Illumination-Inversion and Rotation Invariant Texture Representation Based on Local Complement and Derivative Pattern
-
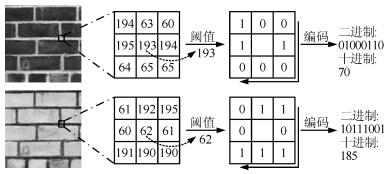
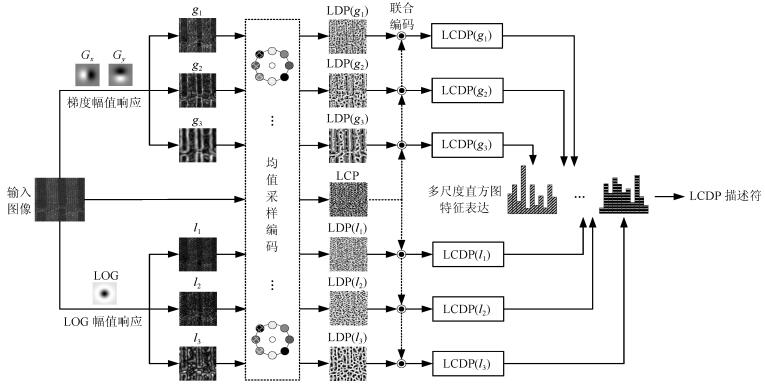
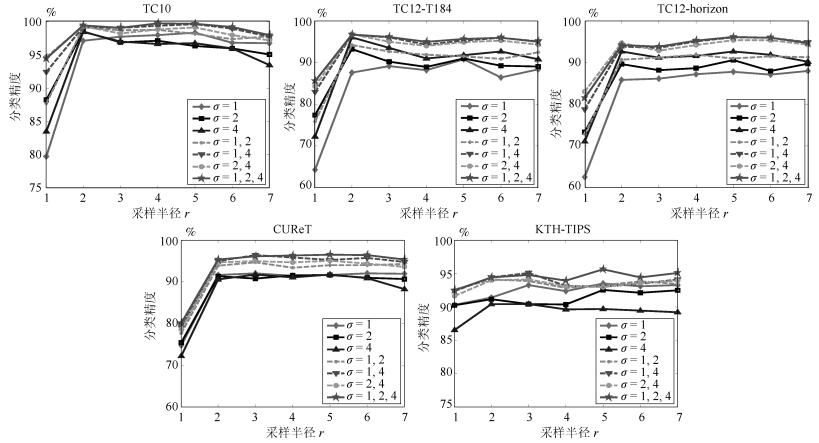
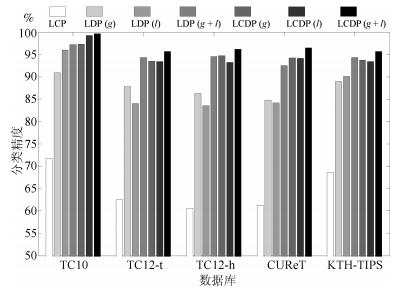
摘要: 针对现有局部二值模式(Local binary pattern, LBP) 算法对光照反转变化敏感和特征描述力不足的问题, 本文提出一种基于局部补数-导数模式(Local complement and derivative pattern, LCDP) 的纹理表达方法. 其中, 局部补数模式(Local complement pattern, LCP) 用于编码原始图像空间中的近邻差分符号信息, 局部导数模式(Local derivative pattern, LDP) 用于编码不同尺度下(一阶和二阶) 高斯导数空间中的近邻差分幅值信息, 二者对光照反转和图像旋转均具有鲁棒性. 为实现对差分符号和差分幅值的联合统计, 同时维持特征的紧致性, 进一步提出基于均值采样的联合编码方案. 最后, 对联合编码的结果进行多尺度直方图特征表达. 实验表明, 该方法能够有效提高线性和非线性光照反转条件下纹理图像的分类精度.Abstract: The existing local binary pattern (LBP) based algorithms are sensitive to inverse illumination changes and have limited ability for feature description. In view of this, a method for texture representation is proposed based on local complement and derivative pattern (LCDP). In LCDP, local complement pattern (LCP) encodes the signs of neighbor difierences in original image space whereas local derivative pattern (LDP) encodes the magnitudes of neighbor difierences in (the flrst and the second order) Gaussian derivative space at difierent scales. Both LCP and LDP are robust to inverse illuminations and image rotation. Furthermore, a joint encoding scheme based on mean sampling is proposed. This is used to establish the joint statistics of difierence signs and difierence magnitudes while remaining compact features. Finally, the texture descriptor is obtained by constructing multi-scale histograms of jointly encoded features. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can efiectively improve the classiflcation accuracy of texture images under both linear and nonlinear inverse illumination conditions.
-
Key words:
- Texture classiflcation /
- feature extraction /
- illumination changes /
- local binary pattern (LBP)
1) 本文责任编委 白翔 -
表 1 不同方法在线性光照反转条件下的分类精度(%)
Table 1 Classification accuracies (%) of different methods under linear inverse illumination conditions
方法 Outex CUReT KTH-TIPS TC10 TC12 tl84 horizon LBP[2] 39.98 39.34 39.63 43.47 47.07 LTP[13] 21.37 37.99 38.91 44.71 54.46 CLBP[16] 24.49 22.12 22.72 34.33 43.15 CLBC[17] 20.20 18.68 18.96 31.02 41.54 LETRIST[18] 32.97 32.37 34.89 43.68 53.75 jcLSFP[19] 33.78 35.49 38.40 49.04 54.54 NRLBP[20] 42.34 42.49 45.26 83.21 87.88 LGP[21] 94.58 78.47 76.65 89.73 88.85 GLBP[22] 93.39 90.43 89.35 88.21 89.12 SLGP[23] 97.79 84.17 83.82 94.87 93.83 SIFT[29] 19.39 14.43 13.75 13.49 27.95 LCP 71.72 62.57 60.56 61.30 68.68 LDP 97.24 94.35 94.58 92.51 94.31 LCDP 99.69 95.63 96.18 96.52 95.68 表 2 不同方法在非线性光照反转条件下的分类精度(%)
Table 2 Classification accuracies (%) of different methods under nonlinear inverse illumination conditions
方法 Outex CUReT KTH-TIPS TC10 TC12 tl84 horizon LBP[2] 40.63 38.91 39.40 43.18 46.93 LTP[13] 36.56 35.32 37.08 43.72 41.66 CLBP[16] 22.99 23.15 23.87 35.59 44.93 CLBC[17] 18.29 18.80 19.75 33.16 42.34 LETRIST[18] 4.17 4.17 4.17 2.30 12.24 jcLSFP[19] 33.88 35.56 37.85 49.45 53.07 NRLBP[20] 42.32 42.94 45.32 69.02 87.73 LGP[21] 91.27 71.08 70.49 85.18 87.49 GLBP[22] 92.79 89.32 88.70 87.90 87.66 SLGP[23] 95.60 75.49 73.63 91.23 90.82 SIFT[29] 11.94 13.61 13.69 17.03 29.88 LCP 71.57 62.19 60.64 61.39 68.51 LDP 96.43 92.77 92.75 90.80 92.05 LCDP 99.61 95.09 95.42 95.81 94.54 表 3 不同方法在原始数据库上的分类精度(%)
Table 3 Classiflcation accuracies (%) of difierent methods on the original databases
方法 Outex CUReT KTH-TIPS TC10 TC12 tl84 horizon LBP[2] 97.16 88.96 83.96 93.52 92.70 LTP[13] 98.65 92.69 89.86 94.46 94.36 CLBP[16] 99.17 95.23 95.58 96.94 96.50 CLBC[17] 99.04 94.10 95.14 96.78 96.39 LETRIST[18] 100.00 99.81 100.00 98.52 98.80 jcLSFP[19] 100.00 99.77 99.93 98.20 98.72 NRLBP[20] 45.96 48.33 50.95 83.08 87.36 LGP[21] 94.58 78.47 76.65 89.86 89.83 GLBP[22] 93.20 90.37 89.26 88.44 87.63 SLGP[23] 97.79 84.17 83.82 94.83 93.71 SIFT[29] 48.61 52.75 53.18 78.12 93.37 LCP 71.72 62.57 60.56 61.41 68.56 LDP 97.24 94.35 94.58 92.37 94.52 LCDP 99.69 95.63 96.18 96.60 95.49 表 4 不同方法在KTH-TIPS数据库上提取单个图像描述符所需的平均时间(秒)
Table 4 Average time (second) for different methods to extract one image descriptor on the KTH-TIPS database
方法 时间 方法 时间 方法 时间 LBP 0.040 LETRIST 0.052 GLBP 0.914 LTP 0.047 jcLSFP 0.077 SLGP 0.084 CLBP 0.063 NRLBP 0.010 SIFT 0.087 CLBC 0.056 LGP 0.041 LCDP 0.139 -
[1] 刘丽, 赵凌君, 郭承玉, 王亮, 汤俊. 图像纹理分类方法研究进展和展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(4): 584-607 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c160452Liu Li, Zhao Ling-Jun, Guo Cheng-Yu, Wang Liang, Tang Jun. Texture classification: state-of-the-art methods and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(4): 584-607 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c160452 [2] Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 971-987 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017623 [3] 何楚, 尹莎, 许连玉, 廖紫纤. 基于局部重要性采样的SAR图像纹理特征提取方法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(2): 316-326 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00316He Chu, Yin Sha, Xu Lian-Yu, Liao Zi-Xian. Feature extraction of SAR image based on local important sampling binary encoding. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(2): 316-326 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00316 [4] Liu X, Wang D. Image and texture segmentation using local spectral histograms. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(10): 3066-3077 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.877511 [5] Song T C, Li H L. WaveLBP based hierarchical features for image classification. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2013, 34(12): 1323-1328 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2013.04.020 [6] Song T C, Li H L. Local polar DCT features for image description. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(1): 59-62 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2229273 [7] Haralick R M, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 1973, SMC-3(6): 610-621 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1973.4309314 [8] Cross G R, Jain A K. Markov random field texture models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1983, 5(1): 25-39 [9] Zhang W C, Shan S G, Gao W, Chen X L. Local Gabor binary pattern histogram sequence (LGBPHS): a novel non-statistical model for face representation and recognition. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005. 786-791 [10] Yalavarthi A, Veeraswamy K, Sheela K A. Content based image retrieval using enhanced Gabor wavelet transform. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer, Communications and Electronics. Jaipur, Rajasthan India: IEEE, 2017. 339-343 [11] 宋克臣, 颜云辉, 陈文辉, 张旭. 局部二值模式方法研究与展望. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(6): 730-744 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00730Song Ke-Chen, Yan Yun-Hui, Chen Wen-Hui, Zhang Xu. Research and perspective on local binary pattern. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(6): 730-744 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00730 [12] Liu L, Fieguth P, Guo Y L, Wang X G, Pietikainen M. Local binary features for texture classification: taxonomy and experimental study. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 62: 135-160 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.08.032 [13] Tan X, Triggs B. Enhanced local texture feature sets for face recognition under difficult lighting conditions. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(6): 1635-1650 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2042645 [14] Song T C, Li H L, Meng F M, Wu Q B, Luo B, Zeng B, Gabbouj M. Noise-Robust texture description using local contrast patterns via global measures. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(1): 93-96 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2293335 [15] Liu L, Long Y L, Fieguth P W, Lao S Y, Zhao G Y. BRINT: binary rotation invariant and noise tolerant texture classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(7): 3071-3084 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2325777 [16] Guo Z H, Zhang L, Zhang D. A completed modeling of local binary pattern operator for texture classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(6): 1657-1663 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2044957 [17] Zhao Y, Huang D S, Jia W. Completed local binary count for rotation invariant texture classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(10): 4492-4497 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2204271 [18] Song T C, Li H L, Meng F M, Wu Q B, Cai J F. LETRIST: locally encoded transform feature histogram for rotation-invariant texture classification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(7): 1565-1579 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2671899 [19] Song T C, Li H L, Meng F M, Wu Q B, Luo B. Exploring space-frequency co-occurrences via local quantized patterns for texture representation. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(8): 2621-2632 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.03.003 [20] Nguyen D T, Zong Z M, Ogunbona P, Li W Q. Object detection using non-redundant local binary patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2010. 4609-4612 [21] Jun B, Choi I, Kim D. Local transform features and hybridization for accurate face and human detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(6): 1423-1436 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.219 [22] He Y G, Sang N. Robust illumination invariant texture classification using gradient local binary patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Workshop on Multi-Platform/Multi-Sensor Remote Sensing and Mapping. Xiamen, China: IEEE, 2011. 1-6 [23] Song T C, Xin L L, Gao C Q, Zhang G, Zhang T Q. Grayscale-Inversion and rotation invariant texture description using sorted local gradient pattern. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(5): 625-629 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2809607 [24] Zhang J, Zhao H, Liang J. Continuous rotation invariant local descriptors for texton dictionary-based texture classification. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2013, 117(1): 56-75 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2012.10.004 [25] Freeman W T, Adelson E H. The design and use of steerable filters. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1991, 13(9): 891-906 doi: 10.1109/34.93808 [26] Liao S C, Zhu X X, Lei Z, Zhang L, Li S Z. Learning multi-scale block local binary patterns for face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Biometrics. Seoul, Korea: Springer, 2007. 828-837 [27] Dana K J, Nayar S K, Ginneken B V, Nayar S K, Koenderink J J. Reflectance and texture of real-world surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 1999, 18(1): 1-34 doi: 10.1145/300776.300778 [28] Hayman E, Caputo B, Fritz M, Eklundh J. On the significance of real-world conditions for material classification. In: Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Computer Vision. Prague, Czech Republic: Springer, 2004. 3024: 253-266 [29] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-Invariant Keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110 doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [30] Lazebnik S, Schmid C, Ponce J. Beyond bags of features: spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 2169-2178 -





 下载:
下载: