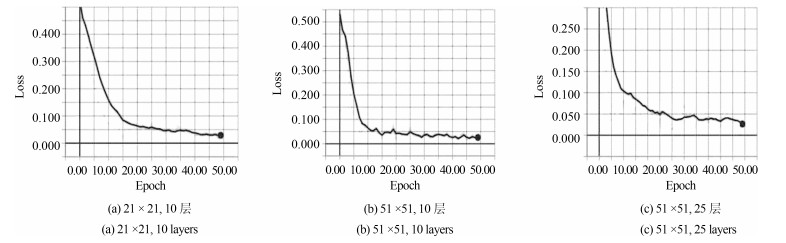
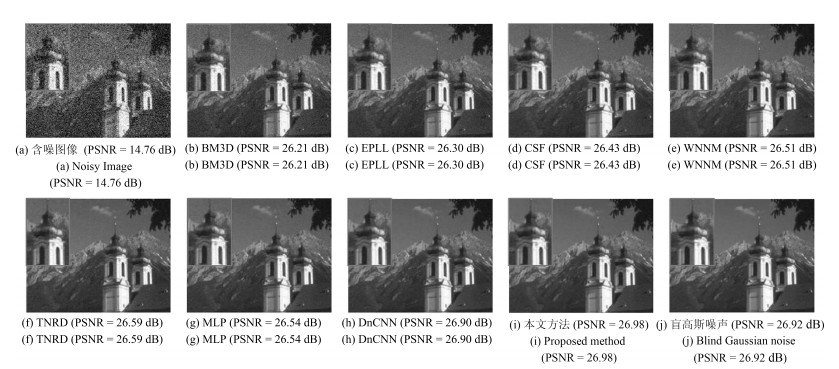
-
摘要: 为了更有效地实现高噪声环境下的图像去噪, 本文提出一种基于深度学习的高噪声图像去噪算法.该算法首先采用递增扩充卷积并且融合批量标准化和Leaky ReLU函数对输入含噪图像进行特征提取与学习; 然后通过结合递减扩充卷积和ReLU函数对提取的特征进行图像重构; 最后通过整合残差学习和批量标准化的端到端网络实现图像与噪声的有效分离.实验结果表明, 本文提出的算法不仅能够有效地去除高噪声环境下的图像噪声, 获得更高的峰值信噪比(Peak signal-to-noise ratio, PSNR)与结构相似度(Structural similarity index, SSIM), 而且还能够有效地改善图像的视觉效果, 具有较好的实用性.Abstract: In order to perform image denoising in high-noise environment more effectively, a high-noise image denoising algorithm based on deep learning is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the proposed algorithm utilized increased expanded convolutional and combined the batch normalization and Leaky ReLU function to extract and learn for the features of noisy image. Secondly, the extracted feature via the decreased expansion convolution and ReLU function for image reconstruction. Finally, the effective separation of image and noise is realized by end-to-end network of integrating the residual learning and batch standardization. The experimental results illustrated that the proposed algorithm removed the image noise more effectively and obtain higher peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM) under high noise environment. In addition, the proposed algorithm also significantly improved the visual effects of images, and had a good practicality.
-
Key words:
- Deep learning /
- image denoising /
- convolutional neural networks (CNN) /
- residual learning /
- batch normalization
1) 本文责任编委 杨健 -
表 1 不同去噪算法在BSD68数据集下的峰值信噪比(PSNR) (dB)
Table 1 The PSNR value using different denoising algorithms at the BSD68 data set (dB)
$\sigma$ BM3D WNNM MLP TNRD DnCNN EPLL CSF 特定噪声模型 随机噪声模型 15 31.07 31.37 – 31.42 31.73 31.21 31.24 31.94 31.85 25 28.57 28.83 28.96 28.92 29.23 28.68 28.74 29.46 29.38 40 26.22 26.33 – 26.49 26.88 26.26 26.30 27.11 27.06 50 25.62 25.87 26.03 25.97 26.23 25.67 – 26.48 26.47 60 23.18 – 23.55 23.43 23.73 23.24 23.27 24.01 24.06 表 2 不同去噪算法在BSD68数据集下的结构相似度
Table 2 The SSIM value using different denoising algorithms at the BSD68 data set
$\sigma$ BM3D WNNM MLP TNRD DnCNN 本文方法1 本文方法2 15 0.8772 0.8774 0.8792 0.8826 0.8826 0.8831 0.8827 25 0.8017 0.8019 0.8120 0.8157 0.8190 0.8193 0.8190 40 0.7223 0.7237 0.7294 0.7310 0.7322 0.7334 0.7331 50 0.6869 0.6871 0.6956 0.7029 0.7076 0.7102 0.7100 60 0.6521 0.6544 0.6643 0.6712 0.6745 0.6796 0.6799 表 3 不同尺寸大小的测试图像去噪运行时间比较($\sigma = 25$) (s)
Table 3 The running time of test images denoising with different size ($\sigma = 25$) (s)
图像块大小(像素) 配置 BM3D WNNM TNRD MLP EPLL CSF DnCNN 特定噪声模型 随机噪声模型 $256\times 256$ CPU/GPU 0.65 203.1 0.45/0.010 1.42 25.4 2.11/– 0.74/0.014 0.68/0.016 0.97/0.020 $512\times 512$ CPU/GPU 2.85 773.2 1.33/0.032 5.51 45.5 5.67/0.92 3.41/0.051 2.98/0.072 3.68/0.083 $1 024\times 1 024$ CPU/GPU 11.89 2 536.4 4.61/0.116 19.4 422.1 40.8/1.72 12.1/0.200 10.7/0.160 13.7/0.173 -
[1] Kostadin D, Alessandro F, Vladimir K, Karen E. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080-2095 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238 [2] 孙伟峰, 戴永寿.采用多级残差滤波的非局部均值图像去噪方法.电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 1999-2006 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZYX201608024.htmSun Wei-Feng, Dai Yong-Shou. Non-local mean image denoising using multi-level residual filtering. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 1999- 2006 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZYX201608024.htm [3] 周飞燕, 金林鹏, 董军.卷积神经网络研究综述.计算机学报, 2017, 40(6): 1229-1251 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201706001.htmZhou Fei-Yan, Jin Lin-Peng, Dong Jun. A review of convolutional neural networks. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(6): 1229-1251 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201706001.htm [4] 罗建豪, 吴建鑫.基于深度卷积特征的细粒度图像分类研究综述.自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1306-1318 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160425Luo Jian-Hao, Wu Jian-Xin. A survey of fine-grained image classification based on deep convolution features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1306-1318 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160425 [5] 唐贤伦, 杜一铭, 刘雨微, 李佳歆, 马艺玮.基于条件深度卷积生成对抗网络的图像识别方法.自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 855-864 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170470Tang Xian-Lun, Du Yi-Ming, Liu Yu-Wei, Li Jia-Xin, Ma Yi-Wei. Image recognition method based on conditional depth convolution to generate anti-network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 855-864 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170470 [6] 金连文, 钟卓耀, 杨钊, 杨维信, 谢泽澄, 孙俊.深度学习在手写汉字识别中的应用综述.自动化学报, 2016, 42(8): 1125-1141 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150725Jin Lian-Wen, Zhong Zhuo-Yao, Yang Zhao, Yang Wei-Xin, Xie Ze-Cheng, Sun Jun. Application of deep learning in handwritten Chinese character recognition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1125-1141 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150725 [7] 李文英, 曹斌, 曹春水, 黄永祯.一种基于深度学习的青铜器铭文识别方法.自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 2023-2030 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180152Li Wen-Ying, Cao Bin, Cao Chun-Shui, Huang Yong-Zhen. A bronze inscription recognition method based on deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 2023-2030 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180152 [8] 姚乃明, 郭清沛, 乔逢春, 陈辉, 王宏安.基于生成式对抗网络的鲁棒人脸表情识别.自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 865-877 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170477Yao Nai-Ming, Guo Qing-Pei, Qiao Feng-Chun, Chen Hui, Wang Hong-An. Robust facial expression recognition based on generative confrontation network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 865-877 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170477 [9] Jain V, Seung H S. Natural image denoising with convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc. 2008. 769-776 [10] Burger H C, Schuler C J, Harmeling S. Image denoising: can plain neural networks compete with BM3D? In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recongnition (CVPR). Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2012. 2392-2399 [11] Chen Y J, Pock T. Trainable nonlinear reaction diffusion: a flexible framework for fast and effective image restoration. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(6): 1256-1272 [12] Xie J Y, Xu L L, Chen E H. Image denoising and inpainting with deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran-Associates Inc. 2012: 341-349 [13] Zhang Q, Li B X. Discriminative K-SVD for dictionary learning in face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2691-2698 [14] Zhang K, Zuo W M, Chen Y J, Meng D Y, Zhang L. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142-3155 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 [15] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Machine Learning. Miami, FL, USA: IEEE, 2015. 448-456 [16] Maas A, Hannun A, Ng A. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2013. [17] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conferenceon Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1026-1034 [18] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference for Learning Representations. San Diego, CA, USA: 2014. 1-14 [19] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770-778 [20] Marill T. Emulating the human interpretation of line-drawings as three-dimensional objects. International Journal of Computer Vision. 1991, 6(2): 147-161 [21] Christos T, Vasileios M, Ioannis P. Linear maximum margin classifier for learning from uncertain data. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(12): 2948-2962 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2772235 [22] Gu S H, Zhang L, Zuo W M, Feng X C. Weighted nuclear norm minimization with application to image denoising. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 2862-2869 [23] Daniel Z, Yair W. From learning models of natural image patches to whole image restoration. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 479- 486 [24] Schmidt U, Roth S. Shrinkage fields for effective image restoration. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 2774-2781 -




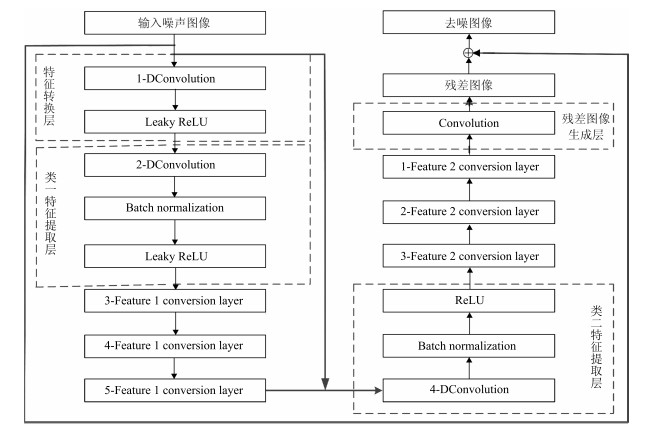
 下载:
下载: