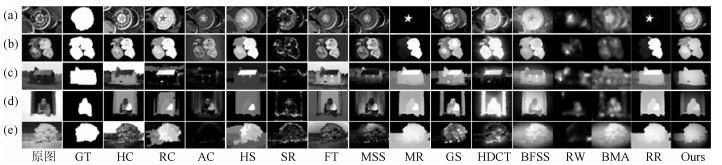
-
摘要: 针对现有图像显著性检测算法中显著目标检测不完整和显著目标内部不均匀的问题,本文提出了一种基于多图流形排序的图像显著性检测算法.该算法以超像素为节点构造KNN图(K nearest neighbor graph)模型和K正则图(K regular graph)模型,分别在两种图模型上利用流形排序算法计算超像素节点的显著性值,并将每个图模型中超像素节点的显著值加权融合得到最终的显著图.在公开的MSRA-10K、SED2和ECSSD三个数据集上,将本文提出的算法与当前流行的14种算法进行对比,实验结果显示本文算法能够完整地检测出显著目标,并且显著目标内部均匀光滑.Abstract: To resolve the incompletion and non-uniform of salient object detection, this paper proposes an image salient object detection algorithm with multi-graph model and manifold ranking. The algorithm uses superpixels as nodes to construct KNN graph model and K regular graph model. For each model, manifold ranking algorithm is used to calculate saliency values of superpixel nodes. The saliency values of the nodes obtained from the two graph models are fused together with different weights to form the image saliency map. On three public available databases, MSRA-10K, SED2 and ECSSD, the proposed algorithm is compared with fourteen state-of-art algorithms. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can detect a salient object completely, yet the object is uniform and smooth inside.
-
Key words:
- Image saliency detection /
- multi-graph model /
- manifold ranking /
- superpixel node
1) 本文责任编委 杨健 -
表 1 K正则图模型、KNN图模型和K正则图模型+ KNN图模型比较
Table 1 The comparison of K regular graph, KNN graph, and K regular graph + KNN graph
MSRA-10K SED2 ECSSD P R F P R F P R F K正则 0.8557 0.7705 0.7948 0.8293 0.6990 0.7524 0.7053 0.6950 0.6344 KNN 0.8627 0.7468 0.7897 0.7918 0.6034 0.6837 0.7231 0.7229 0.6677 K正则+ KNN 0.8723 0.7962 0.8228 0.8080 0.7253 0.7504 0.7279 0.7476 0.6828 表 2 边界假设和全局前景假设比较
Table 2 The comparison of boundary assumption and global foreground assumption
MSRA-10K SED2 ECSSD P R F P R F P R F 边界 0.8815 0.6670 0.7846 0.7267 0.4883 0.6156 0.7927 0.5830 0.6768 全局 0.8723 0.7962 0.8228 0.8080 0.7253 0.7504 0.7279 0.7476 0.6828 表 3 初始显著图和优化后显著图的比较
Table 3 The comparison of original saliency maps and refined saliency maps
MSRA-10K SED2 ECSSD P R F P R F P R F 初始图 0.8723 0.7962 0.8228 0.8080 0.7253 0.7504 0.7279 0.7476 0.6828 优化图 0.8796 0.7880 0.8327 0.8210 0.6729 0.7456 0.7587 0.7152 0.7034 表 4 各种方法在不同数据库上的AUC值和F值
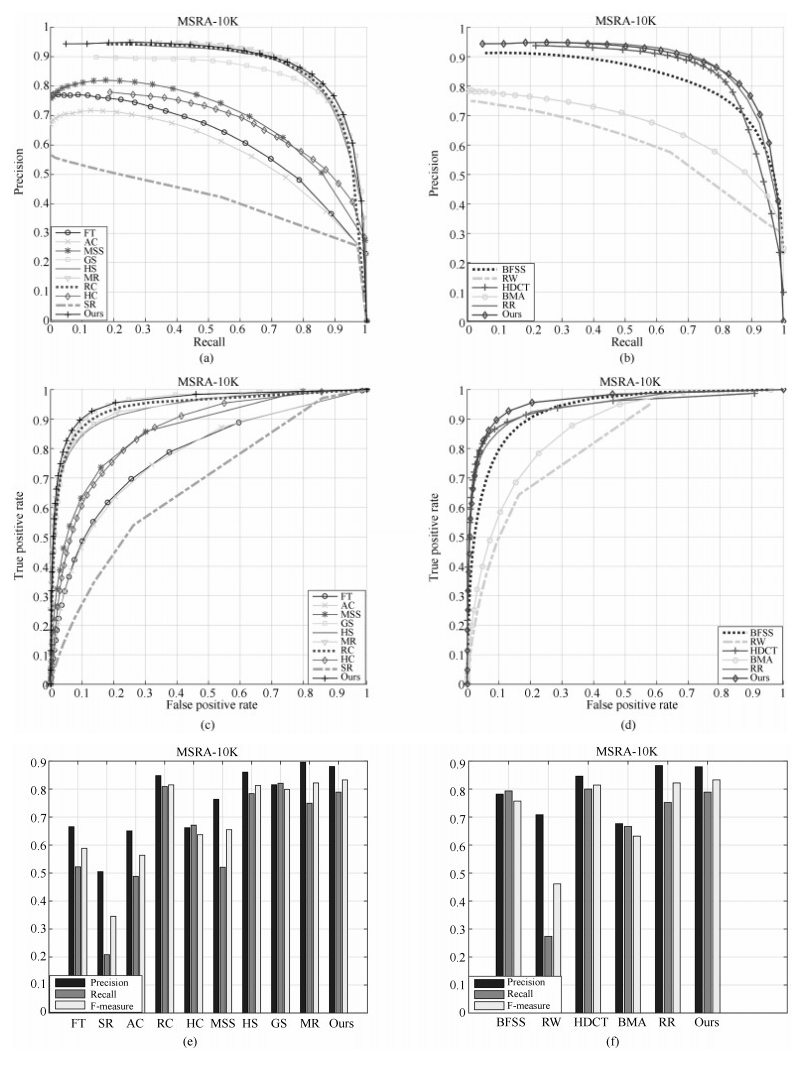
Table 4 The AUC and F values of the various methods on different databases
AUC值 F值 MSRA-10K SED2 ECSSD MSRA-10K SED2 ECSSD HC[8] 0.8589 0.8839 0.7022 0.6370 0.7113 0.4186 RC[8] 0.9406 0.8580 0.8919 0.8150 0.7151 0.6802 AC[6] 0.7767 0.8430 0.6750 0.5636 0.7012 0.4026 HS[7] 0.9353 0.8960 0.8833 0.8128 0.7298 0.6657 SR[12] 0.6716 0.7290 0.6054 0.3454 0.4307 0.3001 FT[10] 0.7797 0.8310 0.6591 0.5884 0.6872 0.3959 MSS[11] 0.8607 0.8768 0.7678 0.6549 0.7125 0.4918 MR[22] 0.9404 0.8618 0.8858 0.8219 0.7227 0.6868 GS[18] 0.9527 0.9055 0.8834 0.7987 0.7546 0.6268 BFSS[13] 0.8807 0.8932 0.8625 0.7570 0.7755 0.6080 RW[20] 0.3976 0.8364 0.7252 0.4614 0.4868 0.3746 HDCT[14] 0.8483 0.9036 0.8644 0.8143 0.7804 0.6673 BMA[15] 0.8605 0.8825 0.7762 0.6318 0.5980 0.4927 RR[21] 0.9423 0.8674 0.8887 0.8219 0.7197 0.6882 本文算法 0.9532 0.8937 0.9114 0.8327 0.7456 0.7034 表 5 各种方法平均运行时间
Table 5 The average runtimes of different methods
SR FT MSS MR GS BFSS RW BMA RR HS HC RC AC HDCT Ours MATLAB 0.02 0.04 1.04 1.10 0.21 7.25 1.33 0.002 1.70 — — — — — 1.30 C++ — — — — — — — — — 0.39 0.01 0.25 0.18 4.12 — -
[1] 罗建豪, 吴建鑫.基于深度卷积特征的细粒度图像分类研究综述.自动化学报, 2017, 43(8):1306-1318 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19105.shtmlLuo Jian-Hao, Wu Jian-Xin. A survey on fine-grained image categorization using deep convolutional features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8):1306-1318 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19105.shtml [2] 王瑞霞, 彭国华.基于黎曼流形稀疏编码的图像检索算法.自动化学报, 2017, 43(5):778-788 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19055.shtmlWang Rui-Xia, Peng Guo-Hua. An image retrieval method with sparse coding based on riemannian manifold. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5):778-788 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19055.shtml [3] 杨赛, 赵春霞, 徐威.一种基于词袋模型的新的显著性目标检测方法.自动化学报, 2016, 42(8):1259-1273 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18915.shtmlYang Sai, Zhao Chun-Xia, Xu Wei. A novel salient object detection method using bag-of-features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(8):1259-1273 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18915.shtml [4] Xu M, Jiang L, Ye Z T, Wang Z L. Bottom-up saliency detection with sparse representation of learnt texture atoms. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 60:348-360 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.023 [5] Goferman S, Zelnikmanor L, Tal A. Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(10):1915-1926 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.272 [6] Achanta R, Estrada F, Wils P, Süsstrunk S. Salient region detection and segmentation. In: Proceedings of Computer Vision Systems, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 5008. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2008. 66-75 [7] Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J P, Jia J Y. Hierarchical saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, OR, USA: IEEE, 2013. 1155-1162 [8] Cheng M M, Mitra N J, Huang X L, Torr P H S, Hu S M. Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3):569-582 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401 [9] Borji A, Itti L. Exploiting local and global patch rarities for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2012. 478-485 [10] Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, FL, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1597-1604 [11] Achanta R, Süsstrunk S. Saliency detection using maximum symmetric surround. In: Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2010. 2653-2656 [12] Hou X D, Zhang L Q. Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1-8 [13] Wang J P, Lu H C, Li X H, Tong N, Liu W. Saliency detection via background and foreground seed selection. Neurocomputing, 2015, 152:359-368 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.10.056 [14] Kim J, Han D, Tai Y W, Kim J. Salient region detection via high-dimensional color transform. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE, 2014. 883-890 [15] Zhang J M, Sclaroff S. Exploiting surroundedness for saliency detection:a boolean map approach. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(5):889-902 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2473844 [16] Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11):1254-1259 doi: 10.1109/34.730558 [17] Harel J, Koch C, Perona P. Graph-based visual saliency. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Canada: ACM, 2006. 545-552 [18] Wei Y C, Wen F, Zhu W J, Sun J. Geodesic saliency using background priors. In: Proceeding of the 2012 European Conference on Computer Vision, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 7574. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2012. 29-42 [19] Li X, Li Y, Shen C H, Dick A, Van Den Hengel A. Contextual hypergraph modeling for salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 3328-3335 [20] Li J, Fang S, Tian Y H, Huang T J, Chen X W. Image saliency estimation via random walk guided by informativeness and latent signal correlations. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2015, 38:3-14 doi: 10.1016/j.image.2015.05.005 [21] Yuan Y C, Li C Y, Kim J, Cai W D, Feng D D. Reversion correction and regularized random walk ranking for saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(3):1311-1322 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2762422 [22] Yang C, Zhang L H, Lu H C, Ruan X, Yang M H. Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: Proceeding of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 3166-3173 [23] Tao D P, Cheng J, Song M L, Lin X. Manifold ranking-based matrix factorization for saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(6):1122-1134 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2461554 [24] Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Süsstrunk S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11):2274-2281 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120 [25] Zhao M Y, Jiao L C, Ma W P, Liu H Y, Yang S Y. Classification and saliency detection by semi-supervised low-rank representation. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 51:281-294 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.09.008 [26] Zhu W J, Liang S, Wei Y C, Sun J. Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: Proceeding of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 2814-2821 [27] Chen J Z, Ma B P, Cao H, Chen J, Fan Y B, Li R, et al. Updating initial labels from spectral graph by manifold regularization for saliency detection. Neurocomputing, 2017, 266:79-90 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.04.066 [28] Li S Q, Zeng C, Fu Y, Liu S P. Optimizing multi-graph learning based salient object detection. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2017, 55:93-105 doi: 10.1016/j.image.2017.03.023 [29] Zhang J X, Ehinger K A, Wei H K, Zhang K J, Yang J Y. A novel graph-based optimization framework for salient object detection. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 64:39-50 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.10.025 [30] Lan Y D, Deng H F, Chen T. A new method of distance measure for graph-based semi-supervised learning. In: Processing of the 2011 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics. Guilin, China: IEEE, 2011. 1444-1448 [31] Jiang H Z, Wang J D, Yuan Z J, Liu T, Zheng N N. Automatic salient object segmentation based on context and shape prior. In: Proceedings of the 22nd British Machine Vision Conference. Dundee, Scotland, British: BMVA Press, 2011. 110.1-110.12 [32] Liu T, Yuan Z J, Sun J, Wang J D, Zheng N N, Tang X O, et al. Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(2):353-367 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.70 [33] Alpert S, Galun M, Brandt A, Basri R. Image segmentation by probabilistic bottom-up aggregation and cue integration. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(2):315-327 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.130 [34] 郭迎春, 袁浩杰, 吴鹏.基于Local特征和Regional特征的图像显著性检测.自动化学报, 2013, 39(8):1214-1224 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18152.shtmlGuo Ying-Chun, Yuan Hao-Jie, Wu Peng. Image saliency detection based on local and regional features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(8):1214-1224 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18152.shtml -




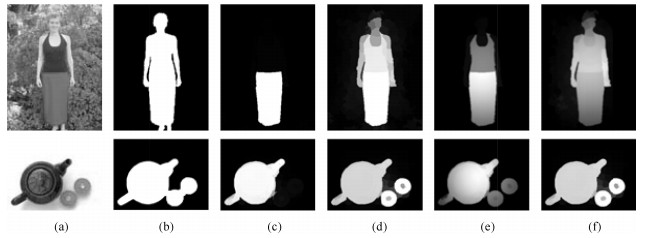
 下载:
下载: