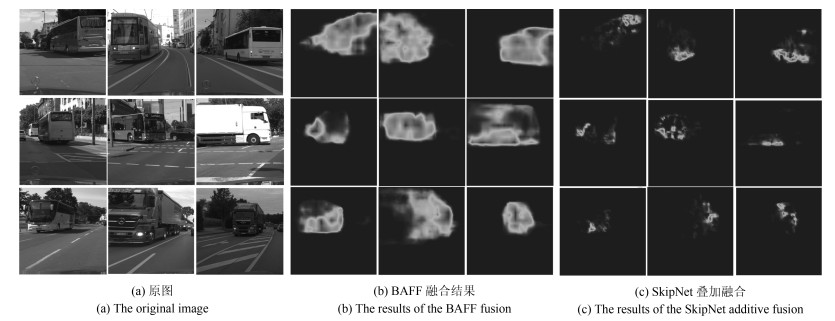
-
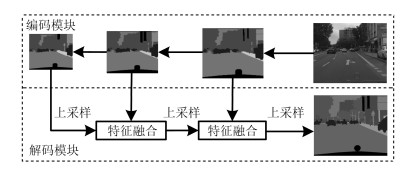
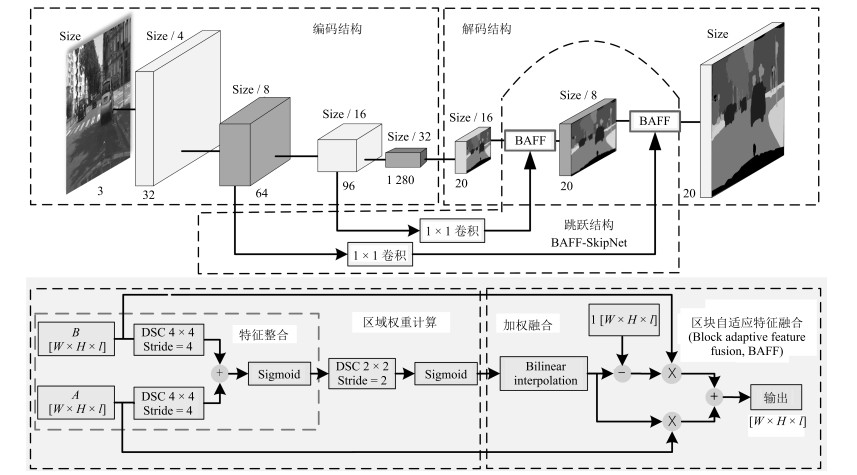
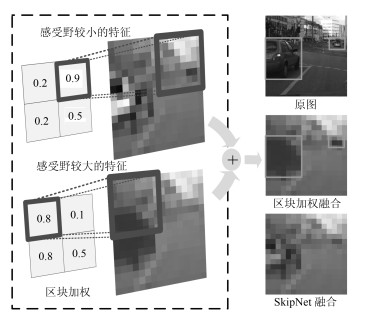
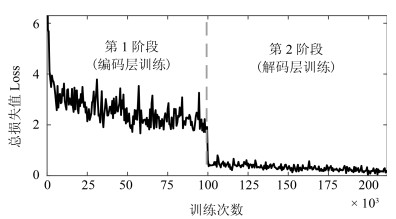
摘要: 近年来结合深度学习的图像语义分割方法日益发展, 并在机器人、自动驾驶等领域中得到应用. 本文提出一种基于区块自适应特征融合(Block adaptive feature fusion, BAFF) 的实时语义分割算法, 该算法在轻量卷积网络架构上, 对前后文特征进行分区块自适应加权融合, 有效提高了实时语义分割精度. 首先, 分析卷积网络层间分割特征的感受野对分割结果的影响, 并在跳跃连接结构(SkipNet) 上提出一种特征分区块加权融合机制; 然后, 采用三维卷积进行层间特征整合, 建立基于深度可分离的特征权重计算网络. 最终, 在自适应加权作用下实现区块特征融合. 实验结果表明, 本文算法能够在图像分割的快速性和准确性之间做到很好的平衡, 在复杂场景分割上具有较好的鲁棒性.Abstract: Recently, image semantic segmentation has made great progress with deep learning, which benefits robotics and automatic driving vehicle. This paper proposes a real-time semantic segmentation algorithm based on block adaptive feature fusion (BAFF). Under the framework of a light convolutional network, a block adaptive feature fusion algorithm is proposed in the context-embedding module, to improve the accuracy of real-time semantic segmentation. First, the problem caused by the different size of receptive field in layers is analyzed, and a feature fusion mechanism with block weight is presented on SkipNet. Then, layers' feature integration is carried on by three-dimension convolution. The feature-weights are calculated by an additional network with depthwise-separable-convolutions (DSC). Finally, the features are fused under adaptive weights. Experiments show that this method obtains excellent segmentation results with a good balance between rapidity and accuracy and owns robustness on segmentation of complex scenes.
-
Key words:
- Deep learning /
- real-time semantic segmentation network /
- block adaptive feature fusion (BAFF) /
- SkipNet
1) 本文责任编委 刘成林 -
表 1 加入BAFF前后的模型复杂度对比
Table 1 Comparisons of model complexity before and after adding BAFF
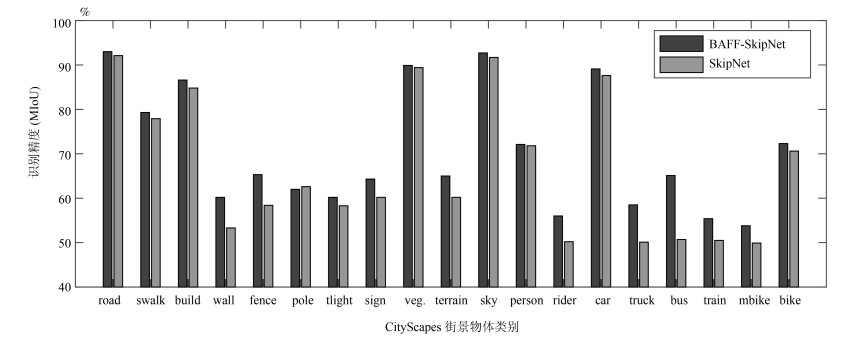
模型 MIoU (%) 运算量(M) 参数量(K) SkipNet 66.8 15 962.99 841.76 BAFF-SkipNet 70.5 15 963.23 843.17 表 2 语义分割各类别精度对比(%)
Table 2 Semantic segmentation accuracy comparison of different types (%)
模型 road swalk build. wall fence pole tlight sign veg. terrain sky person rider car truck bus train mbike bike 本文算法 93.0 79.3 86.6 60.2 65.3 62.0 60.2 64.3 89.9 65.0 92.7 72.1 56.0 89.1 58.5 65.1 55.4 53.8 72.3 ENet[28] 96.3 74.2 85.0 32.1 33.2 43.4 34.1 44.0 88.6 61.4 90.6 65.5 38.4 90.6 36.9 50.5 48.0 38.8 55.4 ContextNet[29] 97.6 79.2 88.8 43.8 42.8 37.9 52.0 58.8 90.0 66.9 91.9 72.1 53.9 91.6 54.0 66.4 58.3 48.9 61.0 ERFNet[30] 97.7 81.0 89.8 42.5 48.0 56.3 59.8 65.3 91.4 68.2 94.2 76.8 57.1 92.8 50.8 60.1 51.8 47.3 61.6 -
[1] Rother C, Kolmogorov V, Blake A. GrabCut-interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM Trans Graphics, 2004, 23(3): 309-314 doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015720 [2] 夏剑峰. 基于数学形态学的癌细胞的分割与识别. 电子科技, 2016, 29(10): 36-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6108.2016.10.018Xia Jian-Feng. Segmentation and recognition of cancer cells based on mathematical morphology. Electronic Science and Technology, 2016, 29(10): 36-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6108.2016.10.018 [3] He X, Zemel R S, Ray D. Learning and incorporating top-down cues in image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision. Graz, Austria: Springer, 2006. 338-351 [4] Raví D, Bober M, Farinella G M, Guarnera M, Battiato S. Semantic segmentation of images exploiting DCT based features and random forest. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 52(3): 260-273 http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=2d9ec586cbd26742062209cc11d28290 [5] Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507 doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [6] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640-651 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [7] Zeiler M D, Krishnan D, Taylor G W, Fergus R. Deconvolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2528-2535 [8] Kirkland E J. Bilinear Interpolation. Advanced Computing in Electron Microscopy. Boston MA, USA: Springer-Verlag, 2010. 261-263 [9] Zhang X Y, Zhou X Y, Lin M X, Sun J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6848-6856 [10] Howard A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W J, Weyand T, Andreetto M, Adam H. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv: 1704. 04861, 2017. [11] Siam M, Gamal M, Abdel-Razek M, Yogamani S, Jagersand M. RTSeg: Real-time semantic segmentation comparative study. In: Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Athens, Greece: IEEE, 2018. [12] Pinheiro P O, Lin T Y, Collobert R, Dollár P. Learning to Refine Object Segments. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 75-91 [13] Lin G S, Milan A, Shen C H, Reid I. RefineNet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. [14] Liu W, Rabinovich A, Berg A C. ParseNet: Looking wider to see better. arXiv: 1506.04579, 2015. [15] Noh H, Hong S, Han B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1520-1528 [16] Dang H T H. A guide to receptive field arithmetic for convolutional neural networks[Online], available: https://medium.com/mlreview/a-guide-to-receptive-field-arithmetic-for-convolutional-neural-networks-e0f514068807, April 5, 2017 [17] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Lille, France: PMLR, 2015. 448-456 [18] Chollet F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. [19] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M L, Zhmoginov A, Chen L C. Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks: Mobile networks for classification, detection and segmentation. arXiv: 1801. 04381. 2018. [20] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI). Switzerland: Springer-verlag, 2015. 234-241 [21] Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv: 1511.07122, 2015. [22] Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S, Sun G, Wu E H. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, arXiv: 1709.01507, 2017. [23] 张婷, 李玉鑑, 胡海鹤, 张亚红. 基于跨连卷积神经网络的性别分类模型. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 858-865 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150658Zhang Ting, Li Yu-Jian, Hu Hai-He, Zhang Ya-Hong. A gender classification model based on cross-connected convolutional neural networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 858-865 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150658 [24] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533-536 doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [25] Michael A N. Neural Networks and Deep Learning[Online], available: http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/, October 2, 2018 [26] Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, Rehfeld T, Enzweiler M, Benenson R, Franke U, Roth S, Schiele B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3213-3223 [27] Garcia-Garcia A, Orts-Escolano S, Oprea S, Villenamartinez V, Garciarodriguez J. A review on deep learning techniques applied to semantic segmentation. arXiv: 1704.06857. 2017. [28] Paszke A, Chaurasia A, Kim S, Culurciello E. ENet: A deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv: 1606.02147. 2016. [29] Poudel R P K, Bonde U, Liwicki S, Zach C. ContextNet: Exploring context and detail for semantic segmentation in real-time. arXiv: 1805.04554. 2018. [30] Romera Eälvarez J M, Bergasa L M, Arroyo R. ERFNet: Efficient residual factorized convnet for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 19(1): 263-272 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8063438 -




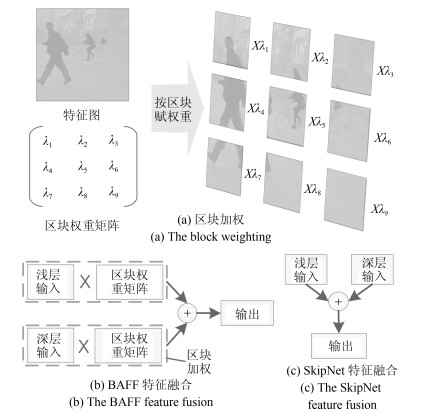
 下载:
下载: