Industrial Process Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis Based on Hybrid Discriminant Analysis
-
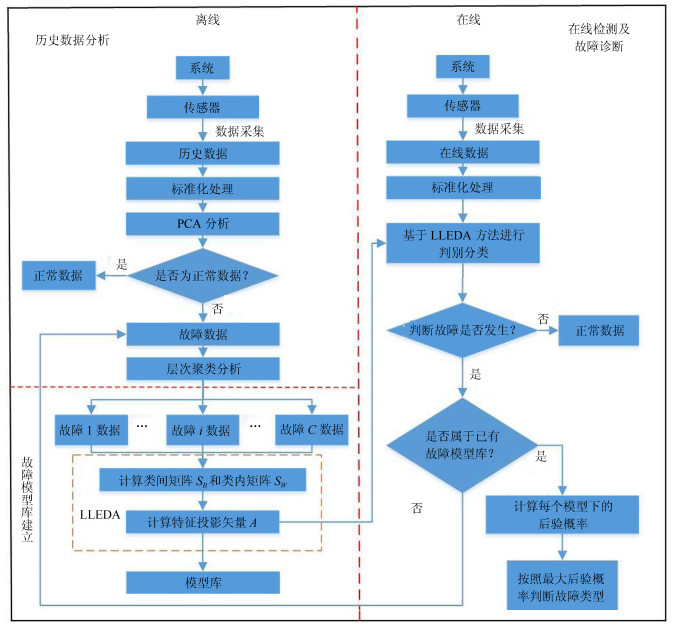
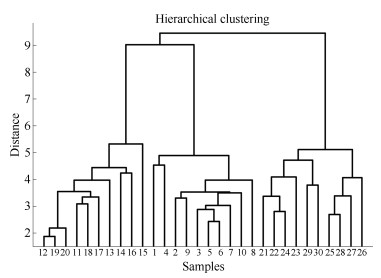
摘要: 工业过程数据具有规模性大、复杂性高、变量多、关联性强等特点.如何从数据出发准确并快速地发现故障并处理, 保证过程高效运行意义重大.本文针对复杂的工业过程, 提出了一种多方法结合的混合型过程监控与故障诊断方法, 完成数据分类, 构建故障模型库, 故障在线诊断及可视化相关处理.首先通过常规主成分分析(Principal component analysis, PCA)方法对历史数据进行初筛, 区分出正常和故障信息, 然后利用聚类方法对故障数据集进行分类, 接着利用局部线性指数判别分析方法(Local linear exponential discriminant analysis, LLEDA)建立故障模型库进而进行故障诊断.本文将基于监督学习的LLEDA方法拓展到无监督学习, 便于复杂工业大量无标签数据的处理.最后利用典型的田纳西伊士曼(Tennessee Eastman, TE)过程对所提出的方法进行有效性验证.
-
关键词:
- 复杂工业过程 /
- 混合型故障诊断 /
- 局部线性指数判别分析 /
- 可视化
Abstract: Industrial process data has the characteristics of large scale, high complexity, multivariable and strong correlation. There is great signiflcance on how to flnd out and deal with the fault from data accurately and quickly, which can help ensure the e–cient operation of the process. The paper proposed a hybrid multi-method process monitoring and fault diagnosis framework for the complex industrial process. The framework include the data classiflcation, model library establishment, timely diagnosis. Firstly, the historical data is simply screened by principal component analysis (PCA) methods to distinguish normal and fault information. Then the clustering method is used to classify the fault data set, and the fault model libraries are established by local linear exponential discriminant analysis (LLEDA) method. Finally, the fault diagnosis is carried out. The LLEDA method based on supervised learning is extended to unsupervised learning, which facilitates the processing of a large number of unlabeled data in complex industries. Finally, a typical Tennessee Eastman process is used to verify the efiectiveness of the proposed method.-
Key words:
- Industrial process /
- hybrid fault diagnosis /
- local linear exponential discriminant analysis (LLEDA) /
- visualization
1) 本文责任编委 穆朝絮 -
表 1 TE故障汇总
Table 1 TE fault summary
编号 描述 类型 IDV (0) 正常操作 - IDV (1) A/C进料比率, B成分不变 阶跃 IDV (2) B成分, A/C进料比不变 阶跃 IDV (3) D的进口温度 阶跃 IDV (4) 反应器冷却水的入口温度 阶跃 IDV (5) 冷凝器冷却水的入口温度 阶跃 IDV (6) A进料损失 阶跃 IDV (7) C存在压力损失-可用性降低 阶跃 IDV (8) A、B、C进料成分 随机变量 IDV (9) D的进料温度 随机变量 IDV (10) C的进料温度 随机变量 IDV (11) 反应器冷却水的入口温度 随机变量 IDV (12) 冷凝器冷却水的入口温度 随机变量 IDV (13) 反应动态 慢漂移 IDV (14) 反应器冷却水阀门 粘住 IDV (15) 冷凝器冷却水阀门 粘住 IDV (16) 未知 未知 IDV (17) 未知 未知 IDV (18) 未知 未知 IDV (19) 未知 未知 IDV (20) 未知 未知 IDV (21) 阀固定在稳态位置 未知的恒定位置 表 2 基于PCA方法的故障识别率
Table 2 Fault recognition rate based on PCA method
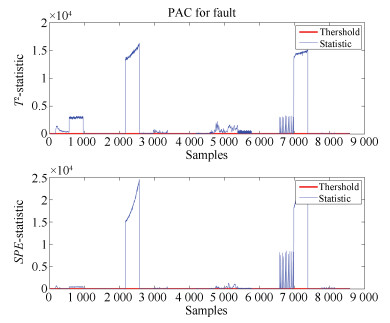
故障识别率 故障1 故障2 故障3 故障4 故障5 故障6 故障7 故障8 故障9 故障10 故障11 故障12 故障13 故障14 故障15 故障16 故障17 故障18 故障19 故障20 故障21 T2 0.5212 0.995 0.9825 0.0225 0.41 0.2625 0.99 1 0.975 0.0362 0.4163 0.9875 0.9513 0.9988 0.0488 0.2325 0.8013 0.8912 0.0675 0.3738 0.3775 SPE 0.8163 0.9988 0.9925 0.2675 1 0.5025 1 1 0.9825 0.235 0.7638 0.99 0.9625 1 0.2625 0.6937 0.975 0.9375 0.5913 0.735 0.6687 表 3 不同方法下故障4, 8和13的识别率
Table 3 Recognition rate of fault 4, 8 and 13 under different methods
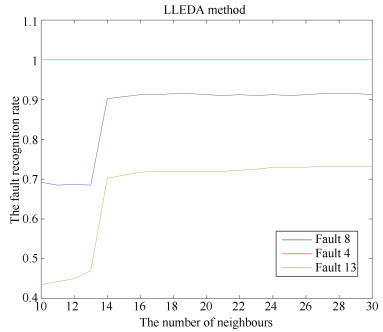
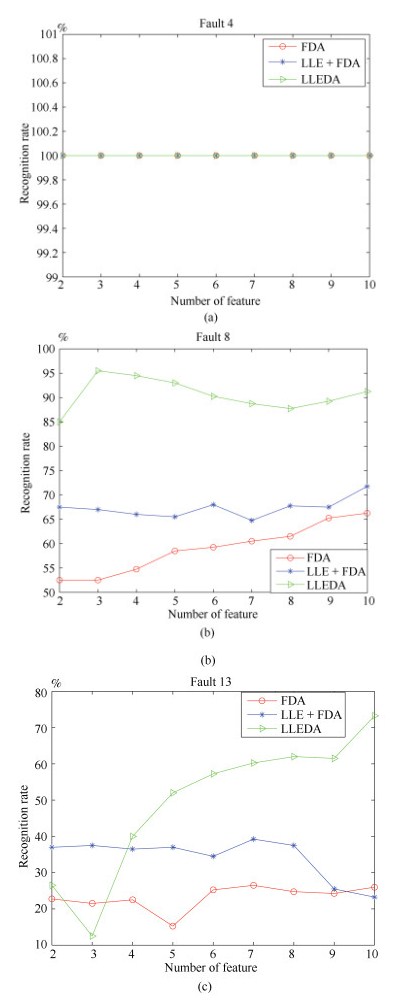
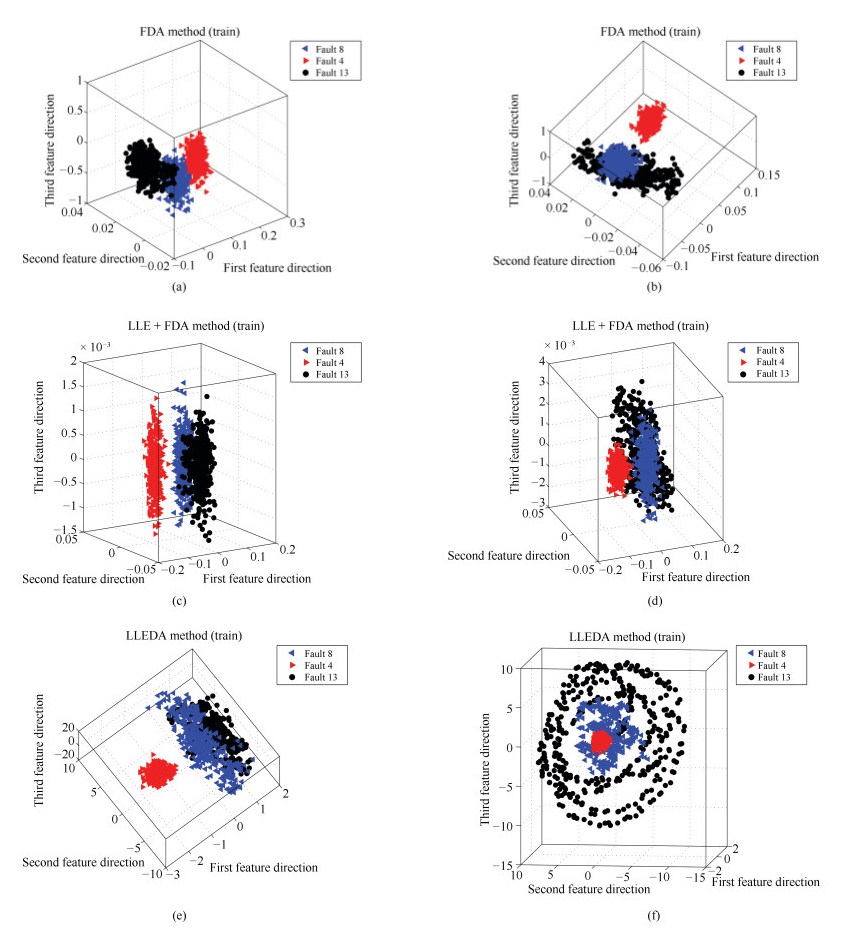
特征向量数 识别率 FDA LLE + EDA LLEDA 2 Fault 8 0.525 0.675 0.85 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.2275 0.37 0.265 3 Fault 8 0.525 0.67 0.955 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.215 0.375 0.125 4 Fault 8 0.5475 0.66 0.945 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.225 0.365 0.4 5 Fault 8 0.585 0.655 0.93 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.585 0.655 0.93 6 Fault 8 0.5925 0.68 0.9025 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.2525 0.345 0.5725 7 Fault 8 0.605 0.6475 0.8875 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.265 0.3925 0.6025 8 Fault 8 0.615 0.6775 0.8775 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.2475 0.375 0.62 9 Fault 8 0.6525 0.675 0.8925 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.2425 0.255 0.615 10 Fault 8 0.6625 0.7175 0.9125 Fault 4 1 1 1 Fault 13 0.26 0.2325 0.7325 -
[1] Ge Z Q, Song Z H, Gao F R. Review of recent research on data-based process monitoring. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(10): 3543-3562 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4e283210b5bf9dbde9c5dbb2fd6682d6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [2] Yin S, Ding S X, Xie X C, Luo H. A review on basic data-driven approaches for industrial process monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(11): 6418-6428 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2301773 [3] Yin S, Gao H J, Kaynak O. Data-driven control and process monitoring for industrial applications-part Ⅰ. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(11): 6356-6359 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2312885 [4] Yin S, Gao H J, Kaynak O. Data-driven control and process monitoring for industrial applications-Part Ⅱ. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(1): 583-586 [5] 文成林, 吕菲亚, 包哲静, 刘妹琴.基于数据驱动的微小故障诊断方法综述.自动化学报, 2016, 42(9): 1285-1299 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c160105Wen Cheng-Lin, Lv Fei-Ya, Bao Zhe-Jing, Liu Mei-Qin. A review of data driven-based incipient fault diagnosis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(9): 1285-1299 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c160105 [6] Yin S, Li X W, Gao H J, Kaynak O. Data-based techniques focused on modern industry: an overview. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(1): 657-667 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8bda8b6d4f3f65fc737e0b39f6cf54e2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [7] Jiang Y C, Yin S. Recursive total principle component regression based fault detection and its application to vehicular cyber-physical systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(4): 1415-1423 doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2752709 [8] Zhang K, Peng K X, Shardt Y A W. A comparison of different statistics for detecting multiplicative faults in multivariate statistics-based fault detection approaches. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 43808-43823 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2862940 [9] Qi X, Luo R Y. Sparse principal component analysis in hilbert space. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 2015, 42(1): 270-289 doi: 10.1111/sjos.12106 [10] Le Thi H A, Phan D N. DC programming and DCA for sparse Fisher linear discriminant analysis. Neural Computing and Applications, 2017, 28(9): 2809-2822 doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2216-9 [11] Zheng J, Song Z. Semisupervised learning for probabilistic partial least aquares regression model and soft sensor application. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 64: 123-131 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2018.01.008 [12] Ge Z Q, Xie L, Kruger U, Song Z H. Local ICA for multivariate statistical fault diagnosis in systems with unknown signal and error distributions. AIChE Journal, 2012, 58(8): 2357-2372 doi: 10.1002/aic.12760 [13] 曹玉苹, 黄琳哲, 田学民.一种基于DIOCVA的过程监控方法.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12): 2072-2080 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c150058Cao Yu-Ping, Huang Lin-Zhe, Tian Xue-Min. A process monitoring method using dynamic input-output canonical variate analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12): 2072-2080 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c150058 [14] Ming A B, Zhang W, Qin Z Y, Chu F L. Fault feature extraction and enhancement of rolling element bearing in varying speed condition. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 76-77: 367-379 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.02.021 [15] Yu J. Nonlinear bioprocess monitoring using multiway kernel localized fisher discriminant analysis. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(6): 3390-3402 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8da00c7b51a00f2a44fa5711f9bafe08 [16] 王晶, 刘莉, 曹柳林, 靳其兵.基于核Fisher包络分析的间歇过程故障诊断.化工学报, 2014, 65(4): 1317-1326 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.04.023Wang Jing, Liu Li, Cao Liu-Lin, Jin Qi-Bing. Fault diagnosis based on kernel Fisher envelope surface for batch processes. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(4): 1317-1326 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.04.023 [17] Zhang J P, Li S Z, Wang J. Manifold learning and applications in recognition. Intelligent Multimedia Processing with Soft Computing. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2005. 281-300 [18] Zhong B, Wang J, Zhou J L, Wu H Y, Jin Q B. Quality-related statistical process monitoring method based on global and local partial least-squares projection. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(6): 1609-1622 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ca4efe313af1ff8f640505725bbaeabc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [19] Luo L J. Process monitoring with global-local preserving projections. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(18): 7696-7705 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a4d644efa75500fa9e28a52cbae466bf&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] 苏祖强, 汤宝平, 邓蕾, 尹爱军.有监督LLTSA特征约简旋转机械故障诊断.仪器仪表学报, 2014, 35(8): 1766-1771 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yqyb201408012Su Zu-Qiang, Tang Bao-Ping, Deng Lei, Yin Ai-Jun. Rotating machinery fault diagnosis with supervised-linear local tangent space alignment for dimension reduction. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(8): 1766-1771 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yqyb201408012 [21] Wang J, Zhong B, Zhou J L. Quality-relevant fault monitoring based on locality-preserving partial least-squares statistical models. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(24): 7009-7020 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e8e68686669984bd3be064894dda9d73 [22] Liu Z, Wang L Y, Zhang Y, Chen C L P. A SVM controller for the stable walking of biped robots based on small sample sizes. Applied Soft Computing, 2016, 38: 738-753 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.029 [23] 阚英男.基于网格近似法的数控机床贝叶斯可靠性评估研究[博士学位论文], 吉林大学, 中国, 2015Kan Ying-Nan. Research on Bayesian Reliability Assessment for NC Machine Tools based on Grid Approximation[Ph. D. Dissertation], Jilin University, China, 2015 [24] 赵孝礼, 赵荣珍, 孙业北, 何敬举.基于正则化核最大边界投影维数约简的滚动轴承故障诊断.振动与冲击, 2017, 36(14): 104-110 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zdycj201714017Zhao Xiao-Li, Zhao Rong-Zhen, Sun Ye-Bei, He Jing-Ju. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on the dimension reduction using the regularized kernel maximum margin projection. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(14): 104-110 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zdycj201714017 [25] Adil M, Abid M, Khan A Q, Mustafa G, Ahmed N. Exponential discriminant analysis for fault diagnosis. Neurocomputing, 2016, 171: 1344-1353 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.07.099 [26] Wang R X, Wang J, Zhou J L, Wu H Y. An improved kernel exponential discriminant analysis for fault identification of batch process. In: Proceedings of the 6th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems. Chongqing, China: IEEE, 2017. 16-21 [27] Han J W, Kamber M, Pei J. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques (Third Edition). San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 2011. 1-18 [28] Chapelle O. Training a support vector machine in the primal. Neural Computation, 2007, 19(5): 1155-1178 doi: 10.1162/neco.2007.19.5.1155 [29] Boutros T, Liang M. Detection and diagnosis of bearing and cutting tool faults using hidden Markov models. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2011, 25(6): 2102-2124 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.01.013 [30] Du J, Wang S P, Zhang H Y. Layered clustering multi-fault diagnosis for hydraulic piston pump. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 36(2): 487-504 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bcf4dcb0467db1182112f614189b8570 [31] Yiakopoulos C T, Gryllias K C, Antoniadis I A. Rolling element bearing fault detection in industrial environments based on a K-means clustering approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(3): 2888-2911 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2f731db23bb777aaf856a77635f47169 [32] Cheng G, Cheng Y L, Shen L H, Qiu J B, Zhang S. Gear fault identification based on Hilbert-Huang transform and SOM neural network. Measurement, 2013, 46(3): 1137-1146 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0af6ae4339a6d5b13f4c46596315b72c [33] 熊浩, 张晓星, 廖瑞金, 常涛, 孙才新.基于动态聚类的电力变压器故障诊断.仪器仪表学报, 2007, 28(3): 456-459 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2007.03.014Xiong Hao, Zhang Xiao-Xing, Liao Rui-Jin, Chang Tao, Sun Cai-Xin. Fault diagnosis of power transformer using dynamic clustering algorithm. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2007, 28(3): 456-459 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2007.03.014 [34] 范志鹏.基于小波与聚类分析相结合的旋转机械的故障诊断[硕士学位论文], 江西理工大学, 中国, 2011Fang Zhi-Peng. Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery Based on Wavelet and Clustering Analysis[Master Thesis], Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, China, 2011 [35] 高宇.基于SOM神经网络的风电电子装置故障诊断.电力系统及其自动化学报, 2010, 22(3): 142-145 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2010.03.026Gao Yu. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine power electronic devices based on SOM neural network. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2010, 22(3): 142-145 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2010.03.026 [36] Wang R X, Wang J, Zhou J L, Wu H Y. Fault diagnosis based on the integration of exponential discriminant analysis and local linear embedding. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 96(2): 463-483 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1002/cjce.22921 [37] Hu Z F, Pan G, Wang Y M, Wu Z H. Sparse principal component analysis via rotation and truncation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(4): 875-890 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=707be0cd4a6c10ba73e8c3866b2d0b3d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [38] Saxena A, Prasad M, Gupta A, Bharill N, Patel O P, Tiwari A, et al. A review of clustering techniques and developments. Neurocomputing, 2017, 267: 664-681 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.06.053 [39] Roweis S T, Saul L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2323-2326 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2323 [40] Zhao H, Liu J W, Dong W, Sun X Y, Ji Y D. An improved case-based reasoning method and its application on fault diagnosis of Tennessee Eastman process. Neurocomputing, 2017, 249: 266-276 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.04.022 [41] Yin S, Zhu X P, Kaynak O. Improved PLS focused on key-performance-indicator-related fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(3): 1651-1658 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f7d63a5b33852ea6ad7ed8c01346803e [42] 惠振东. TE化工过程优化控制仿真系统研究[硕士学位论文], 北方工业大学, 中国, 2017Hui Zhen-Dong. Research on Simulation System of TE Chemical Process Optimization Control[Master Thesis], North China University of Technology, China, 2017 [43] Wang Y Q, Zhang J P, Zeng F M, Wang N, Chen X P, Zhang B, et al. "Learning" can improve the blood glucose control performance for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 2017, 19(1): 41-48 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=17740f9aa67710d280b753d8599d45e9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [44] Zhao D, Shen D, Wang Y Q. Fault diagnosis and compensation for two-dimensional discrete time systems with sensor faults and time-varying delays. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2017, 27(16): 3296-3320 doi: 10.1002/rnc.3742 -





 下载:
下载: