Convex Approximation Based Avoidance Theory and Path Planning MPC for Driver-less Vehicles
-
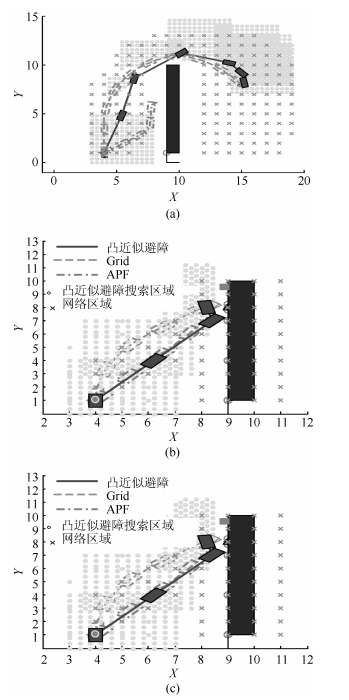
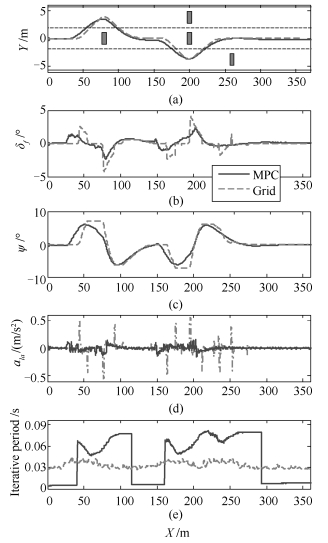
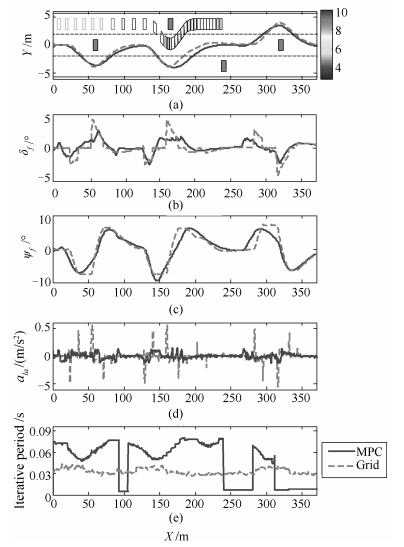
摘要: 提出了一种改进的无人驾驶车辆路径规划方法, 并搭建了相应的软件在环实时仿真系统, 对方法在结构化道路下的复杂动态交通工况进行性能验证.首先, 引入基于凸近似的避障原理, 对障碍物参考点的选取进行优化, 扩大了路径规划的可行域范围.采用改进后的方法, 并结合模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)原理和曲线坐标系统, 综合考虑自车及障碍车的外形、道路几何约束及自车的机械结构约束、路径最短、侧向加速度、道路对中、逐次变道、车距安全度、左变道优先和前轮转角变化率等权重的影响, 实现了车辆在复杂动态交通工况下的路径规划.最后, 以长城H7运动多用途车作为无人驾驶实验及仿真平台, 搭建基于dSPACE多核架构的Carsim + Simulink软件在环实时仿真系统, 对算法进行验证.结果表明, 所提出的方法不仅可获得合理、平滑的行驶路径, 顺利避开运动障碍车的干扰, 而且具有良好的实时性.Abstract: An improved path planning algorithm for the driver-less vehicle is proposed in this paper, and a soft-ware in loop system is set up to evaluate its performance under complex dynamic traffic scenarios. First, a convex approximation based avoidance theory is introduced, and a method to optimize the obstacle's reference point is proposed for enlarging approachable region. Based on the proposed algorithm, the theory of MPC (Model predictive control) and the curvilinear coordination system, and nine key weighting factors are considered thoroughly to achieve an optimal path, including the dimensions of ego and obstacle vehicles, path geometric constraints and ego vehicle's mechanical constraints, shortest path, lateral acceleration, path alignment, lane changing successively, vehicle to vehicle safety distance, left lane changing priority and the rate of front wheel angle change. Finally, the GWM H7 SUV is used as the driver-less prototype vehicle, and a Carsim + Simulink based soft-ware in loop system is set up, via using the dSPACE multi-cores platform, in order to test the proposed algorithm. The simulation test results demonstrate that not only a reasonable and smooth path is achieved to avoid the disturbances from the moving vehicles, but also an expected real-time performance is obtained.
-
Key words:
- Driver-less vehicles /
- path planning /
- convex approximation /
- obstacle avoidance theory /
- model predictive control (MPC)
1) 本文责任编委 李力 -
表 1 长城H7车辆参数值
Table 1 Vehicle parameters of the GWM H7
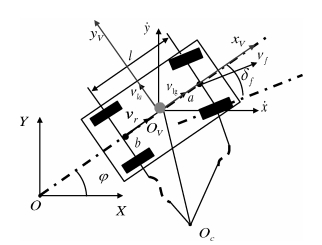
参数 数值 单位 参数 数值 单位 $k_f$ $-$111187 N/rad $I_z$ 3522.1 ${\rm {kg\cdot m}}^{2}$ $k_r$ $-$90773 N/rad $M_v$ 2211 kg $a$ 1.25 m $v_r$ 6 m/s $b$ 1.59 m 表 2 MPC控制系统参数
Table 2 Parameters of MPC system
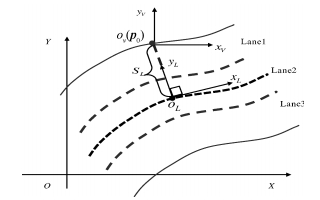
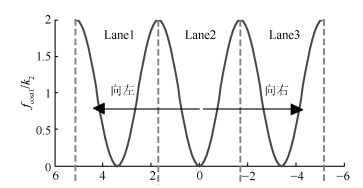
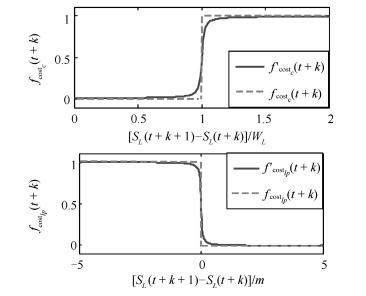
参数 数值 参数 数值 $k_1$ 0.3 $k_6$ 0.2 $k_2$ 8 $k_7$ 0.7 $k_3$ 3 $N$ 3 $k_4$ 2.5 $N_{\mu}$ 1 $k_5$ 15 符号 说明 单位 $a/b$ 前/后轴距离质心的距离 m ${\pmb d_{\ast}}$ 自车外观几何形状向量 m $D_{0}$ 自车停车时自车和障碍车之间的距离 m $I_{z}$ 车辆绕$z$轴的转动惯量 kg$\cdot$s$^2$ $k_{f/r}$ 前/后轮的侧倾刚度 N/rad $l$ 车的轴距 m $M$ 障碍车的数量 $M_{v}$ 车辆质量 kg $N/N_{u}$ 预测/控制步长 $o_{L}$ 车辆质心点$p_{0}$投影到中间车道的最短距离 m $OXY/o_{V}x_{V}y_{V}/o_{L}x_{L}y_{L}$ 大地/车辆/道路坐标系 ${\pmb p}$ 可行域中的点 m ${\pmb p_{0}}$ 自车质心位置 m ${\pmb q_{\ast}}$ 障碍车参考点 $r$ 自车凸多边形外形端点数 $R$ 车辆转弯半径 m $s_{*}$ 障碍车凸多边形外形端点数 $S_{L}$ 车辆质心偏移中间道路的位移量 m $S_{L_ {\rm max/min}}$ 左/右道路边缘的极限位置偏移量 m $t$ 采样时间 s $v_{f/r}$ 自车前/后轴速度 m/s $v_{l}$ 障碍车速 m/s $v_{la/lg}$ 质心的侧/纵向速度 m/s $\dot{v_{la}}$ 质心的侧向加速度 m/s$^{2}$ $v_{rel}$ 自车和障碍车之间的相对速度 m/s ${\pmb w_{\ast}}$ 障碍车(物)外观几何形状向量 m $W_{c}$ 车宽 m $W_{L}$ 实时测得的车道宽 m $x/y$ 自车质心在大地坐标系下的横/纵坐标 m $\dot{x}/\dot{y}$ 质心沿大地坐标系$X/Y$轴的速度 m/s $\delta_{f}$ 前轮转角 rad $\mu_{*}$ 缩放系数 ${\pmb w}$ 障碍车(物)内部点 m $\varphi/\dot{\varphi}/\ddot{\varphi}$ 航向角/横摆角速度/角加速度 rad/rad/s/rad/s$^2$ $\gamma$ 实际车距与安全车距的比值 -
[1] How google's self-driving car works [Online], available: http://news.discovery.com/autos/how-google-self-driving-car-works-111018.html, January 1, 2013 [2] DARPA grand challenge [Online], available: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DARPA Grand Challenge. January 1, 2013 [3] 姜岩, 龚建伟, 熊光明, 陈慧岩.基于运动微分约束的无人车辆纵横向协同规划算法的研究.自动化学报, 2013, 39(12): 2012-2020 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.02012Jiang Yan, Gong Jian-Wei, Xiong Guang-Ming, Chen Hui-Yan. Research on diferential constraints-based planning algorithm for autonomous-driving vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(12): 2012-2020 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.02012 [4] Khatib O. Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulator and mobile robot. The International Journal Robotics Research, 1986, 5(1): 90-98 doi: 10.1177/027836498600500106 [5] Mcfetridge L, Ibrahim M Y. A new methodology of mobile robot navigation: The agoraphilic algorithm. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2009, 25(3): 545-551 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2008.01.008 [6] Zhang Q S, Chen D D, Chen T. An Obstacle Avoidance Method of Soccer Robot Based on Evolutionary Artificial Potential Field. Energy Procedia Part C, 2012, 16: 1792-1798 doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2012.01.276 [7] 杜广龙, 张平.基于人工势场的机器人遥操作安全预警域动态生成方法.机器人, 2012, 34(1): 44-49 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jqr201201007Du Guang-Long, Zhang Ping.A method for generating dynamic security warning region in robotic teleoperation based on artificial potential field. Robot, 2012, 34 (1): 44-49 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jqr201201007 [8] Howden W E. The sofa problem. The Computer Journal, 1968, 11(3): 299-301 doi: 10.1093/comjnl/11.3.299 [9] Guernane R, Achour N. Generating optimized paths for motion planning. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2011, 59(10): 789-800 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2011.06.001 [10] 张纯刚, 席裕庚.全局环境未知时基于滚动窗口的机器人路径规划.中国科学(E辑), 2001, 31(1): 51-58 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-ce200101008Zhang Chun-Gang, XI Yu-Geng. Robust window-based robot path planning when the global environment is unknown. Chinese Science (E), 2001, 31(1): 51-58 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-ce200101008 [11] 刘春明, 李兆斌, 黄振华, 等.基于LSPI和滚动窗口的移动机器人反应式导航方法.中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013(03): 970-977 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zngydxxb201303016Liu Chun-Ming, Li Zhao-Bin, Huang Zhen-Hua, et al. A reactive navigation method of mobile robots based on LSPI and rolling windows. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013(03): 970-977 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zngydxxb201303016 [12] Chou C, Lian F, Wang C. Characterizing indoor environment for robot navigation using velocity space approach with region analysis and look-ahead verification. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2011, 60(2): 442-451 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2010.2058531 [13] Bemporad A, Rocchi C. Decentralized linear time-varying model predictive control of a formation of unmanned aerial vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC) Orlando, FL, USA: IEEE, 2011. 7488-7493 [14] Bemporad A, Pascucci C, Rocchi C. Hierarchical and hybrid model predictive control of quadcopter air vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IFAC Conference on Analysis and Design of Hybrid Systems, Zaragoza, Spain: Elsevier, 2009. [15] Zhi J Z, Schmerling E, Pavone M. A convex optimization approach to smooth trajectories for motion planning with car-like robots. In: Procedings of IEEE 54th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Osaka, Japan: IEEE, 2015. [16] Quinlan S, Khatib O. Elastic bands: Connecting path planning and control. in Proc. IEEE Conference on Robotics and Automation, Atlanta, GA, May 1993(2): 80-807 [17] Janson L, Schmerling E, Clark A, Pavone M. Fast marching tree: a fast marching sampling-based method for optimal motion planning in many dimensions. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2015, 34(7): 883-921 doi: 10.1177/0278364915577958 [18] Tian Y G, Dolan J M, Lee J W. Runtime-bounded tunable motion planning for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ), Gothenburg, Sweden: IEEE, 2016. 1301-1306 [19] Tian Y G, Atwood J, Chi Y D, Dolan J M, Lee J W. Tunable and stable real-time trajectory planning for urban autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2015. 250-256 [20] Ryu J H, Ogay D, Bulavintsev S, Kim H, Park J S. Development and experiences of an autonomous vehicle for high-speed navigation and obstacle avoidance. Frontiers of Intelligent Autonomous Systems. Springer, 2013: 105-116 [21] T Berglund, A Brodnik, H Jonsson, M Staffanson, I Soderkvist. Planning smooth and obstacle-avoiding b-spline paths for autonomous mining vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2010, 7(1): 167-172 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2009.2015886 [22] Perez J, Lattarulo R, Nashashibi F. Dynamic trajectory generation using continuous-curvature algorithms for door to door assistance vehicles. Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Proceedings, IEEE, 2014: 510-515 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC0214340693 [23] Petrov P, Nashashibi F. Modeling And Nonlinear Adaptive Control for Autonomous Vehicle Overtaking. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(4): 1643-1656 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2014.2303995 [24] Brezak M, Petrovic I. Real-time Approximation of Clothoids With Bounded Error for Path Planning Applications. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2014, 3(2): 507-515 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4a6528809b11cf384afa45538b6d5a21 [25] Funke J, Theodosis P, Hindiyeh R, Stanek G, Kritatakirana K, Gerdes C, Langer D, Hernandez M, Muller-Bessler B, Huhnke B. Up to the limits: Autonomous audi TTS. In: Rroceedings of the Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, June 2012: 541-547 [26] Junsoo Kim, Kichun Jo, Wontaek Lim, Minchul Lee, Myoungho Sunwoo. Curvilinear-Coordinate-Based Object and Situation Assessment for Highly Automated Vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(3): 1559-1575 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2014.2369737 [27] Chu K, Lee M, Sunwoo M. Local Path Planning for Off-Road Autonomous Driving With Avoidance of Static Obstacles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(4): 1599-1615 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2198214 [28] Kim J H, Kum D S. Threat Prediction Algorithm based on Local Path Candidates and Surrounding Vehicle Trajectory Predictions for Automated Driving Vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ), COEX, Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2015. 1220-1225 [29] Barfoot T D, Clark C M. Motion Planning for Formations of Mobile Robots. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2004, 45: 65-78 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cd879d19070c8114dcc0b35a6f7de20a [30] Wang H, Kearney J, Atkinson K. Robust and Efficient Computation of The Closest Point on A Spline Curve. In: Procedings of 5th International Conference Curves Surfaces, 2002: 397-406 [31] 席裕庚.预测控制(第二版).北京:国防工业出版社, 2013.Xi Yu-Geng. Predictive Control (Second Edition). Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013. [32] 郭烈, 葛平淑, 张明恒, 李琳辉, 赵一兵.汽车安全辅助驾驶技术.北京:北京大学出版社, 2014.Guo Lie, Ge Pin-Shu, Zhang Ming-Heng, Li Lin-Hui, Zhao Yi-Bing. Automobile Driving Assisted Driving Technology. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2014. [33] 刘明明, 崔春风, 童小娇, 戴彧虹.混合整数非线性规划的算法软件及最新进展, 中国科学:数学, 2016, 46(1): 1-20 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-ca201601001Liu Ming-Ming, Cui Chun-Feng, Tong Xiao-Jiao, Dai Yu-Hong. Algorithm Software for Mixed Integer Nonlinear Programming and Recent Progress, Scientia Sinica (Mathematica) 2016, 46(1): 1-20 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-ca201601001 [34] 陈宝林.最优化理论与算法.北京, 清华大学出版社, 2005.Chen Bao-Lin. Optimization Theory and Algorithm. Beijing, Tsinghua University Press, 2005. [35] Powell M J D. The convergence of variable metric methods for nonlinearly constrained optimization calculations. Nonlinear Programming 3, (O.L. Mangasarian, R.R. Meyer and S.M. Robinson, eds.), Academic Press, 1978. [36] Constrained Optimization, Sequential Quadratic Programming (SQP), Optimization Toolbox User's Guide. Mathworks Inc, 2016. [37] Andersen H, Zhuang J C, You H E, Pendleton S, Marcelo H A. Geometric path tracking algorithm for autonomous driving in pedestrian environment. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Bahff, Canada: IEEE, 2016. 1669-1674 -




 下载:
下载: