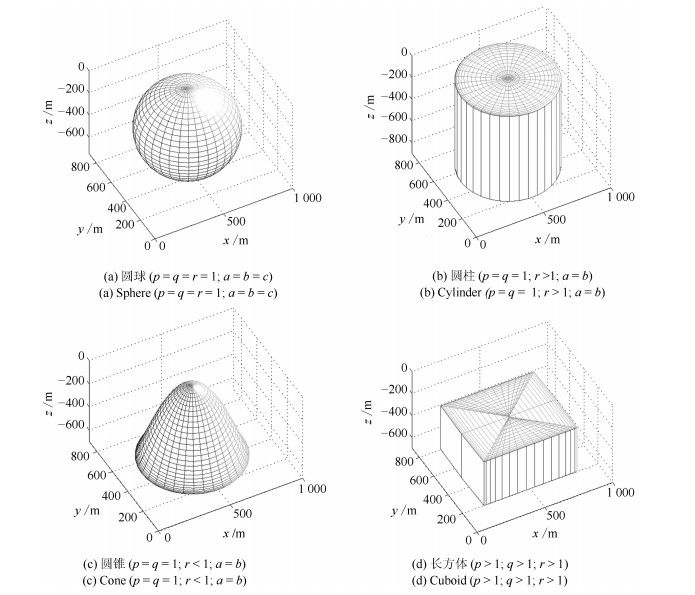
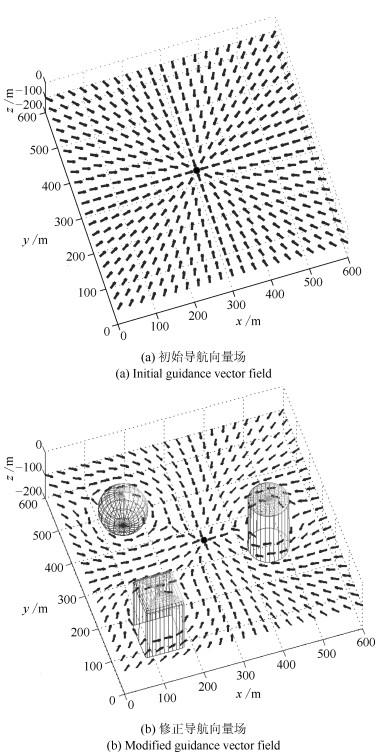
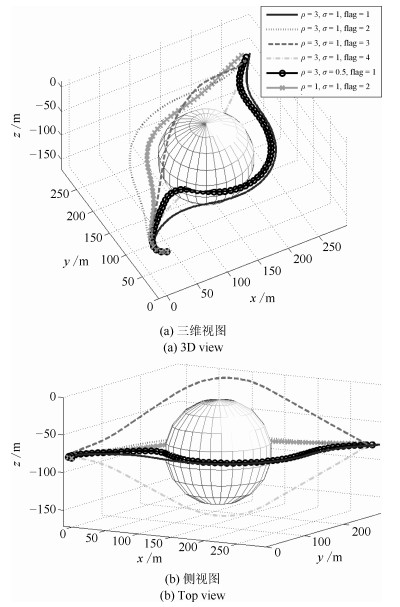
-
摘要: 针对复杂海洋环境下的自治水下机器人(Autonomous underwater vehicle, AUV)三维避障问题, 本文提出了一种高效的修正导航向量场方法.构建自由空间下的初始导航向量场, 引导AUV以最短路径向目标点航行.定义修正矩阵来量化描述障碍物对初始导航向量场的影响, 得到障碍空间下的修正导航向量场, 使得AUV向目标点航行的同时躲避静态障碍.通过结合障碍物运动速度, 分别构建相对初始导航向量场与相对修正导航向量场, 并采取有限时域推演与调整策略, 最终引导AUV安全躲避动态障碍.仿真结果表明, 本方法能较好地应用于复杂海洋环境下的AUV避障任务.Abstract: Obstacle Avoidance for AUV Based on Modified Guidance Vector Field YAO Peng1 XIE Ze-Xiao1 Abstract An efficient method called the modified guidance vector field is proposed to solve the three-dimensional obstacle avoidance problem for autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) in complex ocean environment. The initial guidance vector field in free space is first constructed to guide AUV to the destination along the shortest path. Then the modulation matrix is defined to quantify the influence of obstacles on the initial guidance vector field, and the modified guidance vector field in obstacle space is hence obtained, where AUV will avoid static obstacles when navigating to the destination. The referred velocity of dynamic obstacles is introduced to construct the relative initial/modified guidance vector field, and the limited time domain based derivation and adjustment strategy is also utilized to guide AUV avoiding dynamic obstacles safely. Finally the simulation results demonstrate that this method applies to the obstacle avoidance mission for AUV well in complex ocean environment.
-
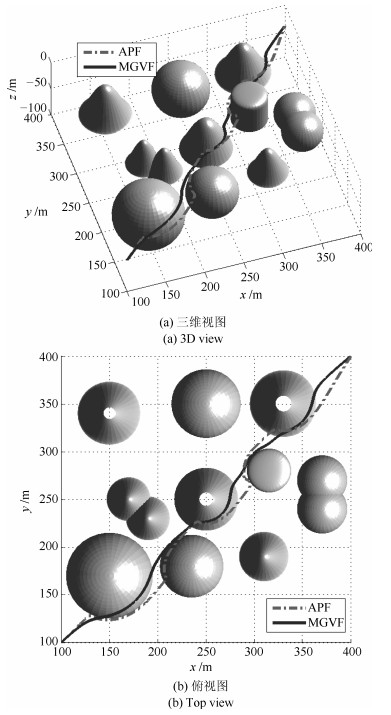
表 1 APF与MGVF方法的量化指标对比
Table 1 Performance indicators of APF and MGVF
方法 $L {\rm{(m)}}$ $GS (^\circ)$ $LS (^\circ)$ $d_{ \text{{AUV- obs}}}^{\min } {\rm{(m)}}$ APF 488 2.08 14.11 0.3 MGVF 453 1.14 5.56 5.6 -
[1] Wynn R B, Huvenne V A I, Le Bas T P, Murton B J, Connelly D P, Bett B J, et al. Autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs): Their past, present and future contributions to the advancement of marine geoscience. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 451-468 doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.012 [2] 谭民, 王硕.机器人技术研究进展.自动化学报, 2013, 39(7): 963-972 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00963Tan Min, Wang Shuo. Research progress on robotics. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(7): 963-972 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00963 [3] Zeng Z, Lian L, Sammut K, He F P, Tang Y L, Lammas A. A survey on path planning for persistent autonomy of autonomous underwater vehicles. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 110: 303-313 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.10.007 [4] Yao P, Wang H L, Su Z K. Real-time path planning of unmanned aerial vehicle for target tracking and obstacle avoidance in complex dynamic environment. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2015, 47: 269-279 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2015.09.037 [5] 申浩宇, 吴洪涛, 陈柏, 丁力, 杨小龙.基于主从任务转化的冗余度机器人避障算法.机器人, 2014, 36(4): 425-429 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jqr201404006Shen Hao-Yu, Wu Hong-Tao, Chen Bo, Ding Li, Yang Xiao-Long. Obstacle avoidance algorithm for redundant robots based on transition between the primary and secondary tasks. Robot, 2014, 36(4): 425-429 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jqr201404006 [6] Fang M C, Wang S M, Wu M C, Lin Y H. Applying the self-tuning fuzzy control with the image detection technique on the obstacle-avoidance for autonomous underwater vehicles. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 93: 11-24 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.11.001 [7] Kamil F, Tang S H, Khaksar W, Zulkifli N, Ahmad S A. A review on motion planning and obstacle avoidance approaches in dynamic environments. Advances in Robotics and Automation, 2015, 4(2): 1000134 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1177/0011000082101002 [8] Garrido S, Moreno L, Abderrahim M, Martin F. Path planning for mobile robot navigation using voronoi diagram and fast marching. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2006. 2376-2381 [9] Sgorbissa A, Zaccaria R. Planning and obstacle avoidance in mobile robotics. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2012, 60(4): 628-638 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2011.12.009 [10] 朱大奇, 孙兵, 李利.基于生物启发模型的AUV三维自主路径规划与安全避障算法.控制与决策, 2015, 30(5): 798-806 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201505004Zhu Da-Qi, Sun Bing, Li Li. Algorithm for AUV's 3-D path planning and safe obstacle avoidance based on biological inspired model. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(5): 798-806 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201505004 [11] Carroll K P, McClaran S R, Nelson E L, Barnett D M, Friesen D K, William G N. AUV path planning: An $A^{\ast}$ approach to path planning with consideration of variable vehicle speeds and multiple, overlapping, time-dependent exclusion zones. In: Proceedings of the 1992 Symposium on Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Technology. Washington, USA: IEEE, 1992. 79-84 [12] 严浙平, 赵玉飞, 陈涛.多约束条件下UUV空间航迹规划.鱼雷技术, 2011, 19(5): 365-369, 375 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1948.2011.05.009Yan Zhe-Ping, Zhao Yu-Fei, Chen Tao. Three-dimensional path planning for UUV with multiple constraints. Torpedo Technology, 2011, 19(5): 365-369, 375 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1948.2011.05.009 [13] Hernández J D, Vidal E, Vallicrosa G, Galceran E, Carreras M. Online path planning for autonomous underwater vehicles in unknown environments. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Washington, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1152-1157 [14] McMahon J, Plaku E. Mission and motion planning for autonomous underwater vehicles operating in spatially and temporally complex environments. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2016, 41(4): 893-912 doi: 10.1109/JOE.2015.2503498 [15] Ademoye T A, Davari A, Cao W. Three dimensional obstacle avoidance maneuver planning using mixed integer linear programming. In: Proceedings of the 12th IASTED International Conference on Robotics and Applications. Honolulu, USA: ACTA Press, 2006. 180-183 [16] Chen D S, Batson R G, Dang Y. Applied Integer Programming: Modeling and Solution. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons, 2010. [17] Saravanakumar S, Asokan T. Multipoint potential field method for path planning of autonomous underwater vehicles in 3D space. Intelligent Service Robotics, 2013, 6(4): 211-224 doi: 10.1007/s11370-013-0138-2 [18] Braginsky B, Guterman H. Obstacle avoidance approaches for autonomous underwater vehicle: Simulation and experimental results. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2016, 41(4): 882-892 doi: 10.1109/JOE.2015.2506204 [19] Li S H, Wang X Y. Finite-time consensus and collision avoidance control algorithms for multiple AUVs. Automatica, 2013, 49(11): 3359-3367 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.08.003 [20] Waydo S, Murray R M. Vehicle motion planning using stream functions. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Taipei, China: IEEE, 2003. 2484-2491 [21] Wang H L, Lyu W T, Yao P, Liang X, Liu C. Three-dimensional path planning for unmanned aerial vehicle based on interfered fluid dynamical system. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(1): 229-239 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2014.12.031 [22] 姚鹏, 王宏伦.基于改进流体扰动算法与灰狼优化的无人机三维航路规划.控制与决策, 2016, 31(4): 701-708 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201604019Yao Peng, Wang Hong-Lun. Three-dimensional path planning for UAV based on improved interfered fluid dynamical system and grey wolf optimizer. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(4): 701-708 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201604019 [23] Kim S, Oh H, Tsourdos A. Nonlinear model predictive coordinated standoff tracking of a moving ground vehicle. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2013, 36(2): 557-566 doi: 10.2514/1.56254 [24] Nadarajah N, Tharmarasa R, McDonald M, Kirubarajan T. IMM forward filtering and backward smoothing for maneuvering target tracking. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(3): 2673-2678 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6237617 -




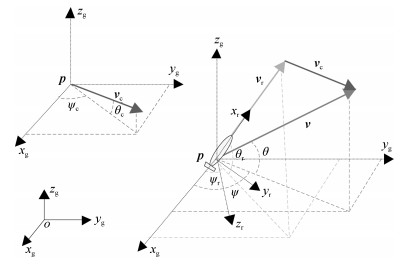
 下载:
下载: