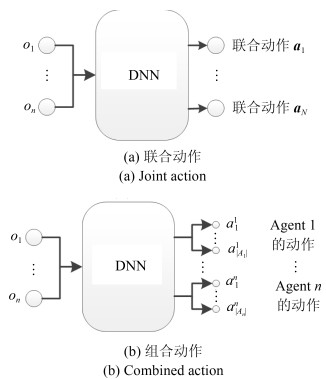
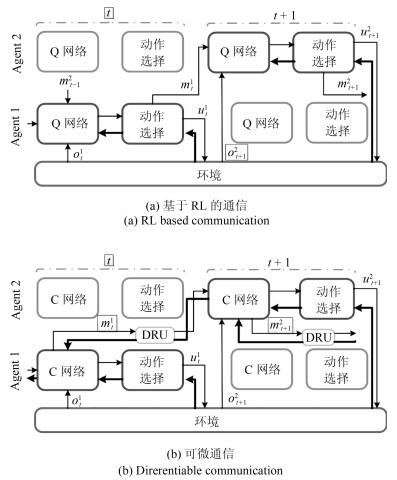
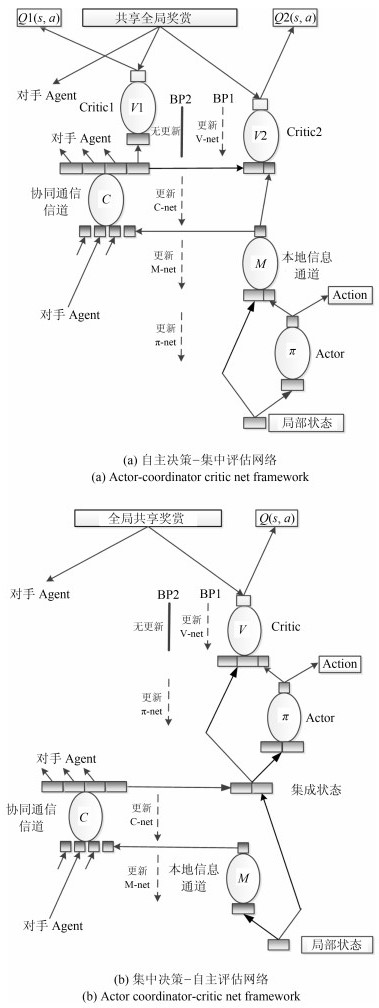
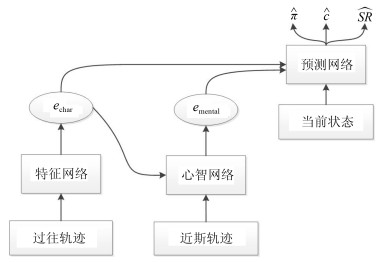
-
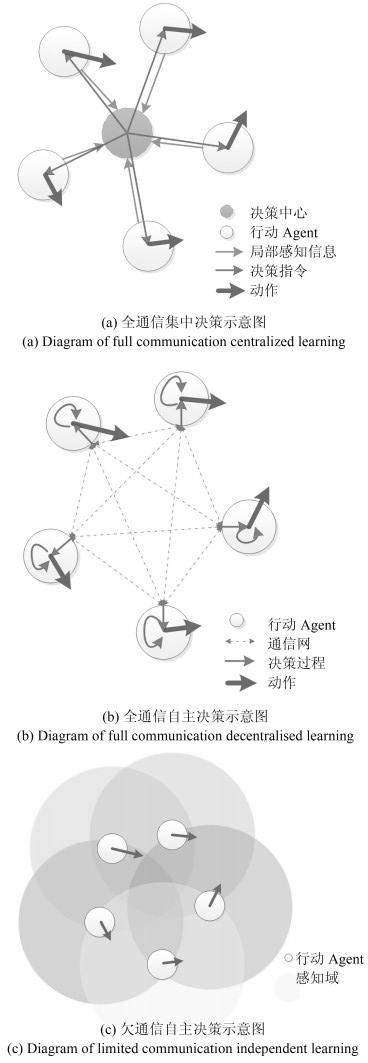
摘要: 近年来, 深度强化学习(Deep reinforcement learning, DRL)在诸多复杂序贯决策问题中取得巨大突破.由于融合了深度学习强大的表征能力和强化学习有效的策略搜索能力, 深度强化学习已经成为实现人工智能颇有前景的学习范式.然而, 深度强化学习在多Agent系统的研究与应用中, 仍存在诸多困难和挑战, 以StarCraft Ⅱ为代表的部分观测环境下的多Agent学习仍然很难达到理想效果.本文简要介绍了深度Q网络、深度策略梯度算法等为代表的深度强化学习算法和相关技术.同时, 从多Agent深度强化学习中通信过程的角度对现有的多Agent深度强化学习算法进行归纳, 将其归纳为全通信集中决策、全通信自主决策、欠通信自主决策3种主流形式.从训练架构、样本增强、鲁棒性以及对手建模等方面探讨了多Agent深度强化学习中的一些关键问题, 并分析了多Agent深度强化学习的研究热点和发展前景.Abstract: Recent years has witnessed the great success of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) in addressing complicated problems, and it is widely used to capture plausible policies in sequential decision-making tasks. Recognized as a promising learning paradigm, the deep reinforcement learning takes advantage of the great power of representations in deep learning and superior capability of policy improvement in reinforcement learning, driving the development of artificial intelligence into a new era. Though the DRL has shown its great power in typical applications, the effective multi-agent DRL still needs further explorations, and a challenging task is to guide multi-agents to play StarCraft Ⅱ, where the environment is partially observed and dynamic. To enable DRL better accommodate the multi-agent environment and overcome challenges, we briefly introduced the foundation of reinforcement learning and then reviewed some representative or state-of-art algorithms of multi-agent DRL, including the deep Q learning algorithm, the deep policy gradient algorithm and related extensions. Meanwhile, some dominant approaches regarding making decisions for multi-agents were elaborated, and we categorized them into three mainstream classes from the aspect of stage of communication in DRL as full communication centralized learning, full communication decentralized learning and limited communication decentralized learning Finally, we discussed some key problems in multi-agent DRL tasks, such as training architecture, example enhancement, robust improvement, and opponent modeling, and highlighted future directions in this issue.
-
Key words:
- Multi-agent system /
- deep learning /
- deep reinforcement learning (DRL) /
- artificial general intelligence
1) 本文责任编委 张俊 -
表 1 与已发表相关论文的研究异同
Table 1 Research's similarities and differences
异同点 深度强化学习综述:兼论计算机围棋的发展 多Agent深度强化学习综述 出发点 深度强化学习的发展, 深度强化学习的在围棋发展中的应用. 深度强化学习方法在多Agent系统中的研究现状 综述角度 从强化学习以及深度学习的研究, 对发展而来的深度强化学习进行论述, 并指出在围棋发展中的应用. 在多Agent系统中, 如何应用深度强化学习, 并从神经网络的搭建结构出发, 对当前的多Agent深度强化学习方法进行分类与研究. 内容安排 讨论了强化学习与深度学习的研究成果及其展望, 论述了深度强化学习的主要神经网络结构.在这一基础上, 对AlphaGo进行了的分析与研究, 展开了对计算机围棋的发展研究, 详细论述了AlphaGo的对决过程, 刻画了结合MCTS的深度强化学习方法在围棋研究中的巨大成功.之后, 讨论了深度强化学习的展望, 分析了在在博弈、连续状态动作, 与其他智能方法结合, 理论分析等方面的发展前景.最后给出了深度强化学习的应用. 根据深度强化学习策略的输出形式, 对深度强化学习方法从深度Q学习和深度策略梯度两个方面进行介绍.之后讨论了在多Agent系统中如何使用深度强化学习方法, 解决多Agent系统所面临的问题, 从多Agent深度强化学习中通信过程的角度对现有的多Agent深度强化学习算法进行归纳, 将其归纳为全通信集中决策、全通信自主决策、欠通信自主决策3种主流形式.深度强化学习引入多Agent系统中, 面临着训练架构、样本增强、鲁棒性以及对手建模等新的挑战, 文章对这些问题进行了讨论与分析. -
[1] Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (2nd edition). MIT Press, 2018. [2] Schmidhuber J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 85-117 http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25462637 [3] LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444 [4] Bengio Y I, Goodfellow J, Courville A. Deep Learning. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2016. [5] Wang Q, Zhao X, Huang J C, Feng Y H, Liu Z, Su Z H, et al. Addressing complexities of machine learning in big data: Principles, trends and challenges from systematical perspectives. Preprints, 2017, DOI: 10.20944/ preprints201710.0076.v1 [6] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu A A, Veness J, Bellemare M G, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533 http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/25719670 [7] 赵冬斌, 邵坤, 朱圆恒, 李栋, 陈亚冉, 王海涛, 等.深度强化学习综述:兼论计算机围棋的发展.控制理论与应用, 2016, 33(6): 701-717Zhao Dong-Bin, Shao Kun, Zhu Yuan-Heng, Li Dong, Chen Ya-Ran, Wang Hai-Tao, et al. Review of deep reinforcement learning and discussions on the development of computer Go. Control Theory and Applications, 2016, 33(6): 701-717 [8] Silver D, Schrittwieser J, Simonyan K, Antonoglou I, Huang A, Guez A, et al. Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354-359 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29052630 [9] Graves A, Wayne G, Reynolds M, Harley T, Danihelka I, Grabska-Barwińska A, et al. Hybrid computing using a neural network with dynamic external memory. Nature, 2016, 538(7626): 471-476 [10] Zhang T Y, Huang M L, Zhao L. Learning structured representation for text classification via reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans, LA, USA: AAAI Press, 2018. 6053-6060 [11] Su P H, Gašić M, Mrkšić N, Rojas-Barahona L M, Ultes S, Vandyke D, et al. On-line active reward learning for policy optimisation in spoken dialogue systems. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Berlin, Germany: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016. [12] 周志华. AlphaGo专题介绍.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 670 http://www.aas.net.cn/article/id/18855Zhou Zhi-Hua. AlphaGo special session: An introduction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 670 http://www.aas.net.cn/article/id/18855 [13] Silver D. Deep reinforcement learning, a tutorial at ICML 2016.[Online], available: https://www.davidsilver.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/deep_rl_tutorial_small_compres-sed.pdf, April 26, 2019 [14] Li Y X. Deep reinforcement learning: An overview. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1701.07274, 2017. [15] Kraemer L, Banerjee B. Multi-agent reinforcement learning as a rehearsal for decentralized planning. Neurocomputing, 2016, 190: 82-94 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231216000783 [16] Pérolat J, Leibo J Z, Zambaldi V, Beattie C, Tuyls K, Graepel T. A multi-agent reinforcement learning model of common-pool resource appropriation. In: Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA, 2017. 3646-3655 [17] Rǎdulescu R, Vrancx P, Nowé A. Analysing congestion problems in multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. São Paulo, Brazil: ACM, 2017. 1705-1707 [18] Schulman J, Moritz P, Levine S, Jordan M, Abbeel P. High-dimensional continuous control using generalized advantage estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1506.02438, 2015. [19] Okdinawati L, Simatupang T M, Sunitiyoso Y. Multi-agent reinforcement learning for collaborative transportation management (CTM). Agent-Based Approaches in Economics and Social Complex Systems IX. Singapore: Springer, 2017. 123-136 [20] De Vrieze C, Barratt S, Tsai D, Sahai A. Cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning for low-level wireless communication. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.04541, 2018. [21] Shalev-Shwartz S, Shammah S, Shashua A. Safe, multi-agent, reinforcement learning for autonomous driving. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1610.03295, 2016. [22] Kurek M, Jaśkowski W. Heterogeneous team deep Q-learning in low-dimensional multi-agent environments. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG). Santorini, Greece: IEEE, 2016. 1-8 [23] Aydin M E, Fellows R. A reinforcement learning algorithm for building collaboration in multi-agent systems. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.10574, 2017. [24] Lin K X, Zhao R Y, Xu Z, Zhou J Y. Efficient large-scale fleet management via multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. London, UK: ACM, 2018. 1774-1783 [25] Conde R, Llata J R, Torre-Ferrero C. Time-varying formation controllers for unmanned aerial vehicles using deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706.01384, 2017. [26] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Graves A, Antonoglou I, Wierstra D, et al. Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.5602, 2013. [27] Van Hasselt H, Guez A, Silver D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Phoenix, USA: AAAI, 2016. [28] Schaul T, Quan J, Antonoglou I, Silver D. Prioritized experience replay. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1511.05952, 2015. [29] Wang Z Y, Schaul T, Hessel M, Van Hasselt H, Lanctot M, De Freitas N. Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. [30] Hausknecht M, Stone P. Deep recurrent Q-learning for partially observable MDPs. In: Proceedings of the 2015 AAAI Fall Symposium on Sequential Decision Making for Intelligent Agents. Arlington, USA: AAAI, 2015. [31] Sorokin I, Seleznev A, Pavlov M, Fedorov A, Ignateva A. Deep attention recurrent Q-network. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1512.01693, 2015. [32] Hessel M, Modayil J, Van Hasselt H, Schaul T, Ostrovski G, Dabney W, et al. Rainbow: Combining improvements in deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.02298, 2017. [33] Srouji M, Zhang J, Salakhutdinov R. Structured control nets for deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm Sweden: PMLR, 2018. [34] Silver D, Lever G, Heess N, Degris T, Wierstra D, Riedmiller M. Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: ACM, 2014. [35] Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N M, Erez T, Tassa Y, et al. Continuous Control with Deep Reinforcement Learning, United States Patent Application 20170024643, 2017. [36] Mnih V, Badia A P, Mirza M, Graves A, Harley T, Lillicrap T P, et al. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 1928-1937 [37] Babaeizadeh M, Frosio I, Tyree S, Clemons J, Kautz J. Reinforcement learning through asynchronous advantage actor-critic on a GPU. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1611.06256, 2016. [38] Jaderberg M, Mnih V, Czarnecki W M, Schaul T, Leibo J Z, Silver D, et al. Reinforcement learning with unsupervised auxiliary tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1611.05397, 2016. [39] Wang J X, Kurth-Nelson Z, Tirumala D, Soyer H, Leibo J Z, Munos R, et al. Learning to reinforcement learn. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1611.05763, 2016. [40] Schulman J, Levine S, Abbeel P, Jordan M, Moritz P. Trust region policy optimization. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lile, France: JMLR.org, 2015. 1889-1897 [41] Wu Y H, Mansimov E, Liao S, Grosse R, Ba J. Scalable trust-region method for deep reinforcement learning using Kronecker-factored approximation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1708.05144. 2017. [42] Wang Z Y, Bapst V, Heess N, Mnih V, Munos R, Kavukcuoglu K, et al. Sample efficient actor-critic with experience replay. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1611.01224, 2016. [43] Schulman J, Wolski F, Dhariwal P, Radford A, Klimov O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.06347, 2017. [44] Panait L, Luke S. Cooperative multi-agent learning: The state of the art. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2005, 11(3): 387-434 [45] Shoham Y, Powers R, Grenager T. If multi-agent learning is the answer, what is the question? Artificial Intelligence, 2007, 171(7): 365-377 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1248180 [46] Tuyls K, Weiss G. Multiagent learning: Basics, challenges, and prospects. AI Magazine, 2012, 33(3): 41-52 [47] Matignon L, Laurent G J, Le Fort-Piat N. Independent reinforcement learners in cooperative Markov games: A survey regarding coordination problems. The Knowledge Engineering Review, 2012, 27(1): 1-31 http://journals.cambridge.org/abstract_S0269888912000057 [48] Buşoniu L, Babuška R, De Schutter B. Multi-agent reinforcement learning: An overview. Innovations in Multi-Agent Systems and Applications-1. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2010. 183-221 [49] Crandall J W, Goodrich M A. Learning to compete, coordinate, and cooperate in repeated games using reinforcement learning. Machine Learning, 2011, 82(3): 281-314 http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=c015746b0e1c3ee07b9c93a30c57416d [50] Müller J P, Fischer K. Application impact of multi-agent systems and technologies: A survey. Agent-Oriented Software Engineering. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2014. 27-53 [51] Weiss G (editor). Multiagent Systems (2nd edition). Cambridge: MIT Press, 2013. [52] Bloembergen D, Tuyls K, Hennes D, Kaisers D. Evolutionary dynamics of multi-agent learning: A survey. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2015, 53(1): 659-697 [53] Hernandez-Leal P, Kaisers M, Baarslag T, De Cote E M. A survey of learning in multiagent environments: Dealing with non-stationarity. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.09183, 2017. [54] Sukhbaatar S, Szlam A, Fergus R. Learning multiagent communication with backpropagation. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 2252-2260 [55] Peng P, Yuan Q, Wen Y, Yang Y D, Tang Z K, Long H T, et al. Multiagent bidirectionally-coordinated nets for learning to play StarCraft combat games. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.10069, 2017. [56] Sunehag P, Lever G, Gruslys A, Czarnecki W M, Zambaldi V, Jaderberg M, et al. Value-decomposition networks for cooperative multi-agent learning based on team reward. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. [57] Kong X Y, Xin B, Liu F C, Wang Y Z. Revisiting the master-slave architecture in multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1712.07305, 2017. [58] Foerster J N, Assael Y M, De Freitas N, Whiteson S. Learning to communicate with deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 2145-2153 [59] Usunier N, Synnaeve G, Lin Z M, Chintala S. Episodic exploration for deep deterministic policies: An application to StarCraft micromanagement tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1609.02993, 2016. [60] Mao H Y, Gong Z B, Ni Y, Xiao Z. ACCNet: Actor-coordinator-critic net for "Learning-to-communicate" with deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706.03235, 2017. [61] Yang Y D, Luo R, Li M N, Zhou M, Zhang W N, Wang J. Mean field multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1802.05438, 2018. [62] Tampuu A, Matiisen T, Kodelja D, Kuzovkin I, Korjus K, Aru J, et al. Multiagent cooperation and competition with deep reinforcement learning. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): Article No. e0172395 [63] Omidshafiei S, Pazis J, Amato C, How J P, Vian J. Deep decentralized multi-task multi-agent reinforcement learning under partial observability. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia, 2017. [64] Palmer G, Tuyls K, Bloembergen D, Savani R. Lenient multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. [65] Foerster J, Nardelli N, Farquhar G, Afouras T, Torr P H S, Kohli P, et al. Stabilising experience replay for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: ACM, 2017. [66] Leibo J Z, Zambaldi V, Lanctot M, Marecki J, Graepel T. Multi-agent reinforcement learning in sequential social dilemmas. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. São Paulo, Brazil: ACM, 2017. 464-473 [67] Lerer A, Peysakhovich A. Maintaining cooperation in complex social dilemmas using deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.01068, 2017. [68] Peysakhovich A, Lerer A. Consequentialist conditional cooperation in social dilemmas with imperfect information. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.06975, 2017. [69] Menda K, Chen Y C, Grana J, Bono J W, Tracey B D, Kochenderfer M J, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for event-driven multi-agent decision processes. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(4): 1259-1268 [70] Lowe R, Wu Y, Tamar A, Harb J, Abbeel P, Mordatch I. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. 6382-6393 [71] Foerster J, Farquhar G, Afouras T, Nardelli N, Whiteson S. Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1705.08926, 2017. [72] Ellowitz J. Multi-agent reinforcement learning and genetic policy sharing. arXiv preprint arXiv: 0812.1599V1, 2018. [73] Gupta J K, Egorov M, Kochenderfer M. Cooperative multi-agent control using deep reinforcement learning. Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Cham: Springer, 2017. 66-83 [74] Chu X X, Ye H J. Parameter sharing deep deterministic policy gradient for cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.00336, 2017. [75] Vinyals O, Ewalds T, Bartunov S, Georgiev P, Vezhnevets A S, Yeo M, et al. StarCraft Ⅱ: A new challenge for reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1708.04782, 2017. [76] Zheng L M, Yang J C, Cai H, Zhang W N, Wang J, Yu Y. MAgent: A many-agent reinforcement learning platform for artificial collective intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1712.00600, 2017. [77] Khan A, Zhang C, Lee D D, Kumar V, Ribeiro A. Scalable centralized deep multi-agent reinforcement learning via policy gradients. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1805.08776, 2018. [78] Chen Y, Zhou M, Wen Y, Yang Y D, Su Y F, Zhang W N, et al. Factorized Q-learning for large-scale multi-agent systems. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Distributed Artificial Intelligence. Beijing, China: ACM, 2019. [79] Brodeur S, Perez E, Anand A, Golemo F, Celotti L, Strub F, et al. HoME: A household multimodal environment. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.11017, 2017. [80] Tian Y D, Gong Q C, Shang W L, Wu Y X, Zitnick C L. ELF: An extensive, lightweight and flexible research platform for real-time strategy games. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. 2656-2666 [81] Bansal T, Pachocki J, Sidor S, Sutskever I, Mordatch I. Emergent complexity via multi-agent competition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.03748, 2017. [82] Lanctot M, Zambaldi V, Gruslys A, Lazaridou A, Tuyls K, Pérolat, et al. A unified game-theoretic approach to multiagent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. 4193-4206 [83] Melo F S, Sardinha A. Ad hoc teamwork by learning teammates$'$ task. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2016, 30(2): 175-219 doi: 10.1007/s10458-015-9280-x [84] Albrecht S V, Liemhetcharat S, Stone P. Special issue on multiagent interaction without prior coordination: Guest editorial. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2017, 31(4): 765-766 [85] Liemhetcharat S, Veloso M. Allocating training instances to learning agents for team formation. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2017, 31(4): 905-940 [86] Chakraborty M, Chua K Y P, Das S, Juba B. Coordinated versus decentralized exploration in multi-agent multi-armed bandits. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Melbourne, Australia: International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization, 2017. 164-170 [87] Huang V, Ley T, Vlachou-Konchylaki M, Hu W F. Enhanced experience replay generation for efficient reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1705.08245, 2017. [88] Kumar A, Biswas A, Sanyal S. eCommerceGAN: A generative adversarial network for E-commerce. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.03244, 2018. [89] Andersen P A. Deep reinforcement learning using capsules in advanced game environments. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.09597, 2018. [90] Sabour S, Frosst N, Hinton G E. Dynamic routing between capsules. In: Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA, 2017. 3859-3869 [91] Corneil D, Gerstner W, Brea J. Efficient model-based deep reinforcement learning with variational state tabulation. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. [92] Nishio D, Yamane S. Faster deep Q-learning using neural episodic control. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.01968, 2018. [93] Pritzel A, Uria B, Srinivasan S, Puigdoménech A, Vinyals O, Hassabis D, et al. Neural episodic control. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.01988, 2017. [94] Ha D, Schmidhuber J. World models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1803.10122, 2018. [95] Gregor K, Papamakarios G, Besse F, Buesing L, Weber T. Temporal difference variational auto-encoder. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1806.03107, 2018. [96] Piergiovanni A J, Wu A, Ryoo M S. Learning real-world robot policies by dreaming. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1805. 07813, 2018. [97] Goel V, Weng J, Poupart P. Unsupervised video object segmentation for deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada, 2018. [98] Pinto L, Davidson J, Sukthankar R, Gupta A. Robust adversarial reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: ACM, 2017. [99] Pattanaik A, Tang Z Y, Liu S J, Bommannan G, Chowdhary G. Robust deep reinforcement learning with adversarial attacks. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. [100] El Mhamdi E M, Guerraoui R, Hendrikx H, Maurer A. Dynamic safe interruptibility for decentralized multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. [101] Hernandez-Leal P, Kaisers M. Towards a fast detection of opponents in repeated stochastic games. In: Proceedings of 2017 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. São Paulo, Brazil: Springer, 2017. 239-257 [102] Hernandez-Leal P, Zhan Y S, Taylor M E, Sucar L E, De Cote E M. Efficiently detecting switches against non-stationary opponents. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2017, 31(4): 767-789 [103] Hernandez-Leal P, Zhan Y S, Taylor M E, Sucar L E, De Cote E M. An exploration strategy for non-stationary opponents. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2017, 31(5): 971-1002 [104] Yu C, Zhang M J, Ren F H, Tan G Z. Multiagent learning of coordination in loosely coupled multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(12): 2853-2867 [105] Lowe R, Wu Y, Tamar A, Harb J, Abbeel P, Mordatch I. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. 6382-6393 [106] Rabinowitz N C, Perbet F, Song F, Zhang C Y, Ali E, Botvinick M. Machine theory of mind. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. [107] He H, Boyd-Graber J, Kwok K, Daumé H. Opponent modeling in deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 1804-1813 [108] Foerster J, Chen R Y, Al-Shedivat M, Whiteson S, Abbeel P, Mordatch I. Learning with opponent-learning awareness. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. [109] Hong Z W, Su S Y, Shann T Y, Chang Y H, Lee C Y. A deep policy inference Q-network for multi-agent systems. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1712.07893, 2017. [110] Raileanu R, Denton E, Szlam A, Fergus R. Modeling others using oneself in multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. -




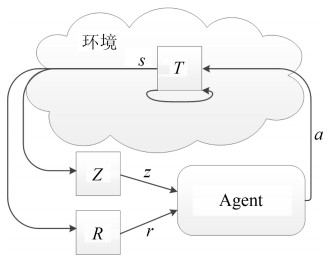
 下载:
下载: