-
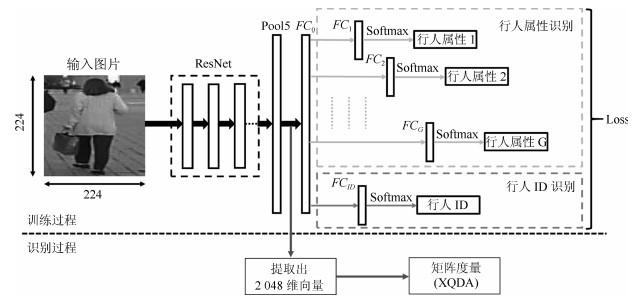
摘要: 为了提高基于深度学习和属性学习的行人再识别的识别精度,提出一种联合识别行人属性和行人ID的神经网络模型.相对于已有的同类方法,该模型有三大优点:1)为了提高网络在微调后的判别能力,在网络中增加了一层保证模型迁移能力的全连接层;2)基于各属性样本的数量,在损失函数中对各属性的损失进行了归一化处理,避免数据集中属性类之间的数量不均衡对识别效果的影响;3)利用数据中各属性分布的先验知识,通过数量占比来调整各属性在损失层中的权重,避免数据集中各属性正负样本的数量不均衡对识别的影响.实验结果表明,本文提出的算法具有较高的识别率,其中在Market1501数据集上,首位匹配率达到了86.90%,在DukeMTMC数据集上,首位匹配率达到了72.83%,在PETA数据集上,首位匹配率达到了75.68%,且对光照变化、行人姿态变化、视角变化和遮挡都具有很好的鲁棒性.Abstract: In order to improve the recognition accuracy of pedestrian recognition based on deep learning and attribute learning, a new neural network model is proposed to identify pedestrian attributes and IDs. Compared with the existing methods, this model has three advantages, one is to increase an all connected layer in the network to guarantee the model's migration which improves the network's discriminant ability after fine-tuning; Second, based on the number of samples of each attribute, we normalized processing the loss of each attribute in the loss function, to avoid the number of disequilibrium effect between classes among the data set which attributes to identify results; third, use the data of each attribute distribution in the prior knowledge, through a number of ratios to adjust each attribute's weight to avoid the influence of positive and negative samples' disequilibrium. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has high recognition rate, the rank-1 accuracy reached 86.90% on Market1501 dataset, 72.83% on DukeMTMC dataset and 75.68% on PETA dataset, it also shows that the proposed algorithm has good robustness on illumination changes, pedestrians posture changes, perspective changes and occlusions.1) 本文责任编委 王亮
-
表 1 Market 1501数据集中的属性类别
Table 1 The attribute category of Market 1501 dataset
属性类($G$) 属性 数量($K$) Gender male, female 2 Age child, teenager 4 Hair length long, short 2 Lower clothing length long, short 2 Lower clothing type pants, dress 2 Wearing hat yes, no 2 Carrying bag yes, no 2 Carrying backpack yes, no 2 Carrying handbag yes, no 2 Upper clothing color black, white, red$\cdots$ 8 Lower clothing color black, white, pink$\cdots$ 9 表 2 Market 1501数据集中行人属性训练样本数量及占比
Table 2 Statistics of Market 1501 dataset
属性 数量 占比 属性 数量 占比 upblack 113 0.15 male 431 0.57 upwhite 228 0.30 female 320 0.43 upred 78 0.10 short hair 506 0.67 uppurple 30 0.04 long hair 245 0.33 upyellow 36 0.05 long sleeve 39 0.05 upgray 86 0.11 short sleeve 712 0.95 upblue 46 0.06 long lower body 110 0.15 upgreen 56 0.07 short lower body 641 0.85 handbag no 665 0.89 dress 294 0.39 handbag yes 86 0.11 pants 457 0.61 young 14 0.02 downgray 123 0.16 teenager 569 0.76 downblack 293 0.39 adult 160 0.21 downwhite 58 0.08 old 8 0.01 downpink 29 0.04 bag no 566 0.75 downpurple 2 0.00 bag yes 185 0.25 downyellow 10 0.01 backpack no 552 0.74 downblue 123 0.16 backpack yes 199 0.26 downgreen 14 0.02 hat no 731 0.97 downbrown 69 0.09 hat yes 20 0.03 表 3 Market 1501数据集各属性识别准确率(%)
Table 3 Accuracy rate of each attribute recognition of Market 1501 dataset (%)
属性 gender age hair L.slv L.low S.cloth B.pack H.bag bag C.up C.low mean APR 86.45 87.08 83.65 93.66 93.32 91.46 82.79 88.98 75.07 73.4 69.91 85.33 本文算法 86.73 88.14 84.12 93.5 94.54 91.86 85.99 90.67 82.36 77.83 73.82 86.32 表 4 DukeMTMC数据集各属性识别准确率(%)
Table 4 Accuracy rate of each attribute recognition of DukeMTMC dataset (%)
属性 gender hat boots L.up B.pack H.bag bag C.shoes C.up C.low mean APR 82.61 86.94 86.15 88.04 77.28 93.75 82.51 90.19 72.29 41.48 80.12 本文算法 82.73 89.02 87.17 89.33 81.33 95.81 86.74 93.12 73.04 43.21 82.15 表 5 PETA数据集各属性识别准确率(%)
Table 5 Accuracy rate of each attribute recognition of PETA dataset (%)
属性 gender age carry style hat hair shoes K.up K.low bag glasses mean APR 89.51 86.37 78.28 84.69 92.12 89.41 78.95 88.34 84.81 86.76 72.61 84.71 本文算法 90.11 85.32 85.39 85.43 92.63 88.6 82.32 88.97 86.82 88.06 78.33 88.54 表 6 Market 1501数据集行人再识别结果
Table 6 Re-id results of the Market 1501 dataset
方法 rank-1 rank-5 rank-10 rank-20 mAP DADM[17] 39.4 - - - 19.6 MBC[18] 45.56 67 76 82 26.11 SML[19] 45.16 68.12 76 84 - DLDA[20] 48.15 - - - 29.94 DNS[21] 55.43 - - - 29.87 LSTM[8] 61.6 - - - 35.3 S-CNN[22] 65.88 - - - 39.55 2Stream[23] 79.51 90.91 94.09 96.23 59.87 GAN[13] 79.33 - - - 55.95 Pose[24] 78.06 90.76 94.41 96.52 56.23 Deep[25] 83.7 - - - 65.5 APR 84.29 93.2 95.19 97 64.67 本文-$F{{C}_{0}}$ 85.37 94.05 96.13 97.31 65.11 本文-归一化 84.92 93.75 95.92 97.46 64.82 本文-权重 85.67 94.69 96.75 97.94 65.23 本文-归一化+权重 86.31 94.97 97.10 98.01 65.46 本文 86.90 95.37 97.03 98.17 65.87 表 7 DukeMTMC数据集行人再识别结果
Table 7 Re-id results of the DukeMTMC dataset
表 8 PETA数据集行人再识别结果
Table 8 Re-id results of the PETA dataset
方法 rank-1 mAP mA ikSVM[26] 41.12* 26.87* 69.5 MRFr2[27] 51.71* 30.77* 75.6 ACN[28] 59.04* 35.89* 81.15 DeepMAR[10] 64.58* 41.12* 82.6 WPAL[29] 68.14* 42.68* 85.5 APR 71.29* 45.31* 84.71* 本文-$F{{C}_{0}}$ 72.82 47.75 86.24 本文-归一化 73.63 47.86 87.01 本文-权重 73.14 47.51 87.28 本文-归一化+权重 74.57 49.69 88.05 本文 75.68 51.03 88.54 -
[1] Farenzena M, Bazzani L, Perina A, Murino V, Cristani M. Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2360-2367 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5539926 [2] Pedagadi S, Orwell J, Velastin S, Boghossian B. Local fisher discriminant analysis for pedestrian re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 3318-3325 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6619270 [3] 种衍文, 匡湖林, 李清泉.一种基于多特征和机器学习的分级行人检测方法.自动化学报, 2012, 38(3):375-381 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17688.shtmlChong Yan-Wen, Kuang Hu-Lin, Li Qing-Quan. Two-stage pedestrian detection based on multiple features and machine learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(3):375-381 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17688.shtml [4] Zheng W S, Gong S G, Xiang T. Person re-identification by probabilistic relative distance comparison. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2011. 649-656 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5995598 [5] 齐美彬, 檀胜顺, 王运侠, 刘皓, 蒋建国.基于多特征子空间与核学习的行人再识别.自动化学报, 2016, 42(2):299-308 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18819.shtmlQi Mei-Bin, Tan Sheng-Shun, Wang Yun-Xia, Liu Hao, Jiang Jian-Guo. Multi-feature subspace and kernel learning for person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(2):299-308 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18819.shtml [6] 于雪松, 刘家锋, 唐降龙, 黄剑华.基于概率模型的行人四肢自遮挡的检测.自动化学报, 2010, 36(4):610-615 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13712.shtmlYu Xue-Song, Liu Jia-Feng, Tang Xiang-Long, Huang Jian-Hua. Estimating the pedestrian 3D motion indoor via hybrid tracking model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(4):610-615 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13712.shtml [7] Li W, Zhao R, Xiao T, Wang X G. Deepreid: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 152-159 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6909421 [8] Varior R R, Shuai B, Lu J W, Xu D, Wang G. A siamese long short-term memory architecture for human re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. 135-153 [9] Liu H, Feng J S, Qi M B, Jiang J G, Yan S C. End-to-end comparative attention networks for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7):3492-3506 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2700762 [10] Li D W, Chen X T, Huang K Q. Multi-attribute learning for pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR). Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IEEE, 2015. 111-115 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7486476/ [11] Lin Y T, Zheng L, Zheng Z D, Wu Y, Yang Y. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1703.07220, June 14, 2018. [12] Zheng L, Shen L Y, Tian L, Wang S J, Wang J D, Tian Q. Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1116-1124 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=7410490 [13] Zheng Z D, Zheng L, Yang Y. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.07717, June 14, 2018. [14] Zhang C L, Luo J H, Wei X S, Wu J X. In defense of fully connected layers in visual representation transfer. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia. Harbin, China: Springer-Verlag, 2017. 807-817 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-77383-4_79 [15] Visin F, Kastner K, Cho K, Matteucci M, Courville A, Bengio Y. ReNet: a recurrent neural network based alternative to convolutional networks[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1505.00393, June 14, 2018. [16] Liao S C, Hu Y, Zhu X Y, Li S Z. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2197-2206 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=7298832 [17] Su C, Zhang S L, Xing J L, Gao W, Tian Q. Deep attributes driven multi-camera person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2016. 475-491 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_30 [18] Ustinova E, Ganin Y, Lempitsky V. Multi-region bilinear convolutional neural networks for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. Lecce, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1-6 http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.05300 [19] Jose C, Fleuret F. Scalable metric learning via weighted approximate rank component analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2016. 875-890 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46454-1_53 [20] Wu L, Shen C H, van den Hengel A. Deep linear discriminant analysis on fisher networks:a hybrid architecture for person re-identification. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 65:238-250 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.12.022 [21] Zhang L, Xiang T, Gong S G. Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1239-1248 [22] Varior R R, Haloi M, Wang G. Gated siamese convolutional neural network architecture for human re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham, Switerland: Springer, 2016. 791-808 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_48 [23] Zheng Z D, Zheng L, Yang Y. A discriminatively learned CNN embedding for person reidentification. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2018, 14(1):Article No.13 https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.05666 [24] Zheng L, Huang Y J, Lu H C, Yang Y. Pose invariant embedding for deep person re-identification[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.07732, June 14, 2018. [25] Geng M Y, Wang Y W, Xiang T, Tian Y H. Deep transfer learning for person re-identification[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.05244, June 14, 2018. [26] Maji S, Berg A C, Malik J. Classification using intersection kernel support vector machines is efficient. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4587630 [27] Deng Y B, Luo P, Loy C C, Tang X O. Learning to recognize pedestrian attribute[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1501.00901, June 14, 2018. [28] Sudowe P, Spitzer H, Leibe B. Person attribute recognition with a jointly-trained holistic CNN model. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 329-337 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=7406400&navigation=1 [29] Yu K, Leng B, Zhang Z, Li D W, Huang K Q. Weakly-supervised learning of mid-level features for pedestrian attribute recognition and localization[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.05603, June 14, 2018. -




 下载:
下载:





