Video-EEG Based Collaborative Emotion Recognition Using LSTM and Information-Attention
-
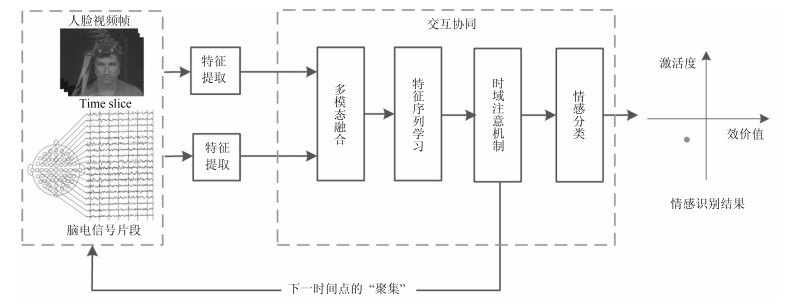
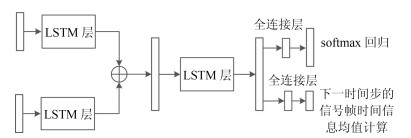
摘要: 基于视频-脑电信号交互协同的情感识别是人机交互重要而具有挑战性的研究问题.本文提出了基于长短记忆神经网络(Long-short term memory, LSTM)和注意机制(Attention mechanism)的视频-脑电信号交互协同的情感识别模型.模型的输入是实验参与人员观看情感诱导视频时采集到的人脸视频与脑电信号, 输出是实验参与人员的情感识别结果.该模型在每一个时间点上同时提取基于卷积神经网络(Convolution neural network, CNN)的人脸视频特征与对应的脑电信号特征, 通过LSTM进行融合并预测下一个时间点上的关键情感信号帧, 直至最后一个时间点上计算出情感识别结果.在这一过程中, 该模型通过空域频带注意机制计算脑电信号${\alpha}$波, ${\beta}$波与${\theta}$波的重要度, 从而更加有效地利用脑电信号的空域关键信息; 通过时域注意机制, 预测下一时间点上的关键信号帧, 从而更加有效地利用情感数据的时域关键信息.本文在MAHNOB-HCI和DEAP两个典型数据集上测试了所提出的方法和模型, 取得了良好的识别效果.实验结果表明本文的工作为视频-脑电信号交互协同的情感识别问题提供了一种有效的解决方法.Abstract: Video-EEG based collaborative emotion recognition is an important yet challenging problem in research of human-computer interaction. In this paper, we propose a novel model for video-EEG based collaborative emotion recognition by virtue of long-short term memory neural network (LSTM) and attention mechanism. The inputs of this model are the facial videos and EEG signals collected from a participant who is watching video clips for emotional inducement. The output is the participant's emotion states. At each time step, the model employs convolution neural network (CNN) to extract features from video frames and corresponding EEG slices. Then it employs LSTM to iteratively fuse the multi-modal features and predict the next key-emotion frame until it yields the emotion state at the last time step. Within the process, the model computes the importance of different frequency-band EEG signals, i.e. ${\alpha}$ wave, ${\beta}$ wave, and ${\theta}$ wave, through spatial band attention, in order to effectively use the key information of EEG signals. With the temporal attention, it predicts the next key emotion frame in order to take advantage of the temporal key information of emotional data. Experiments on MAHNOB-HCI dataset and DEAP dataset show encouraging results and demonstrate the strength of our model. The results show that the proposed method presents a different perspective for effective collaborative emotion recognition.
-
Key words:
- Emotion recognition /
- long-short term memory neural network (LSTM) /
- temporal-spatial attention /
- multi-modal fusion
1) 本文责任编委 张道强 -
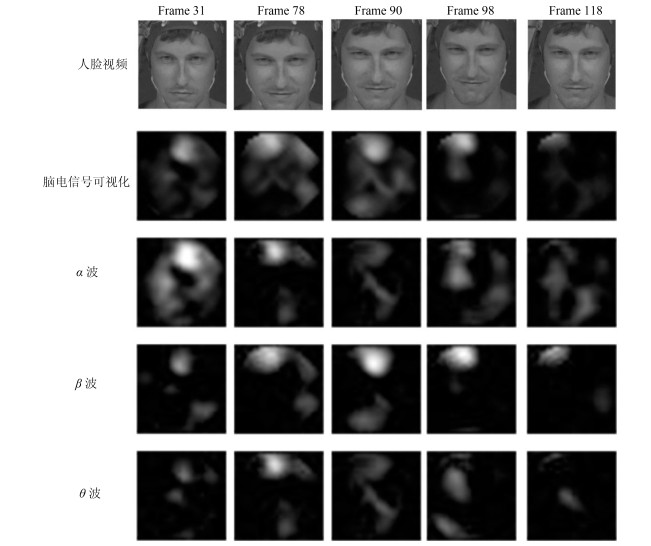
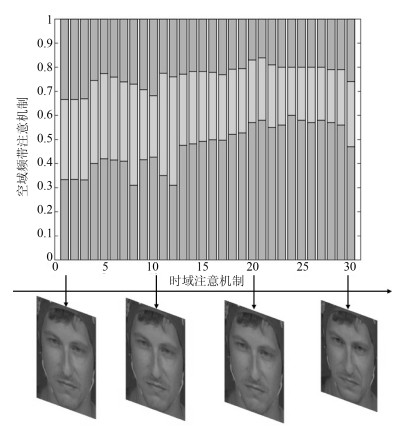
图 5 人脑电信号可视化示意图(从上到下:人脸视频帧; 对应的脑电信号可视化图; ${\alpha}$波可视化图; ${\beta}$波可视化图; ${\theta}$波可视化图.从左到右:情感信号第31帧; 第78帧; 第90帧; 第98帧; 第118帧)
Fig. 5 The visualization of EEG signals (From top to down: video frames; the visualization of corresponding EEG signals; the visualization of ${\alpha}$ wave; the visualization of ${\beta}$ wave; the visualization of ${\theta}$ wave. From left to right: the 31st frame; the 78th frame; the 90th frame; the 98th frame; the 118th frame in the emotion data)
图 7 本文模型在MANNOB-HCI数据集上的可视化识别结果(从上到下分别为三组情感数据中的人脸视频.从左到右分别为情感数据; Groundtruth与本文模型的识别结果)
Fig. 7 The visualization of results of the proposed model on MAHNOB-HCI dataset (From up to down: three groups of emotion data. From left to right: emotion data; the groundtruth and results of the proposed model)
表 1 激活度和效价值的三分类
Table 1 Valence and arousal class with range
激活度 效价值 Low 1~4.5 1~4.5 Medium 4.5~5.5 4.5~5.5 High 5.5~9 5.5~9 表 2 不同方法在MAHNOB-HCI数据集与DEAP数据集上的识别效果
Table 2 The recognition result of different methods on MAHNOB-HCI dataset and DEAP dataset
激活度 效价值 CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ Baseline[15](MAHNOB-HCI) 67.7 0.620 ${\bf{76.1}}$ ${\bf{0.740}}$ Koelstra et al.[10] (MAHNOB-HCI) 72.5 0.709 73.0 0.718 Huang et al.[11] (MAHNOB-HCI) 63.2 66.3 VGG-16+本文模型(MAHNOB-HCI) ${\bf{73.1}}$ ${\bf{0.723}}$ 74.5 0.730 VGG-16+本文模型(DEAP) ${\bf{85.8}}$ ${\bf{84.3}}$ 表 3 本文提出的情感识别模型的识别准确率和F1-${score}$(MAHNOB-HCI数据集)
Table 3 The classification rate and F1-${score}$ of ablation studies on MAHNOB-HCI dataset
激活度 效价值 CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ w/o band and temp 66.4 0.650 68.9 0.678 w/o band 70.9 0.690 73.0 0.711 w/o temporal 69.7 0.680 70.4 0.695 vis-EEG-LSTM ${\bf{73.1}}$ ${\bf{0.723}}$ ${\bf{74.5}}$ ${\bf{0.730}}$ 表 4 本文提出的情感识别模型的识别准确率和F1-${score}$ (DEAP数据集)
Table 4 The classification rate and F1-${score}$ of ablation studies on DEAP dataset
激活度 效价值 CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ w/o band and temp 79.1 0.774 78.5 0.770 w/o band 83.1 0.816 82.5 0.809 w/o temporal 78.1 0.754 81.4 0.805 vis-EEG-LSTM ${\bf{85.8}}$ ${\bf{0.837}}$ ${\bf{84.3}}$ ${\bf{0.831}}$ 表 5 两种单模态情感识别与多模态情感识别的识别准确率和F1-${score}$ (MAHNOB-HCI数据集)
Table 5 The classification rate and F1-${score}$ of uni-modal and bi-modal emotion recognition on MAHNOB-HCI dataset
激活度 效价值 CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ 人脸视频 70.8 0.691 72.9 0.711 脑电信号 69.9 0.673 73.3 0.720 人脸视频+脑电信号 ${\bf{73.1}}$ ${\bf{0.723}}$ ${\bf{74.5}}$ ${\bf{0.730}}$ 表 6 两种单模态情感识别与多模态情感识别的识别准确率和F1-${score}$(DEAP数据集)
Table 6 The classification rate and F1-${score}$ of uni-modal and bi-modal emotion recognition on DEAP dataset
激活度 效价值 CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ CR ($\%$) F1-${score}$ 人脸视频 67.1 0.653 66.3 0.650 脑电信号 84.7 0.815 83.4 0.819 人脸视频+脑电信号 ${\bf{85.8}}$ ${\bf{0.837}}$ ${\bf{84.3}}$ ${\bf{0.831}}$ -
[1] Bynion T M, Feldner M T. Self-Assessment Manikin. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2017. 1-3 [2] Lin J C, Wu C H, Wei W L. Error weighted semi-coupled hidden Markov model for audio-visual emotion recognition. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2012, 14(1): 142-156 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=267b730d55360c483c4723906b231f35 [3] Jiang D, Cui Y, Zhang X, Fan P, Ganzale I, Sahli H. Audio visual emotion recognition based on triple-stream dynamic bayesian network models. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction. Berlin, GER: Springer-Verlag, 2011. 609-618 [4] Xie Z, Guan L. Multimodal information fusion of audio emotion recognition based on kernel entropy component analysis. International Journal of Semantic Computing, 2013, 7(1): 25-42 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1142_S1793351X13400023 [5] Khorrami P, Le Paine T, Brady K. How deep neural networks can improve emotion recognition on video data. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. New York, USA: IEEE, 2016. 619-623 [6] Liu J, Su, Y, Liu, Y. Multi-modal emotion recognition with temporal-band attention based on lstm-rnn. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia. Berlin, GER: Springer, 2017. 194-204 [7] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2012. 1097-1105 [8] Sak H, Senior A, Beaufays F. Long short-term memory based recurrent neural network architectures for large vocabulary speech recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1402.1128, 2014. [9] He L, Jiang D, Yang L, Pei E, Wu P, Sahli H. Multimodal affective dimension prediction using deep bidirectional long short-term memory recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Workshop on Audio/visual Emotion Challenge. New York, USA: ACM, 2015. 73-80 [10] Koelstra S, Patras I. Fusion of facial expressions and EEG for implicit affective tagging. Image and Vision Computing, 2013, 31(2): 164-174 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=04f03f0fd646221b3872240005017d1c [11] Huang X, Kortelainen J, Zhao G, Li X, Moilanen A, Seppanen T, Pietikainen M. Multi-modal emotion analysis from facial expressions and electroencephalogram. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2016, 147: 114-124 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c0dd5236bcdae70bcbb065ddb2279f4a [12] Zhalehpour S, Akhtar Z, Erdem C E. Multimodal emotion recognition with automatic peak frame selection. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications. New York, USA: IEEE, 2014. 116-121 [13] Xu K, Ba J L, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhutdinov R, Zemel R S, Bengio Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, 2015. 2048-2057 [14] 刘畅, 刘勤让.使用增强学习训练多焦点聚焦模型.自动化学报, 2017, 43(9): 1563-1570 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160643Liu Chang, Liu Qin-Rang. Using reinforce learning to train multi attention model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(9): 1563-1570 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160643 [15] Soleymani M, Lichtenauer J, Pun T, Pantic M. A multi-modal affective database for affect recognition and implicit tagging. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 42-55 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2197062 [16] Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2015. 91-99 [17] Mowla M R, Ng S C, Zilany M S A, Paramesran R. Artifacts-matched blind source separation and wavelet transform for multichannel EEG denoising. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2015, 22(3): 111-118 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=facdf66f1c48f19f20fba5c0f305d929 [18] Bashivan P, Rish I, Yeasin M, Codella N. Learning representations from EEG with deep recurrent-convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Learning Representation. San Juan, Puerto Rico: ICLR, 2016. [19] Anzai Y. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Elsevier, 2012. [20] Lei T, Barzilay R, Jaakkola T. Rationalizing neural predictions. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. British Columbia, Canada: ACL, 2016. 107-117 [21] Yu A W, Lee H, Le Q V. Learning to skim text. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.06877, 2017. [22] Rubinstein R Y, Kroese D P. Simulation and the Monte Carlo Method. John Wiley & Sons, 2008. 167-168 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=539488 [23] Koelstra S, Muhl C, Soleymani M, Lee S, Yazdani A, Ebrahimi T, Pun T, Nijholt A, Patras I. Deap: A database for emotion analysis using physiological signals. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 18-31 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5871728/ [24] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980, 2014. [25] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: