-
摘要: 邻域粗糙集可以直接处理数值型数据, F- 粗糙集是第一个动态粗糙集模型. 针对动态变化的数值型数据, 结合邻域粗糙集和F- 粗糙集的优势, 提出了F- 邻域粗糙集和F- 邻域并行约简. 首先, 定义了F- 邻域粗糙集上下近似、边界区域; 其次, 在F- 邻域粗糙集中提出了F- 属性依赖度和属性重要度矩阵; 根据F- 属性依赖度和属性重要度矩阵分别提出了属性约简算法, 证明了两种约简方法的约简结果等价; 最后, 比对实验在UCI数据集、真实数据集和MATLAB生成数据集上完成, 实验结果显示, 与相关算法比较, F- 邻域粗糙集可以获得更好的分类准确率. 为粗糙集在大数据方面的应用增加了一种新方法.Abstract: Neighborhood rough sets can directly process numerical data, and F-rough sets are the flrst dynamic rough set model. For dynamic numerical data, combined the advantages of neighborhood rough sets and F-rough sets, Fneighborhood rough sets and its reducts are proposed. Firstly, three uncertainty regions are deflned in F-neighborhood rough sets, including upper and lower approximations, and boundary regions. Secondly, F-dependence degree and an attribute signiflcance matrix are created, and then two attribute reduction algorithms are proposed, which can deal with hybrid data. The obtained reducts with these two algorithms are proved to be equivalent. Finally, the comparison experiments are performed on UCI data sets, real data sets and MATLAB generated data sets. The experimental results show that F-neighborhood rough sets have advantages over related algorithms on the classiflcation accuracy rates. A new method is added for the application of rough sets in big data.
-
Key words:
- Neighborhood rough sets /
- F-rough sets /
- attribute reduction /
- attribute signiflcance matrix
1) 本文责任编委 张敏灵 -
表 1 邻域决策子系统NDT1
Table 1 A neighborhood decision subsystem NDT1
U1 f(x, a) f(x, b) f(x, c) f(x, d) x1 0.1 0.6 0.1 0 x2 1.5 1.0 0.3 0 x3 1.6 1.2 0.4 1 x4 0.3 0.9 0.2 0 x5 1.3 1.5 0.5 1 表 2 邻域决策子系统NDT2
Table 2 A neighborhood decision subsystem NDT2
U1 f(y, a) f(y, b) f(y, c) f(y, d) y1 1.1 2.1 0.6 1 y2 1.3 1.9 2.2 1 y3 1.2 0.5 2.4 1 y4 1.0 0.8 2.1 0 y5 1.1 0.6 1.6 0 表 3 数据集描述
Table 3 Description of datasets
名称 样本量 属性量 分类数目 Iris 150 4 3 wpbc 198 33 2 soy 47 35 4 sonar 208 60 2 wine 178 13 3 abalone 4 177 8 3 spambase 4 601 57 2 debrecen 1 151 19 2 EEGEye 14 980 14 2 Cevaluation 240 26 2 Rapequality 138 10 2 Generated data 1 000 40 2 表 4 δ=0.1时两种算法约简的结果
Table 4 Results of two algorithm reductions when δ=0.1
数据集 NRS NPRMS (或NPRAS) 属性数目 分类准确率 属性数目 分类准确率 Iris 4 0.93333 3 0.93333 wpbc 6 0.625 7 0.65 soy 2 1 2 1 sonar 5 0.64286 10 0.69048 wine 5 0.86111 4 0.88889 abalone 8 0.83713 8 0.83713 spambase 8 0.88587 9 0.89239 debrecen 3 0.60435 4 0.62609 EEGEye 4 0.71996 5 0.8004 Cevaluation 2 0.89583 4 0.91667 Rapequality 4 0.92857 4 0.92857 Generated data 4 0.565 5 0.665 表 5 δ=0.05时两种算法约简的结果
Table 5 Results of two algorithm reductions when δ=0.05
数据集 NRS NPRMS (或NPRAS) 属性数目 分类准确率 属性数目 分类准确率 Iris 3 0.86667 3 0.93333 wpbc 4 0.675 6 0.725 soy 2 1 2 1 sonar 4 0.71429 7 0.69048 wine 3 0.77778 5 0.83333 abalone 8 0.83713 8 0.83713 spambase 7 0.87065 9 0.87065 debrecen 3 0.57391 3 0.63043 EEGEye 4 0.71996 5 0.8004 Cevaluation 2 0.8125 3 1 Rapequality 4 0.92857 4 0.92857 Generated data 3 0.635 5 0.67 表 6 δ=0.01时两种算法约简的结果
Table 6 Results of two algorithm reductions when δ=0.01
数据集 NRS NPRMS (或NPRAS) 属性数目 分类准确率 属性数目 分类准确率 Iris 3 0.86667 3 0.93333 wpbc 3 0.675 4 0.85 soy 2 1 2 1 sonar 3 0.64286 4 0.7381 wine 3 0.86111 3 0.94444 abalone 5 0.83832 6 0.8479 spambase 8 0.87283 9 0.87609 debrecen 2 0.54783 3 0.6913 EEGEye 4 0.71996 5 0.8004 Cevaluation 2 0.8125 2 1 Rapequality 2 0.89286 4 0.92857 Generated data 3 0.595 4 0.64 表 7 在各个数据集中三种算法约简的结果
Table 7 Results of three algorithmic reductions in each dataset
数据集 NRS OPRMAS PCA NPRMS (或NPRAS) 属性数目 分类准确率 属性数目 分类准确率 属性数目 分类准确率 属性数目 分类准确率 Iris 3 0.86667 3 0.9 3 0.96667 3 0.93333 wpbc 3 0.675 9 0.725 4 0.55 4 0.85 soy 2 1 2 0.66667 2 0.77778 2 1 sonar 3 0.64286 7 0.80952 4 0.61905 4 0.7381 wine 3 0.86111 4 0.77778 3 0.91667 3 0.94444 abalone 5 0.83832 8 0.83713 6 0.48862 6 0.8479 spambase 8 0.87283 20 0.92283 9 0.87174 9 0.87609 debrecen 2 0.54783 11 0.6087 3 0.56522 3 0.6913 EEGEye 4 0.71996 14 0.83678 5 0.72664 5 0.8004 Cevaluation 2 0.8125 2 1 2 0.8125 2 1 Rapequality 2 0.89286 6 0.89286 4 0.89286 4 0.92857 Generated data 3 0.595 15 0.575 4 0.57 4 0.64 -
[1] Jensen R, Shen Q. Fuzzy-rough attribute reduction with application to web categorization. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2004. 141(3): 469-485 doi: 10.1016/S0165-0114(03)00021-6 [2] Hu Q H, Yu D R, Xie Z X. Information-preserving hybrid data reduction based on fuzzy-rough techniques. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 27(5): 414-423 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.09.004 [3] Hall M A. Correlation-based feature selection for discrete and numeric class machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 2015. 359-366 [4] Dash M, Liu H. Consistency-based search in feature selection. Artificial Intelligence, 2003, 151(1-2): 155-176 doi: 10.1016/S0004-3702(03)00079-1 [5] Pawlak Z. Rough sets. International Journal of Information and Computer Science, 1982, 11(5): 341-356 doi: 10.1007/BF01001956 [6] Sakai H, Chakraborty M K, Hassanien A E, Sakai H, Chakraborty M K, Hassanien A E, Ślęzak D, Zhu W. Rough sets, fuzzy sets, data mining and granular computing. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on RSFDGrC. Delhi, India: Springer, 2009. [7] 尹林子, 阳春华, 王晓丽, 桂卫华. 基于标记可辨识矩阵的增量式属性约简算法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(3): 397-404 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00397Yin Lin-Zi, Yang Chun-Hua, Wang Xiao-Li, Gui Wei-Hua. An incremental algorithm for attribute reduction based on labeled discernibility matrix. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(3): 397-404 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00397 [8] 王加阳, 陈松乔, 罗安. 粗集动态约简研究. 小型微型计算机系统, 2006, (11): 2056-2060 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2006.11.015Wang Jia-Yang, Chen Song-Qiao, Luo An. Study for dynamic reduct based on rough set. Mini-micro Systems, 2006, (11): 2056-2060 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2006.11.015 [9] 徐菲菲, 雷景生, 毕忠勤, 苗夺谦, 杜海舟. 大数据环境下多决策表的区间值全局近似约简. 软件学报, 2014, 25(9): 2119-2135 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB201409017.htmXu Fei-Fei, Lei Jing-Sheng, Bi Zhong-Qin, Miao Duo-Qian, Du Hai-Zhou. Approaches to approximate reduction with interval-valued multi-decision tables in big data. Journal of Software, 2014, 25(9): 2119-2135 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB201409017.htm [10] 邓大勇, 徐小玉, 黄厚宽. 基于并行约简的概念漂移探测. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 52(5): 1071-1079 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201505011.htmDeng Da-Yong, Xu Xiao-Yu, Huang Hou-Kuan. Conceptual drifting detecti for categorical evolving data based on parallel reducts. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 52(5): 1071-1079 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201505011.htm [11] 陈泽华, 马贺. 基于粒矩阵的多输入多输出真值表快速并行约简算法. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(5): 1260-1265 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201505038.htmChen Ze-Hua, Ma He. Granular matrix based rapid parallel reduction algorithm for MIMO truth table. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2015, 37(5): 1260- 1265 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201505038.htm [12] Wang F, Xu J, Li L. A novel rough set reduct algorithm to feature selection based on artificial fish swarm algorith. Advances in Swarm Intelligence, ICSI 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, 2014. 24-33 [13] 胡清华, 于达仁, 谢宗霞. 基于邻域粒化和粗糙逼近的数值属性约简. 软件学报, 2008, (3): 640-649 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB200803018.htmHu Qing-Hua, Yu Da-Ren, Xie Zong-Xia. Numerical attribute reduction based on neighborhood granulation and rough approximation. Journal of Software, 2008, (3): 640- 649 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB200803018.htm [14] 胡清华, 赵辉, 于达仁. 基于邻域粗糙集的符号与数值属性快速约简算法. 模式识别与人工智能, 2008, 21(6): 732-738 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2008.06.004Hu Qing-Hua, Zhao Hui, Yu Da-Ren. Efficient symbolic and numerical attribute reduction with neighborhood rough sets. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2008, 21(6): 732-738 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2008.06.004 [15] 徐波, 张贤勇, 冯山. 邻域粗糙集的加权依赖度及其启发式约简算法. 模式识别与人工智能, 2018, 31(3): 256-264 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201803007.htmXu Bo, Zhang Xian-Yong, Feng Shan. Weighted dependence of neighborhood rough sets and its heuristic reduction algorithm. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 31(3): 256-264 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201803007.htm [16] Wang Q, Qian Y H, Liang X Y, Guo Q, Liang J Y. Local neighborhood rough set. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 151: 53-64 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950705118301886 [17] Wang C Z, Shao M W, He Q, Qian Y H, Qi Y L. Feature subset selection based on fuzzy neighborhood rough sets. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 111: 173-179 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2016.08.009 [18] Chen Y M, Zeng Z Q, Lu J W. Neighborhood rough set reduction with fish swarm algorithm. Soft Computing, 2016, 21(23): 1-12 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3156578 [19] 段洁, 胡清华, 张灵均, 钱宇华, 李德玉. 基于邻域粗糙集的多标记分类特征选择算法. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 52(1): 56-65 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201501007.htmDuan Jie, Hu Qing-Hua, Zhang Ling-Jun, Qian Yu-Hua, Li De-Yu. Feature selection for multi-label classification based on neighborhood rough sets. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 52(1): 56-65 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201501007.htm [20] Chen H M, Li T R, Cai Y, Luo C, Fujita H. Parallel attribute reduction in dominance-based neighborhood rough set. Information Sciences, 2016, 373: 351-368 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.09.012 [21] Kumar S U, Inbarani H H. PSO-based feature selection and neighborhood rough set-based classification for BCI multiclass motor imagery task. Neural Computing and Applications, 2017, 28(11): 3239-3258 doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2236-5 [22] Meng D, Zhang X H, Qin K Y. Soft Rough Fuzzy Sets and Soft Fuzzy Rough Sets. Pergamon Press, 2011. [23] 赵涛, 肖建. 基于包含度的区间二型模糊粗糙集. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(10): 1714-1721 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01714Zhao Tao, Xiao Jian. Interval type-2 fuzzy rough sets based on inclusion measures. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(10): 1714-1721 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01714 [24] Aggarwal M. Probabilistic variable precision fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 24(1): 29 -39 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2015.2426204 [25] Lin Y J, Li Y W, Wang C X, Chen J K. Attribute reduction for multi-label learning with fuzzy rough set. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 152: 51-61 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.04.004 [26] Deng D Y, Yan D X, Chen L. Attribute significance for F- parallel reducts. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Granular Computing. Kaohsiung, China: IEEE, 2012. 156-161 [27] 邓大勇, 陈林. 并行约简与F- 粗糙集. 云模型与粒计算. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 210-228Deng Da-Yong, Chen Lin. Parallel reduction and F-rough Sets. Cloud Model and Granular Computing. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. 210-228 [28] 邓大勇, 徐小玉, 裴明华. F- 模糊粗糙集及其约简. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 38(1): 58-66 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJSZ201501010.htmDeng Da-Yong, Xu Xiao-Yu, Pei Ming-Hua. F-fuzzy rough sets and its reducts. Journal of Zhejiang Normal University (Natural Science), 2015, 38(1): 58-66 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJSZ201501010.htm [29] 邓大勇, 李亚楠, 黄厚宽. F- 粗糙集视角的概念漂移与属性约简. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1781-1789 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170213Deng Da-Yong, Li Ya-Nan, Huang Hou-Kuan. Concept drift and attribute reduction from the viewpoint of F-rough sets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1781-1789 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170213 [30] 邓大勇, 卢克文, 黄厚宽, 邓志轩. 概念的属性约简及异构数据概念漂移探测, 电子学报, 2015, 2018, 46(5): 1234-1239 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU201805032.htmDeng Da-Yong, Lu Ke-Wen, Huang Hou-Kuan, Deng Zhi-Xuan. Attribute reduction for concepts and concept drifting detection in heterogeneous data. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(5): 1234-1239 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU201805032.htm -




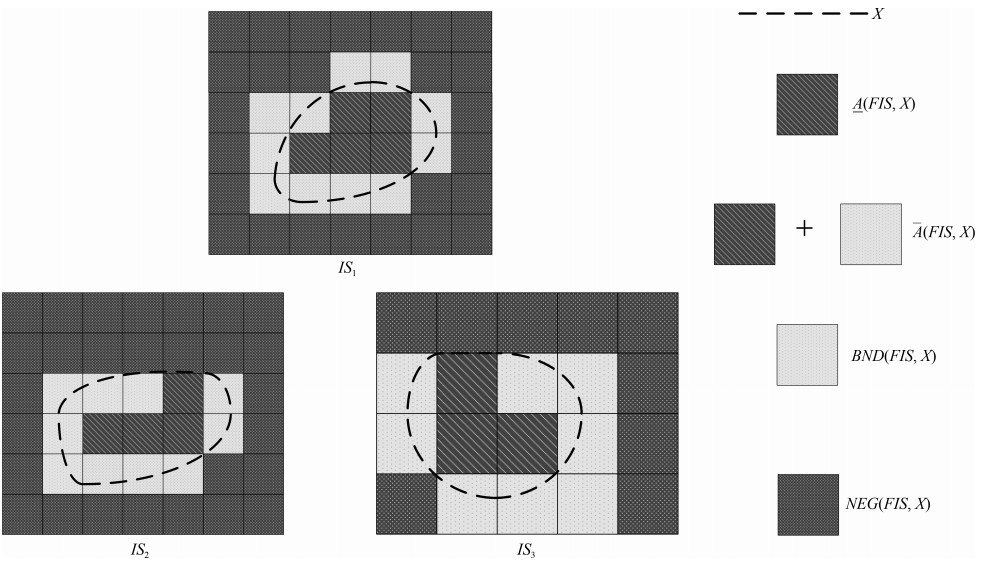
 下载:
下载:


