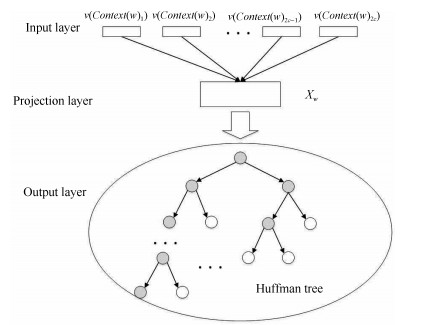
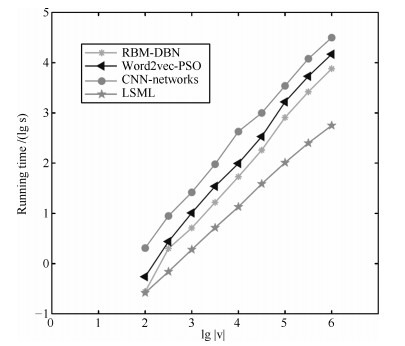
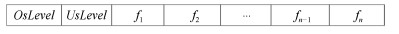-
摘要: 链路预测中普遍存在两大问题:特征提取困难和类别数据不平衡.本文借鉴文本处理中的深度学习特征提取算法和优化问题中的粒子群算法, 提出一种基于词向量的粒子群优化算法(Word2vec-PSO).该方法首先通过随机游走产生网络序列后, 利用Word2vec算法对节点序列特征提取.然后在有监督的条件下, 利用粒子群算法对提取好的特征进行筛选, 并确定重采样的参数来解决类别数据不平衡问题, 并分析了不同链路预测算法的计算复杂性.最后将本文的算法与基于相似性、基于深度学习、基于不平衡数据的3类链路预测算法, 在4个不同的时序网络中进行实证对比研究.结果表明, 本文提出的链路预测算法预测精度较高, 算法更加稳定且具有普适性.Abstract: There are two major problems in the link prediction: The difficulty of feature extraction and the imbalance of class data. In this paper, an algorithm based on word vector is proposed by using the deep learning feature extraction algorithm in text processing and the particle swarm optimization algorithm in the optimization problem. The method firstly generates a set of node sequences through random walks, and uses the Word2vec algorithm to extract node sequence features. Then, under the supervised conditions, the particle swarm algorithm was used to filter the extracted features, and the resampling parameters were determined to solve the imbalance problem of category data. It also analyzes the computational complexity of different link prediction algorithms. Finally, the algorithm of this paper is compared with three link prediction algorithms based on similarity, deep learning, and unbalanced data, and empirically studied in four different time series networks. The results show that the link prediction algorithm proposed in this paper has more accurate prediction accuracy and is more stable and universal.
-
Key words:
- Link prediction /
- feature extraction /
- imbalance problems /
- deep learning /
- particle swarm optimization
-
表 1 本文用到的数据集概况
Table 1 Overview of the data sets used in this article
数据集 网络类型 节点数 边数 Citeseer 著作网络 3 327 4 732 Cora 著作网络 2 708 5 429 Pubmed 著作网络 19 717 44 338 微博关系网络 虚拟社交网络 65 775 266 144 表 2 相似性预测链路算法
Table 2 Similarity link prediction algorithm
链路预测算法 算法公式 算法概述 Common neighbor [3] $S_{ij}=| \Gamma(i)\cap\Gamma(j) | $ 共同邻居节点的个数 Jaccard$'$s coefficient [24] $S_{ij}=\frac{|\Gamma(i)\cap\Gamma(j)|}{|\Gamma(i)\cup\Gamma(j)|} $ 邻居节点集合的交集与邻居节点集合的并集的比值 Adamic Adar [25] $S_{ij}=\sum\limits_{x\in\Gamma(i)\cup\Gamma(j)}\frac{1}{\ln k_x} $ 共同邻居节点度的对数的倒数之和 表 3 复杂网络其他特征提取算法
Table 3 Other feature extraction algorithms for complex networks
链路预测算法 算法公式 算法概述 Likelihood supervised machinelearning [7] Similarityindex+ Classical machine learning 以相似性指标为特征, 利用传统机器学习算法进行训练 RBM-DBN link prediction [8] $F(v)=-\sum\limits_i v_ia_i-\sum\limits_j \ln(1+E^{h_j}) $ 利用受限玻尔兹曼机提取特征, 深度信念网络进行训练 Convolutional networks [9] $Z=f(X, A)=softmax(\hat{A}ReLu(\hat{A}XW^{(0)}))W $ 利用卷积神经网络对网络提取特征, 卷积层后面连接softmax层进行分类 表 4 链路预测其他处理类别不平衡问题算法
Table 4 Link prediction other processing category imbalance problem algorithm
链路预测算法 算法公式 算法概述 AUC-logistic regression [26] $\varphi_{AUC \text{-}Logistic}=\sum\limits_{(i, j, z)\in T}1(x_i^{\rm{T}}Mx_j-x_i^{\rm{T}}Mx_z)$ 对特征矩阵$M$进行逻辑回归训练, 目标函数是AUC值 Rank-SVM [27] $\varphi_{SVM}=\sum\limits_{(i, j, z)\in T}\max(0, 1+x_i^{\rm{T}}Mx_z-x_i^{\rm{T}}Mx_j)$ 利用支持向量机学习节点连接概率的大小排序 Entropy algorithm [28] $\min\limits_M L(M)=\lambda\Omega(M)+\sum\limits_{q\in V}\varphi(S^R(M), R^q) $ 利用交叉熵算法, 使得网络全局交叉熵损失最小化, 处理类别不平衡节点对 表 5 本算法与其他链路预测算法结果对比
Table 5 Comparison of the algorithm with other link prediction algorithms
链路预测算法 Citeseer Cora Pubmed Weibo AUC $P$ AUC $P$ AUC $P$ AUC $P$ Common neighbor 0.567 0.632 0.616 0.696 0.561 0.669 0.542 0.615 Jaccard's 0.568 0.651 0.616 0.694 0.564 0.668 0.540 0.618 Adamic Adar 0.675 0.690 0.679 0.711 0.584 0.702 0.559 0.621 Common neighbor 0.656 0.759 0.715 0.784 0.827 0.853 0.687 0.741 Jaccard's 0.673 0.753 0.524 0.612 0.643 0.781 0.664 0.727 Adamic Adar 0.789 0.731 0.744 0.829 0.687 0.778 0.765 0.854 Common neighbor 0.752 0.857 0.711 0.773 0.781 0.829 0.545 0.628 Jaccard's 0.861 0.934 0.689 0.746 0.718 0.805 0.712 0.802 Adamic Adar 0.762 0.860 0.797 0.805 0.810 0.865 0.786 0.851 Word2vec-PSO 0.818 0.872 0.801 0.823 0.867 0.913 0.833 0.875 -
[1] Fayyad U. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter. New York: ACM, 2002 [2] Albert R, Barabási A L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Review of Modern Physics, 2002, 74 (1): 47 [3] Liben-Nowell D, Kleinberg J. The link prediction problem for social networks. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. New Orleans, LA, USA: ACM, 2003. 556-559 [4] Zhou T, Lv L Y, Zhang Y C. Predicting missing links via local information. The European Physical Journal B, 2009, 71(4): 623-630 doi: 10.1140/epjb/e2009-00335-8 [5] Keck F, Bouchez A, Franc A, Rimet F. Linking phylogenetic similarity and pollution sensitivity to develop ecological assessment methods: A test with river diatoms. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 53(3): 856-864 doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.12624 [6] Benchettara N, Kanawati R, Rouveirol C. Supervised machine learning applied to link prediction in bipartite social networks. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining. Odense, Denmark: IEEE, 2010. 326-330 [7] Popescul R, Ungar L H. Statistical relational learning for link prediction. In: Proceedings of the 2003 Workshop on Learning Statistical Models from Relational Data. IJCAI, 2003. [8] Liu F, Liu B Q, Sun C J, Liu M, Wang X L. Deep learning approaches for link prediction in social network services. International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. 425-432 [9] Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18 (7): 1527-1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [10] Kipf T N, Welling M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv: 1609.02907, 2016 [11] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014 [12] Lowrance C J, Lauf A P, Kantardzic M. A fuzzy-based machine learning model for robot prediction of link quality. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence. Athens, Greece: IEEE, 2017. 1-8 [13] Perozzi B, Al-Rfou R, Skiena S. Deepwalk: Online learning of social representations. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York, USA: ACM, 2014: 701-710 [14] Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv: 1301.3781, 2013 [15] Hochreiter S, and Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 1997(9): 1735-1780 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=90ef9e6cc88d24a0a6ea3a10a47b9214&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [16] Barabási A L, Albert R, Jeong H. Scale-free characteristics of random networks: The topology of the world-wide web. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2000, 281(1-4): 69-77 doi: 10.1016/S0378-4371(00)00018-2 [17] Vermeulen T, Huffman E H. Ion exchange column performance – hydrogen cycle rates in nonaqueous solvents. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1953, 45(8): 1658-1664 doi: 10.1021/ie50524a024 [18] Chawla N V, Bowyer K W, Hall L O, Kegelmeyer W P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16: 321-357 doi: 10.1613/jair.953 [19] Kennedy J, Eberhart R. Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Perth, WA, Australia: IEEE, 2002. 1942-1948 [20] Golicher D, Ford A, Cayuela L, Newton A. Pseudo-absences, pseudo-models and pseudo-niches: Pitfalls of model selection based on the area under the curve. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2012, 26(11): 2049-2063 doi: 10.1080/13658816.2012.719626 [21] Fiala D. Mining citation information from CiteSeer data. Scientometrics, 2011, 86(3): 553-562 doi: 10.1007/s11192-010-0326-1 [22] Lunin V V, Dobrovetsky E, Khutoreskaya G, Zhang R G, Joachimiak A, Doyle D A, et al. Crystal structure of the CorA Mg$^{2+}$ transporter. Nature, 2006, 440(7085): 833-837 doi: 10.1038/nature04642 [23] Falk E, Shah P K, Fuster V. Coronary plaque disruption. Circulation, 1995, 92(3): 657-671 doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.92.3.657 [24] Jaccard P. Etude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et des Jura. Bulletin del la Societe Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles, 1901, 37(142): 547-579 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=673152eb1f4946650883c42963fac7cf&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [25] Adamic L A, Adar E. Friends and neighbors on the Web. Social Networks, 2003, 25 (3): 211-230 doi: 10.1016/S0378-8733(03)00009-1 [26] Menon A K, Elkan C. Link prediction via matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the 2011 European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2011. 437-452 [27] Yazdani M, Collobert R, Popescubelis A. Learning to rank on network data. International Journal of Information Management, 2013, 6(3): 187-188 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f734e58e43982e03885f90a0f592d20f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [28] Li B P, Chaudhuri S, Tewari A. Handling class imbalance in link prediction using learning to rank techniques. arXiv: 1511.04383, 2016 -




 下载:
下载: