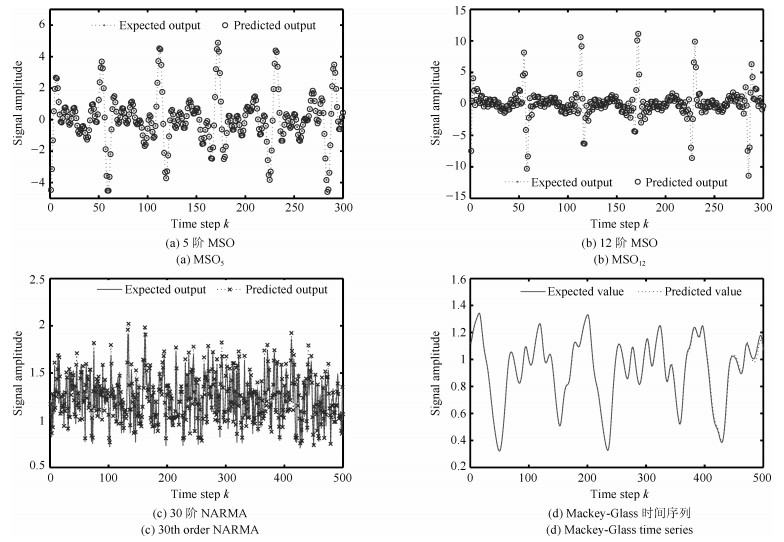
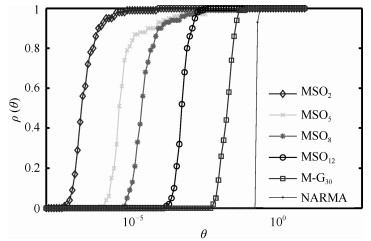
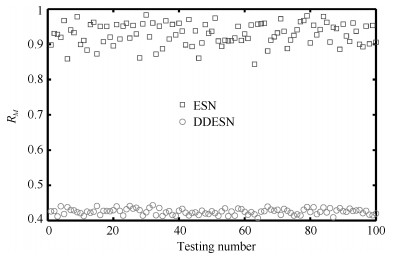
-
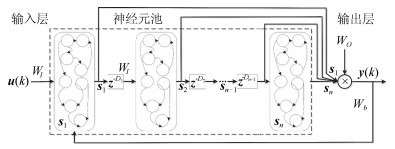
摘要: 为提高回声状态网络对于时间序列预测问题的处理能力, 本文提出了一种延迟深度回声状态网络构造方法.该方法将多个子神经元池顺序连接, 每两个相邻的子神经元池之间嵌入了一个滞后环节.由于滞后环节的存在,该网络可将长时记忆任务转化为一系列短时记忆任务, 从而简化长时依赖问题的求解, 同时降低神经元池的构建难度.实验表明, 该网络具有强大的短时记忆容量, 对初始参数有较好的鲁棒性, 对时间序列预测问题的处理能力也比常规回声状态网络有显著提高.Abstract: To improve the prediction ability of echo state network (ESN) on time series problems, this paper proposes a delayed deep ESN (DDESN) constructing method. In this scheme, multiple sub-reservoirs are connected one by one in sequence, and time delay modules are inserted between every two adjacent sub-reservoirs. The DDESN can transfer a long-term memory task into a series of short-term memory tasks because of the existence of the delay links. It simplifles the solution to long-term dependent task and reduces the di–culty of building a reservoir. Experimental results show that the proposed DDESN has stronger short-term memory capacity, better robustness to randomly initialized parameters, and higher performance on solving time series tasks than a standard ESN.
-
Key words:
- Artiflcial neural networks /
- echo state network /
- deep learning /
- short-term memory capacity /
- time series prediction
1) 本文责任编委 刘青山 -
表 1 ESN及DDESN参数设置
Table 1 Parameters settings for ESN and DDESN
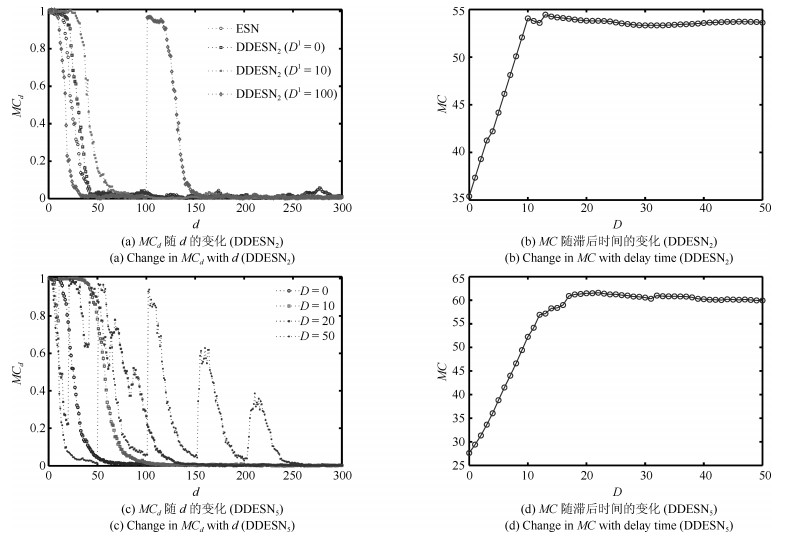
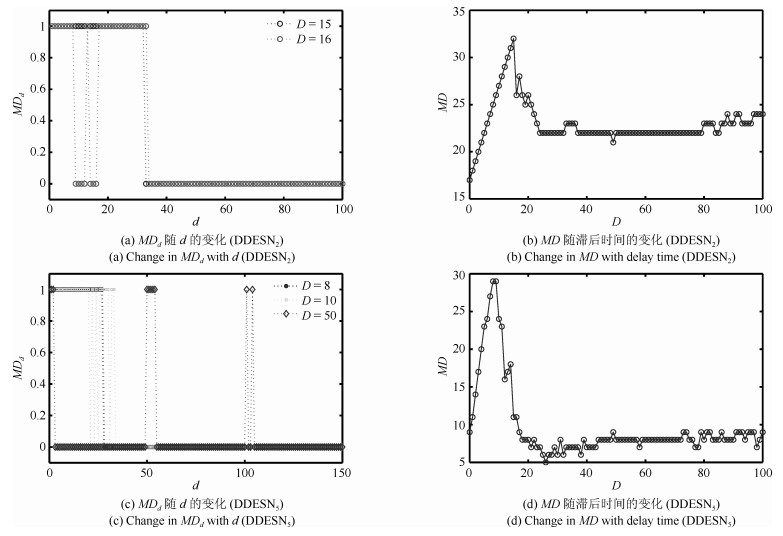
Model $n$ $N^i$ $D^i$ $\rho^i$ $MC_{\max}$ ESN 1 100 0 0.95 31.08 DDESN$_2$ 2 50 0 $\sim$ 100 0.95 54.02 DDESN$_5$ 5 20 0 $\sim$ 50 0.95 62.07 表 2 参数设置
Table 2 Parameter settings
表 3 Mackey-Glass预测性能
Table 3 Prediction performance for Mackey-Glass
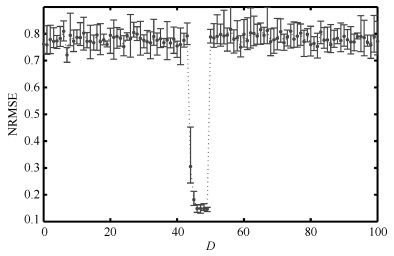
Task ESN D & S ESN DDESN $\mathrm{NRMSE}_{84}$ 0.140 0.031 5$.81\times10^{-3}$ NRMSE120 0.220 0.049 0.010 表 4 不同ESN模型的性能比较(MSO任务)
Table 4 Performance comparison of different ESN models (MSO tasks)
Task DDESN Balanced ESN[19] Evolutionary[27] D & S ESN[22] Evolino[28] MSO$_2$ $3.95\times10^{-8}$ $2.51\times10^{-12}$ $3.92\times10^{-8}$ $3.02\times10^{-9}$ $4.15\times10^{-3}$ MSO$_5$ $6.84\times10^{-7}$ $1.06\times10^{-6}$ $2.54\times10^{-2}$ $8.21\times10^{-5}$ $0.166$ MSO$_8$ $6.89\times10^{-6}$ $2.73\times10^{-4}$ $4.96\times10^{-3}$ $-$ $-$ MSO$_{12}$ $1.50\times10^{-4}$ $-$ $-$ $-$ $-$ 表 5 DDESN的鲁棒性测试结果
Table 5 Robustness testing results of DDESN
Task NARMA MSO$_{2}$ MSO$_{5}$ MSO$_{8}$ MSO$_{12}$ M-G$_{30}$ 最大NRMSE 0.2369 $7.03\times 10^{-5}$ $4.44\times 10^{-3}$ $6.33\times 10^{-2}$ $3.10\times 10^{-3}$ 0.0874 最小NRMSE 0.1968 $3.95\times 10^{-8}$ $6.84\times 10^{-7}$ $5.17\times 10^{-6}$ $1.50\times 10^{-4}$ 0.0058 平均NRMSE 0.2151 $1.06\times 10^{-6}$ $1.42\times 10^{-4}$ $7.17\times 10^{-4}$ $6.44\times 10^{-4}$ 0.0224 NRMSE标准差 0.0089 $7.03\times 10^{-6}$ $7.17\times 10^{-4}$ $6.31\times 10^{-3}$ $4.41\times 10^{-4}$ 0.0130 -
[1] Qiao J F, Wang L, Yang C L, Gu K. Adaptive Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm based echo state network for chaotic time series prediction. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 10720-10732 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2810190 [2] Jaeger H, Haas H. Harnessing nonlinearity: Predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. Science, 2004, 304(5667): 78-80 doi: 10.1126/science.1091277 [3] Xu M L, Han M. Adaptive elastic echo state network for multivariate time series prediction. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(10): 2173-2183 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2467167 [4] Han M, Xu M L. Laplacian echo state network for multivariate time series prediction. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks - Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 238-244 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cb55b15e28bcf33693db131d308e5bf4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Scardapane S, Wang D H, Panella M. A decentralized training algorithm for echo state networks in distributed big data applications. Neural Networks, 2016, 78: 65-74 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2015.07.006 [6] Bo Y C, Zhang X. Online adaptive dynamic programming based on echo state networks for dissolved oxygen control. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 62: 830-839 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.09.015 [7] Wootton A J, Taylor S L, Day C R, Haycock P W. Optimizing echo state networks for static pattern recognition. Cognitive Computation, 2017, 9(3): 391-399 doi: 10.1007/s12559-017-9468-2 [8] Trentin E, Scherer S, Schwenker F. Emotion recognition from speech signals via a probabilistic echo-state network. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2015, 66: 4-12 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2014.10.015 [9] 许美玲, 韩敏.多元混沌时间序列的因子回声状态网络预测模型.自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 1042-1046 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140604Xu Mei-Ling, Han Min. Factor echo state network for multivariate chaotic time series prediction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5): 1042-1046 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140604 [10] Jaeger H. Reservoir riddles: Suggestions for echo state network research. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Montreal, Quebec, Canada: IEEE, 2005. 1460-1462 [11] Ozturk M C, Xu D M, Príncipe J C. Analysis and design of echo state networks. Neural Computation, 2007, 19(1): 111-138 doi: 10.1162/neco.2007.19.1.111 [12] Xue Y B, Yang L, Haykin S. Decoupled echo state networks with lateral inhibition. Neural Networks, 2007, 20(3): 365-376 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e384cb32526eba071c56d92ae0bf4a70 [13] Qiao J F, Li F J, Han H G, Li W J. Growing echo-state network with multiple subreservoirs. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(2): 391-404 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2514275 [14] 韩红桂, 乔俊飞, 薄迎春.基于信息强度的RBF神经网络结构设计研究.自动化学报, 2012, 38(7): 1083-1090 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01083Han Hong-Gui, Qiao Jun-Fei, Bo Ying-Chun. On structure design for RBF neural network based on information strength. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(7): 1083-1090 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01083 [15] Huang G B, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N. A generalized growing and pruning RBF (GGAP-RBF) neural network for function approximation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2005, 16(1): 57-67 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0794f8a0aaa8d3898a169ecb821642ee [16] Dutoit X, Schrauwen B, Van Campenhout J, Stroobandt D, Van Brussel H, Nuttin M. Pruning and regularization in reservoir computing. Neurocomputing, 2009, 72(7-9): 1534-1546 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2008.12.020 [17] Rodan A, Tino P. Minimum complexity echo state network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(1): 131-144 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2089641 [18] Koryakin D, Lohmann J, Butz M V. Balanced echo state networks. Neural Networks, 2012, 36: 35-45 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2012.08.008 [19] Jaeger H. Short Term Memory in Echo State Networks, GMD-Report 152, Fraunhofer Institute for Autonomous Intelligent Systems, Germany, 2002. [20] Schrauwen B, Wardermann M, Verstraeten D, Steil J J, Stroobandt D. Improving reservoirs using intrinsic plasticity. Neurocomputing, 2008, 71(7-9): 1159-1171 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2007.12.020 [21] Holzmann G, Hauser H. Echo state networks with filter neurons and a delay-sum readout. Neural Networks, 2010, 23(2): 244-256 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7da0cd4e35aa87559b40e1e9c1111afe&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [22] 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃.深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望.自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160822Zhang Hui, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Advances and perspectives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160822 [23] Gallicchio C, Micheli A, Pedrelli L. Deep reservoir computing: A critical experimental analysis. Neurocomputing, 2017, 268: 87-99 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.089 [24] Prokhorov D. Echo state networks: Appeal and challenges. In: Proceeding of the 2005 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Montreal, Quebec, Canada: IEEE, 2005. 1463-1466 [25] Azaria M, Hertz D. Time delay estimation by generalized cross correlation methods. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing, 1984, 32(2): 280-285 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=65b15152398b79989ee725cfb289d91c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [26] Knapp C, Carter G. The generalized correlation method for estimation of time delay. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing, 1976, 24(4): 320-327 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=333b2c6d3506162357c6d8a138425866&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [27] Roeschies B, Igel C. Structure optimization of reservoir networks. Logic Journal of the IGPL, 2010, 18(5): 635-669 doi: 10.1093/jigpal/jzp043 [28] Schmidhuber J, Wierstra D, Gagliolo M, Gomez F. Training recurrent networks by evolino. Neural Computation, 2007, 19(3): 757-779 doi: 10.1162/neco.2007.19.3.757 -




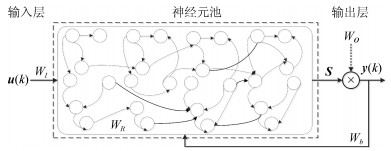
 下载:
下载: