair-polar coordinate-based cancelable fingerprint templates. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(10): 2555−2564 [23] Yang W C, Hu J K, Wang S, Yang J C. Cancelable fingerprint templates with delaunay triangle-based local structures. Cyberspace Safety and Security and Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2013, 8300: 81−91 [24] Jin Z, Lim M H, Teoh A B J, Goi B M. A non-invertible randomized graph-based Hamming embedding for generating cancelable fingerprint template. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 42(6): 137−147 [25] Wang S, Hu J K. Alignment-free cancelable fingerprint template design: A densely infinite-to-one mapping (DITOM) approach. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(12): 4219−4137 [26] Das P, Karthik K, Garai B C. A robust alignment-free fingerprint hashing algorithm based on minimum distance graphs. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(9): 3373−3388 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.02.022 [27] Ali S, Ganapathi I I, Prakash S. Robust technique for fingerprint template protection. IET Biometrics, 2018, 7(6): 536−549 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2018.04.013 [28] 惠妍, 张雪锋. 基于局部细节点三维映射的指纹模板生成方法. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(1): 42−56Hui Yan, Zhang Xue-Feng. A fingerprint template generating method based on local minutiae three-dimensional mapping. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2019, 49(1): 42−56 -




 下载:
下载: