-
摘要:
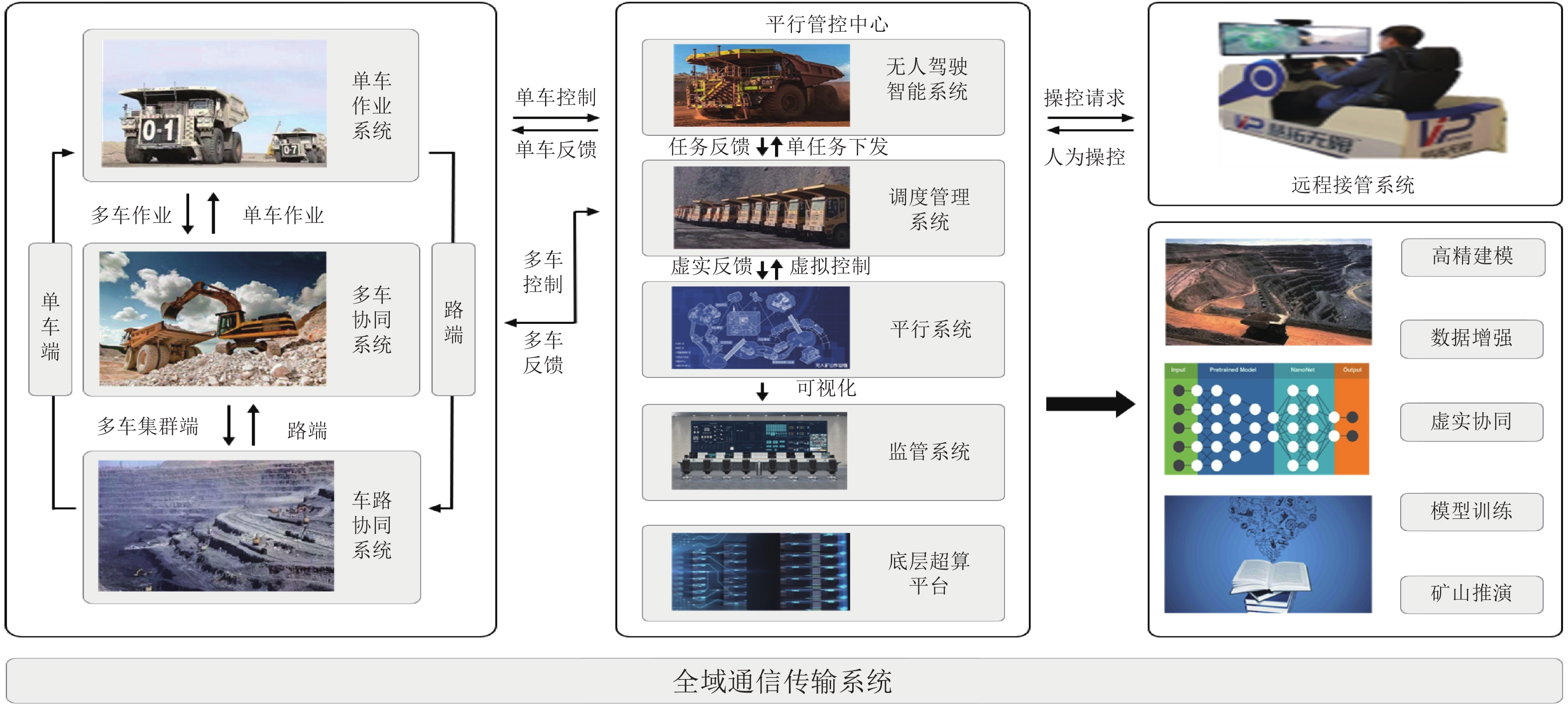
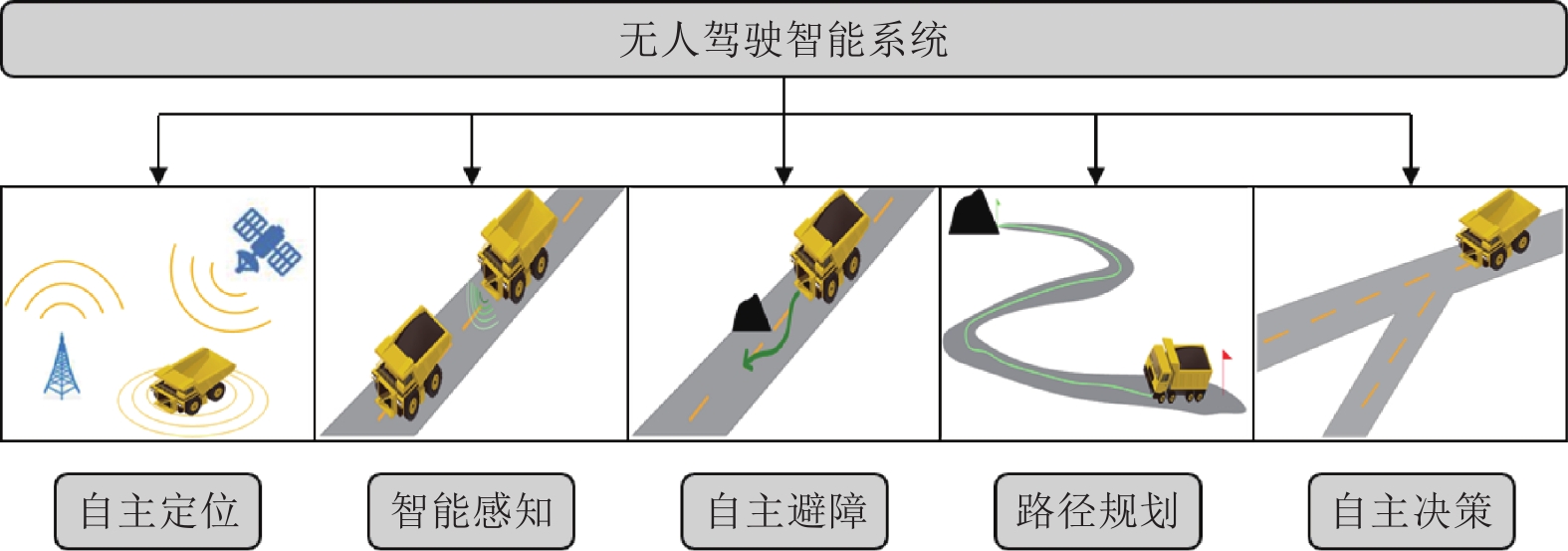
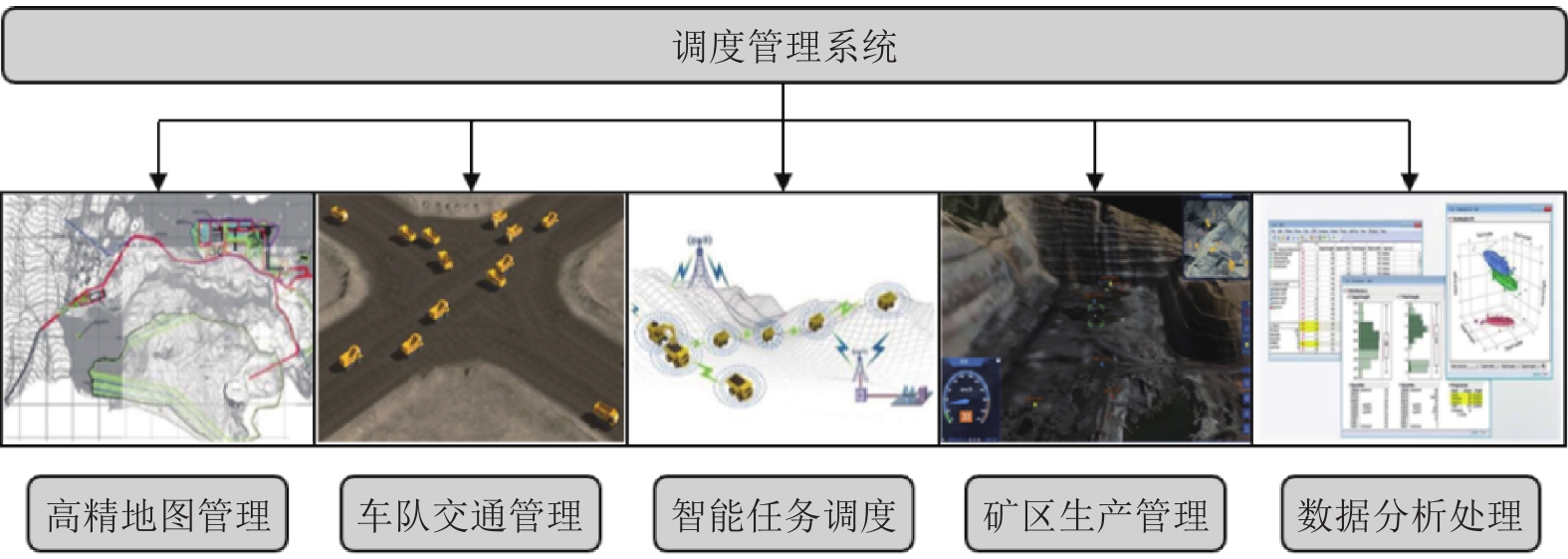
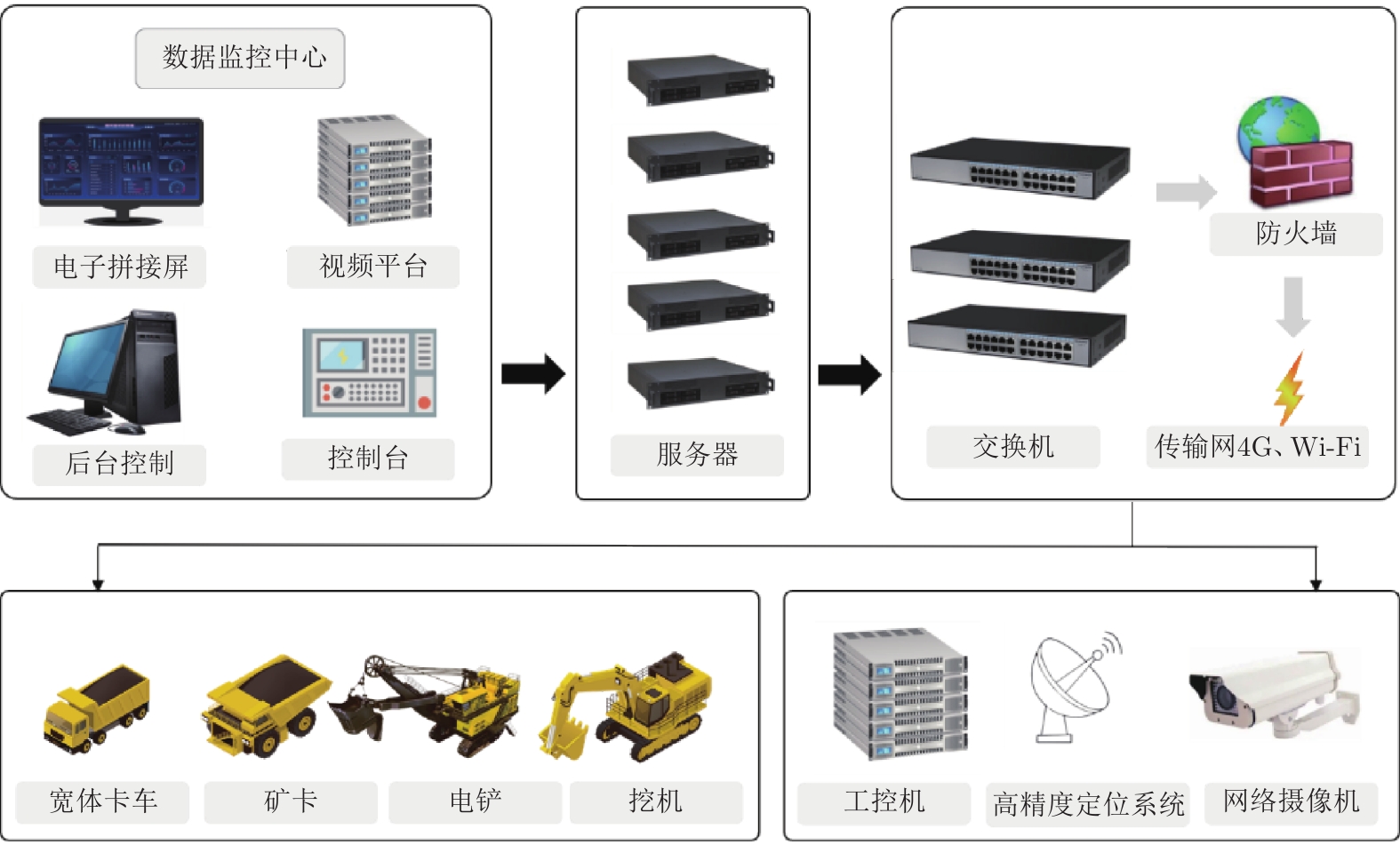
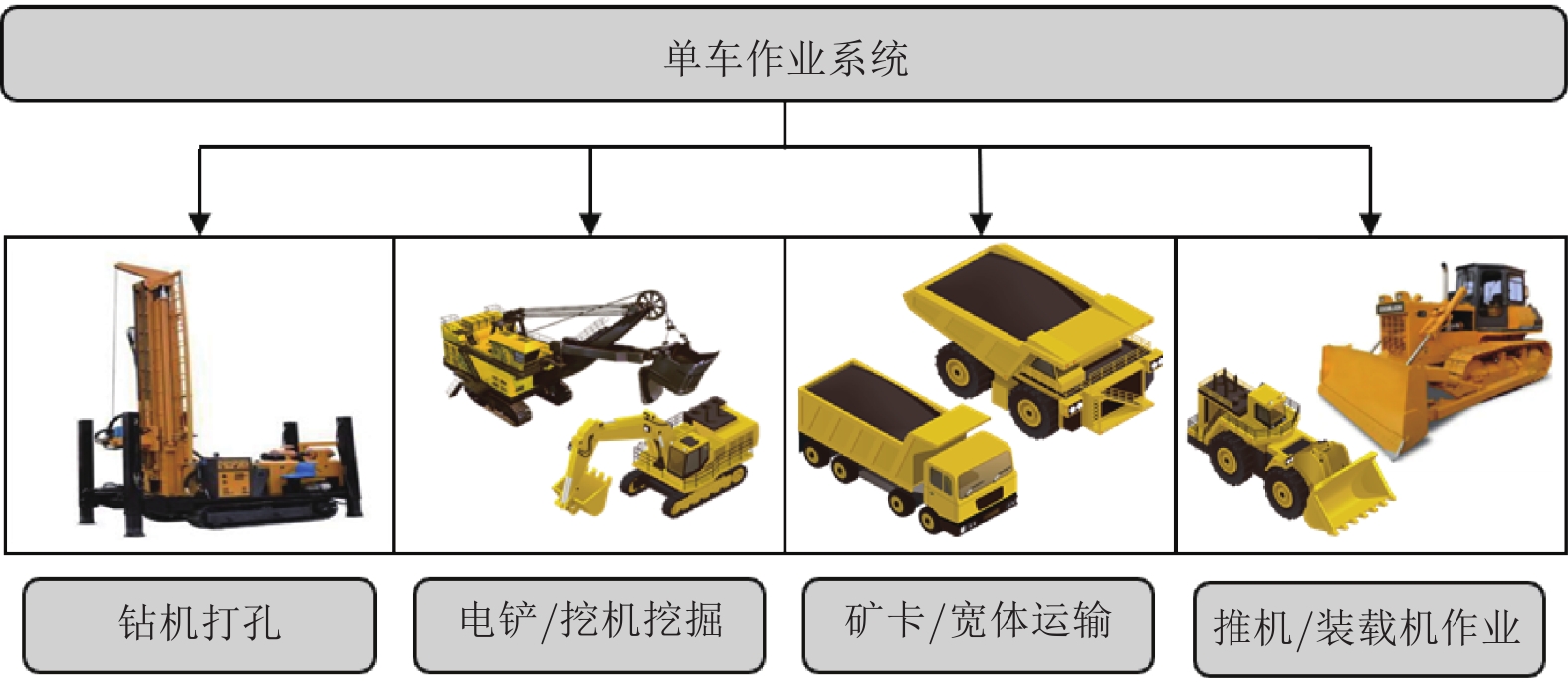
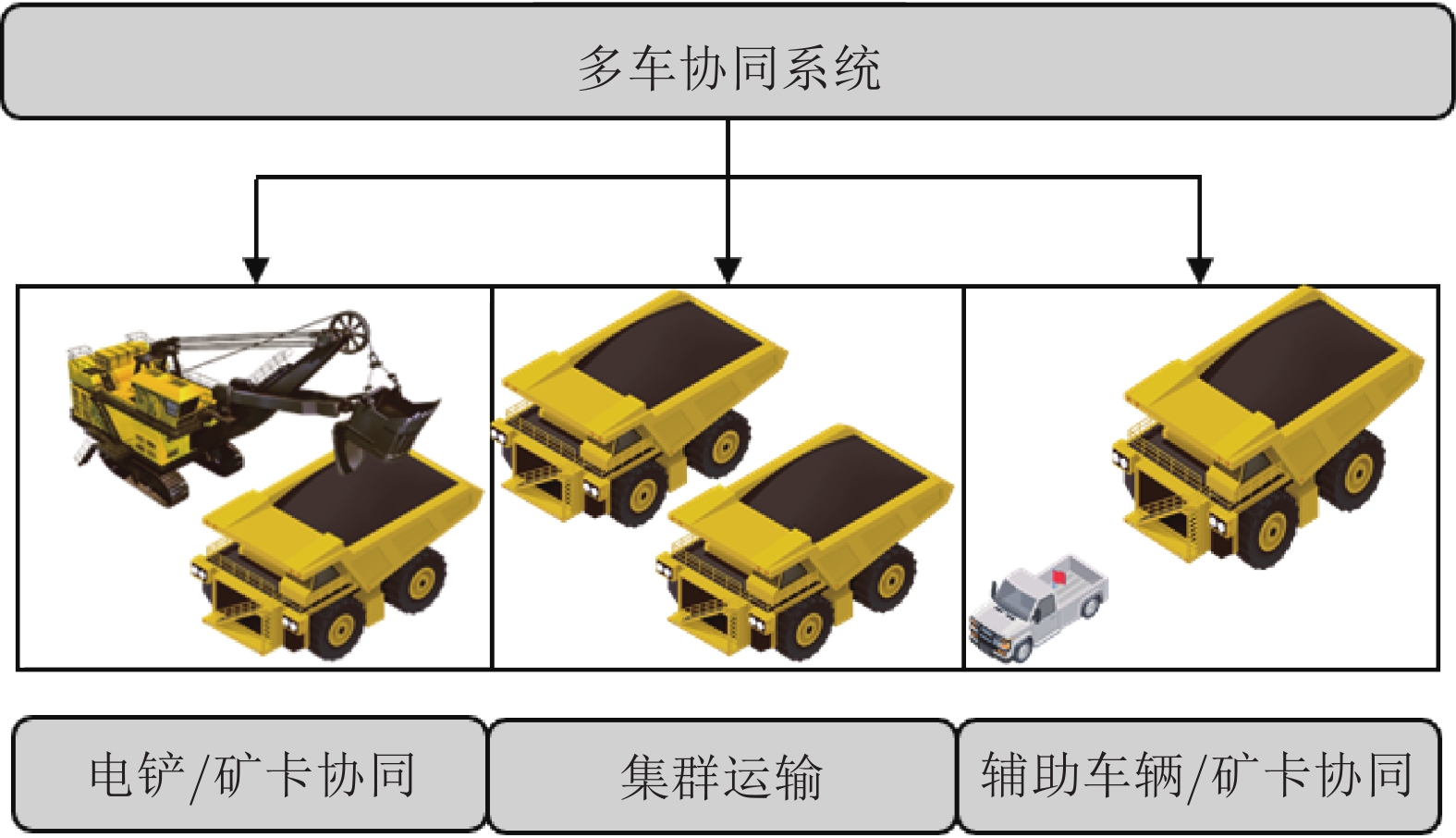
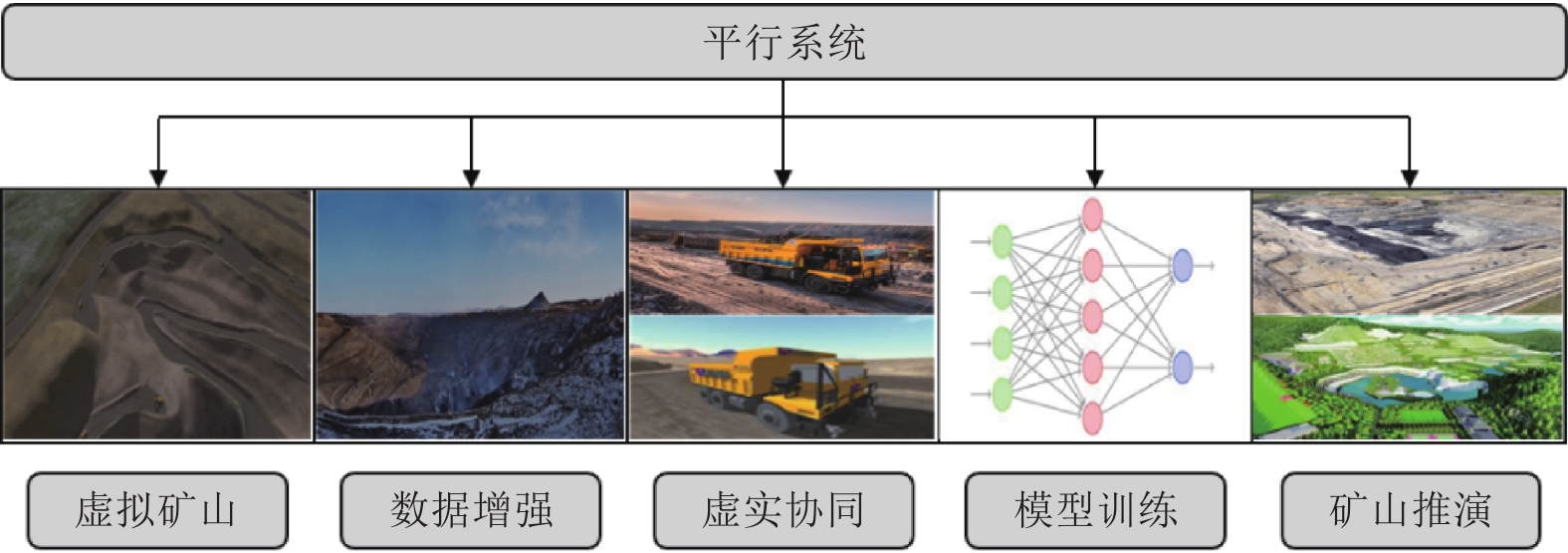
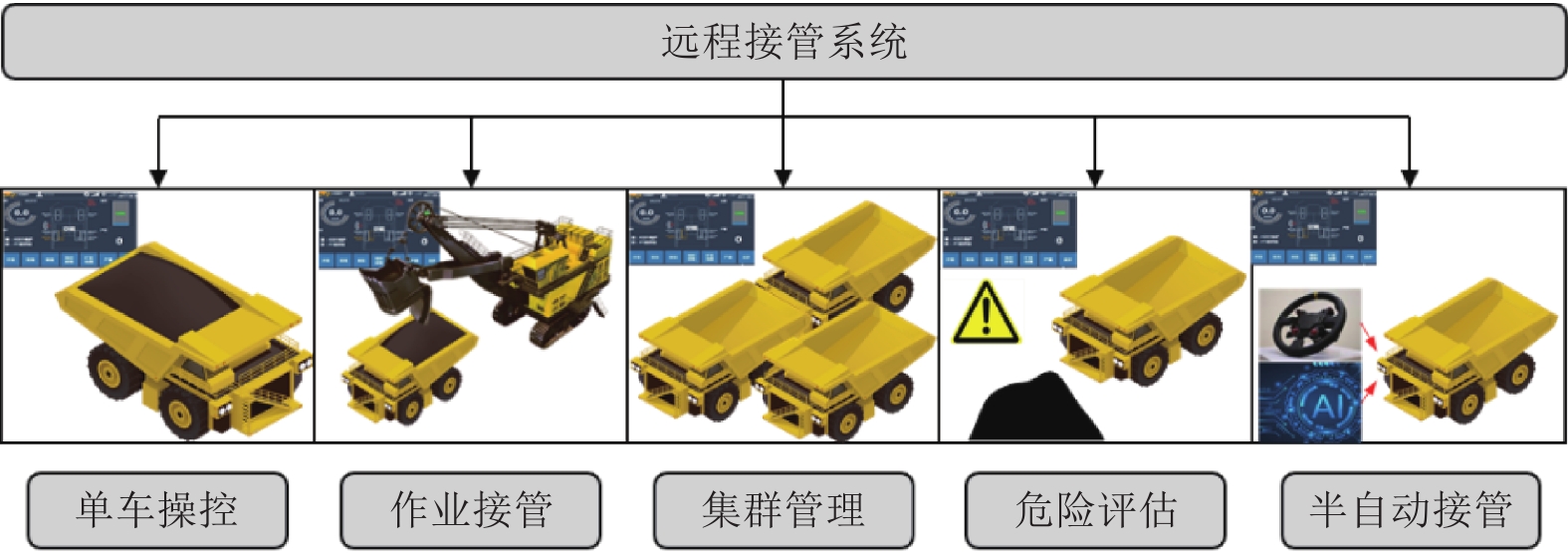
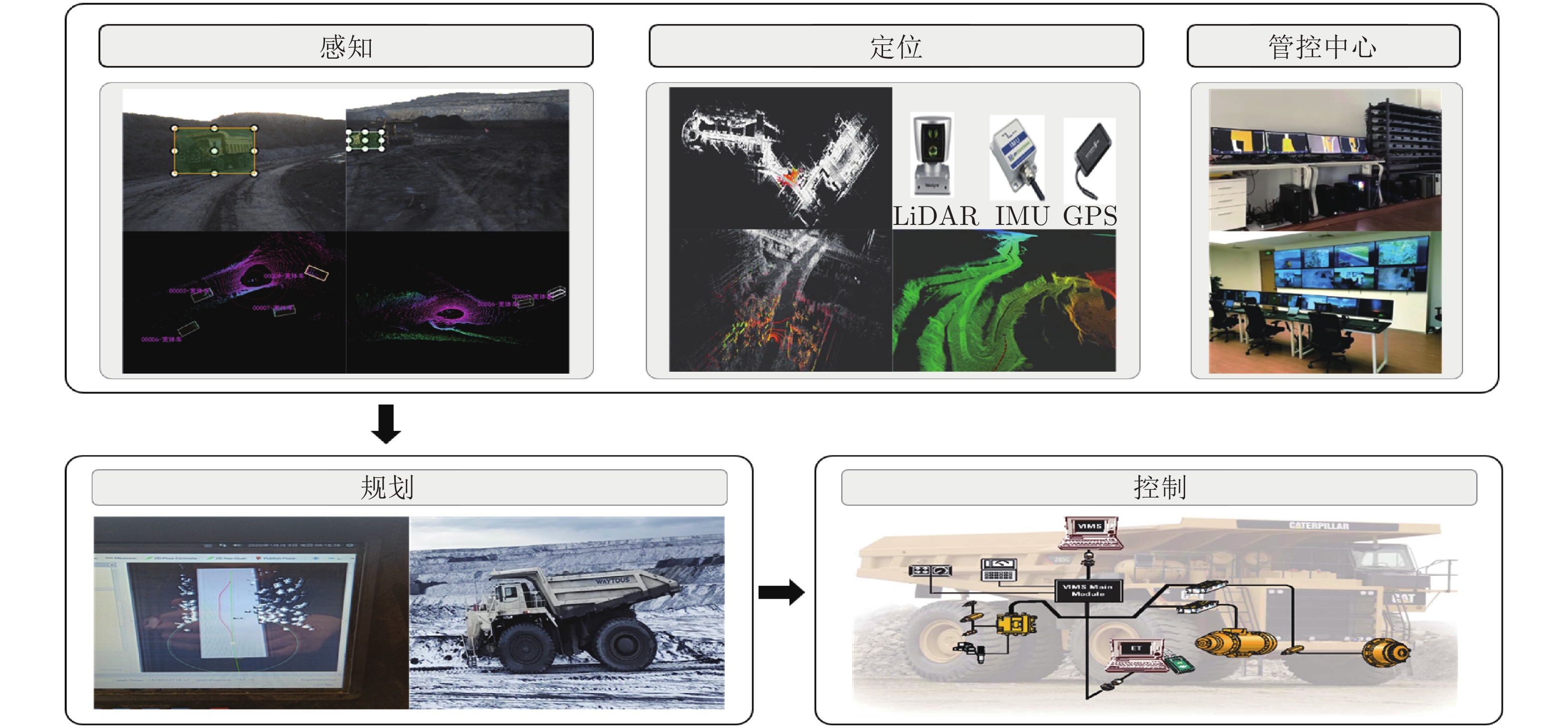
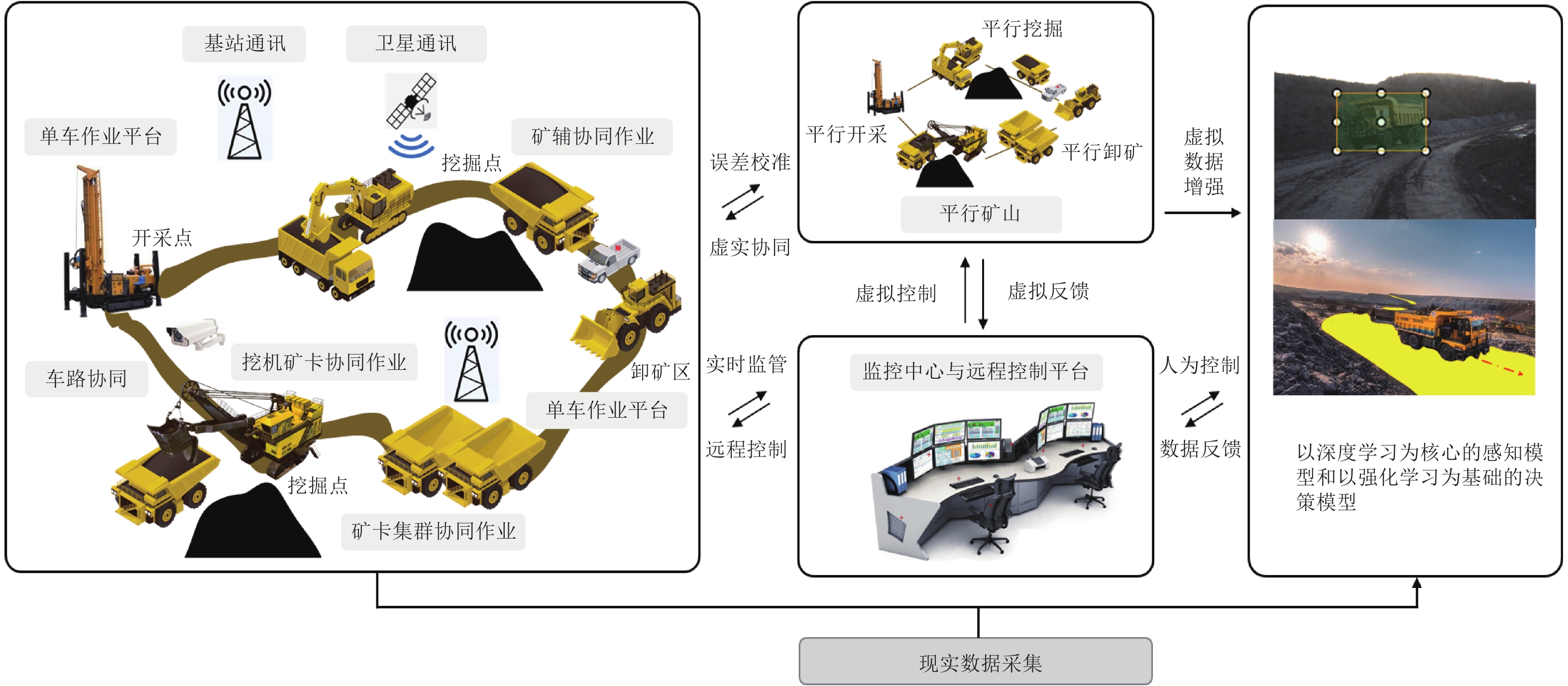
针对新时代下我国矿区智能化发展诉求与矿山无人化进程中遇到的复现难、协同难的技术问题, 本文融合智慧矿山理念、ACP (Artificial societies + computational experiments + parallel execution)平行智能理论和新一代智能技术, 设计并实现了智慧矿山操作系统 (Intelligent mine operation system, IMOS), 为平行矿山智能管理与控制一体化提出了解决方案. 本文首先分析露天煤矿产业发展趋势; 国内外露天矿山智能化发展情况; 面向露天矿山无人化与智能化需求, 深度融合数字四胞胎理论, 设计了虚实融合的IMOS架构; 详细阐述了IMOS子系统架构与功能, 包括: 单车作业系统、多车协同系统、车路协同系统、无人驾驶智能系统、调度管理系统、平行系统、监管系统、远程接管系统和通信系统; 并探讨了IMOS关键技术, 即平行矿山仿真建模技术、无人驾驶技术、矿区通信技术和协同作业技术. 该操作系统是国内首套露天矿山无人化与智能化的一体化解决方案, 并能够迁移到不同矿区不同作业场景, 推动矿区智能化无人化发展, 减少人工干预从而降低安全风险, 大幅度降低人工成本, 提高生产作业效率, 并可结合社会发展要素为实现绿色可持续发展矿区提供支撑.
Abstract:In view of the development of coal mine industries in China, the requests to unmanned mines are urgently and immediately. In this paper, the parallel management and control of mining operating infrastructure that integrates the smart mine theories, the ACP (artificial societies + computational experiments + parallel execution) based parallel intelligence approaches and the new generation of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies (including data fusion, knowledge graph, edge computing, etc.) is proposed. The intelligent mine operation system (IMOS) that realizes parallel mining is designed. This paper analyzes the development trends of open-pit coal mines industries, the stages of current researches on intelligentization of open-pit mines at home and abroad, and deeply integrates with digital quadruple theory to design the IMOS architecture. Besides, the IMOS subsystems are introduced in details, including: the single-vehicle operating subsystem, multi-vehicle collaboration subsystem, vehicle-road collaboration subsystem, unmanned intelligent subsystem, dispatch management subsystem, parallel management and control subsystem, supervisory subsystem, remote takeover subsystem and communication subsystem; and the key technologies in IMOS are discussed. The smart mine operating system presented in this paper is the first systemic integrative solution for unmanned and intelligent mine, which covered all scenarios in open-pit mine intelligence, and taking social development factors as the measurement for mining area sustainable development.
1) 收稿日期 2020-11-08 录用日期 2021-03-12 Manuscript received November 8, 2020; accepted March 12, 2021 广东省重点领域研发计划 (2020B090921003), 英特尔智能网联汽车大学合作研究中心项目 ( “ICRI-IACV”)资助 Supported by Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2020B090921003) and Intel Collaborative Research Institute for Intelligent and Automated Connected Vehicles ( “ICRI-IACV”) 本文责任编委 孙长银 Recommended by Associate Editor SUN Chang-Yin 1. 中国科学院自动化研究所复杂系统管理与控制国家重点实验室 北京 100190 中国 2. 中山大学计算机学院 广州 510006 中国3. 青岛慧拓智能机器有限公司 青岛 266109 中国 4. 青岛智能产业技术研究院 青岛 266109 中国 5. 中国矿业大学 (北京) 北京 100083 中国 6. 中国科学院大学人工智能学院 北京 100049 中2) 国 7. 吉林大学计算机科学与技术学院 长春 130012 中国 8. 滑铁卢大学机械与机电工程系 滑铁卢 ON N2L 3G1 加拿大 1. State Key Laboratory for Management and Control of Systems, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China 2. School of Data and Computer Science,Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China 3. Vehicle Intelligence Pioneers, Inc., Qingdao 266109, China 4. Qingdao Academy of Intelligent Industries, Qingdao 266109, China 5. Chi- na University of Mining and Technology−Beijing, Beijing 100083, China 6. School of Artificial Intelligence, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China 7. College of Com-puter Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China 8. Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo ON N2L 3G1, Canada -
[1] 王国法, 任怀伟, 庞义辉, 曹现刚, 赵国瑞, 陈洪月, 等. 煤矿智能化(初级阶段)技术体系研究与工程进展. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(7): 1−27Wang Guo-Fa, Ren Huai-Wei, Pang Yi-Hui, Cao Xian-Gang, Zhao Guo-Rui, Chen Hong-Yue, et al. Research and engineering progress of intelligent coal mine technical system in early stages. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(7): 1−27 [2] 王国法, 徐亚军, 张金虎, 张坤, 马英, 陈洪月. 煤矿智能化开采新进展. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(1): 1−10Wang Guo-Fa, Xu Ya-Jun, Zhang Jing-Hu, Zhang Kun, Ma Ying, Chen Hong-Yue. New development of intelligent mining in coal mines. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(1): 1−10 [3] 张帆, 葛世荣, 李闯. 智慧矿山数字孪生技术研究综述. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(7): 168−176Zhang Fan, Ge Shi-Rong, Li Chuang. Research summary on digital twin technology for smart mines. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(7): 168−176 [4] 葛世荣, 张帆, 王世博, 王忠宾. 数字孪生智采工作面技术架构研究. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(6): 1925−1936Ge Shi-Rong, Zhang Fan, Wang Shi-Bo, Wang Zhong-Bin. Digital twin for smart coal mining workface: Technological frame and construction. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(6): 1925−1936 [5] 吴群英, 蒋林, 王国法, 叶鸥, 蒋泽军, 董立红, 等. 智慧矿山顶层架构设计及其关键技术. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(7): 80−91Wu Qun-Ying, Jiang Lin, Wang Guo-Fa, Ye Ou, Jiang Ze-Jun, Dong Li-Hong, et al. Top-level architecture design and key technologies of smart mine. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(7): 80−91 [6] Ren S L, Tao Z G, He M C, Pang S H, Li M N, Xu H T. Stability analysis of open-pit gold mine slopes and optimization of mining scheme in Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Mountain Science, 2020, 17(12): 2997−3011 doi: 10.1007/s11629-020-6217-x [7] Wang F-Y, Saridis G N. A coordination theory for intelligent machines. Automatica, 1990, 26(5): 833−844 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(90)90001-X [8] Wang F-Y, Kyriakopoulos K J, Tsolkas A, Saridis G N. A petri-net coordination model for an intelligent mobile robot. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1991, 21(4): 777−789 doi: 10.1109/21.108296 [9] Schooley L C, Zeigler B P, Cellier F E, Wang F-Y. High-autonomy control of space resource processing plants. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 1993, 13(3): 29−39 doi: 10.1109/37.214942 [10] Lever P, Wang F-Y, Shi X B. An intelligent task control system for dynamic mining environments. AIME Transactions on Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration, 1994, 174(1): 165−174 [11] Wang F-Y. Shadow Systems: A New Concept for Nested and Embedded Co-Simulation for Intelligent Systems. University of Arizona, USA, 1994. [12] Wang F-Y, Marefat M, Lever P J A, Schooley L. An intelligent robotic vehicle for Lunar/Martian applications. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Engineering, Construction, and Operations in Space. Albuquerque, NM, 1994. [13] Lever P J A, Wang F-Y, Chen D Q. A fuzzy control system for an automated mining excavator. In: Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 1994. 3284−3289 [14] Shi X B, Wang F-Y, Lever P J A. Experimental results of robotic excavation using fuzzy behavior control. Control Engineering Practice, 1996, 4(2): 145−152 doi: 10.1016/0967-0661(95)00220-0 [15] Shi X B, Lever P J A, Wang F-Y. Fuzzy behavior integration and action fusion for robotic excavation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1996, 43(3): 395−402 doi: 10.1109/41.499812 [16] Wu L, Xu Y, Wang F-Y, Lin Y, Li P, Liu W. Supervised learning of longitudinal driving behavior for intelligent vehicles using Neuro-Fuzzy networks: Initial experimental results. International Journal of Intelligent Control and Systems, 1999, 3(4): 443−464 [17] Wang F-Y, Huang Z Y, Chen D D, Lever P. Refinement and generation of decision rules through training and augmentation of neural networks. International Journal of Intelligent Control and Systems, 1998, 2(3): 329−360 [18] Wang F-Y. ABCS: Agent-Based Control Systems, in SIE Working Paper. Tucson, AZ: Univ. Arizona, 1998. [19] Wang F-Y. aDCS: Agent-Based Distributed Control Systems, Univ. Arizona, Tucson, AZ, PARCS Tech. Rep., 1999. [20] Wu Q L, Wang F-Y, Lin Y T. A mobile-agent based distributed intelligent control system architecture for home automation. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. e-Systems and e-Man for Cybernetics in Cyberspace (Cat. No. 01CH37236). Tucson, AZ, USA: IEEE, 2001. 1648−1653 [21] Wang F-Y. Agent-based control for fuzzy behavior programming in robotic excavation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2004, 12(4): 540−548 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2004.832522 [22] Wang F-Y. Agent-based control for networked traffic management systems. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2005, 20(5): 92−96 doi: 10.1109/MIS.2005.80 [23] Shi X B, Lever P J A, Wang F-Y. Autonomous Rock Excavation: Intelligent Control Techniques and Experimentation. River Edge, NJ, USA: World Scientific Publishing Co., 1998. [24] Li L, Wang F-Y. Advanced Motion Control and Sensing for Intelligent Vehicles. Boston, MA, USA: Springer, 2007. [25] 王飞跃. 平行系统方法与复杂系统的管理和控制. 控制与决策, 2004, 19(5): 485−489, 514 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2004.05.002Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel system methods for management and control of complex systems. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(5): 485−489, 514 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2004.05.002 [26] 王飞跃. 平行驾驶与平行矿山: 智慧矿业的系统智能基础. 青岛智能产业技术研究院报告, 2017.Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel Driving and Parallel Mining: Systems Intelligence for Smart Mining Industries. QAII Technical Report, 2017. [27] 王飞跃. 关于复杂系统研究的计算理论与方法. 中国基础科学, 2004, 6(5): 3−10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2004.05.001Wang Fei-Yue. Computational theory and method on complex system. China Basic Science, 2004, 6(5): 3−10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2004.05.001 [28] 王飞跃. 人工社会、计算实验、平行系统——关于复杂社会经济系统计算研究的讨论. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2004, 1(4): 25−35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.04.002Wang Fei-Yue. Artificial societies, computational experiments, and parallel systems: A discussion on computational theory of complex social-economic systems. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2004, 1(4): 25−35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.04.002 [29] Wang F-Y. Parallel control and management for intelligent transportation systems: Concepts, architectures, and applications. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2010, 11(3): 630−638 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2010.2060218 [30] 王飞跃. 系统软件化与系统工程5.0: 社会物理网络系统+平行系统+软件定义的系统. 复杂性与智能化, 2015, 10(3): 4−5Wang Fei-Yue. Systems softwarization and systems 5.0: Cyber physical social systems + parallel systems + software defined systems. Complexity and Intelligence, 2015, 10(3): 4−5 [31] Wang F-Y. The emergence of intelligent enterprises: From CPS to CPSS. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2010, 25(4): 85−88 doi: 10.1109/MIS.2010.104 [32] 熊刚, 王飞跃, 侯家琛, 董西松, 张家麟, 付满昌. 提高核电站安全可靠性的平行系统方法. 系统工程理论与实践, 2012, 32(5): 1018−1026 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2012.05.014Xiong Gang, Wang Fei-Yue, Hou Jia-Chen, Dong Xi-Song, Zhang Jia-Lin, Fu Man-Chang. To improve safety and reliability of nuclear power plant with parallel system method. Systems Engineering-Theory and Practice, 2012, 32(5): 1018−1026 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2012.05.014 [33] 王坤峰, 苟超, 王飞跃. 平行视觉: 基于ACP的智能视觉计算方法. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1490−1500Wang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel vision: An ACP-based approach to intelligent vision computing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1490−1500 [34] 杨柳青, 王飞跃, 张艳丽, 韩双双, 杨坚, 赵恺, 等. 基于ACP方法的城市平行停车系统. 指挥与控制学报, 2015, 1(4): 384−390Yang Liu-Qing, Wang Fei-Yue, Zhang Yan-Li, Han Shuang-Shuang, Yang Jian, Zhao Kai, et al. The urban parallel parking system based on ACP approach. Journal of Command and Control, 2015, 1(4): 384−390 [35] 王飞跃. 平行控制: 数据驱动的计算控制方法. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 293−302Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel control: A method for data-driven and computational control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 293−302 [36] 袁勇, 王飞跃. 平行区块链: 概念、方法与内涵解析. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(10): 1703−1712Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel blockchain: Concept, methods and issues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10): 1703−1712 [37] Gao Y Q, Wang F-Y, Sun W P, Dong X S, Liu X W, Li S S. A CDIO-based social manufacturing laboratory: Prototype for CPSS-based production processes. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Annual Conference and Exposition. New Orleans, LA, USA: ASEE, 2016. 1−11 [38] Wang F-Y, Zheng N N, Cao D P, Martinez C M, Li L, Liu T. Parallel driving in CPSS: A unified approach for transport automation and vehicle intelligence. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(4): 577−587 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510598 [39] 王飞跃, 汤淑明. 人工交通系统的基本思想与框架体系. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2004, 1(2): 52−59 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.02.008Wang Fei-Yue, Tang Shu-Ming. Concepts and frameworks of artificial transportation systems. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2004, 1(2): 52−59 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.02.008 [40] Zheng X L, Zeng D, Li H Q, Wang F-Y. Analyzing open-source software systems as complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2008, 387(24): 6190−6200 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2008.06.050 [41] Li L, Wang X, Wang K F, Lin Y L, Xin J M, Chen L, et al. Parallel testing of vehicle intelligence via virtual-real interaction. Science Robotics, 2019, 4(28): eaaw4106 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aaw4106 [42] Chen L, Wang Q, Lu X K, Cao D P, Wang F-Y. Learning driving models from parallel end-to-end driving data set. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(2): 262−273 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2952735 [43] 王飞跃, 王艳芬, 陈薏竹, 田永林, 齐红威, 王晓, 等. 联邦生态: 从联邦数据到联邦智能. 智能科学与技术学报, 2020, 2(4): 305−313Wang Fei-Yue, Wang Yan-Fen, Chen Yi-Zhu, Tian Yong-Lin, Qi Hong-Wei, Wang Xiao, et al. Federated ecology: From federated data to federated intelligence. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2020, 2(4): 305−313 [44] Li L, Lin Y L, Zheng N N, Wang F-Y. Parallel learning: A perspective and a framework. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(3): 389−395 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510493 [45] Xing Y, Lv C, Wang H J, Cao D P, Velenis E, Wang F-Y. Driver activity recognition for intelligent vehicles: A deep learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5379−5390 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2908425 [46] Lu J W, Wei Q L, Wang F-Y. Parallel control for optimal tracking via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(6): 1662−1674 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003426 [47] Wei Q L, Li H Y, Wang F-Y. Parallel control for continuous-time linear systems: A case study. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(4): 919−928 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003216 [48] Wang F-Y, Zheng N N, Li L, Xin J M, Wang X, Xu L H, et al. China’s 12-year quest of autonomous vehicular intelligence: The intelligent vehicles future challenge program. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2021, 13(2): 6−19 doi: 10.1109/MITS.2021.3058623 [49] Chen L, Hu X M, Tang B, Cheng Y. Conditional DQN-based motion planning with fuzzy logic for autonomous driving. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3025671 [50] Li J G, Zhan K. Intelligent mining technology for an underground metal mine based on unmanned equipment. Engineering, 2018, 4(3): 381−391 doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2018.05.013 [51] Guo H X, Zhu K J, Ding C, Li L L. Intelligent optimization for project scheduling of the first mining face in coal mining. Expert Systems with Applications, 2010, 37(2): 1294−1301 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2009.06.025 [52] Lilic N, Obradovic I, Cvjetic A. An intelligent hybrid system for surface coal mine safety analysis. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2010, 23(4): 453−462 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2010.01.025 [53] Song D D, Ren Z H, Gu Y X. Design and implement of an intelligent coal mine monitoring system. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Electronic Measurement and Instruments. Xi' an, China: IEEE, 2007. 4-849−4-852 [54] Zhang Z R, Liu G Q, Bai X S, Yang G L. Research on intelligent control of the dust in coal mining. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 482-484: 1805−1808 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.482-484.1805 [55] Ghasemi E, Ataei M, Shahriar K. An intelligent approach to predict pillar sizing in designing room and pillar coal mines. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2014, 65: 86−95 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.11.009 [56] Zhou T P. Application of data mining in coal mine safety decision system based on rough set. In: Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Intelligent Computing. Huangshan, China: Springer, 2012. 34−41 [57] Wang D H, Shi Y N, Chen W B. Design of coal mining roof pressure monitoring system based on Labview. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 488−489: 1019−1022 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.488-489.1019 [58] Zhang Y H, Fu G H, Zhao Z G, Huang Z A, Li H C, Yang J X. Discussion on application of IOT technology in coal mine safety supervision. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 43: 233−237 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.08.040 [59] Gao Y, Ai Y F, Tian B, Chen L, Wang J, Cao D P, et al. Parallel end-to-end autonomous mining: An IoT-oriented approach. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(2): 1011−1023 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2948470 [60] 刘腾, 王晓, 邢阳, 高玉, 田滨, 陈龙. 基于数字四胞胎的平行驾驶系统及应用. 智能科学与技术学报, 2019, 1(1): 40−51 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-6652.201902Liu Teng, Wang Xiao, Xing Yang, Gao Yu, Tian Bin, Chen Long. Research on digital quadruplets in cyber-physical-social space-based parallel driving. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2019, 1(1): 40−51 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-6652.201902 [61] 杨超, 高玉, 艾云峰, 田滨, 陈龙, 王健, 等. 端对端平行无人矿山系统及其关键技术. 智能科学与技术学报, 2019, 1(3): 228−240Yang Chao, Gao Yu, Ai Yun-Feng, Tian Bin, Chen Long, Wang Jian, et al. End-to-end parallel autonomous mining systems and key technologies. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2019, 1(3): 228−240 [62] 王晓, 要婷婷, 韩双双, 曹东璞, 王飞跃. 平行车联网: 基于ACP的智能车辆网联管理与控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(8): 1391−1404Wang Xiao, Yao Ting-Ting, Han Shuang-Shuang, Cao Dong-Pu, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel internet of vehicles: The ACP-based networked management and control for intelligent vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(8): 1391−1404 [63] Liu T, Wang H, Tian B, Ai Y F, Chen L. Parallel distance: A new paradigm of measurement for parallel driving. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(4): 1169−1178 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911633 [64] Liu T, Tian B, Ai Y F, Wang F-Y. Parallel reinforcement learning-based energy efficiency improvement for a cyber-physical system. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(2): 617−626 [65] 杨林瑶, 陈思远, 王晓, 张俊, 王成红. 数字孪生与平行系统: 发展现状、对比及展望. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2001−2031Yang Lin-Yao, Chen Si-Yuan, Wang Xiao, Zhang Jun, Wang Cheng-Hong. Digital twins and parallel systems: State of the art, comparisons and prospect. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2001−2031 [66] 沈宇, 王晓, 韩双双, 陈龙, 王飞跃. 代理技术Agent在智能车辆与驾驶中的应用现状. 指挥与控制学报, 2019, 5(2): 87−98 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2019.02.0087Shen Yu, Wang Xiao, Han Shuang-Shuang, Chen Long, Wang Fei-Yue. Agent-based technology in intelligent vehicles and driving: State-of-the-art and prospect. Journal of Command and Control, 2019, 5(2): 87−98 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2019.02.0087 [67] 段伟. 平行仿真的内涵、发展与应用. 指挥与控制学报, 2019, 5(2): 82−86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2019.02.0082Duan Wei. Parallel simulation: Motivation, concept and application. Journal of Command and Control, 2019, 5(2): 82−86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2019.02.0082 [68] 刘昕, 王晓, 张卫山, 汪建基, 王飞跃. 平行数据: 从大数据到数据智能. 模式识别与人工智能, 2017, 30(8): 673−681Liu Xin, Wang Xiao, Zhang Wei-Shan, Wang Jian-Ji, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel data: From big data to data intelligence. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2017, 30(8): 673−681 [69] Chen L, Fan L, Xie G D, Huang K, Nuchter A. Moving-object detection from consecutive stereo pairs using slanted plane smoothing. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(11): 3093−3102 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2680538 [70] Zhao Z Q, Zheng P, Xu S T, Wu X D. Object detection with deep learning: A review. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(11): 3212−3232 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2876865 [71] Chen L, Zhan W J, Tian W, He Y H, Zou Q. Deep integration: A multi-label architecture for road scene recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(10): 4883−4898 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2913079 [72] Xing Y, Lv C, Wang H J, Wang H, Ai Y F, Cao D P, et al. Driver lane change intention inference for intelligent vehicles: Framework, survey, and challenges. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4377−4390 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2903299 [73] Xing Y, Tian B, Lv C, Cao D P. A two-stage learning framework for driver lane change intention inference. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(5): 638−643 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.04.204 -




 下载:
下载: