Robust Regularized RVFLNs Modeling of Molten Iron Quality in Blast Furnace Ironmaking
-
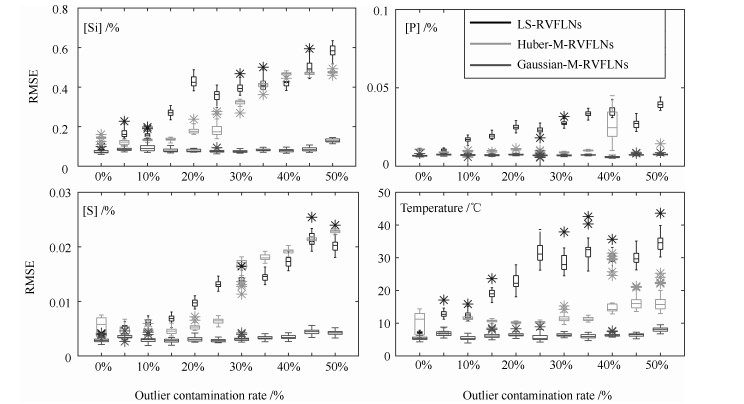
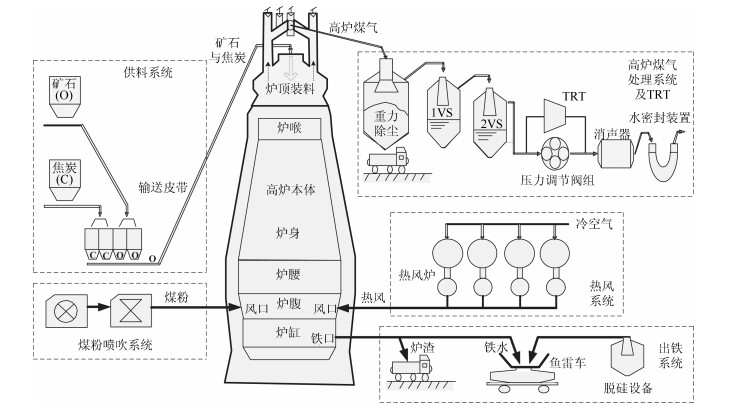
摘要: 高炉炼铁过程运行优化与控制依赖于可靠、稳定的难测铁水质量(Molten iron quality, MIQ)指标模型.针对现有MIQ建模方法的不足, 本文提出一种新型的数据驱动鲁棒正则化随机权神经网络(Random vector functional-link networks, RVFLNs)算法, 用于实现MIQ指标在线估计的鲁棒建模.首先, 为了提高建模效率和降低计算复杂度, 采用数据驱动典型相关性分析方法从众多变量中提取与MIQ相关性最强的变量作为建模输入变量; 其次, 由于传统RVFLNs网络的输出权值由最小二乘估计获得, 易受离群数据影响而鲁棒性差, 引入基于Gaussian分布加权的M估计技术, 提出新型鲁棒RVFLNs算法建立多元MIQ指标的鲁棒模型; 同时, 在鲁棒加权后的最小二乘损失函数基础上, 进一步引入${L_1}$和${L_2}$两个正则化项以构成优化目标函数的Elastic net, 用于稀疏化RVFLNs网络的输出权值矩阵, 解决RVFLNs网络多重共线性和过拟合的问题.最后, 基于某大型高炉工业数据, 进行充分数据实验, 结果表明所提方法具有更高的建模与估计精度以及较强的鲁棒性能.
-
关键词:
- RVFLNs /
- 鲁棒建模 /
- Gaussian分布加权M估计 /
- 高炉炼铁 /
- 铁水质量
Abstract: Optimal operation and control of a practical blast furnace (BF) ironmaking process depend largely on a reliable model of molten iron quality (MIQ) indices that can not be measured online. Aiming at the shortcomings of the existing MIQ modeling methods, a new data-driven robust regularized random vector functional-link networks (RVFLNs) algorithm is proposed to realize robust modeling of MIQ indices. First, to improve modeling efficiency and reduce computational complexity, the data-driven canonical correlation analysis (CCA) is employed to identify the most influential components from multitudinous factors that affect the MIQ indices to serve as the input variables. Next, since the output weights of traditional RVFLNs are obtained by the least squares approach, the robustness may decrease when the training dataset is contaminated with outliers. To solve this problem, the robust RVFLNs model of MIQ using Gaussian distribution weighted M-estimation is established. Simultaneously, on the basis of the least-square loss function of the robustness, the ${L_1}$ regularization and ${L_2}$ regularization are introduced to achieve sparse output weight and prevent the overfitting and multicollinearity of the RVFLNs model by forming the Elastic net that optimizes the objective function. Finally, experiments using industrial data from a large balst furnace have demonstrated that the proposed method produces a higher modeling, estimating accuracy and stronger robustness than other modeling methods.-
Key words:
- Random vector functional-link networks (RVFLNs) /
- robust modeling /
- Gaussian distribution weighted M-estimator /
- blast furnace ironmaking /
- molten iron quality (MIQ)
1) 本文责任编委 贺威 -
表 1 典型相关系数的显著性检验
Table 1 Significance test of canonical correlation coefficient
典型变量 显著性检验指标 Wilk's Chi-SQ DF Sig. 1 0.337 299.701 72 0 2 0.527 176.485 51 0 3 0.754 77.786 32 0 4 0.958 11.678 15 0.703 表 2 高炉本体参数典型变量的标准化系数
Table 2 Standardized canonical coefficients of BF body variables
影响变量 典型变量 变量权值 1 2 3 4 冷风流量 14.821 2.609 $-3.502$ $-24.047$ 11.95769 送风比 $-0.669 $ 1.803 0.658 3.633 1.695912 热风压力 0.724 2.664 $-2.139$ -0.209 2.885878 压差 2.749 1.384 $ -0.527$ 2.382 2.655439 顶压富氧率 $-0.06$ $ -0.712$ 0.95 -0.022 0.865848 透气性 5.292 5.441 $-6.701$ 10.201 9.263463 阻力系数 0.801 0.268 $ -4.063$ 8.006 2.505639 热风温度 0.587 $-0.469$ $ -1.356$ $-0.268$ 1.23674 富氧流量 11.697 $ -4.429$ 0.07 1.748 9.493758 富氧率 -5.751 3.556 $ -4.229$ $-4.556$ 7.362393 设定喷煤量 $-0.931$ 3.284 4.027 $ -0.233$ 4.222921 鼓风湿度 0.533 0.805 1.932 $-0.465$ 1.654862 理论燃烧温度 $-3.408$ 2.774 5.055 1.685 5.906544 标准风速 $-2.222$ $ -0.705$ 2.385 6.454 2.824337 实际风速 $ -0.224 $ 0.023 0.55 $-0.767$ 0.401351 鼓风动能 $-1.85 $ $-1.067$ $-0.255$ $-0.002$ 1.815443 炉腹煤气量 $ -14.106 $ $-6.874$ 0.208 15.053 12.34763 炉腹煤气指数 0.292 0.651 $-0.006$ $ -0.198$ 0.535663 -
[1] 宋贺达, 周平, 王宏, 柴天佑.高炉炼铁过程多元铁水质量非线性子空间建模及应用.自动化学报, 2016, 42(11): 1664-1679 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150819Song He-Da, Zhou Ping, Wang Hong, Chai Tian-You. Nonlinear subspace modeling of multivariate molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(11): 1664-1679 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150819 [2] Zhou P, Guo D W, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven robust M-LS-SVR-based NARX modeling for estimation and control of molten iron quality indices in blast furnace ironmaking. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(9): 4007-4021 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2749412 [3] Gao C H, Jian L, Luo S H. Modeling of the thermal state change of blast furnace hearth with support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(2): 1134-1145 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2159693 [4] Kuang S B, Li Z Y, Yan D L, Qi Y H, Yu A B. Numerical study of hot charge operation in ironmaking blast furnace. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 63: 45-56 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2013.11.002 [5] 周平, 张丽, 李温鹏, 戴鹏, 柴天佑.集成自编码与PCA的高炉多元铁水质量随机权神经网络建模.自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1799-1811 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170299Zhou Ping, Zhang Li, Li Wen-Peng, Dai Peng, Chai Tian-You. Autoencoder and PCA based RVFLNs modeling for multivariate molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1799-1811 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170299 [6] Jian L, Gao C H, Xia Z H. Constructing multiple kernel learning framework for blast furnace automation. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2012, 9(4): 763-777 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2012.2211100 [7] Gao C H, Ge Q H, Jian L. Rule extraction from fuzzy-based blast furnace SVM multiclassifier for decision-making. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2014, 22(3): 586-596 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2269145 [8] 蒋朝辉, 董梦林, 桂卫华, 阳春华, 谢永芳.基于Bootstrap的高炉铁水硅含量二维预报.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 715-723 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150574Jiang Zhao-Hui, Dong Meng-Lin, Gui Wei-Hua, Yang Chun-Hua, Xie Yong-Fang. Two-dimensional prediction for silicon content of hot metal of blast furnace based on Bootstrap. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 715-723 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150574 [9] de Castro J A, Nogami H, Yagi J I. Three-dimensional multiphase mathematical modeling of the blast furnace based on the multifluid model. ISIJ International, 2002, 42(1): 44-52 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.42.44 [10] de Castro J A, Nogami H, Yagi J I. Transient mathematical model of blast furnace based on multi-fluid concept, with application to high PCI operation. ISIJ International, 2000, 40(7): 637-646 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.40.637 [11] 储满生, 王宏涛, 柳政根, 唐珏.高炉炼铁过程数学模拟的研究进展.钢铁, 2014, 49(11): 1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6764.2014.11.001Chu Man-Sheng, Wang Hong-Tao, Liu Zheng-Gen, Tang Jue. Research progress on mathematical modeling of blast furnace ironmaking process. Iron and Steel, 2014, 49(11): 1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6764.2014.11.001 [12] Lvanov E B, Klimovitskii M D, Anisimov E F. Expert system for blast-furnace operators. Metallurgist, 2011, 54(11-12): 730-736 doi: 10.1007/s11015-011-9366-x [13] Liu J K, Wang S Q. Construction of the inference engine of blast furnace expert system. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 1998, 5(2): 22-27 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d63816e95b6e5b4ec6c58e1412491df1 [14] Shi L, Li Z L, Li J P. Model of hot metal silicon content in blast furnace based on principal component analysis application and partial least square. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2011, 18(10): 13-16 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60015-6 [15] Saxén H, Gao C H, Gao Z W. Data-driven time discrete models for dynamic prediction of the hot metal silicon content in the blast furnace -- a review. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4): 2213-2225 doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2226897 [16] Yuan M, Zhou P, Li M L, Li R F, Wang H, Chai T Y. Intelligent multivariable modeling of blast furnace molten iron quality based on dynamic AGA-ANN and PCA. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2015, 22(6): 487-495 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30031-5 [17] 王炜, 陈畏林, 叶勇, 徐智慧, 贾斌.神经网络在高炉铁水硫含量预报中的应用.钢铁, 2006, 41(10): 19-22 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gt200610004Wang Wei, Chen Wei-Lin, Ye Yong, Xu Zhi-Hui, Jia Bin. Application of neural network to predict sulphur content in hot metal. Iron and Steel, 2006, 41(10): 19-22 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gt200610004 [18] Yan W W, Tang D, Lin Y J. A data-driven soft sensor modeling method based on deep learning and its application. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(5): 4237-4245 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2622668 [19] Ma J M, Jiang H C, Huang K Z, Bi Z Q, Man K L. Novel field-support vector regression-based soft sensor for accurate estimation of solar irradiance. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2017, 64(12): 3183-3191 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2746091 [20] Zhou P, Yuan M, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven dynamic modeling for prediction of molten iron silicon content using ELM with self-feedback. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015: Article ID 326160 [21] Zhou P, Yuan M, Wang H, Wang Z, Chai T Y. Multivariable dynamic modeling for molten iron quality using online sequential random vector functional-link networks with self-feedback connections. Information Sciences, 2015, 325: 237-255 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.07.002 [22] Sargin M E, Yemez Y, Erzin E, Tekalp A M. Audiovisual synchronization and fusion using canonical correlation analysis. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2007, 9(7): 1396-1403 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2007.906583 [23] Pao Y H, Takefuji Y. Functional-link net computing: theory, system architecture, and functionalities. Computer, 1992, 25(5): 76-79 doi: 10.1109/2.144401 [24] Igelnik B, Pao Y H. Stochastic choice of basis functions in adaptive function approximation and the functional-link net. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1995, 6(6): 1320-1329 doi: 10.1109/72.471375 [25] Pao Y H, Park G H, Sobajic D J. Learning and generalization characteristics of the random vector functional-link net. Neurocomputing, 1994, 6(2): 163-180 doi: 10.1016/0925-2312(94)90053-1 [26] Scardapane S, Wang D H, Panella M, Uncini A. Distributed learning for random vector functional-link networks. Information Sciences, 2015, 301: 271-284 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.01.007 [27] Zhang L, Suganthan P N. A comprehensive evaluation of random vector functional link networks. Information Sciences, 2016, 367-368: 1094-1105 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.09.025 [28] Schmidt W F, Kraaijveld M A, Duin R P W. Feedforward neural networks with random weights. In: Proceedings of 1992 Pattern Recognition Conference B: Pattern Recognition Methodology and Systems. The Hague: IEEE, 1992. 1-4 [29] Huber P J, Ronchetti E M. Robust Statistics (Second Edition). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2009. [30] Valdora M, Yohai V J. Robust estimators for generalized linear models. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2014, 146: 31-48 doi: 10.1016/j.jspi.2013.09.016 [31] Fan J, Yan A L, Xiu N H. Asymptotic properties for M-estimators in linear models with dependent random errors. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2014, 148: 49-66 doi: 10.1016/j.jspi.2013.12.005 [32] Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. Journal of Statistical Software, 2010, 33(1): 1-22 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_81a46bf667066119552ea0da1acfb673 [33] Zou H, Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 2005, 67(2): 301-320 doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00503.x -




 下载:
下载: