A Compressed Sensing Reconstruction Based on Elastic Collision and Gradient Pursuit Strategy for WSNs
-
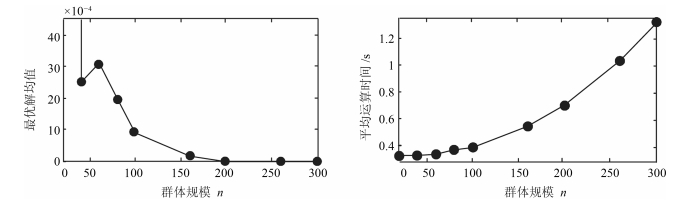
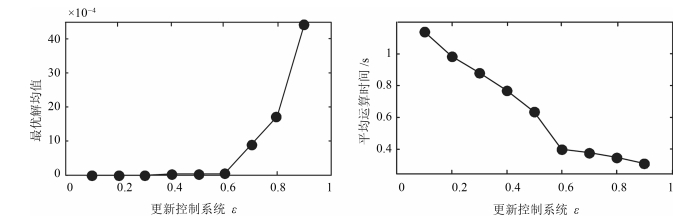
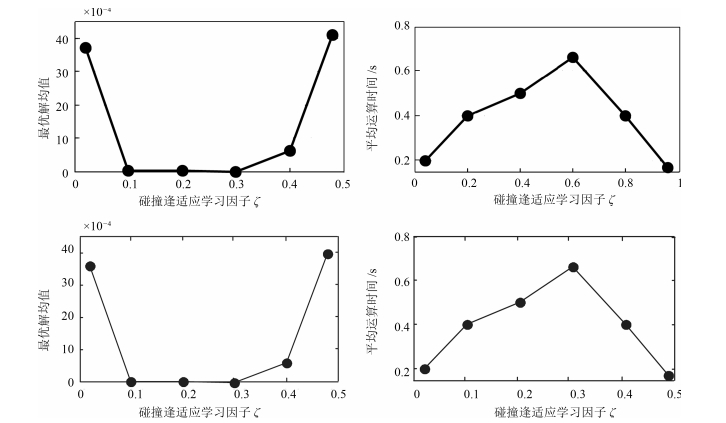
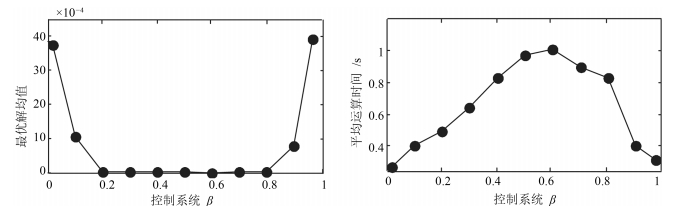
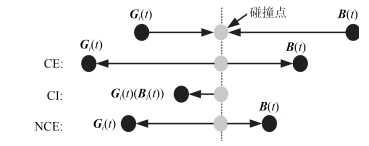
摘要: 为提高压缩感知(Compressed sensing, CS)大规模稀疏信号重构精度, 提出了一种联合弹性碰撞优化与改进梯度追踪的WSNs (Wireless sensor networks)压缩感知重构算法.首先, 创新地提出一种全新的智能优化算法---弹性碰撞优化算法(Elastic collision optimization algorithm, ECO), ECO模拟物理碰撞信息交互过程, 利用自身历史最优解和种群最优解指导进化方向, 并且个体以N(0, 1)概率形式散落于种群最优解周围, 在有效提升收敛速度的同时扩展了个体搜索空间, 理论定性分析表明ECO依概率1收敛于全局最优解, 而种群多样性指标分析证明了算法全局寻优能力.其次, 针对贪婪重构算法高维稀疏信号重构效率低、稀疏度事先设定的缺陷, 在设计重构有效性指数的基础上将ECO应用于压缩感知重构算法中, 并引入拟牛顿梯度追踪策略, 从而实现对大规模稀疏度未知数据的准确重构.最后, 利用多维测试函数和WSNs数据采集环境进行仿真, 仿真结果表明, ECO在收敛精度和成功率上具有一定优势, 而且相比于其他重构算法, 高维稀疏信号重构结果明显改善.Abstract: In order to improve the precision of compressed sensing (CS) sparse reconstruction algorithm, a CS reconstruction algorithm based on elastic collision optimization (ECO) and improved gradient pursuit strategy for WSNs is proposed. First of all, a new intelligent optimization computing technology: ECO is put forward. Referred to physical collision information interaction process, the historical optimal solution and population optimal solution are used to guide evolutionary direction and individuals are spread around the optimal solution in the form of N(0, 1), which helps to improve the convergence speed and extend the individual search space. Qualitative analysis shows that ECO can converge to the global optimal solution in probability 1 and the analysis of the diversity index shows that the algorithm has the ability of global optimization. Secondly, aiming at the defects of greedy reconstruction algorithm as low reconstruction efficiency and sparsity set in advance for high dimensional sparse signals, the ECO is applied to the CS reconstruction algorithm on the basis of the design validity index, and the quasi Newton gradient pursuit strategy is also introduced, which helps to realize the accurate reconstruction of large scale sparse data. Finally, simulation is carried out using multidimensional test functions and WSNs data acquisition environment. The simulation results show that ECO has certain advantages in convergence accuracy and success rate, and compared with other reconstruction algorithms, the reconstruction results significantly improved for high dimensional sparse signal.
-
Key words:
- Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) /
- elastic collision optimization (ECO) /
- convergence efficiency /
- compressed sensing (CS) /
- sparse reconstruction algorithm
1) 本文责任编委 杨健 -
表 1 基准测试函数
Table 1 Benchmark functions
函数名称 目标函数 维数 取值范围 Scaffer $ \begin{aligned} f_{1} \left(x \right)= 0.5-\frac{[{\sin^{2}\left({x_{1}^{2} +x_{2}^{2} } \right)^{0.5}}]}{[{1+0.001\left({x_{1}^{2} +x_{2}^{2} } \right)^{2}}]} \end{aligned} $ 2 [0, 1] Sphere $ f_{2} \left(x \right)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^n {x_{i}^{2} } $ 5 $ (-30, 30) $ Griewank $ \begin{aligned} f_{3} \left(x \right)=\frac{1}{4000}\sum\limits_{i=1}^n {x_{i}^{2} } - \prod\limits_{i=1}^n {\cos \left({\frac{x_{i} }{\sqrt{i}}} \right)} +1 \end{aligned} $ 20 $ (-30, 30) $ Scaffer7 $ \begin{aligned} f_{4} \left(x \right)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n-1} {\left({x_{i}^{2} +x_{i+1}^{2} } \right)^{0.25}} \times [{\sin^{2}({50\left({x_{i}^{2} +x_{i+1}^{2} } \right)^{0.1}})+2}] \end{aligned} $ 30 $ (-100, 100) $ Rastrigin $ \begin{aligned} f_{5} \left(x \right)= \sum\limits_{i=1}^n {({x_{i}^{2} -10\cos 2\pi x_{i} +10})} \end{aligned} $ $ n $ $ (-5.12, 5.12) $ Rosenrrock $ \begin{aligned} f_{6} \left(x \right)= \sum\limits_{i=1}^n {[{100\left({x_{i+1} -x_{i}^{2} } \right)^{2}+x_{i}^{2} }]} \end{aligned} $ $ n $ $ (-30, 30) $ 表 2 不同函数收敛性能指标对比结果
Table 2 Comparison results of convergence performance indexes of different functions
$ f $ 算法 $ Su $ (%) $ Max $ $ Min $ $ \overline {Ave} $ $ T$ (s) $ f_{1} $ ECO 100 -0.997 -1 -0.999 6.79 PSO 12 -0.23 -0.95 -0.68 11.37 DSA 100 -0.96 -1 -0.98 6.13 SWPA 100 -0.93 -1 -0.97 7.74 $ f_{2} $ ECO 100 1.78E-6 0 6.37E-10 6.37 PSO 100 5.27E-4 5.77E-6 1.19E-4 12.76 DSA 100 6.27E-3 3.09E-4 1.62E-3 8.36 SWPA 100 1.04E-4 3.33E-5 6.24E-5 14.55 $ f_{3} $ ECO 100 7.24E-4 0 1.29E-3 10.88 PSO 0 1.51 0.012 0.84 15.27 DSA 98 3.28E-3 1.93E-3 2.74E-3 12.70 SWPA 100 6.53E-3 2.85E-3 3.48E-3 11.09 $ f_{4} $ ECO 100 2.81E-5 6.34E-8 7.11E-7 22.16 PSO 0 17.11 6.25 10.78 27.94 DSA 79 0.07 1.83E-2 0.04 11.22 SWPA 80 0.18 3.64E-72 0.01 14.55 $ f_{5} $ ECO 100 1.11E-6 0 4.89E-9 7.41 PSO 0 20.47 11.25 19.86 10.28 DSA 65 0.063 3.21E-2 0.017 6.89 SWPA 86 0.025 4.44E-3 0.008 8.77 $ f_{6} $ ECO 17 0.467 0.013 0.227 15.23 PSO 0 88.171 21.073 44.110 20.79 DSA 0 22.145 6.667 8.936 18.81 SWPA 11 6.652 2.147 3.667 12.56 表 3 不同重构评价指标对比
Table 3 Comparison of evaluation indexes of different reconfiguration
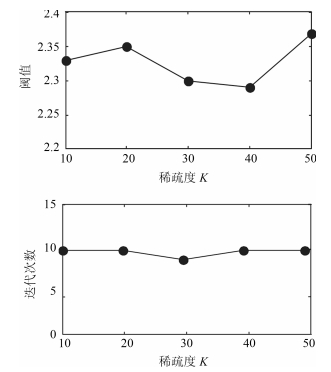
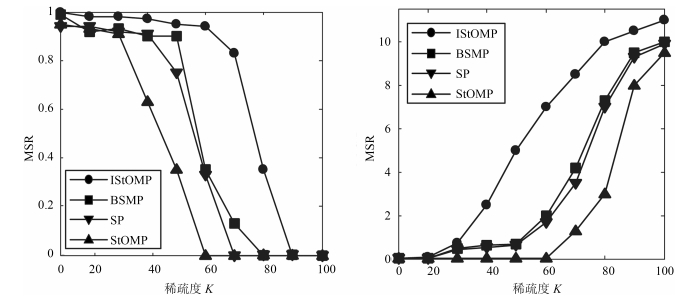
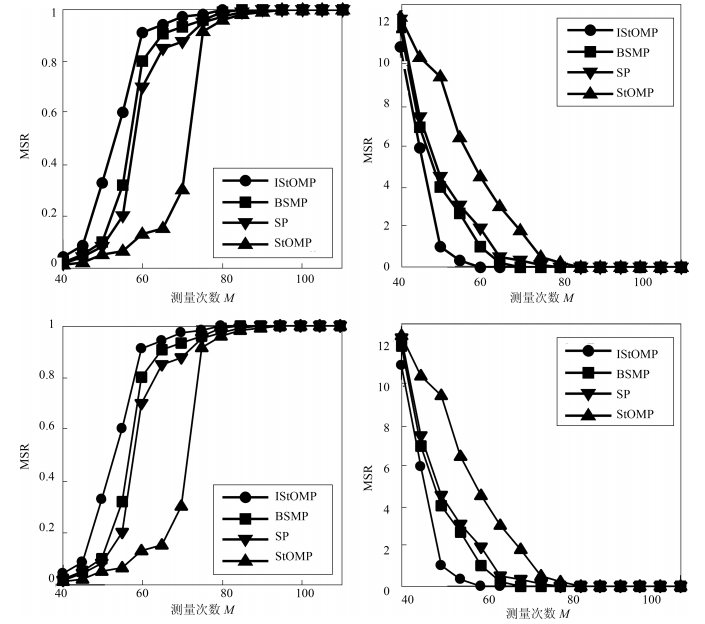
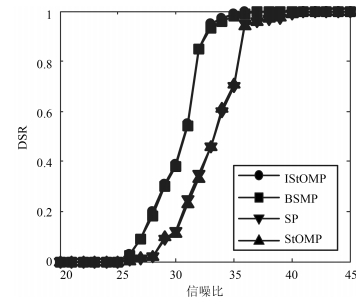
重构算法稀疏度 $ K=15 $ MSE DSR (%) $ \overline {T_{l} } $ (s) SNR IStOMP 1.23 100 14.881 39.114 StOMP 91.27 7 9.524 27.047 SP 12.54 89 6.227 36.541 BSMP 16.76 99 8.123 35.046 -
[1] Luo C, Wu F, Sun J, Chen C W. Efficient measurement generation and pervasive sparsity for compressive data gathering. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(12): 3728-3738 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c2a1c12bd89e33b724c1e1e60d41dd00 [2] Kennedy J, Eberhart R C. Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Perth, Australia: IEEE, 1995. 1942-1948 [3] Colorni A, Dorigo M, Maniezzo V. Distributed optimization by ant colonies. In: Proceedings of the First European Conference on Artificial Life. Paris, France: Elsevier Publishing, 1991. 134-142 [4] Eusuff M M, Lansey K E. Optimization of water distribution network design using the shuffled frog leaping algorithm. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 2003, 129(3): 210-225 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0e23c56470bc29ab284b932833c2fe22 [5] Tan Y, Zhu Y C. Fireworks algorithm for optimization. In: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Advances in Swarm Intelligence. Beijing, China: Springer-Verlag, 2010. 355-364 [6] 莫修文, 张强, 陆敬安.模拟退火法建立数字岩心的一种补充优化方案.地球物理学报, 2016, 59(5): 1831-1838 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201605026Mo Xiu-Wen, Zhang Qiang, Lu Jing-An. A complement optimization scheme to establish the digital core model based on the simulated annealing method. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(5): 1831-1838 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201605026 [7] 李宝磊, 施心陵, 苟常兴, 吕丹桔, 安镇宙, 张榆锋.多元优化算法及其收敛性分析.自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 949-959 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140585Li Bao-Lei, Shi Xin-Ling, Gou Chang-Xing, Lv Dan-Ju, An Zhen-Zhou, Zhang Yu-Feng. Multivariant optimization algorithm and its convergence analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5): 949-959 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140585 [8] Ebrahimi D, Assi C. Network coding-aware compressive data gathering for energy-efficient wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 2015, 11(4): Article No. 61 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8f2aa328e1976324b2567f8fb8839203 [9] Liang J J, Qin A K, Suganthan P N, Baskar S. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2006, 10(3): 281-295 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cf4e7f5803244a494e7503db7e0301fc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [10] 马卫, 孙正兴.采用搜索趋化策略的布谷鸟全局优化算法.电子学报, 2015, 43(12): 2429-2439 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dianzixb201512013Ma Wei, Sun Zheng-Xing. A global cuckoo optimization algorithm using coarse-to-fine search. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43(12): 2429-2439 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dianzixb201512013 [11] 田瑾.高维多峰函数的量子行为粒子群优化算法改进研究.控制与决策, 2016, 31(11): 1967-1972 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201611006Tian Jin. Improvement of quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm for high-dimensional and multi-modal function. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(11): 1967-1972 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201611006 [12] Lee K S, Geem Z W. A new meta-heuristic algorithm for continuous engineering optimization: harmony search theory and practice. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 194(36-38): 3902-3933 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cf8b4b943f7d683011d8b80fe90e576f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] 崔晓晖, 印桂生, 董红斌.面向服务匹配问题的协同演化算法.软件学报, 2015, 26(7): 1601-1614 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb201507004Cui Xiao-Hui, Yin Gui-Sheng, Dong Hong-Bin. Co-evolutionary algorithm for web service matching. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(7): 1601-1614 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb201507004 [14] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb200904014 [15] 王艳芬, 丛潇雨, 孙彦景.一种稀疏度自适应超宽带信道估计算法.电子科技大学学报, 2017, 46(3): 498-504 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjdxxb201703004Wang Yan-Fen, Cong Xiao-Yu, Sun Yan-Jing. Sparsity adaptive algorithm for ultra-wideband channel estimation. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017, 46(3): 498-504 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjdxxb201703004 [16] 杨成, 冯巍, 冯辉, 杨涛, 胡波.一种压缩采样中的稀疏度自适应子空间追踪算法.电子学报, 2010, 38(8): 1914-1917 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dianzixb201008032Yang Cheng, Feng Wei, Feng Hui, Yang Tao, Hu Bo. A sparsity adaptive subspace pursuit algorithm for compressive sampling. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(8): 1914-1917 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dianzixb201008032 [17] Candés E J, Wakin M B. An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21-30 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f038caf0ee508db10a5b5fd193679bc2 [18] 方红, 杨海蓉.贪婪算法与压缩感知理论.自动化学报, 2011, 37(12): 1413-1421 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.01413Fang Hong, Yang Hai-Rong. Greedy algorithms and compressed sensing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(12): 1413-1421 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.01413 [19] Jing M L, Zhou X Q, Qi C. Quasi-newton iterative projection algorithm for sparse recovery. Neurocomputing, 2014, 144: 169-173 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=931bdad879f0a11b0d9e3465eb736397 [20] Wu T Q, Yao M, Yang J H. Dolphin swarm algorithm. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2016, 17(8): 717-729 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjdxxbc-e201608001 [21] 薛俊杰, 王瑛, 李浩, 肖吉阳.一种狼群智能算法及收敛性分析.控制与决策, 2016, 31(12): 2131-2139 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201612003Xue Jun-Jie, Wang Ying, Li Hao, Xiao Ji-Yang. A smart wolf pack algorithm and its convergence analysis. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(12): 2131-2139 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201612003 [22] 刘盼盼, 李雷, 王浩宇.压缩感知中基于变尺度法的贪婪重构算法的研究.通信学报, 2014, 35(12): 98-105 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/txxb201412012Liu Pan-Pan, Li Lei, Wang Hao-Yu. Research on greedy reconstruction algorithms of compressed sensing based on variable metric method. Journal on Communications, 2014, 35(12): 98-105 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/txxb201412012 [23] Dai W, Milenkovic O. Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(5): 2230-2249 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_0803.0811 [24] Sun B, Shan X, Wu K, Xiao Y. Anomaly detection based secure in-network aggregation for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 2013, 7(1): 13-25 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=79912c1f6f0509917d4454d2752aa4a4 -




 下载:
下载: