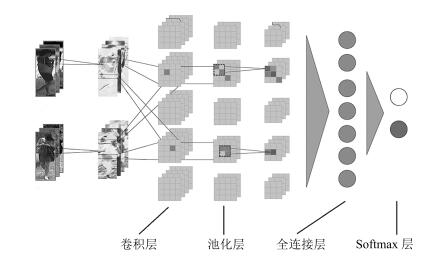
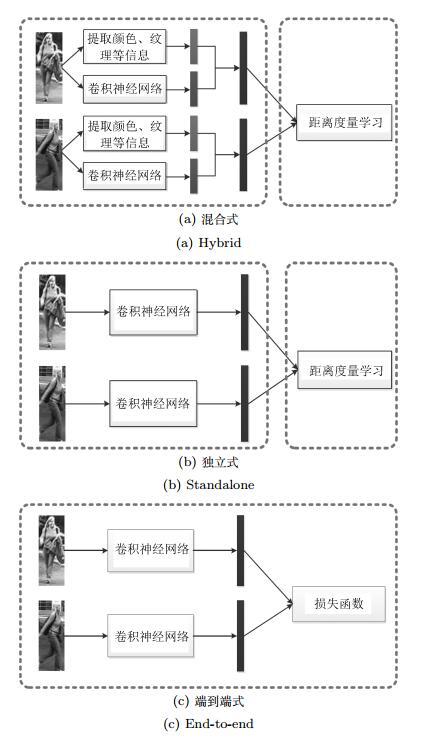
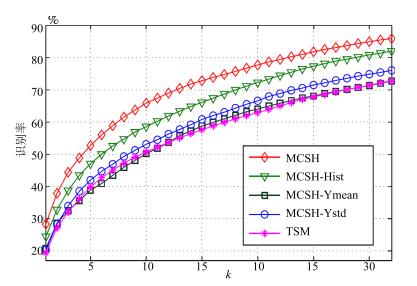
-
摘要: 行人再识别指的是判断不同摄像头下出现的行人是否属于同一行人, 可以看作是图像检索的子问题, 可以广泛应用于智能视频监控、安保、刑侦等领域.由于行人图像的分辨率变化大、拍摄角度不统一、光照条件差、环境变化大、行人姿态不断变化等原因, 使得行人再识别成为目前计算机视觉领域一个既具有研究价值又极具挑战性的研究热点和难点问题.早期的行人再识别方法大多基于人工设计特征, 在小规模数据集上开展研究.近年来, 大规模行人再识别数据集不断推出, 以及深度学习技术的迅猛发展, 为行人再识别技术的发展带来了新的契机.本文对行人再识别的发展历史、研究现状以及典型方法进行梳理和总结.首先阐述了行人再识别的基本研究框架, 然后分别针对行人再识别的两个关键技术(特征表达和相似性度量), 进行了归纳总结, 重点介绍了目前发展迅猛的深度学习技术在行人再识别中的应用.另外, 本文对行人再识别中代表性的数据集以及在各个数据集上可以取得优异性能的方法进行了分析和比较.最后对行人再识别技术的未来发展趋势进行了展望.Abstract: Person re-identification aims to associate the same person across different views and can be taken as a subproblem of image retrieval.It has extensive application prospects in many areas such as intelligent video surveillance, security, and criminal investigation.Due to poor illumination condition, image resolution, camera viewpoint, environment, and pedestrian pose, person re-identification has become one of the challenging problems in computer vision.Early person re-identification methods mostly rely on hand-crafted features and researches are conducted on small-scale datasets.In recent years, the emergence of large-scale datasets and rapid development of deep learning techniques provide person re-identification with new opportunities.This survey gives a detailed overview of the history, state of the art, and typical methods in this domain.Firstly, the general framework of person re-identification is presented.Then, feature representation, similarity measurement, and two key aspects of person re-identification, are further summarized, respectively.We also highlight the application of rapid developing deep learning techniques to person re-identification.Moreover, the representative datasets of person re-identification and methods of obtaining excellent performance on each dataset are analyzed and compared.Finally, the future trends of this field are discussed.1) 本文责任编委 黄庆明
-
表 1 典型行人图像分割方法
Table 1 Typical segmentation methods of pedestrian image
分割方式 对应文献 主要思想 上下半身分割 [3, 5] 提取行人的前景图像, 分成头部、躯干和腿部三部分.对后两部分计算垂直对称轴.对提取的特征根据与垂直对称轴的距离进行加权, 从而减少行人姿态变化的影响.缺点是分割过程过于复杂. 条纹分割 [6-7] 分成六个水平条, 分别对应于行人头部、水平躯干的上下部、腿部的上下部分.然后提取水平条内的ELF特征, 减少了视角变化对识别的影响.缺点是会造成水平条内空间细节信息的损失. 滑动窗分割 [8] 利用滑动窗来描述行人图像的局部细节信息, 在每个滑动窗内提取颜色和纹理特征.缺点是特征维数过大. 三角形分割 [2] 利用局部运动特征对行人图像进行三角形时空分割.缺点是分割结果不够准确. 表 2 Market-1501数据集上不同深度模型对首轮识别率的影响
Table 2 Rank-1 matching rates of different deep models in Market-1501
表 3 基于深度学习的方法目前所取得的最好效果
Table 3 The best results of deep learning-based methods
表 4 常用行人再识别数据集及其参数
Table 4 Popular person re-identification datasets and their parameters
表 5 行人再识别图像数据集上取得优异性能的方法对比
Table 5 Comparison of state-of-the-art methods on image-based person re-identification datasets
数据集 算法 人工设计/深度学习 rank-1(%) rank-5(%) rank-10(%) rank-20(%) 年份 SCSP[66] 人工 53.5 82.6 91.5 96.6 2016年 VIPeR FFN[50] 深度 51.1 81 91.4 96.9 2016年 HIPHOP[58] 深度 54.2 82.4 91.5 96.9 2017年 Zhang等[63] 人工 65 85 89.9 94.4 2016年 CUHK01 FFN 深度 55.5 78.4 83.7 92.6 2016年 HIPHOP 深度 78.8 92.6 95.3 97.8 2017年 Zheng等[64] 深度 85.8 94.4 96.4 97.5 2016年 Market-1501 SOMAnet[67] 深度 81.3 92.6 95.3 97.1 2017年 WARCA[68] 人工 45.1 68.1 76 84 2016年 表 6 行人再识别视频数据集上取得优异性能的方法对比
Table 6 Comparison of state-of-the-art methods on video-based person re-identification datasets
数据集 算法 人工设计/深度学习 rank-1 (%) rank-5 (%) rank-10 (%) rank-20 (%) 年份 zhang等[60] 深度 83.3 93.3 - 96.7 2017年 PRID-2011 McLaughlin等[45] 深度 70 90 95 97 2016年 TAPR[24] 人工 68.6 94.6 97.4 98.9 2016年 Zhang等[60] 深度 60.2 85.1 - 94.2 2017年 iLIDS-VID McLaughlin等[45] 深度 58 84 91 96 2016年 TAPR 人工 55 87.5 93.8 97.2 2016年 Zhang等[60] 深度 55.5 70.2 - 80.2 2017年 MARS CNN+XQDA[4] 深度 65.3 80.2 - 89 2016年 LOMO+XQDA[4] 人工 30.7 46.6 - 60.9 2016年 -
[1] Porikli F.Inter-camera color calibration by correlation model function.In: Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Image Processing.Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2003.Ⅱ-133-6 [2] Gheissari N, Sebastian T B, Hartley R.Person reidentification using spatiotemporal appearance.In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New York, USA: IEEE, 2006.1528-1535 [3] Farenzena M, Bazzani L, Perina A, Murino V, Cristani M.Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features.In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2010.2360-2367 [4] Zheng L, Bie Z, Sun Y F, Wang J D, Su C, Wang S J, et al.MARS: a video benchmark for large-scale person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016.868-884 [5] Bazzani L, Cristani M, Murino V.Symmetry-driven accumulation of local features for human characterization and re-identification.Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2013, 117 (2):130-144 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2012.10.008 [6] Gray D, Tao H.Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features.In: Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision.Marseille, France: Springer, 2008.262-275 [7] Zheng W S, Gong S G, Xiang T.Reidentification by relative distance comparison.IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35 (3):653-668 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.138 [8] Liao S C, Hu Y, Zhu X Y, Li S Z.Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015.2197-2206 [9] Zeng M Y, Wu Z M, Tian C, Zhang L, Hu L.Efficient person re-identification by hybrid spatiogram and covariance descriptor.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops.Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015.48-56 [10] Ma B P, Su Y, Jurie F.Covariance descriptor based on bio-inspired features for person re-identification and face verification.Image and Vision Computing, 2014, 32(6-7):379-390 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2014.04.002 [11] Matsukawa T, Okabe T, Suzuki E, Sato Y.Hierarchical Gaussian descriptor for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016.1363-1372 [12] Zhao R, Ouyang W L, Wang X G.Person re-identification by saliency learning.IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39 (2):356-370 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2544310 [13] Kviatkovsky I, Adam A, Rivlin E.Color invariants for person reidentification.IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35 (7):1622-1634 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.246 [14] 齐美彬, 檀胜顺, 王运侠, 刘皓, 蒋建国.基于多特征子空间与核学习的行人再识别.自动化学报, 2016, 42 (2):229-308 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18819.shtmlQi Mei-Bin, Tan Sheng-Shun, Wang Yun-Xia, Liu Hao, Jiang Jian-Guo.Multi-feature subspace and kernel learning for person re-identification.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42 (2):229-308 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18819.shtml [15] Zhao R, Ouyang W L, Wang X G.Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Portland, OR, USA: IEEE, 2013.3586-3593 [16] Zhao R, Ouyang W L, Wang X G.Learning mid-level filters for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE, 2014.144-151 [17] Gong S G, Cristani M, Yan S C, Loy C C.Person Re-Identification.London:Springer, 2014.139-160 [18] Layne R, Hospedales T M, Gong S G.Person re-identification by attributes.In: Proceedings of the 2012 British Machine Vision Conference.Surrey, UK: BMVA Press, 2012. [19] Shi Z Y, Hospedales T M, Xiang T.Transferring a semantic representation for person re-identification and search.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015.4184-4193 [20] Su C, Yang F, Zhang S L, Tian Q, Davis L S, Gao W.Multi-task learning with low rank attribute embedding for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015.3739-3747 [21] Caruana R A.Multitask learning: a knowledge-based source of inductive bias.In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Machine Learning.Amherst, USA: Elsevier, 1993.41-48 [22] Gray D, Brennan S, Tao H.Evaluating appearance models for recognition, reacquisition, and tracking.In: Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Performance Evaluation for Tracking and Surveillance.Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2007.1-7 [23] You J J, Wu A C, Li X, Zheng W S.Top-push video-based person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016.1345-1353 [24] Gao C X, Wang J, Liu L Y, Yu J G, Sang N.Temporally aligned pooling representation for video-based person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Image Processing.Phoenix, AZ, USA: IEEE, 2016.4284-4288 [25] Wang T Q, Gong S G, Zhu X T, Wang S J.Person re-identification by video ranking.In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision.Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014.688-703 [26] Man J, Bhanu B.Individual recognition using gait energy image.IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28 (2):316-322 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2006.38 [27] Klaser A, Marszalek M, Schmid C.A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3D-gradients.In: Proceedings of the 19th British Machine Vision Conference.Leeds, UK: British Machine Vision Association, 2008, 275: 1-10 [28] Bhattachayya A.On a measure of divergence between two statistical populations defined by their probability distributions.Bulletin Calcutta Mathematical Society, 1943, 35:99-109 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022247X89903351 [29] De Maesschalck R, Jouan-Rimbaud D, Massart D L.The mahalanobis distance.Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2000, 50 (1):1-18 doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(99)00047-7 [30] Xing E P, Ng A Y, Jordan M I, Russell S J.Distance metric learning, with application to clustering with side-information.In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 2002.521-528 [31] Zheng W S, Gong S G, Xiang T.Person re-identification by probabilistic relative distance comparison.In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Colorado Springs, CO, USA: IEEE, 2011.649-656 [32] Weinberger K Q, Saul L K.Fast solvers and efficient implementations for distance metric learning.In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning.Helsinki, Finland: ACM, 2008.1160-1167 [33] Davis J V, Kulis B, Jain P, Sra S, Dhillon I S.Information-theoretic metric learning.In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning.Corvalis, Oregon, USA: ACM, 2007.209-216 [34] Guillaumin M, Verbeek J, Schmid C.Is that you? Metric learning approaches for face identification.In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Vision.Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2009.498-505 [35] Köestinger M, Hirzer M, Wohlhart P, Roth P M, Bischof H.Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints.In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2012.2288-2295 [36] Karanam S, Li Y, Radke R J.Sparse re-id: block sparsity for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops.Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015.33-40 [37] Karanam S, Li Y, Radke R J.Person re-identification with discriminatively trained viewpoint invariant dictionaries.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015.4516-4524 [38] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E.Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks.In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2012.1097-1105 [39] 管皓, 薛向阳, 安志勇.深度学习在视频目标跟踪中的应用进展与展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42 (6):834-847 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18874.shtmlGuan Hao, Xue Xiang-Yang, An Zhi-Yong.Advances on application of deep learning for video object tracking.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42 (6):834-847 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18874.shtml [40] 常亮, 邓小明, 周明全, 武仲科, 袁野, 杨硕, 等.图像理解中的卷积神经网络.自动化学报, 2016, 42 (9):1300-1312 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18919.shtmlChang Liang, Deng Xiao-Ming, Zhou Ming-Quan, Wu Zhong-Ke, Yuan Ye, Yang Shuo, et al.Convolutional neural networks in image understanding.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42 (9):1300-1312 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18919.shtml [41] 段艳杰, 吕宜生, 张杰, 赵学亮, 王飞跃.深度学习在控制领域的研究现状与展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42 (5):643-654 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18852.shtmlDuan Yan-Jie, Lv Yi-Sheng, Zhang Jie, Zhao Xue-Liang, Wang Fei-Yue.Deep learning for control:the state of the art and prospects.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42 (5):643-654 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18852.shtml [42] 金连文, 钟卓耀, 杨钊, 杨维信, 谢泽澄, 孙俊.深度学习在手写汉字识别中的应用综述.自动化学报, 2016, 42 (8):1125-1141 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18903.shtmlJin Lian-Wen, Zhong Zhuo-Yao, Yang Zhao, Yang Wei-Xin, Xie Ze-Cheng, Sun Jun.Applications of deep learning for handwritten Chinese character recognition:a review.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42 (8):1125-1141 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18903.shtml [43] Li W, Zhao R, Xiao T, Wang X G.DeepReID: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE, 2014.152-159 [44] Ahmed E, Jones M, Marks T K.An improved deep learning architecture for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015.3908-3916 [45] McLaughlin N, Martinez Del Rincon J, Miller P.Recurrent convolutional network for video-based person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016.1325-1334 [46] Yan Y C, Ni B B, Song Z C, Ma C, Yan Y, Yang X K.Person re-identification via recurrent feature aggregation.In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016.701-716 [47] Cheng D, Gong Y H, Zhou S P, Wang J J, Zheng N N.Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016.1335-1344 [48] Wu S X, Chen Y C, Li X, Wu A C, You J J, Zheng W S.An enhanced deep feature representation for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision.Lake Placid, NY, USA: IEEE, 2016.1-8 [49] Li Y J, Zhuo L, Hu X C, Zhang J.A combined feature representation of deep feature and hand-crafted features for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing.Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2016.224-227 [50] Chan T H, Jia K, Gao S H, Lu J W, Zeng Z N, Ma Y.PCANet:a simple deep learning baseline for image classification? IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24 (12):5017-5032 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dianzixb201608028 [51] Zheng L, Wang S J, Tian L, He F, Liu Z Q, Tian Q.Query-adaptive late fusion for image search and person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015.1741-1750 [52] Zheng L, Huang Y J, Lu H C, Yang Y.Pose invariant embedding for deep person re-identification.arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1701.07732, 2017. [53] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J.Deep residual learning for image recognition.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016.770-778 [54] Zheng L, Zhang H H, Sun S Y, Chandraker M, Yang Y, Tian Q.Person re-identification in the wild.arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1604.02531, 2016. [55] Zheng L, Shen L Y, Tian L, Wang S L, Wang J D, Tian Q.Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark.In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015.1116-1124 [56] Simonyan K, Zisserma A.Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition.arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [57] Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B.In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification.arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1703.07737, 2017. [58] Chen Y C, Zhu X T, Zheng W S, Lai J H.Person re-identification by camera correlation aware feature augmentation.IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40 (2):392-408 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2666805 [59] Li W, Zhao R, Wang X G.Human reidentification with transferred metric learning.In: Proceedings of the 11th Asian Conference on Computer Vision.Daejeon, Korea: Springer, 2012.31-44 [60] Zhang W, Hu S N, Liu K.Learning compact appearance representation for video-based person re-identification.arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1702.06294, 2017. [61] Su C, Zhang S L, Xing J L, Gao W, Tian Q.Deep attributes driven multi-camera person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016.475-491 [62] Zhu J Q, Liao S C, Yi D, Lei Z, Li S Z.Multi-label CNN based pedestrian attribute learning for soft biometrics.In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Biometrics.Phuket, Thailand: IEEE, 2015.535-540 [63] Zhang L, Xiang T, Gong S G.Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016.1239-1248 [64] Zheng Z D, Zheng L, Yang Y.A discriminatively learned CNN embedding for person re-identification.arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1611.05666, 2016. [65] Hirzer M, Beleznai C, Roth P M, Bischof H.Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification.In: Proceedings of the 17th Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis.Ystad, Sweden: Springer, 2011.91-102 [66] Chen D P, Yuan Z J, Chen B D, Zheng N N.Similarity learning with spatial constraints for person re-identification.In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016.1268-1277 [67] Barbosa I B, Cristani M, Caputo B, Rognhaugen A, Theoharis T.Looking beyond appearances: synthetic training data for deep CNNs in re-identification.arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1701.03153, 2017. [68] Jose C, Fleuret F.Scalable metric learning via weighted approximate rank component analysis.In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016.875-890 [69] Yu D, Li J.Recent progresses in deep learning based acoustic models.IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(3), 396-409 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510508 -




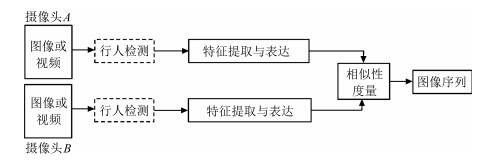
 下载:
下载: