Automatic Liver Segmentation From CT Volumes Based on Level Set and Shape Descriptor
-
摘要: 肝脏分割是计算机辅助肝脏疾病诊断的重要前提和基础.本文提出了一种新的基于水平集和形状描述符的腹部CT序列图像肝脏自动分割方法.首先, 对原始腹部CT序列图像进行预处理, 去除与肝脏不相关的器官和组织.然后, 利用灰度偏移场, 结合周长项、距离正则项和相邻切片肝脏分割结果构建水平集能量函数, 实现CT序列肝脏自动分割.为避免分割误差累积, 提出一种基于形状描述符和瓶颈率的肝脏边缘优化方法, 在每张切片分割完毕后去除由于灰度重叠造成的过分割.通过对XHCSU14数据库和Sliver07数据库中腹部CT序列的肝脏分割实验, 以及与其他肝脏分割算法的比较, 表明了本文方法的有效性, 且分割精度高, 鲁棒性强.Abstract: Liver segmentation is an important prerequisite and basis for computer-assisted liver disease diagnosis. This paper proposes a novel method for automatic liver segmentation from CT volume based on level set and shape descriptor. First, irrelevant tissues and organs are removed from original CT volume. Then, intensity bias field together with perimeter term, distance regular term, and segmentation result of neighbor slice is utilized to construct a level set energy function, through which initial liver segmentation results for the CT volume are generated automatically. To avoid segmentation error accumulation, a liver boundary refinement method based on shape descriptor and bottleneck rate is proposed for each initial segmented slice to remove over-segmentation regions caused by intensity overlap. The experiments on CT volumes from XHCSU14 and Sliver07 databases, as well as the comparison with other algorithms show that our method can segment livers effectively with high accuracy and robustness.
-
Key words:
- Liver segmentation /
- level set /
- shape descriptor /
- abdominal CT image
1) 本文责任编委 张道强 -
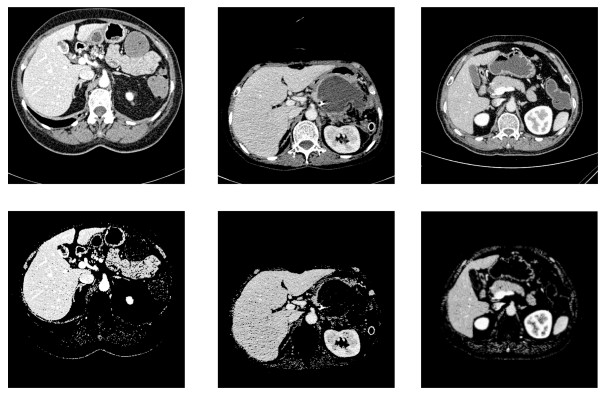
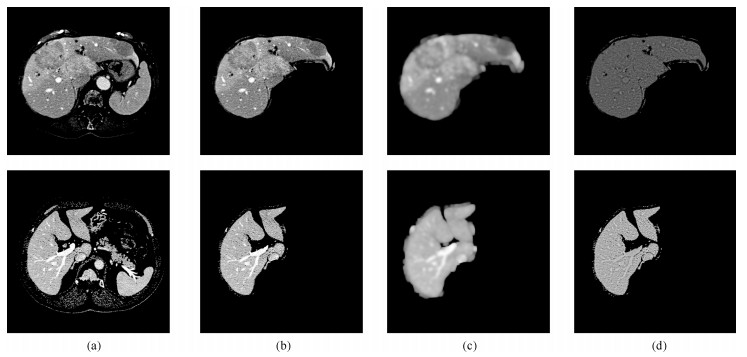
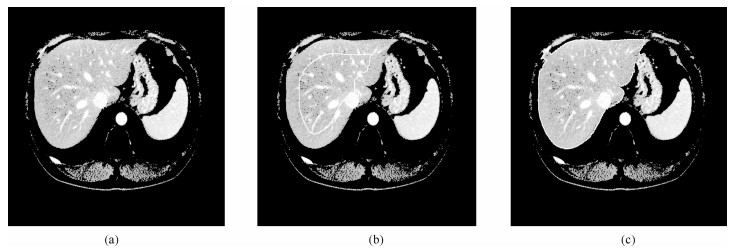
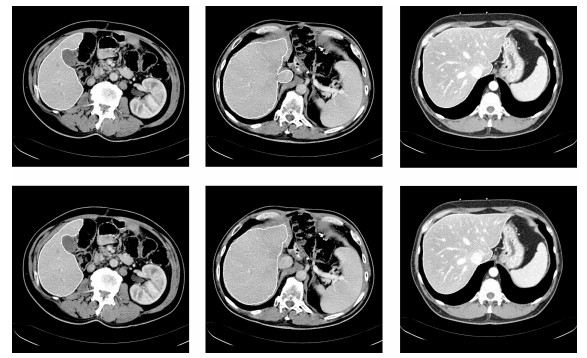
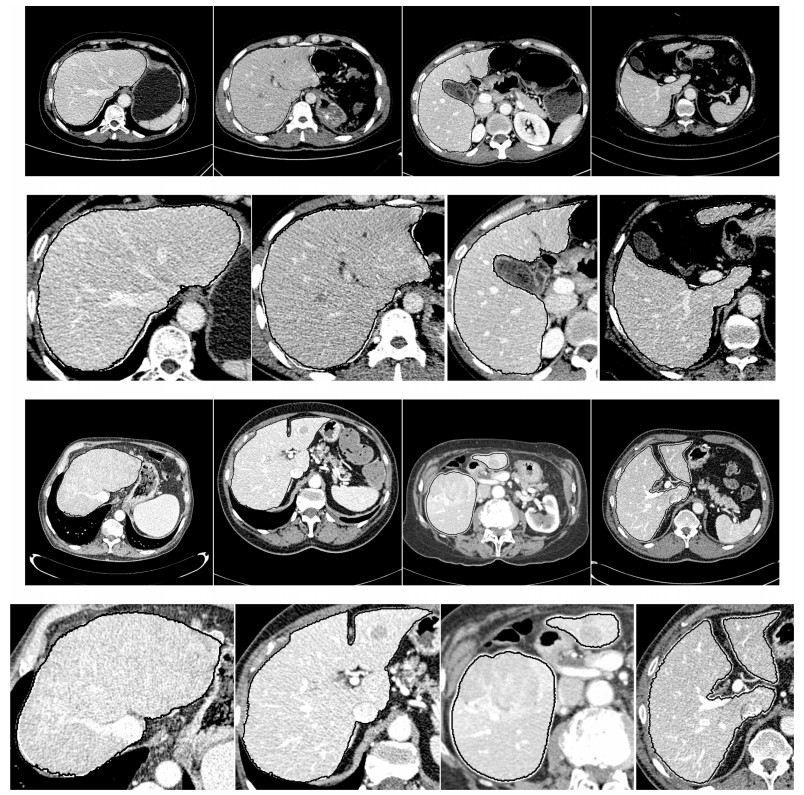
图 8 部分切片肝脏分割结果.第一行: XHCSU14数据库肝脏分割结果; 第三行: Sliver07数据库肝脏分割果; 第二和第四行:肝脏分割果局部放大图.(白色曲线表示专家标记肝脏区域, 黑色曲线表示本文算法肝脏分割结果)
Fig. 8 Some examples of liver segmentation results. First and third rows: Examples of liver segmentation results on XHCSU14 and Sliver07 databases, respectively; Second and fourth rows: Partial enlarged liver segmentation results(The white and black curves are segmentation results of experts and the proposed method, respectively)
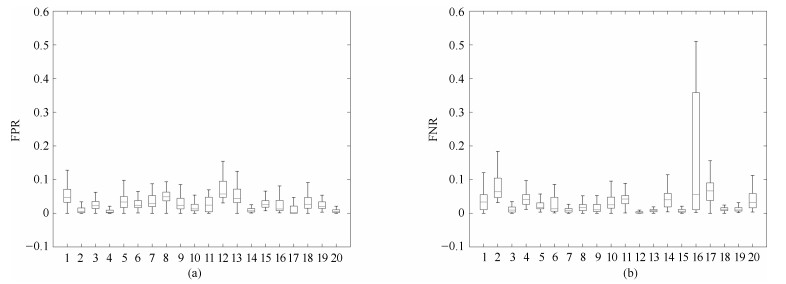
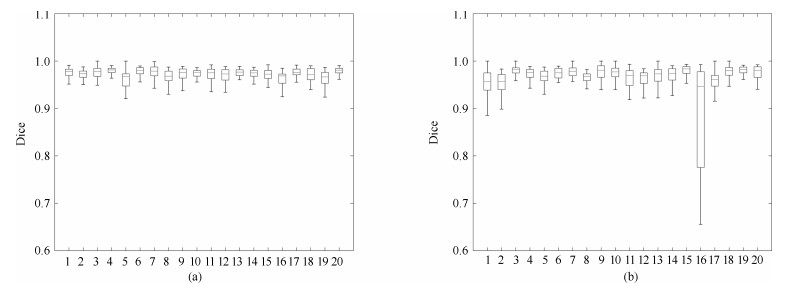
图 11 XHCSU14数据库和Sliver07数据库Dice系数分布图. (a) XHCSU14数据库肝脏分割结果Dice系数分布图; (b) Sliver07数据库肝脏分割结果Dice系数分布图
Fig. 11 Dice coefficients distributions for XHCSU14 and Sliver07 databases, respectively. (a) The Dice similar coefficients distribution of XHCSU14 database; (b) The Dice similar coefficients distribution of Sliver07 database
表 1 XHCSU14数据库分割性能比较(均值$\pm $标准差)
Table 1 Segmentation performance comparison on XHCSU14 database (mean $\pm$ std)
方法 VOE (%) RVD (%) ASD (mm) RMSD (mm) MSD (mm) 文献[4] 8.1$\pm $1.6 5.4$\pm $3.7 1.3$\pm $0.3 2.8$\pm $0.9 42.5$\pm $18.0 文献[6] 10.2$\pm $2.1 2.6$\pm $2.4 1.5$\pm $0.3 2.6$\pm $1.3 27.5$\pm $10.6 文献[7] 5.4$\pm $0.8 $-0.3\pm 1.3$ 0.8$\pm $0.1 1.3$\pm $0.3 20.5$\pm $7.4 本文方法 5.3$\pm $0.8 2.1$\pm $1.0 0.7$\pm $0.1 1.2$\pm $0.3 19.0$\pm $6.5 表 2 Sliver07数据库分割性能比较(均值$\pm $标准差)
Table 2 Segmentation performance comparison on Sliver07 database (mean $\pm$ std)
方法 VOE (%) RVD (%) ASD (mm) RMSD (mm) MSD (mm) 文献[4] 7.4$\pm $1.9 4.6$\pm $2.8 1.2$\pm $0.4 2.8$\pm $1.3 38.5$\pm $18.0 文献[6] 8.9$\pm $2.2 2.3$\pm $2.0 1.4$\pm $0.3 2.4$\pm $1.2 24.3$\pm $9.6 文献[7] 5.8$\pm $3.2 $-0.1\pm 4.1$ 1.0$\pm $0.5 2.0$\pm $1.2 21.2$\pm $9.3 本文方法 5.7$\pm $3.0 $-0.5\pm 4.0$ 1.1$\pm $0.5 2.1$\pm $1.3 21.5$\pm $10.7 -
[1] Fu J, Wang H Y. Precision diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer in China. Cancer Letters, 2018, 412(3): 283-288 [2] Zeng Y Z, Zhao Y Q, Liao S H, Liao M, Chen Y, Liu X Y. Liver vessel segmentation based on centerline constraint and intensity model. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2018, 45: 192-201 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2018.05.035 [3] 李祥霞, 李彬, 田联房, 张莉, 朱文博.基于稀疏表示和随机游走的磨玻璃型肺结节分割.自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1637-1647 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170420Li Xiang-Xia, Li Bin, Tian Lian-Fang, Zhang Li, Zhu Wen-Bo. Segmentation of ground glass opacity pulmonary nodules with sparse representation and random walk. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1637-1647 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170420 [4] Liao M, Zhao Y Q, Liu X Y, Zeng Y Z, Zou B J, Wang X F. Automatic liver segmentation from abdominal CT volumes using graph cuts and border marching. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2017, 143: 1-12 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.02.015 [5] Li C M, Huang R, Ding Z H, Gatenby J C, Metaxas D N, Gore J C. A level set method for image segmentation in the presence of intensity inhomogeneities with application to MRI. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(7): 2007-2016 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2146190 [6] Lu X Q, Wu J S, Ren X Y, Zhang B H, Li Y H. The study and application of the improved region growing algorithm for liver segmentation. Optik, 2014, 125(9): 2142-2147 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.10.049 [7] Yang X P, Yu H C, Choi Y, Lee W, Wang B J, Yang J. A hybrid semi-automatic method for liver segmentation based on level-set methods using multiple seed points. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2014, 113(1): 69-79 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.08.019 [8] Zhang S T, Zhan Y Q, Dewan M, Huang J Z, Metaxas D N, Zhou X S. Towards robust and effective shape modeling: sparse shape composition. Medical Image Analysis, 2012, 16(1): 265-277 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2011.08.004 [9] Tong T, Wolz R, Wang Z H, Gao Q Q, Misawa K, Fujiwara M. Discriminative dictionary learning for abdominal multi-organ segmentation. Medical Image Analysis, 2015, 23(1): 92-104 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.04.015 [10] Dou Q, Yu L Q, Chen H, Jin Y M, Yang X, Qin J. 3D deeply supervised network for automated segmentation of volumetric medical images. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 41: 40-54 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.05.001 [11] 林懿伦, 戴星原, 李力, 王晓, 王飞跃.人工智能研究的新前线:生成式对抗网络.自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 775-792 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.y000002Lin Yi-Lun, Dai Xing-Yuan, Li Li, Wang Xiao, Wang Fei-Yue. The new frontier of AI research: generative adversarial networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 775-792 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.y000002 [12] 田娟秀, 刘国才, 谷珊珊, 鞠忠建, 刘劲光, 顾冬冬.医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战.自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 401-424 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153Tian Juan-Xiu, Liu Guo-Cai, Gu Shan-Shan, Ju Zhong-Jian, Liu Jin-Guang, Gu Dong-Dong. Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 401-424 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153 [13] Watt J M, Linguraru M G, Summers R M. Affine invariant parameterization to assess local shape in abdominal organs. SPIE Medical Imaging. 2011, 7965(1): 554-561 [14] Heimann T, Ginneken B V, Styner M, Arzhaeva Y, Aurich V, Bauer C. Comparison and evaluation of methods for liver segmentation from CT datasets. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2009, 28(8): 1251-1265 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2013851 [15] Lu F, Wu F, Hu P J, Peng Z Y, Kong D X. Automatic 3D liver location and segmentation via convolutional neural networks and graph cut. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2017, 12(2): 171-182 doi: 10.1007/s11548-016-1467-3 [16] Hu P J, Wu F, Peng J L, Ping L, Kong D X. Automatic 3D liver segmentation based on deep learning and globally optimized surface evolution. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2016, 61(24): 8676-8698 -




 下载:
下载: