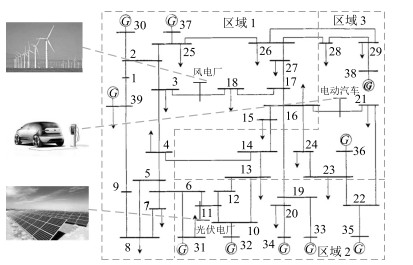
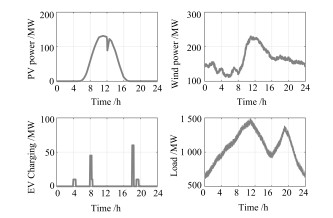
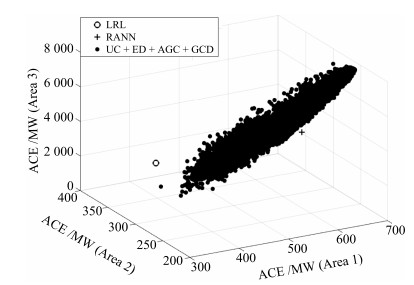
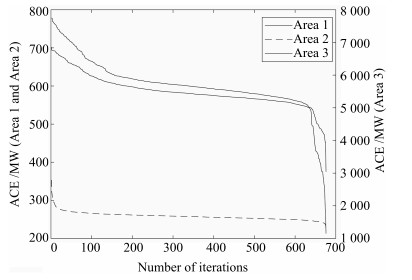
Lazy Reinforcement Learning Through Parallel Systems and Social System for Real-time Economic Generation Dispatch and Control
-
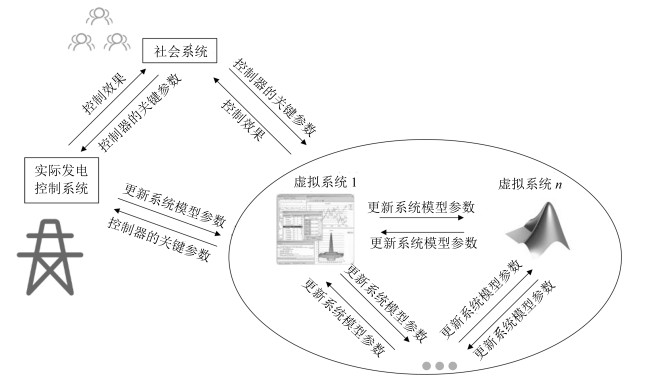
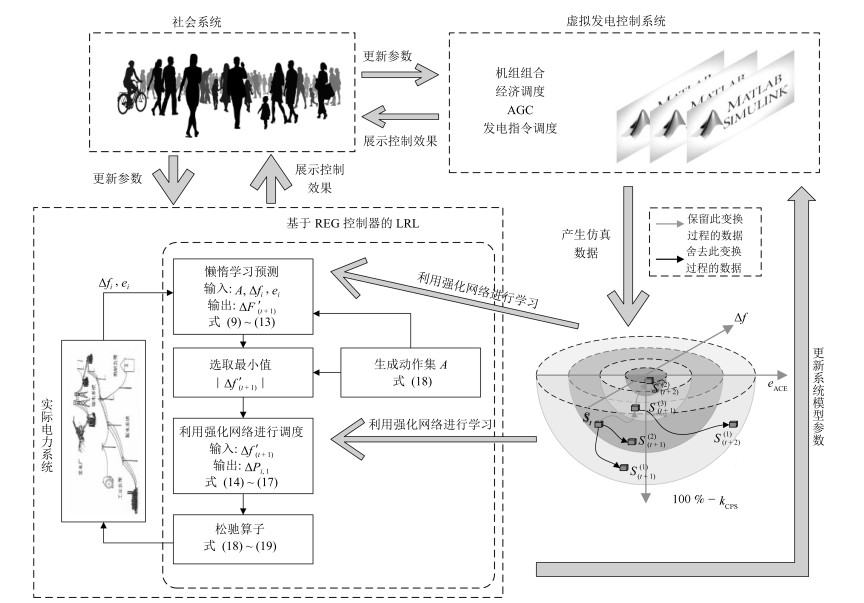
摘要: 为解决电力系统中存在的多种时间尺度下经济调度和发电控制的协同问题,即长时间尺度下优化,短时间尺度下优化和实时控制的问题,本文提出了一种统一时间尺度的实时经济发电调度和控制框架,并为该框架提出了懒惰强化学习方法(Lazy reinforcement learning,LRL).该方法将懒惰控制器引入以人工社会——计算实验——平行执行和社会系统为基础的强化学习中,使得机组组合,经济调度,自动发电控制和发电命令调配的问题有机结合在一起,取代过去传统的发电控制框架.为了减少仿真所需的真实时间,平行系统包含多个虚拟系统和一个真实系统.仿真实验比较了懒惰学习算法,松弛人工网络以及4608种组合常规发电控制算法在IEEE新英格兰10机39节点仿真系统的控制效果.实验表明,懒惰强化学习方法的控制效果最优.仿真结果验证了懒惰强化学习方法在基于ACP和社会系统的REG框架下具有有效性和可行性.Abstract: To mitigate the coordinated problem of multi-time scale economic dispatch and generation control in power systems, i.e., long term time scale optimization, short term time scale optimization, and real-time control, a real-time economic generation dispatch and control (REG) framework with a unified time scale is designed in this paper. With a lazy operator employed into reinforcement learning based on artificial societies-computational experiments-parallel execution (ACP) and social system, a lazy reinforcement learning (LRL) is proposed for the REG framework, which, being an alternative to conventional generation control framework, combines unit commitment, economic dispatch, automatic generation control, and generation command dispatch. To reduce the time of simulations, parallel systems which contain multiple virtual systems and a real system, are built. Compared with 4608 combined conventional generation control algorithms and relaxed artificial neural network in the simulation of IEEE 10-generator 39-bus New-England power system, the LRL obtains the best optimal control performance. Simulation results have verified the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed LRL based on ACP and social system for the REG framework.1) 本文责任编委 王占山
-
表 1 频率调节方式与传统发电调控框架之间的关系
Table 1 Relationship between regulation processes and conventional generation control framework
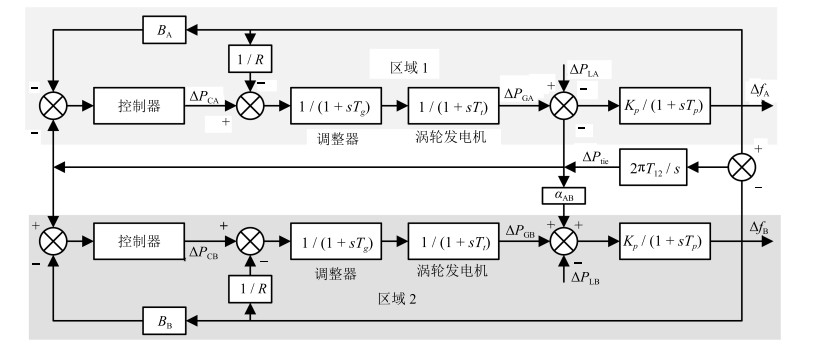
传统发电控制 调节方式 算法类型 时间间隔(s) 输入 输出 UC 三次调频 优化算法 86 400 $ PD_{i, t} $ $u_{i, t, j}, P_{j, t}$ ED 二次调频 优化算法 900 $PD_i$ $P_{i, j}$ AGC 二次调频 控制算法 4 $e_{i}, \Delta f_i$ $ \Delta P_i$ GCD 二次调频 优化算法 4 $\Delta P_i$ $\Delta P_{i, j}$ 表 2 懒惰强化学习输入输出量
Table 2 Inputs and outputs of lazy reinforcement learning
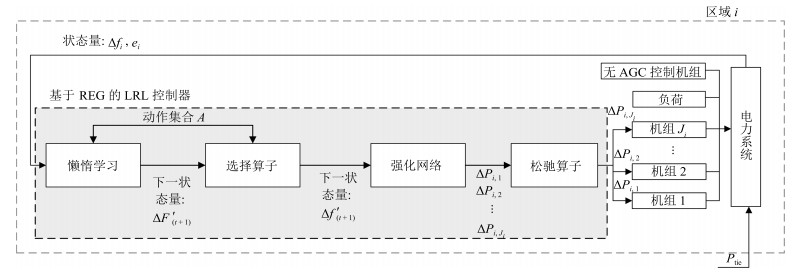
输入输出 懒惰学习 强化网络 懒惰强化学习 输入量 $\Delta {f_i}, {e_i}, {\bf \it {A}}$ $\Delta {F'_{i, (t + 1)}}$ $\Delta {f_i}, {e_i}$ 输出量 ${\Delta {f'_{i, (t + 1)}}}$ $\Delta {P_{i, j}}, $
$i = 1, 2, \cdots, {J_i}$$\Delta {P_{i, j}}, $
$i = 1, 2, \cdots, {J_i}$表 3 仿真所用的算法
Table 3 Algorithms for this simulation
序号 UC ED AGC GCD 1 模拟退火算法(SAA) SAA PID控制 SAA 2 多元优化(MVO) MVO 滑模控制器 MVO 3 遗传算法(GA) GA 自抗扰控制 GA 4 灰狼算法(GWO) GWO 分数阶PID控制 GWO 5 粒子群优化(PSO) PSO 模糊逻辑控制器 PSO 6 生物地理优化(BBO) BBO Q学习 BBO 7 飞蛾扑火算法(MFO) MFO Q($\lambda$)学习 MFO 8 鲸鱼群算法(WOA) WOA R($\lambda$)学习 WOA 9 固定比例 10 松弛人工神经网络(RANN) 11 懒惰强化学习(LRL) 表 4 各对比算法的缩写
Table 4 Abbreviation of compared algorithms
缩写 全称 意义 UC Unit commitment 机组组合 ED Economical dispatch 经济调度 AGC Automatic generation control 自动发电控制 GCD Generation command dispatch 发电指令调度 RL Reinforcement learning 强化学习 REG Real-time economic generation dispatch and control 实时经济调度与控制 ACP Artificial societies- computational experiments-parallel execution 人工社会-计算实验-平行执行 CPS Cyber-physical system 信息物理系统 CPSS Cyber-physical-social systems 信息物理社会融合系统 LRL Lazy reinforcement learning 懒惰强化学习 RANN Relaxed artificial neural network 松弛人工神经网络 SAA Simulated annealing algorithm 模拟退火算法 MVO Multi-verse optimizer 多元优化 GA Genetic algorithm 遗传算法 GWO Gray wolf optimizer 灰狼算法 PSO Particle swarm optimization 粒子群优化 BBO Biogeography-based optimization 生物地理优化 MFO Moth-flame optimization 飞蛾扑火算法 WOA Whale optimization algorithm 鲸鱼群算法 LOOCV Leave-one-out cross-validation 留一法交叉校验 BPNN Back propagation neural network 反向传播神经网络 表 5 机组参数表
Table 5 Parameters of the generators
机组编号 30 37 39 31 32 33 34 35 36 38 机组最小连续开机时间$T_j^{\mathrm{min-up}}$ (h) 8 8 5 5 6 3 3 1 1 1 机组最小连续关机时间$T_j^{\mathrm{min-down}}$ (h) 8 8 5 5 6 3 3 1 1 1 机组最大出力$P_j^{\min}$ (MW) 455 455 130 130 162 80 85 55 55 55 机组最小出力$P_j^{\max}$ (MW) 150 150 20 20 25 20 25 10 10 10 热启动成本$SU_{\mathrm{H}, j}$ (t/(MW $\cdot$ h)) 4 500 5 000 550 560 900 170 260 30 30 30 冷启动成本$SU_{\mathrm{C}, j}$ (t/(MW $\cdot$ h)) 9 000 10 000 1 100 1 120 1 800 340 520 60 60 60 冷启动时间$T_j^{\mathrm{cold}}$ (h) 5 5 4 4 4 2 2 0 0 0 ED成本系数$a_j$ 0.675 0.45 0.563 0.563 0.45 0.563 0.563 0.337 0.315 0.287 ED成本系数$b_j$ 360 240 299 299 240 299 299 181 168 145 ED成本系数$c_j$ 11 250 7 510 9 390 9 390 7 510 9 390 9 390 5 530 5 250 5 270 ED排放系数$\alpha _j$ 3.375 1.125 1.689 1.576 1.17 1.576 1.576 0.674 0.63 0.574 ED排放系数$\beta _j$ 1 800 600 897 837 624 837 837 362 404 290 ED排放系数$\gamma _j$ 56 250 18 770 28 170 26 290 19 530 26 290 26 290 11 060 13 800 10 540 表 6 机组组合问题参数表
Table 6 Parameters for unit commitment problem
UC问题的负荷时段(h) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 UC问题的负荷值$PD_t$ (WM) 700 750 850 950 1 000 1 100 1 150 1 200 1 300 1 400 1 450 1 500 UC问题的旋转备用$SR_t$ (WM) 70 75 85 95 100 110 115 120 130 140 145 150 UC问题的负荷时段(h) 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 UC问题的负荷值$PD_t$ (WM) 1 400 1 300 1 200 1 050 1 000 1 100 1 200 1 400 1 300 1 100 900 800 UC问题的旋转备用$SR_t$ (WM) 140 130 120 105 100 110 120 140 130 110 90 80 表 7 UC算法仿真结果统计
Table 7 Statistic of simulation results obtained by the UC
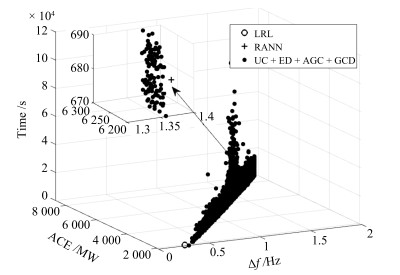
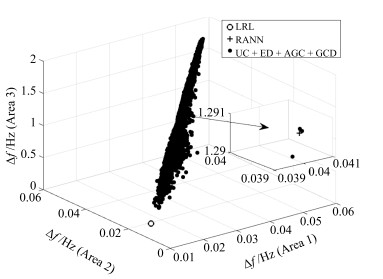
算法 ACE1 (MW) $\Delta f_1$ (Hz) ACE2 (MW) $\Delta f_2$ (Hz) ACE3 (MW) $\Delta f_3$ (Hz) SAA 573.8904 0.038235 258.7798 0.03752 5 527.9746 1.3137 MVO 575.3672 0.038274 259.9265 0.037558 5 532.6202 1.3154 GA 603.4391 0.041805 258.6484 0.041041 6 052.2806 1.4428 GWO 616.064 0.043454 257.6107 0.042653 6 290.0843 1.5017 PSO 575.7172 0.038264 260.3543 0.037555 5 535.1644 1.3159 BBO 574.2769 0.038213 259.349 0.037499 5 522.5691 1.3131 MFO 569.7159 0.037685 259.1499 0.036984 5 441.3487 1.2932 WOA 645.5906 0.047207 255.8246 0.04639 6 844.8509 1.6369 RANN 553.4032 0.039963 224.1748 0.039083 5 431.2844 1.2907 LRL 441.9225 0.010254 389.9905 0.0095612 1 023.1919 0.23743 表 8 ED算法仿真结果统计
Table 8 Statistic of simulation results obtained by the ED algorithms
算法 ACE1 (MW) $\Delta f_1$ (Hz) ACE2 (MW) $\Delta f_2$ (Hz) ACE3 (MW) $\Delta f_3$ (Hz) SAA 587.8414 0.039976 258.2767 0.039234 5 777.5755 1.3756 MVO 588.177 0.039978 258.5125 0.039245 5 782.3567 1.3768 GA 589.4091 0.040193 257.6335 0.039479 5 818.9809 1.3856 GWO 587.6547 0.039959 258.0923 0.039228 5 780.4664 1.3763 PSO 587.858 0.039915 258.8111 0.039182 5 771.2924 1.3741 BBO 588.0198 0.039924 258.9211 0.039192 5 770.4608 1.3739 MFO 588.1836 0.039988 258.4948 0.03925 5 778.844 1.3759 WOA 588.6974 0.040103 257.7113 0.039387 5 805.4046 1.3823 RANN 553.4032 0.039963 224.1748 0.039083 5 431.2844 1.2907 LRL 441.9225 0.010254 389.9905 0.0095612 1 023.1919 0.23743 表 9 AGC算法仿真结果统计
Table 9 Statistic of simulation results obtained by the AGC algorithms
算法 ACE1 (MW) $\Delta f_1$ (Hz) ACE2 (MW) $\Delta f_2$ (Hz) ACE3 (MW) $\Delta f_3$ (Hz) PID控制 591.3081 0.040435 257.518 0.039717 5 854.0102 1.3939 滑动模式控制器 590.7335 0.040374 257.4495 0.039656 5 844.7291 1.3916 自抗扰控制 591.3771 0.040424 257.6773 0.039707 5 853.0488 1.3937 分数阶PID控制 591.1007 0.040437 257.3069 0.039715 5 852.7478 1.3936 模糊逻辑控制 591.951 0.040504 257.6024 0.039781 5 863.4785 1.3963 Q学习 591.3603 0.040452 257.4572 0.039727 5 855.1339 1.3942 Q($\lambda$)学习 591.0772 0.040419 257.4421 0.039696 5 849.9705 1.393 R($\lambda$)学习 591.7282 0.040494 257.469 0.03977 5 862.7832 1.3961 RANN 553.4032 0.039963 224.1748 0.039083 5 431.2844 1.2907 LRL 441.9225 0.010254 389.9905 0.0095612 1 023.1919 0.23743 表 10 GCD算法仿真结果统计
Table 10 Statistic of simulation results obtained by the GCD algorithms
算法 ACE1 (MW) $\Delta f_1$ (Hz) ACE2 (MW) $\Delta f_2$ (Hz) ACE3 (MW) $\Delta f_3$ (Hz) SAA 591.3081 0.040435 257.518 0.039717 5 854.0102 1.3939 MVO 590.7335 0.040374 257.4495 0.039656 5 844.7291 1.3916 GA 591.3771 0.040424 257.6773 0.039707 5 853.0488 1.3937 GWO 591.1007 0.040437 257.3069 0.039715 5 852.7478 1.3936 PSO 591.951 0.040504 257.6024 0.039781 5 863.4785 1.3963 BBO 591.3603 0.040452 257.4572 0.039727 5 855.1339 1.3942 MFO 591.0772 0.040419 257.4421 0.039696 5 849.9705 1.393 WOA 591.7282 0.040494 257.469 0.03977 5 862.7832 1.3961 固定比例 509.0391 0.028801 282.0332 0.027609 3 973.743 0.94347 RANN 553.4032 0.039963 224.1748 0.039083 5 431.2844 1.2907 LRL 441.9225 0.010254 389.9905 0.0095612 1 023.1919 0.23743 -
[1] 王宗杰, 郭志忠, 王贵忠, 吴志琪.高比例可再生能源电网功率平衡的实时调度临界时间尺度研究.中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(S1):39-46 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb2017z1005Wang Zong-Jie, Guo Zhi-Zhong, Wang Gui-Zhong, Wu Zhi-Qi. On the critical timescale of real-time dispatch considering power balancing under power systems with high proportional intermittent power sources. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(S1):39-46 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb2017z1005 [2] Liang Z T, Liang J, Zhang L, Wang C F, Yun Z H, Zhang X. Analysis of multi-scale chaotic characteristics of wind power based on Hilbert-Huang transform and Hurst analysis. Applied Energy, 2015, 159:51-61 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.08.111 [3] 覃岭, 林济铿, 戴赛, 王海林, 郑卫红.基于改进轻鲁棒优化模型的风、火机组组合.中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(15):4108-4118 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201615011Qin Ling, Lin Ji-Keng, Dai Sai, Wang Hai-Lin, Zheng Wei-Hong. Improved light robust optimization model based wind-thermal unit commitment. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(15):4108-4118 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201615011 [4] 陈典, 钟海旺, 夏清.基于全成本电价的安全约束经济调度.中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(5):1190-1199 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201605003Chen Dian, Zhong Hai-Wang, Xia Qing. Security constrained economic dispatch based on total cost price. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(5):1190-1199 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201605003 [5] 范刘洋, 汪可友, 吴巍, 李国杰, 葛延峰.多时间尺度的电力系统鲁棒调度研究.电网技术, 2017, 41(5):1576-1582 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dwjs201705030Fan Liu-Yang, Wang Ke-You, Wu Wei, Li Guo-Jie, Ge Yan-Feng. A study of multi-time scale robust schedule and dispatch methodology. Power System Technology, 2017, 41(5):1576-1582 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dwjs201705030 [6] 胡林, 申建建, 唐海.考虑复杂约束的水电站AGC控制策略.中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(19):5643-5654 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201719013Hu Lin, Shen Jian-Jian, Tang Hai. Automatic generation control strategies of hydropower plant considering complex constraints. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(19):5643-5654 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201719013 [7] Yu T, Wang Y M, Ye W J, Zhou B, Chan K W. Stochastic optimal generation command dispatch based on improved hierarchical reinforcement learning approach. IET Generation. Transmission and Distribution, 2011, 5(8):789-797 doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd.2010.0600 [8] Zhang X S, Yu T, Yang B, Li L. Virtual generation tribe based robust collaborative consensus algorithm for dynamic generation command dispatch optimization of smart grid. Energy, 2016, 101:34-51 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.02.009 [9] 张孝顺, 余涛, 唐捷.基于分层相关均衡强化学习的CPS指令优化分配算法.电力系统自动化, 2015, 39(8):80-86 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxtzdh201508013Zhang Xiao-Shun, Yu Tao, Tang Jie. Optimal CPS command dispatch based on hierarchically correlated equilibrium reinforcement learning. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39(8):80-86 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxtzdh201508013 [10] Abass Y A, Al-Awami A T, Jamal T. Integrating automatic generation control and economic dispatch for microgrid real-time optimization. In:Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). Boston, USA:IEEE, 2016. 1-5 [11] Yang M, Wang M Q, Cheng F L, Lee W J. Robust economic dispatch considering automatic generation control with affine recourse process. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2016, 81:289-298 doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2016.02.033 [12] Li N, Zhao C H, Chen L J. Connecting automatic generation control and economic dispatch from an optimization view. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2016, 3(3):254-264 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2015.2459451 [13] 唐捷, 张泽宇, 程乐峰, 张孝顺, 余涛.基于CEQ(λ)强化学习算法的微电网智能发电控制.电测与仪表, 2017, 54(1):39-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1390.2017.01.007Tang Jie, Zhang Ze-Yu, Cheng Le-Feng, Zhang Xiao-Shun, Yu Tao. Smart generation control for micro-grids based on correlated equilibrium Q(λ) learning algorithm. Electrical Measurement and Instrumentation, 2017, 54(1):39-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1390.2017.01.007 [14] 余涛, 周斌, 陈家荣.基于多步回溯Q(λ)学习的互联电网随机最优CPS控制.电工技术学报, 2011, 26(6):179-186 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGJS201106029.htmYu Tao, Zhou Bin, Chan Ka-Wing. Stochastic optimal CPS control for interconnected power grids using multi-step backtrack Q(λ) learning. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2011, 26(6):179-186 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGJS201106029.htm [15] 王飞跃.人工社会、计算实验、平行系统—关于复杂社会经济系统计算研究的讨论.复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2004, 1(4):25-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.04.002Wang Fei-Yue. Artificial societies, computational experiments, and parallel systems:a discussion on computational theory of complex social-economic systems. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2004, 1(4):25-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.04.002 [16] Wang F Y. Parallel control and management for intelligent transportation systems:concepts, architectures, and applications. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2010, 11(3):630-638 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2010.2060218 [17] 白天翔, 王帅, 沈震, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃.平行机器人与平行无人系统:框架、结构、过程、平台及其应用.自动化学报, 2017, 43(2):161-175 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18998.shtmlBai Tian-Xiang, Wang Shuai, Shen Zhen, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel robotics and parallel unmanned systems:framework, structure, process, platform and applications. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(2):161-175 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18998.shtml [18] 袁勇, 王飞跃.平行区块链:概念、方法与内涵解析.自动化学报, 2017, 43(10):1703-1712 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2017/V43/I10/1703Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel blockchain:concept, methods and issues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10):1703-1712 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2017/V43/I10/1703 [19] 李力, 林懿伦, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃.平行学习—机器学习的一个新型理论框架.自动化学报, 2017, 43(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.01.001Li Li, Lin Yi-Lun, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel learning—a new framework for machine learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.01.001 [20] 熊刚, 王飞跃, 侯家琛, 董西松, 张家麟, 付满昌.提高核电站安全可靠性的平行系统方法.系统工程理论与实践, 2012, 32(5):1018-1026 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2012.05.014Xiong Gang, Wang Fei-Yue, Hou Jia-Chen, Dong Xi-Song, Zhang Jia-Lin, Fu Man-Chang. To improve safety and reliability of nuclear power plant with parallel system method. Systems Engineering-Theory and Practice, 2012, 32(5):1018-1026 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2012.05.014 [21] Wang F Y. The emergence of intelligent enterprises:from CPS to CPSS. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2010, 25(4):85-88 doi: 10.1109/MIS.2010.104 [22] 邓建玲, 王飞跃, 陈耀斌, 赵向阳.从工业4.0到能源5.0:智能能源系统的概念、内涵及体系框架.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12):2003-2016 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18774.shtmlDeng Jian-Ling, Wang Fei-Yue, Chen Yao-Bin, Zhao Xiang-Yang. From industries 4.0 to energy 5.0:concept and framework of intelligent energy systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12):2003-2016 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18774.shtml [23] 王进, 周宇轩, 戴伟, 李亚峰, 宋翼颉. NSGA-Ⅱ算法的改进及其在风火机组多目标动态组合优化中的应用.电力系统及其自动化学报, 2017, 29(2):107-111 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.02.018Wang Jin, Zhou Yu-Xuan, Dai Wei, Li Ya-Feng, Song Yi-Jie. Improvement of NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm and its application to multi-objective dynamic unit commitment optimization with wind-thermal power. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2017, 29(2):107-111 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.02.018 [24] 刘洪, 陈星屹, 李吉峰, 徐科.基于改进CPSO算法的区域电热综合能源系统经济调度.电力自动化设备, 2017, 37(6):193-200 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlzdhsb201706027Liu Hong, Chen Xing-Yi, Li Ji-Feng, Xu Ke. Economic dispatch based on improved CPSO algorithm for regional power-heat integrated energy system. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2017, 37(6):193-200 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlzdhsb201706027 [25] 李正茂, 张峰, 梁军, 贠志皓, 张旭.计及附加机会收益的冷热电联供型微电网动态调度.电力系统自动化, 2015, 39(14):8-15 doi: 10.7500/AEPS20141109002Li Zheng-Mao, Zhang Feng, Liang Jun, Yun Zhi-Hao, Zhang Xu. Dynamic scheduling of CCHP type of microgrid considering additional opportunity income. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39(14):8-15 doi: 10.7500/AEPS20141109002 [26] Faris H, Aljarah I, Mirjalili S. Training feedforward neural networks using multi-verse optimizer for binary classification problems. Applied Intelligence, 2016, 45(2):322-332 doi: 10.1007/s10489-016-0767-1 [27] Yang B, Jiang L, Wang L, Yao W, Wu Q H. Nonlinear maximum power point tracking control and modal analysis of DFIG based wind turbine. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2016, 74:429-436 doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.07.036 [28] Zeng G Q, Chen J, Dai Y X, Li L M, Zheng C W, Chen M R. Design of fractional order PID controller for automatic regulator voltage system based on multi-objective extremal optimization. Neurocomputing, 2015, 160:173-184 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.02.051 [29] Pan I, Das S. Fractional-order load-frequency control of interconnected power systems using chaotic multi-objective optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 29:328-344 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2014.12.032 [30] Shabani H, Vahidi B, Ebrahimpour M. A robust PID controller based on imperialist competitive algorithm for load-frequency control of power systems. ISA Transactions, 2013, 52(1):88-95 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2012.09.008 [31] Mohanty P K, Sahu B K, Pati T K, Panda S, Kar K S. Design and analysis of fuzzy PID controller with derivative filter for AGC in multi-area interconnected power system. IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 2016, 10(15):3764-3776 doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd.2016.0106 [32] Dahiya P, Sharma V, Naresh R. Automatic generation control using disrupted oppositional based gravitational search algorithm optimised sliding mode controller under deregulated environment. IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 2016, 10(16):3995-4005 doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd.2016.0175 [33] 姚书龙, 刘志刚, 张桂南, 向川.基于自抗扰控制的牵引网网压低频振荡抑制方法.电网技术, 2016, 40(1):207-213 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dwjs201601028Yao Shu-Long, Liu Zhi-Gang, Zhang Gui-Nan, Xiang Chuan. A novel approach based on ADRC to traction network voltage low frequency oscillation suppression research. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(1):207-213 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dwjs201601028 [34] 杨平, 董国威.互联电网AGC的分数阶PID控制.电力系统及其自动化学报, 2013, 25(3):124-129 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2013.03.024Yang Ping, Dong Guo-Wei. Fractional order PID control for AGC of interconnected power system. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2013, 25(3):124-129 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2013.03.024 [35] 张孝顺, 李清, 余涛, 陈柏熹.基于协同一致性迁移Q学习算法的虚拟发电部落AGC功率动态分配.中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(5):1455-1466 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201705020Zhang Xiao-Shun, Li Qing, Yu Tao, Chen Bai-Xi. Collaborative consensus transfer Q-learning based dynamic generation dispatch of automatic generation control with virtual generation tribe. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(5):1455-1466 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201705020 [36] 余涛, 袁野.基于平均报酬模型全过程R(λ)学习的互联电网CPS最优控制.电力系统自动化, 2010, 34(21):27-33 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxtzdh201021005Yu Tao, Yuan Ye. An average reward model based whole process R(λ)-learning for optimal CPS control. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2010, 34(21):27-33 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxtzdh201021005 [37] Zhang Y, Liu X J, Qu B. Distributed model predictive load frequency control of multi-area power system with DFIGs. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(1):125-135 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510346 -





 下载:
下载: