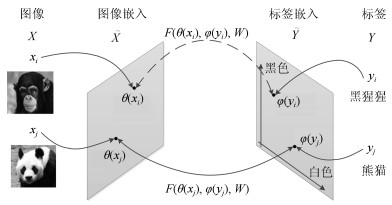
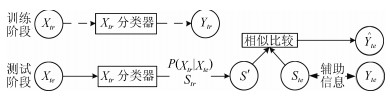
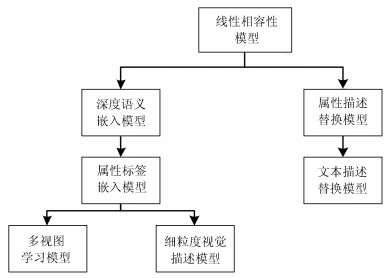
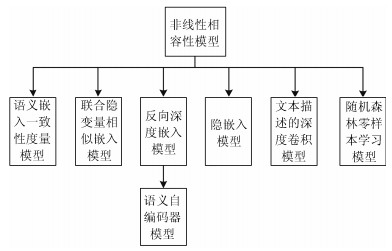
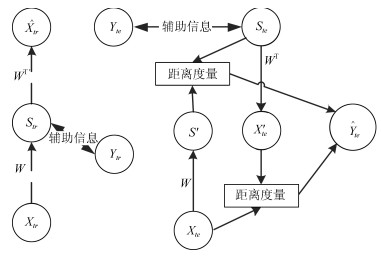
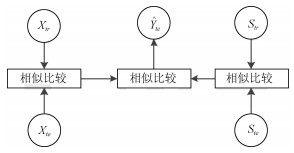
-
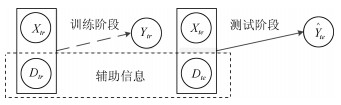
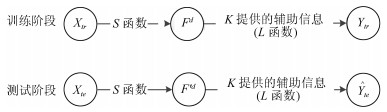
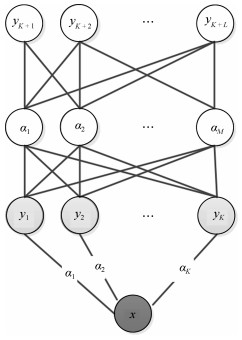
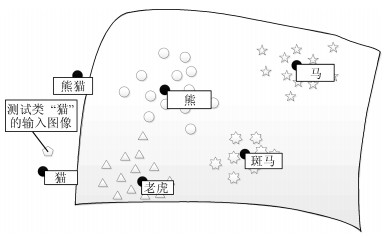
摘要: 近几年来, 深度学习在机器学习研究领域中取得了巨大的突破, 深度学习能够很好地实现复杂问题的学习, 然而, 深度学习最大的弊端之一, 就是需要大量人工标注的训练数据, 而这需要耗费大量的人力成本.因此, 为了缓解深度学习存在的这一问题, Palatucci等于2009年提出了零样本学习(Zero-shot learning).零样本学习是迁移学习的一种特殊场景, 在零样本学习过程中, 训练类集和测试类集之间没有交集, 需要通过训练类与测试类之间的知识迁移来完成学习, 使在训练类上训练得到的模型能够成功识别测试类输入样例的类标签.零样本学习的意义不仅在于可以对难以标注的样例进行识别, 更在于这一方法模拟了人类对于从未见过的对象的认知过程, 零样本学习方法的研究, 也会在一定程度上促进认知科学的研究.鉴于零样本学习的应用价值、理论意义和未来的发展潜力, 文中系统综述了零样本学习的研究进展, 首先概述了零样本学习的定义, 介绍了4种典型的零样本学习模型, 并对零样本学习存在的关键问题及解决方法进行了介绍, 对零样本学习的多种模型进行了分类和阐述, 并在最后指明了零样本学习进一步研究中需要解决的问题以及未来可能的发展方向.Abstract: In recent years, deep learning has made great breakthroughs in the field of the machine learning. The application of deep learning can be especially useful for coping with some complicated problems. However, one of the biggest drawbacks of the deep learning is that it requires a great amount of manual data annotation, this issue requires a lot of labor costs. Therefore, in order to alleviate the burden of deep learning, Palatucci et al. proposed zero-shot learning in 2009. Zero-shot learning is a special scenario of transfer learning. In the zero-shot learning progress, the samples of training and test classes do not intersect. It is necessary to complete the training by realizing the knowledge transfer between training class and test class, in order to successfully identify the label of the test class instance. The significance of zero-shot learning lies not only in the identification of difficult-to-annotate, but also in the fact that this method simulates the human cognitive process of objects that have never been seen before, so the study of zero-shot learning will contribute to the advancement of human cognitive science research. In view of the application value, theoretical significance and future development potential of zero-shot learning, this paper systematically reviews the research progress of zero-shot learning. First, the definition of zero-shot learning is summarized, then we introduce four typical zero-shot learning models, and the systematic problems in the zero-shot learning and the solution methods are introduced. We have categorized and elaborated on the multiple models of zero-shot learning. At the end, we pointed out the problems that need to be solved in the further study of zero-shot learning and possible future development directions.
-
Key words:
- Zero-shot learning /
- description /
- attribute /
- training class /
- test class /
- embedded space
1) 本文责任编委 张敏灵 -
表 1 5种数据集属性介绍
Table 1 Introduction to the attributes of the five datasets
数据集 AWA CUB aPY SUN AwA2 图像个数 30 475 11788 15 539 14 340 37 322 类个数 50 200 32 17 50 属性个数 85 312 64 102 85 注释水平 每一类 每张图片 每张图片 每张图片 每一类 注释类型(实值或布尔值) 兼有 兼有 兼有 布尔 兼有 表 2 多个模型在4个数据集下的实验结果
Table 2 Experimental results of the models under four data
-
[1] Schölkopf B, Smola A J. Learning with Kernels. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2001. [2] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: MIT Press, 2012. 1097-1105 [3] Gregor K, Danihelka I, Graves A, Rezende D J, Wierstra D. DRAW: a recurrent neural network for image generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1502.04623, 2015. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=046d1bffdbfb5068f065d8bdf9403628&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [4] Biederman I. Recognition-by-components: a theory of human image understanding. Psychological Review, 1987, 94(2): 115-147 doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.94.2.115 [5] Yao B P, Khosla A, Li F F. Combining randomization and discrimination for fine-grained image categorization. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2011. 1577-1584 [6] Murphy G L. The Big Book of Concepts. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2004. https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/big-book-concepts [7] Koggalage R, Halgamuge S K. Reducing the number of training samples for fast support vector machine classification. Neural Information Processing, 2004, 2(3): 57-65 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d54b53441cc53c03e26037d670f4bc72&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [8] Li F F, Fergus R, Perona P. One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28(4): 594-611 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2006.79 [9] Santoro A, Bartunov S, Botvinick M, Wierstra D, Lillicrap T. One-shot learning with memory-augmented neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1605.06065, 2016. [10] Fanello S R, Gori I, Metta G, Odone F. One-shot learning for real-time action recognition. In: Proceedings of Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. 31-40 [11] Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345-1359 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 [12] Bakker B, Heskes T. Task clustering and gating for Bayesian multitask learning. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003, 4(12): 83-99 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=065e5313fe59658a6e44688df00aff1b [13] Bonilla E V, Agakov F V, Williams C K I. Kernel multi-task learning using task-specific features. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Atherton, USA: PMLR, 2007. 43-50 [14] Lampert C H, Nickisch H, Harmeling S. Learning to detect unseen object classes by between-class attribute transfer. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2009. 951-958 [15] Palatucci M, Pomerleau D, Hinton G, Mitchell T M. Zero-shot learning with semantic output codes. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2009. 1410-1418 [16] Ba J L, Swersky K, Fidler S, Salakhutdinov R. Predicting deep zero-shot convolutional neural networks using textual descriptions. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 4247-4255 [17] Zhang L, Xiang T, Gong S G. Learning a deep embedding model for zero-shot learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1611.05088, 2016. [18] Zhang D, Liu Y, Si L. Serendipitous learning: learning beyond the predefined label space. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Diego, USA: ACM, 2011. 1343-1351 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a5c71403e19916c25cb401816c1c4b16&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [19] Du C, Zhuang F, He J, He Q, Long G. Learning beyond predefined label space via bayesian nonparametric topic modelling. In: Proceedings of Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Cham, Riva del Garda, Italy: Springer, 2016. 148-164 [20] Zhuang F Z, Luo P, Shen Z Y, He Q, Xiong Y H, Shi Z Z. D-LDA: a topic modeling approach without constraint generation for semi-defined classification. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2010. 709-718 [21] Larochelle H, Erhan D, Bengio Y. Zero-data learning of new tasks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Chicago, USA: AAAI, 2013. 646-651 [22] Socher R, Ganjoo M, Sridhar H, Bastani O, Manning C D, Ng A Y. Zero-shot learning through cross-modal transfer. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: MIT Press, 2013. 935-943 [23] Romera-Paredes B, Torr P H S. An embarrassingly simple approach to zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: ACM, 2015. 2152-2161 [24] Qiao R Z, Liu L Q, Shen C H, van den Hengel A. Less is more: zero-shot learning from online textual documents with noise suppression. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2249-2257 [25] Dietterich T G, Bakiri G. Solving multiclass learning problems via error-correcting output codes. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 1994, 2: 263-286 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_cs%2f9501101 [26] Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J. The Elements of Statistical Learning. New York: Springer, 2001. [27] Sloman S A. Feature-based induction. Cognitive Psychology, 1993, 25(2): 231-280 doi: 10.1006/cogp.1993.1006 [28] Osherson D, Smith E E, Myers T S, Shafir E, Stob M. Extrapolating human probability judgment. Theory & Decision, 1994, 36(2): 103-129 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1acd40713768044e31d5634955b76578&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [29] Ferrari V, Zisserman A. Learning visual attributes. In: Proceedings of the 21st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2007. 433-440 [30] van de Weijer J, Schmid C, Verbeek J. Learning color names from real-world images. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1-8 [31] Yanai K, Barnard K. Image region entropy: a measure of "visualness" of web images associated with one concept. In: Proceedings of the 13th Annual ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York, USA: ACM, 2005. 419-422 [32] Farhadi A, Endres I, Hoiem D, Forsyth D. Describing objects by their attributes. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2009. Miami Beach, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1778-1785 [33] Lampert C H, Nickisch H, Harmeling S. Attribute-based classification for zero-shot visual object categorization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(3): 453-465 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=485cb3a8f8e0a8984bad0fe6069ea2d9 [34] Suzuki M, Sato H, Oyama S, Kurihara M. Transfer learning based on the observation probability of each attribute. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2014. 3627-3631 [35] Kovashka A, Parikh D, Grauman K. WhittleSearch: image search with relative attribute feedback. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 2973-2980 [36] Parkash A, Parikh D. Attributes for classifier feedback. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012. 354-368 [37] Kulkarni G, Premraj V, Dhar S, Li S M, Choi Y J, Berg A C, et al. Baby talk: understanding and generating simple image descriptions. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Colorado Springs, USA: IEEE, 2011. 1601-1608 [38] Kumar N, Berg A, Belhumeur P N, Nayar S. Describable visual attributes for face verification and image search. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(10): 1962-1977 doi: 10.1109-TPAMI.2011.48/ [39] Liu J, Kuipers B, Savarese S. Recognizing human actions by attributes. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Colorado Springs, USA: IEEE, 2011. 3337-3344 [40] Patterson G, Hays J. SUN attribute database: discovering, annotating, and recognizing scene attributes. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 2751-2758 [41] Feris R, Siddiquie B, Zhai Y, Petterson J, Brown L, Pankanti S. Attribute-based vehicle search in crowded surveillance videos. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval. Trento, Italy: ACM, 2011. Article No. 18 [42] Fu Y W, Hospedales T M, Xiang T, Fu Z Y, Gong S G. Transductive multi-view embedding for zero-shot recognition and annotation. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 584-599 [43] Chao W L, Changpinyo S, Gong B, Sha F. An empirical study and analysis of generalized zero-shot learning for object recognition in the wild. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 52-68 [44] Lazaridou A, Dinu G, Baroni M. Hubness and pollution: delving into cross-space mapping for zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Beijing, China: ACL, 2015. 270-280 [45] Norouzi M, Mikolov T, Bengio S, Singer Y, Shlens J, Frome A, et al. Zero-shot learning by convex combination of semantic embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.5650, 2013 [46] Changpinyo S, Chao W L, Gong B Q, Sha F. Synthesized classifiers for zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 5327-5336 [47] Radovanović M, Nanopoulos A, Ivanović M. Hubs in space: popular nearest neighbors in high-dimensional data. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11: 2487-2531 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cd255ab6835ff4b1191724b737470cd3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [48] Radovanović M, Nanopoulos A, Ivanović M. On the existence of obstinate results in vector space models. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Geneva, Switzerland: ACM, 2010. 186-193 [49] Dinu G, Lazaridou A, Baroni M. Improving zero-shot learning by mitigating the hubness problem. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6568, 2014 [50] Kodirov E, Xiang T, Fu Z Y, Gong S G. Unsupervised domain adaptation for zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2452-2460 [51] Harris Z S. Distributional structure. Word, 1954, 10(2-3): 146-162 doi: 10.1080/00437956.1954.11659520 [52] Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: MIT Press, 2013. 3111-3119 [53] Pennington J, Socher R, Manning C D. GloVe: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). Doha, Qatar: ACL, 2014. 1532-1543 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=537a8511c9ae20478a13d76f2a1e7035&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [54] Blanchard E, Harzallah M, Briand H, Kuntz P. A typology of ontology-based semantic measures. In: EMOI-INTEROP. Portugal: Springer, 2005. 160 [55] Frome A, Corrado G S, Shlens J, Bengio S, Dean J, Ranzato M, et al. DeViSE: a deep visual-semantic embedding model. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: MIT Press, 2013. 2121-2129 [56] Akata Z, Perronnin F, Harchaoui Z, Schmid C. Label-embedding for attribute-based classification. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 819-826 [57] Akata Z, Reed S, Walter D, Lee H, Schiele B. Evaluation of output embeddings for fine-grained image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2927-2936 [58] Reed S, Akata Z, Lee H, Schiele B. Learning deep representations of fine-grained visual descriptions. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 49-58 [59] Kodirov E, Xiang T, Gong S G. Semantic autoencoder for zero-shot learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.08345, 2017 [60] Bucher M, Herbin S, Jurie F. Improving semantic embedding consistency by metric learning for zero-shot classiffication. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 730-746 [61] Zhang Z M, Saligrama V. Zero-shot learning via joint latent similarity embedding. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 6034-6042 [62] Xian Y Q, Akata Z, Sharma G, Nguyen Q, Hein M, Schiele B. Latent embeddings for zero-shot classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 69-77 [63] Jayaraman D, Grauman K. Zero-shot recognition with unreliable attributes. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2014. 3464-3472 [64] Zhang Z M, Saligrama V. Zero-shot learning via semantic similarity embedding. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE 2015. 4166-4174 [65] Zhao B, Wu B T, Wu T F, Wang Y Z. Zero-shot learning posed as a missing data problem. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1612.00560, 2016 [66] Zhang Z M, Saligrama V. Zero-shot recognition via structured prediction. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 533-548 [67] Wang D H, Li Y, Lin Y T, Zhuang Y T. Relational knowledge transfer for zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 13th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Phoenix, USA: AAAI, 2016. 2145-2151 [68] Luo C Z, Li Z T, Huang K Z, Feng J S, Wang M. Zero-shot learning via attribute regression and class prototype rectification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(2): 637-648 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cc3cb532b2789d33ffe0a8326dbeeec3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [69] Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2014. 1-9 [70] Lu Y. Unsupervised learning on neural network outputs: with application in zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2016. 3432-3438 [71] Baldi P, Hornik K. Neural networks and principal component analysis: learning from examples without local minima. Neural Networks, 1989, 2(1): 53-58 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=71193a90089a19100017f3263a421ddb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [72] Hyvarinen A. Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1999, 10(3): 626-634 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=df2ada21711f3db3a676da39586b8210 [73] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L J, Li K, Fei-Fei L. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami Beach, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248-255 [74] Song J, Shen C C, Yang Y Z, Liu Y, Song M L. Transductive unbiased embedding for zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1024-1033 [75] Guo Y C, Ding G G, Jin X M, Wang J M. Transductive zero-shot recognition via shared model space learning. In: Proceedings of the 13th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Phoenix, USA: AAAI Press, 2016. 3434-3500 [76] Xian Y Q, Lampert C H, Schiele B, Akata Z. Zero-shot learning-A comprehensive evaluation of the good, the bad and the ugly. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.00600, 2017 [77] Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, Perona P, Belongie S. The caltech-UCSD birds-200-2011 dataset, Computation & Neural Systems Technical Report, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, 2011. https://authors.library.caltech.edu/27452/1/CUB_200_2011.pdf [78] Xiao J X, Hays J, Ehinger K A, Oliva A, Torralba A. Sun database: large-scale scene recognition from abbey to zoo. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 3485-3492 [79] Antol S, Zitnick C L, Parikh D. Zero-shot learning via visual abstraction. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 401-416 [80] Robyns P, Marin E, Lamotte W, Quax P, Singelée D, Preneel B. Physical-layer fingerprinting of LoRa devices using supervised and zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Security and Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks. Boston, Massachusetts: ACM, 2017. 58-63 [81] Yang Y, Luo Y D, Chen W L, Shen F M, Shao J, Shen H T. Zero-shot hashing via transferring supervised knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ACM, 2016. 1286-1295 [82] Johnson M, Schuster M, Le Q V, Krikun M, Wu Y H, Chen Z F, et al. Google's multilingual neural machine translation system: enabling zero-shot translation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1611.04558, 2016. [83] Veeranna S P, Nam J, Mencía E L, Furnkranz J. Using semantic similarity for multi-label zero-shot classification of text documents. In: Proceeding of European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning. Bruges, Belgium: Elsevier, 2016. 423-428 -




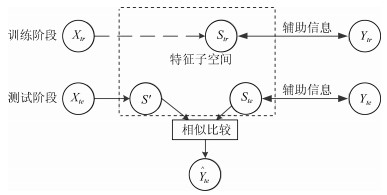
 下载:
下载: