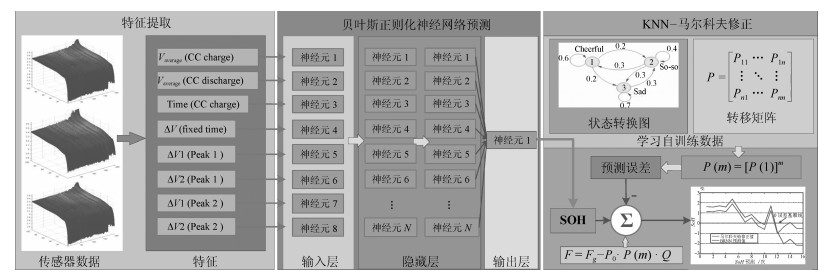
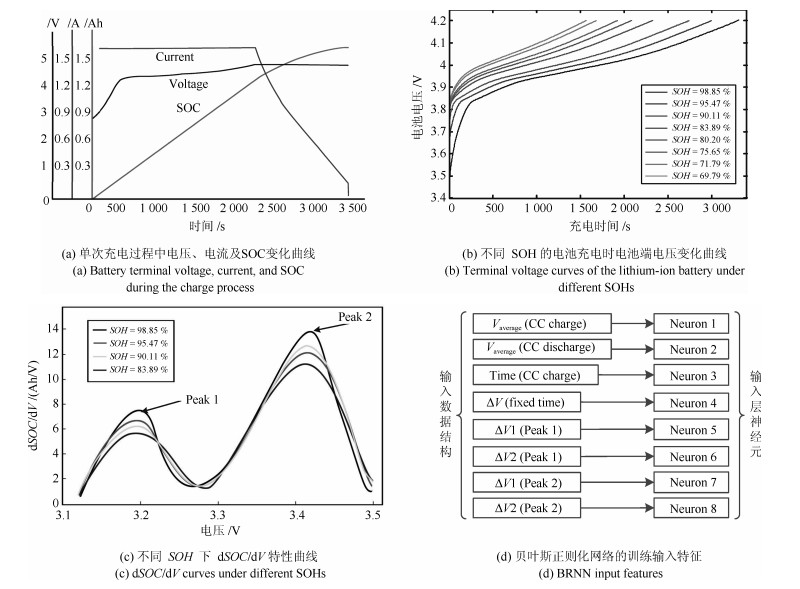
A Modified Strategy Using the KNN-Markov Chain for SOH Estimation of Lithium Batteries
-
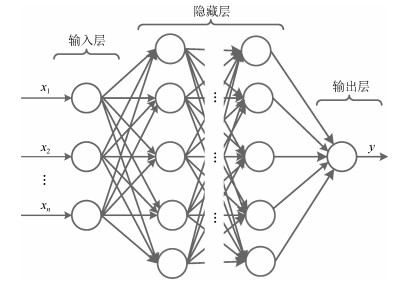
摘要: 锂离子电池的健康状态(State of health, SOH)是决定电池使用寿命的关键因素.由于锂电池生产工艺、工作环境和使用习惯等的差异性导致其衰退特性具有较大差异, 因此锂电池SOH难以精确估算.本文采用数据驱动的方式通过对采集的电压数据进行特征提取, 使用贝叶斯正则化神经网络对锂电池SOH进行预测, 同时引入KNN-马尔科夫修正策略对预测结果进行修正.实验结果证明, 贝叶斯正则化算法对锂电池SOH的预测准确度较高, KNN-马尔科夫修正策略提高了预测的精确度和鲁棒性, 组合预测模型对锂电池SOH的平均预测误差小于$1\,\%$, 与采用数据分组处理方法(Group method of data handling, GMDH)、概率神经网络(Probabilistic neural network, PNN)、循环神经网络(Recurrent neural network, RNN)的预测精度进行对比, 该模型的预测精度分别提高了$33.3\,\%$、$48.7\,\%$和$53.1\,\%$.Abstract: The state of health (SOH) of lithium batteries is a critical factor in determining the battery's end-of-service-life. The differences of the Lithium-ion battery's production process, work environment, and use habit etc. lead to the massive differences of the battery's fade characteristics, which, in turn, inaccurate estimation of their battery's SOH. In this paper, the data-driven method was employed for experimental feature extraction. Besides, this paper presents an SOH estimation method based on the Bayesian-regularization neural network and the KNN-Markov chain used for amending the prediction results. Experimental results show that the Bayesian-regularization neural network applied to the SOH estimation could obtain superior accuracy performance, and by combining the KNN-Markov chain, the prediction accuracy (the average prediction error of SOH less than 1 %) could be improved. On the whole, the combined model shows good robustness. Compared with the group method of data handling (GMDH), probabilistic neural network (PNN) and recurrent neural network (RNN), the prediction accuracy of the model was improved by 33.3 %, 48.7 % and 53.1 % respectively.
-
Key words:
- Lithium battery SOH /
- feature extraction /
- multilayer feedforward neural network /
- Bayesian regularization /
- Markov chain
1) 本文责任编委 曹向辉 -
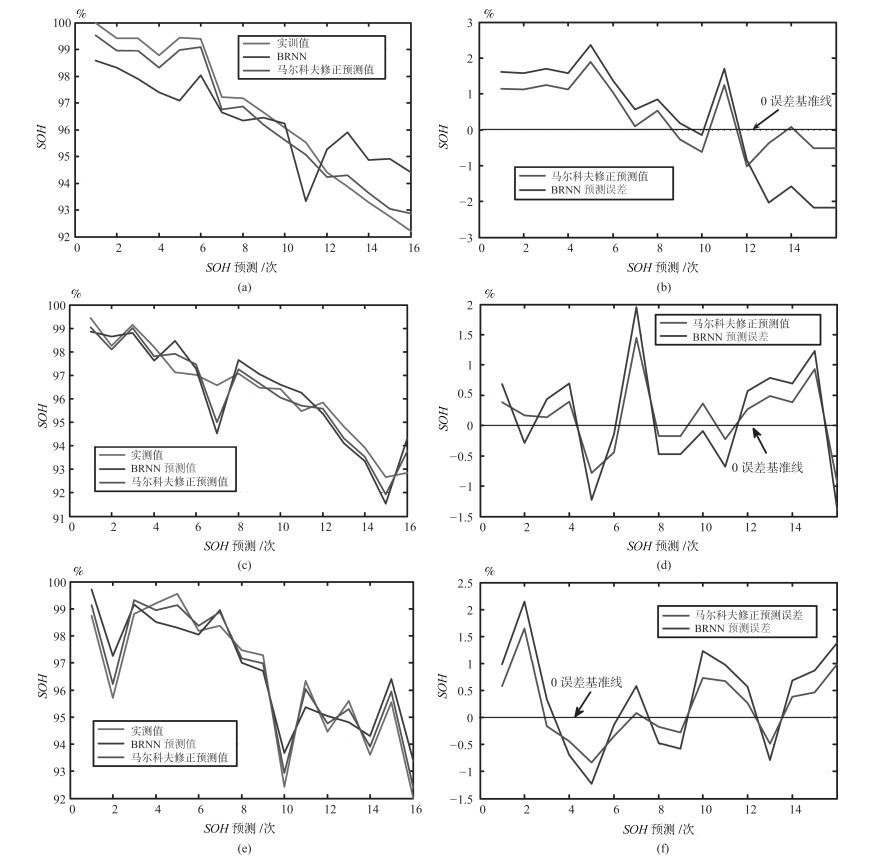
表 1 BRNN预测值相对误差及状态划分
Table 1 BRNN prediction error and state division
序号 实测值 预测值 相对误差(%) 归一化相对误差(%) 状态 1 0.6445 0.6431 -0.2172 0.4569 2 2 0.7480 0.7253 -3.0347 0.1425 1 3 0.9665 0.9646 -0.1965 0.4496 2 4 0.9502 0.9508 0.0631 0.4865 3 5 0.5802 0.5695 -1.8442 0.3194 1 6 0.7556 0.7344 -2.8057 0.1647 1 7 0.9294 0.9301 0.0753 0.4879 3 8 0.9222 0.9440 2.3639 0.7994 3 9 0.6808 0.6927 1.7479 0.6533 1 10 0.8615 0.8503 -1.3001 0.3123 1 11 0.7556 0.7619 0.8338 0.5706 3 12 0.6445 0.6431 -0.2172 0.4569 2 表 2 BRNN预测误差及马尔科夫修正误差
Table 2 BRNN prediction and Markov correction error
序号 实测值 预测值 修正前误差(%) 修正后误差(%) 1 1.0000 0.9809 1.9090 1.4446 2 0.9942 0.9753 1.8847 1.4203 3 0.9941 0.9741 2.0029 1.5385 4 0.9878 0.9720 1.5855 1.1211 5 0.9665 0.9646 0.1857 -0.2787 6 0.9607 0.9623 -0.1558 -0.6202 7 0.9554 0.9333 2.2035 1.7391 8 0.9387 0.9590 -2.0253 -0.3699 9 0.9329 0.9486 -1.5736 0.0818 10 0.9222 0.9440 -2.1778 -0.5224 表 3 KNN-马尔科夫修正结果
Table 3 KNN-Markov correction results
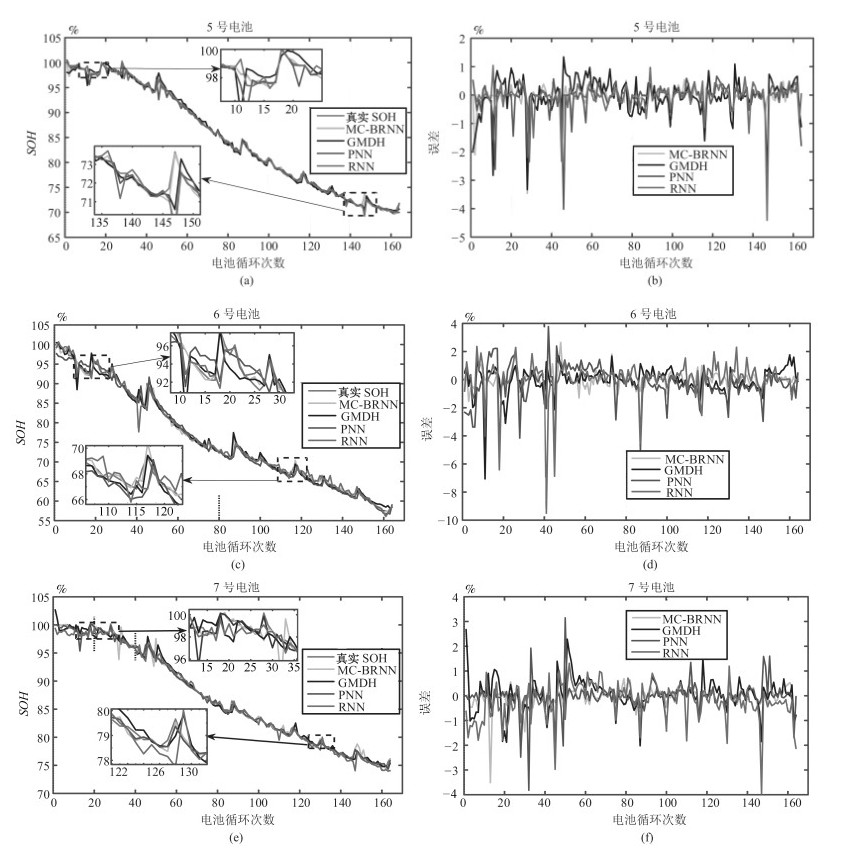
编号 $5\#$电池 $6\#$电池 $7\#$电池 有无修正 无 有 无 有 无 有 MAE (%) 0.47 0.35 0.52 0.43 0.44 0.37 MSE (%$^2$) 0.49 0.37 0.52 0.40 0.48 0.37 表 4 各算法准确度对比
Table 4 Comparison of accuracy of each algorithm
编号 $5\#$电池 $6\#$电池 $7\#$电池 算法 MC-BRNN GMDH PNN RNN MC-BRNN GMDH PNN RNN MC-BRNN GMDH PNN RNN MAE ($\%$) 0.35 0.52 0.64 0.67 0.43 0.61 0.81 0.93 0.37 0.59 0.79 0.83 MSE ($\%^2$) 0.37 0.67 0.94 1.21 0.40 0.88 1.30 2.35 0.37 0.58 1.57 1.95 表 5 各算法的时间复杂度对比(s)
Table 5 Comparison of time complexity of each algorithm (s)
算法 MC-BRNN GMDH PNN RNN 5号电池 1.5101 1.1184 0.2994 4.5942 6号电池 1.4361 1.1948 0.2442 3.7446 7号电池 1.5559 1.1103 0.2748 4.8092 平均值 1.5007 1.1399 0.2726 4.3826 -
[1] Cheng K W E, Divakar B P, Wu H J, Ding K, Ho H F. Battery-management system (BMS) and SOC development for electrical vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2011, 60(1): 76-88 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2010.2089647 [2] 陈虹, 宫洵, 胡云峰, 刘奇芳, 高炳钊, 郭洪艳.汽车控制的研究现状与展望.自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 322-346 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00322Chen Hong, Gong Xun, Hu Yun-Feng, Liu Qi-Fang, Gao Bing-Zhao, Guo Hong-Yan. Automotive control: The state of the art and perspective. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 322-346 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00322 [3] Scrosati B, Garche J. Lithium batteries: Status, prospects and future. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(9): 2419-2430 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.11.048 [4] Andre D, Appel C, Soczka-Guth T, Sauer D U. Advanced mathematical methods of SOC and SOH estimation for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 224: 20-27 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.10.001 [5] Galeotti M, Ciná L, Giammanco C, Cordiner S, Carlo D A. Performance analysis and SOH (state of health) evaluation of lithium polymer batteries through electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Energy, 2015, 89: 678-686 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2015.05.148 [6] Chen Z, Mi C C, Fu Y H, Xu J, Gong X Z. Online battery state of health estimation based on genetic algorithm for electric and hybrid vehicle applications. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 240: 184-192 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.03.158 [7] Mejdoubi A E, Oukaour A, Chaoui H, Gualous H, Sabor J, Slamani Y. State-of-charge and state-of-health lithium-ion batteries' diagnosis according to surface temperature variation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(4): 2391-2402 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2509916 [8] Liu D T, Pang J Y, Zhou J B, Peng Y, Pecht M. Prognostics for state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on combination Gaussian process functional regression. Microelectronics Reliability, 2013, 53(6): 832-839 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2013.03.010 [9] Moura S J, Chaturvedi N A, Krstić M. Adaptive partial differential equation observer for battery state-of-charge/state-of-health estimation via an electrochemical model. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2014, 136(1): 011015 doi: 10.1115/1.4024801 [10] Ng K S, Moo C S, Chen Y P, Hsieh Y C. Enhanced coulomb counting method for estimating state-of-charge and state-of-health of lithium-ion batteries. Applied Energy, 2009, 86(9): 1506-1511 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2008.11.021 [11] Lievre A, Sari A, Venet P, Hijazi A, Ouattara-Brigaudet M, Pelissier S. Practical online estimation of lithium-ion battery apparent series resistance for mild hybrid vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(6): 4505-4511 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2446333 [12] Plett G L. Extended Kalman filtering for battery management systems of LiPB-based HEV battery packs: Part 1. Background. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 134(2): 252-261 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.02.031 [13] Wu J, Wang Y J, Zhang X, Chen Z H. A novel state of health estimation method of Li-ion battery using group method of data handling. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 327: 457-464 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.07.065 [14] Wu J, Zhang C B, Chen Z H. An online method for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation using importance sampling and neural networks. Applied Energy, 2016, 173: 134-140 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.057 [15] Klass V, Behm M, Lindbergh G. A support vector machine-based state-of-health estimation method for lithium-ion batteries under electric vehicle operation. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 270: 262-272 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.07.116 [16] Eddahech A, Briat O, Bertrand N, Delétage J Y, Vinassa J M. Behavior and state-of-health monitoring of Li-ion batteries using impedance spectroscopy and recurrent neural networks. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2012, 42(1): 487-494 [17] Lin H T, Liang T J, Chen S M. Estimation of battery state of health using probabilistic neural network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(2): 679-685 doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2222650 [18] Basheer I A, Hajmeer M. Artificial neural networks: fundamentals, computing, design, and application. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2000, 43(1): 3-31 doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00201-3 [19] Lam C H, Shin F G. Formation and dynamics of modules in a dual-tasking multilayer feed-forward neural network. Physical Review E, 1998, 58(3): 3673-3677 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.58.3673 [20] Sun Z, Chen Y, Li X Y, Qin X L, Wang H Y. A Bayesian regularized artificial neural network for adaptive optics forecasting. Optics Communications, 2017, 382: 519-527 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.08.035 [21] 杨海深, 傅红卓.基于贝叶斯正则化BP神经网络的股票指数预测.科学技术与工程, 2009, 9(12): 3306-3310, 3318 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2009.12.029Yang Hai-Shen, Fu Hong-Zhuo. Stock index forecast based on Bayesian regularization BP neural network. Science Technology and Engineering, 2009, 9(12): 3306-3310, 3318 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2009.12.029 [22] 李红霞, 许士国, 范垂仁.基于贝叶斯正则化神经网络的径流长期预报.大连理工大学学报, 2006, 46(S1): 174-177 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLLG2006S1029.htmLi Hong-Xia, Xu Shi-Guo, Fan Chui-Ren. Long-term prediction of runoff based on Bayesian regulation neural network. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2006, 46(S1): 174-177 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLLG2006S1029.htm [23] Neal R M. Markov chain sampling methods for dirichlet process mixture models. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2000, 9(2): 249-265 [24] 李新德, 董清泉, 王丰羽, 雒超民.一种基于马尔科夫链的冲突证据组合方法.自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 914-927 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140681Li Xin-De, Dong Qing-Quan, Wang Feng-Yu, Luo Chao-Min. A method of conflictive evidence combination based on the Markov chain. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5): 914-927 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140681 [25] NASA. PCoE datasets: battery data set[Online], available: https://ti.arc.nasa.gov/tech/dash/groups/pcoe/prognostic-data-repository/, August 22, 2017. [26] 陈峭岩, 魏克新.电动汽车电池SOH的信号统计分析.电源技术, 2016, 40(2): 342-344 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2016.02.032Chen Qiao-Yan, Wei Ke-Xin. Signal Statistic analysis for electric vehicle battery SOH. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 40(2): 342-344 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2016.02.032 [27] Weng C H, Feng X N, Sun J, Peng H. State-of-health monitoring of lithium-ion battery modules and packs via incremental capacity peak tracking. Applied Energy, 2016, 180: 360-368 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.07.126 [28] 叶涛, 朱学峰, 李向阳, 史步海.基于改进$ k$-最近邻回归算法的软测量建模.自动化学报, 2007, 33(9): 996-999 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO200709021.htmYe Tao, Zhu Xue-Feng, Li Xiang-Yang, Shi Bu-Hai. Soft sensor modeling based on a modified k-nearest neighbor regression algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2007, 33(9): 996-999 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO200709021.htm [29] 薛鹏松, 冯民权, 邢肖鹏.基于马尔科夫链改进灰色神经网络的水质预测模型.武汉大学学报(工学版), 2012, 45(3): 319-324 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD201203010.htmXue Peng-Song, Feng Min-Quan, Xing Xiao-Peng. Water quality prediction model based on Markov chain improving gray neural network. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2012, 45(3): 319-324 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD201203010.htm -




 下载:
下载: