-
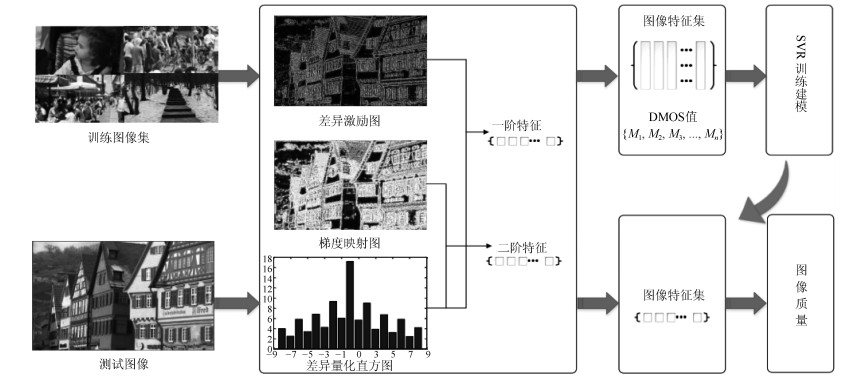
摘要: 为了衡量图像的降质程度, 充分考虑像素间的相关性, 提出了一种基于差异激励的无参考图像质量评价算法.该算法根据韦伯定律求得差异激励图, 并依据各向异性得到差异激励的梯度映射图; 然后量化差异激励得到差异量化图, 并分别与差异激励图与梯度映射图进行加权融合; 最后利用求得的特征, 通过支持向量回归(Support vector regression, SVR)预测得出图像质量的客观评价值.在LIVE、MLIVE、MDID2013和MDID2016等多个数据库中测试显示, 该算法稳定性强, 复杂度低, 能准确反映人类对图像质量的视觉感知效果.Abstract: In order to estimate the degradation of the image distortion level and consider the correlation among pixels, a no-reference image quality assessment algorithm based on differential excitation is proposed in this article. According to the Weber$'$s law, the differential excitation map was obtained and the gradient map of differential excitation was obtained by anisotropy. Then, the differential quantization map was obtained by quantifying differential excitation, and weighted fusion with differential excitation map and gradient map is carried out respectively. Finally, the objective evaluation value of image quality is obtained by support vector regression (SVR) prediction using the acquired features. In LIVE and MLIVE and MDID2013 and MDID2016 databases, the experiment shows that the algorithm is highly robust and low complexity, which can accurately reflect the human image quality of visual perception.
-
Key words:
- Image quality assessment /
- Weber's law /
- differential incentives /
- gradient mapping
1) 本文责任编委 刘跃虎 -
表 1 本文选用的6个图像库描述
Table 1 The descriptions of six image databases selected in this paper
图像库 参考图像 失真类型 图像个数 LIVE 29 JPEG2000压缩 953 JPEG压缩 高斯白噪声 高斯模糊 快衰弱 CSIQ 30 加性高斯噪声 900 高斯模糊 对比度改变 粉红噪声 MLIVE 15 JPEG压缩 450 JPEG2000压缩 模糊+压缩 模糊+噪声 MDID2013 12 模糊+压缩+噪声 324 MDID2016 20 噪声+模糊+对比度+压缩+ JP2K压缩 1 600 TID2013 25 #1加性高斯噪声 #13 JPEG2000传输误差 3 000 #2彩色分量中的差分加性噪声 #14无偏心率类型噪声 #3空域相关噪声 #15不同强度局部块失真 #4掩膜噪声 #16均值平移 #5高频噪声 #17对比度改变 #6脉冲噪声 #18色彩饱和度改变 #7量化噪声 #19乘性高斯噪声 #8高斯模糊 #20舒适噪声 #9图像去噪 #21噪声图像的有损压缩 #10 JPEG压缩 #22图像的颜色量化及波动 #11 JPEG2000压缩 #23图像色差 #12 JPEG传输误差 #24稀疏采样及重构 表 2 LIVE和CSIQ数据库中单一型算法质量评价性能对比
Table 2 Comparison of performance evaluation of single algorithm in LIVE and CSIQ databases
LIVE (953 images) CSIQ (900 images) 算法 CC SROCC RMSE CC SROCC RMSE DIIVINE[5] 0.893 0.885 11.168 0.797 0.810 0.275 BRISQUE[6] 0.944 0.947 7.795 0.728 0.740 0.325 NIQE[7] 0.909 0.908 11.376 0.756 0.739 0.340 IL-NIQE[8] 0.906 0.903 10.824 0.732 0.718 0.354 NR-GLBP[9] 0.942 0.935 9.075 0.847 0.801 0.174 NRSL[10] 0.957 0.953 8.018 0.859 0.851 0.109 本文算法 0.963 0.961 7.052 0.858 0.839 0.117 表 3 TID2013数据库中算法质量评价性能指标SROCC对比(3 000幅图)
Table 3 Comparison of quality evaluation performance indexes of algorithm in TID2013 database (3 000 images)
算法 #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 #8 #9 #10 #11 #12 #13 #14 #15 #16 #17 #18 #19 #20 #21 #22 #23 #24 All BRISQUE[6] 0.706 0.523 0.776 0.295 0.836 0.802 0.682 0.861 0.500 0.790 0.779 0.254 0.723 0.213 0.197 0.217 0.079 0.113 0.674 0.198 0.627 0.849 0.724 0.811 0.567 NR-GLBP[9] 0.466 0.591 0.759 0.491 0.875 0.693 0.833 0.878 0.721 0.844 0.867 0.440 0.594 0.226 0.204 0.105 0.123 0.023 0.580 0.447 0.507 0.762 0.748 0.830 0.679 NRSL[10] 0.813 0.457 0.867 0.393 0.902 0.787 0.700 0.886 0.795 0.818 0.891 0.345 0.805 0.117 0.323 0.136 0.194 0.110 0.753 0.434 0.751 0.866 0.694 0.887 0.661 NFERM[13] 0.851 0.520 0.846 0.521 0.894 0.857 0.785 0.888 0.741 0.797 0.920 0.381 0.718 0.176 0.081 0.238 0.056 0.029 0.762 0.206 0.401 0.848 0.684 0.878 0.652 GWH-GLBP[14] 0.736 0.358 0.814 0.412 0.874 0.795 0.757 0.838 0.811 0.890 0.901 0.494 0.656 0.326 0.344 0.341 0.252 0.420 0.601 0.624 0.664 0.741 0.919 0.898 0.655 本文算法 0.768 0.454 0.861 0.537 0.885 0.814 0.752 0.908 0.859 0.853 0.940 0.544 0.754 0.426 0.480 0.275 0.442 0.507 0.706 0.680 0.823 0.839 0.948 0.903 0.691 表 4 MLIVE、MDID2013和MDID2016数据库中混合型算法质量评价性能指标对比
Table 4 Comparison of quality evaluation performance indicators of hybrid algorithm in MLIVE, MDID2013 and MDID2016 databases
算法 MLIVE MDID2013 MDID2016 (450 images) (324 images) (1 600 images) CC SROCC RMSE CC SROCC RMSE CC SROCC RMSE SISBLM[10] 0.925 0.907 7.198 0.910 0.905 0.019 0.633 0.655 1.708 HOSA[12] 0.926 0.902 6.974 0.892 0.872 0.021 0.566 0.551 1.871 NFERM[13] 0.919 0.899 7.458 0.871 0.855 0.025 0.496 0.451 1.915 GWH-GLBP[14] 0.945 0.939 6.061 0.913 0.907 0.019 0.891 0.886 1.004 本文算法 0.957 0.942 5.736 0.916 0.904 0.019 0.903 0.892 0.947 表 5 测试不同训练与测试比例的SROCC和CC的中值(1 000次)
Table 5 Median values of SROCC and CC for different training and test ratios (1 000 times)
LIVE MLIVE 测试集和训练集比例 指标 JP2K JPEG GBLUR FF WN ALL GB + JPEG GB + WN ALL 70 $\%$与30 $\%$ SROCC 0.9496 0.9592 0.9419 0.8848 0.9752 0.9604 0.9372 0.9438 0.9366 CC 0.9613 0.9768 0.9504 0.8958 0.9804 0.9624 0.9598 0.9535 0.9506 60 $\%$与40 $\%$ SROCC 0.9479 0.9570 0.9397 0.8732 0.9747 0.9578 0.9266 0.9321 0.9278 CC 0.9594 0.9750 0.9468 0.8875 0.9796 0.9610 0.9483 0.9401 0.9414 50 $\%$与50 $\%$ SROCC 0.9466 0.9546 0.9363 0.8674 0.9743 0.9559 0.9204 0.9240 0.9223 CC 0.9587 0.9738 0.9413 0.8839 0.9791 0.9595 0.9437 0.9357 0.9364 40 $\%$与60 $\%$ SROCC 0.9409 0.9521 0.9320 0.8606 0.9706 0.9522 0.9063 0.9053 0.9046 CC 0.9520 0.9691 0.9369 0.8744 0.9789 0.9568 0.9243 0.9167 0.9164 30 $\%$与70 $\%$ SROCC 0.9351 0.9465 0.9253 0.8514 0.9645 0.9463 0.9040 0.8984 0.8976 CC 0.9457 0.9651 0.9287 0.8611 0.9781 0.9507 0.9206 0.9101 0.9112 20 $\%$与80 $\%$ SROCC 0.9253 0.9345 0.9138 0.8329 0.9612 0.9345 0.8864 0.8785 0.8811 CC 0.9351 0.9540 0.9150 0.8468 0.9748 0.9387 0.9079 0.8862 0.8918 表 6 CSIQ数据库中不同失真类型的性能评价
Table 6 Performance evaluation of different distortion types in CSIQ database
类型 CC SROCC RMSE KROCC JP2K 0.9046 0.8741 7.6044 0.6966 JPEG 0.9360 0.9194 6.5040 0.8151 GBLUR 0.8858 0.9016 7.8402 0.7320 WN 0.9377 0.9238 6.3493 0.7591 ALL 0.9167 0.8953 7.2687 0.7378 表 7 LIVE数据库中失真类型的识别准确率(1 000次)
Table 7 Recognition accuracy of distortion type in LIVE database (1 000 times)
类型 JP2K JPEG GBLUR FF WN ALL 准确率 87.94 $\%$ 100 $\%$ 97.82 $\%$ 90.26 $\%$ 100 $\%$ 95.39 $\%$ 表 8 图像质量评价算法运行时间
Table 8 Running time of image quality evaluation algorithm
IQA model DIIVINE BRISQUE NIQA SISBLM HOSA NFERM GWH-GLBP 本文算法 Time (s) 0.18 15.8 2.72 3.73 0.35 55.1 0.27 0.33 -
[1] 王朝云, 蒋刚毅, 郁梅, 陈芬.基于流形特征相似度的感知图像质量评价.自动化学报, 2016, 42(7): 1113-1124 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150559Wang Chao-Yun, Jiang Gang-Yi, Yu Mei, Chen Fen. Manifold feature similarity based perceptual image quality assessment. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1113-1124 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150559 [2] 南栋, 毕笃彦, 马时平, 凡遵林, 何林远.基于分类学习的去雾后图像质量评价算法.自动化学报, 2016, 42(2): 270-278 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c140854Nan Dong, Bi Du-Yan, Ma Shi-Ping, Fan Zun-Lin, He Lin-Yuan. A quality assessment method with classified-learning for Dehazed images. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(2): 270-278 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c140854 [3] 王志明.无参考图像质量评价综述.自动化学报, 2015, 41(6): 1062-1079 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140404Wang Zhi-Ming. Review of no-reference image quality assessment. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(6): 1062-1079 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140404 [4] 陈勇, 帅锋, 樊强.基于自然统计特征分布的无参考图像质量评价.电子信息学报, 2016, 38(7): 1645-1653 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkxxk201607010Chen Yong, Shuai Feng, Fan Qiang. A no-reference image quality assessment based on distribution characteristics of natural statistics. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2016, 38(7): 1645-1653 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkxxk201607010 [5] Moorthy A K, Bovik A C. Blind image quality assessment: From natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(12): 3350-3364 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2147325 [6] Mittal A, Moorthy A K, Bovik A C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(12): 4695-4708 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2214050 [7] Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik A C. Making a "completely blind" image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209-212 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260636803_Making_a_Completely_Blind_Image_Quality_Analyzer [8] Zhang L, Zhang L, Bovik A C. A feature-enriched completely blind image quality evaluator. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(8): 2579-2591 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2426416 [9] Zhang M, Muramatsu C, Zhou X R, Hara T, Fujita H. Blind image quality assessment using the joint statistics of generalized local binary pattern. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(2): 207-210 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/265555808_Blind_Image_Quality_Assessment_using_the_Joint_Statistics_of_Generalized_Local_Binary_Pattern [10] Li Q L, Lin W S, Xu J T, Fang Y M. Blind image quality assessment using statistical structural and luminance features. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2016, 18(12): 2457-2469 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2016.2601028 [11] 张敏辉, 杨剑.评价SAR图像去噪效果的无参考图像质量指标.重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 30(04): 530-536 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqydxyxb-zrkx201804014Zhang Min-Hui, Yang Jian. A new referenceless image quality index to evaluate denoising performance of SAR images. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Natural Science Edition, 2018, 30(04): 530-536 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqydxyxb-zrkx201804014 [12] Xu J T, Ye P, Li Q H, Du H Q, Liu Y, Doermann D. Blind image quality assessment based on high order statistics aggregation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(9): 4444-4457 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2585880 [13] Gu K, Zhai G T, Yang X K, Zhang W J. Using free energy principle for blind image quality assessment. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(1): 50-63 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2014.2373812 [14] Li Q H, Lin W S, Fang Y M. No-reference quality assessment for multiply-distorted images in gradient domain. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(4): 541-545 [15] 卢彦飞, 张涛, 章程.应用log-Gabor韦伯特征的图像质量评价.光学精密工程, 2015, 23(11): 3259-3269 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc201511031Lu Yan-Fei, Zhang Tao, Zhang Cheng. Image quality assessment using log-Gabor Weber feature. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(11): 3259-3269 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc201511031 [16] 丁绪星, 朱日宏, 李建欣.一种基于人眼视觉特性的图像质量评价.中国图象图形学报, 2004, 9(2): 190-194 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2004.02.012Ding Xu-Xing, Zhu Ri-Hong, Li Jian-Xin. A criterion of image quality assessment based on property of HVS. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2004, 9(2): 190-194 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2004.02.012 [17] Chen J, Shan S G, He C, Zhao G Y, Pietikainen M, Chen X L, et al. WLD: A robust local image descriptor. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9): 1705-1720 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.155 [18] Sheikh H R, Wang Z, Cormack L, et al. LIVE image quality assessment database release 2[Online], available: http://ive.ece.utexas.edu/research/quality, October 22, 2005 [19] Ding L, Huang H, Zang Y. Image quality assessment using directional anisotropy structure measurement. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1799-1809 http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039816644010_5e60.html [20] Larsson J, Landy M S, Heeger D J. Orientation-selective adaptation to first- and second-order patterns in human visual cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 2006, 95(2): 862-881 [21] Gu K, Zhai G T, Yang X K, Zhang W J. Hybrid no-reference quality metric for singly and multiply distorted images. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2014, 60(3): 555-567 doi: 10.1109/TBC.2014.2344471 [22] Sun W, Zhou F, Liao Q M. MDID: A multiply distorted image database for image quality assessment. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61(1): 153-168 [23] Yu X, Yang E H, Wang H Q. Down-sampling design in DCT domain with arbitrary ratio for image/video transcoding. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(1): 75-89 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f1f3f5442589f45bf9a7d645a1fa5916 [24] Wu F, Yu E, Yu P, Zhang K, Song Z. Modeling and prediction of the air permeability of fabrics based on the support vector machine. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2017, 45(4): 1388-1395 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=48b8c07c52998562469b78f3b28312a5 [25] Chang C C, Lin C J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2011, 2(3): Article No. 27 [26] Ponomarenko N, Ieremeiev O, Lukin V, Egiazarian K, et al. Color image database TID2013: Peculiarities and preliminary results. In: Proceedings of the 4th Europian Workshop on Visual Information Processing EUVIP2013. Paris, France: 2013. 6 [27] Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik A C. Making a "om-pletely blind" image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process-ing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209-212 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/260636803_Making_a_Completely_Blind_Image_Quality_Analyzer -





 下载:
下载: