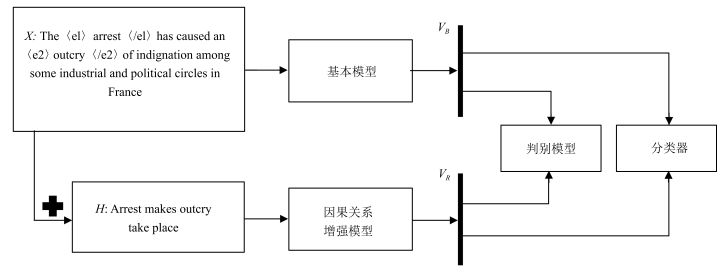
-
摘要: 因果关系抽取在事件预测、情景生成、问答以及文本蕴涵等任务上都有重要的应用价值.但多数现有的因果关系抽取方法都需要人工定义模式和约束,且严重依赖知识库.为此,本文利用生成式对抗网络(Generative adversarial networks,GAN)的对抗学习特性,将带注意力机制的双向门控循环单元神经网络(Bidirectional gated recurrent units networks,BGRU)与对抗学习相融合,通过重定义生成模型和判别模型,基本的因果关系抽取网络能够与判别网络形成对抗,进而从因果关系解释信息中获得高区分度的特征.实验结果表明,与当前用于因果关系抽取的方法相比较,该方法表现出更优的抽取效果.Abstract: Causality extraction is of important practical value in tasks such as event prediction, scenario generation, question answering, and textual implication; but most of the existing causality extraction methods require artificial definition of patterns and constraints and are heavily dependent on knowledge base. In this paper, the bidirectional gated recurrent units networks (BGRU) with attention mechanism are merged with confrontational learning by leveraging the confrontational learning characteristics of generative adversarial networks (GAN). Through redefining the generator and discriminator, the basic causality extraction network can construct a confrontation with the discriminator, and then obtain a high distinguishing feature from the causality interpretation information. Our experiments show that our approach leads to an improved performance over strong baselines.1) 本文责任编委 李力
-
表 1 数据集的构造说明
Table 1 Description of the dataset
关系类型 数据来源 数据条数 因果关系 SemEval 1 331 新闻语料人工标注 700 非因果关系 SemEval 1 900 表 2 BGRU因果关系抽取结果(%)
Table 2 Results of BGRU causality extraction (%)
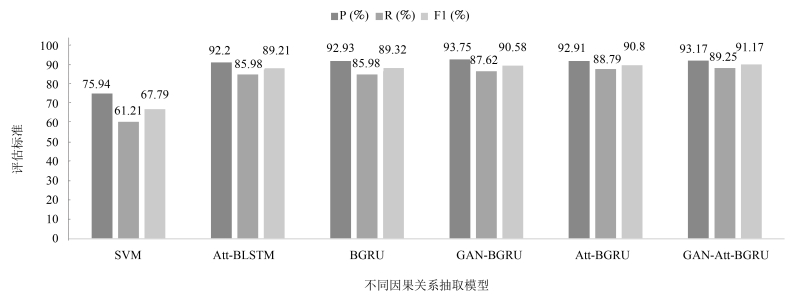
Model P R F1 B-BGRU 92.93 85.98 89.32 R-BGRU 93.74 94.39 94.06 表 3 GAN框架下的因果关系抽取(%)
Table 3 Causality extraction under GAN framework (%)
Model P R F1 B-BGRU 92.93 85.98 89.32 GAN-BGRU 93.75 87.62 90.58 表 4 带注意力机制的GAN框架下的因果关系抽取(%)
Table 4 Causality extraction under GAN framework with attention (%)
Model P R F1 B-Att-BGRU 92.91 88.79 90.80 R-Att-BGRU 94.63 94.63 94.63 GAN-Att-BGRU 93.17 89.25 91.17 -
[1] Radinsky K, Davidovich S, Markovitch S. Learning causality for news events prediction. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on World Wide Web. Lyon, France: ACM, 2012. 909-918 [2] Hashimoto C, Torisawa K, Kloetzer J, Sano M, Varga I, Oh J H, et al. Toward future scenario generation: extracting event causality exploiting semantic relation, context, and association features. In: Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Baltimore, MD, USA: ACL, 2014. 987-997 [3] Girju R. Automatic detection of causal relations for question answering. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACL Workshop on Multilingual Summarization and Question Answering. Sapporo, Japan: ACL, 2003. 76-83 [4] Oh J H, Torisawa K, Hashimoto C, Sano M, De Saeger S, Ohtake K. Why-question answering using intra-and inter-sentential causal relations. In: Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Sofia, Bulgaria: ACL, 2013. 1733-1743 [5] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, QC, Canada: NIPS, 2014. 2672-2680 [6] Abe S, Inui K, Matsumoto Y. Two-phased event relation acquisition: coupling the relation-oriented and argument-oriented approaches. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Manchester, United Kingdom: ACM, 2008. 1-8 [7] Do Q X, Chan Y S, Roth D. Minimally supervised event causality identification. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Edinburgh, United Kingdom: ACM, 2011. 294-303 [8] Hashimoto C, Torisawa K, De Saeger S, Oh J H, Kazama J. Excitatory or inhibitory: a new semantic orientation extracts contradiction and causality from the web. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning. Jeju Island, Korea: ACM, 2012. 619-630 [9] Rink B, Harabagiu S. UTD: classifying semantic relations by combining lexical and semantic resources. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Los Angeles, California, USA: ACM, 2010. 256-259 [10] Zeng D J, Liu K, Lai S W, Zhou G Y, Zhao J. Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Dublin, Ireland: ACL, 2014. 2335-2344 [11] Mikolov T, Karafiát M, Burget L, Černocký J, Khudanpur S. Recurrent neural network based language model. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Makuhari, Chiba, Japan: DBLP, 2010. 1045-1048 [12] Zhang D X, Wang D. Relation classification via recurrent neural network. arXiv: 1508. 01006, 2015. [13] Zhang S, Zheng D Q, Hu X C, Yang M. Bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification. In: Proceedings of the 29th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation. Shanghai, China: PACLIC, 2015. 73-78 [14] Zhou P, Shi W, Tian J, Qi Z Y, Li B C, Hao H W, et al. Attention-based bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Berlin, Germany: ACL, 2016. 207-212 [15] Chung J Y, Gulcehre C, Cho K H, Bengio Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv: 1412. 3555, 2014. [16] Zhang Y Z, Gan Z, Carin L. Generating text via adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Workshop on Adversarial Training. Barcelona, Spain: NIPS, 2016. [17] Yu L T, Zhang W N, Wang J, Yu Y. SeqGAN: sequence generative adversarial nets with policy gradient. In: Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, California, USA: AAAI, 2017. 2852-2858 [18] Li J W, Monroe W, Shi T L, Jean S, Ritter A, Jurafsky D. Adversarial learning for neural dialogue generation. arXiv: 1701. 06547, 2017. [19] Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein GAN. arXiv: 1701. 07875, 2017. [20] Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, Dumoulin V, Courville A. Improved training of Wasserstein GANs. In: Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, CA, USA: NIPS, 2017. 5769-5779 -





 下载:
下载: