Piecewise Planar Urban Scene Reconstruction Using Structure Priors and Cooperative Optimization
-
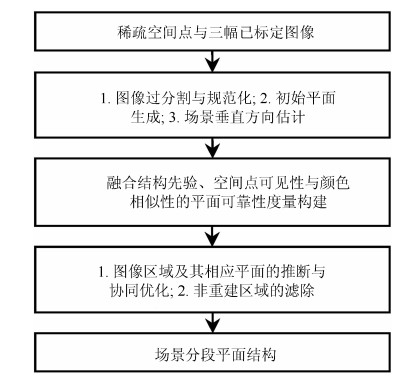
摘要: 在基于图像的城市场景三维重建中,场景分段平面重建算法可以克服场景中的弱纹理、光照变化等因素的影响而快速恢复场景完整的近似结构.然而,在初始空间点较为稀疏、候选平面集不完备、图像过分割质量较低等问题存在时,可靠性往往较低.为了解决此问题,本文根据城市场景的结构特征构造了一种新颖的融合场景结构先验、空间点可见性与颜色相似性的平面可靠性度量,然后采用图像区域与相应平面协同优化的方式对场景结构进行了推断.实验结果表明,本文算法利用稀疏空间点即可有效重建出完整的场景结构,整体上具有较高的精度与效率.Abstract: In the image-based 3D scene reconstruction, piecewise planar stereo methods can effectively recover complete and approximate structures of a scene by overcoming some interference factors such as textureless regions and illumination variations. However, they could be unreliable when some problem (e.g., sparse initial 3D points, incomplete candidate planes and inaccurate image over-segmentation) is involved. In order to address these problems, according to the structure characteristics of urban scenes, a novel plane reliability measurement is presented by incorporating scene structure priors, 3D point visibility and color similarity. Then, the scene is reconstructed in a progressive refinement manner so as to jontly optimize image regions and their associated planes. Experimental results on a variety of urban scenes show that the proposed method can effectively reconstruct the complete structures of a scene with high efficiency and accuracy only using sparse 3D points.
-
Key words:
- Urban scene /
- piecewise planar reconstruction /
- image over-segmentation /
- prior knowledge
1) 本文责任编委 王亮 -
图 11 图 10 (b)~10 (d)中矩形区域内平面结构的放大显示
Fig. 11 Close-ups of the plane structures in the rectangles in Fig. 10 (b)~10 (d)
表 1 参数设置
Table 1 Parameters setting
参数 默认值 功能描述 $\gamma$ 0.6 相关性度量 ${\lambda_{\rm occ}}$ 2 遮挡惩罚量 ${\lambda_{\rm err}}$ 4 空间可见性冲突惩罚量 ${\lambda_{\rm dis}}$ 4 空间平面间断惩罚量 $\mu$ 0.6 场景结构先验松驰量 $\delta$ 0.5 颜色特征差异截断阈值 $\vartheta$ 0.9 天空区域语义阈值 表 2 初始化
Table 2 Initialization
数据集 空间点 超像素 线段 平面 Valbonne 561 360 362 17 Wadham 2 120 1 243 838 38 City#1 2 234 2 793 1 588 11 City#2 1 503 2 643 1 297 7 表 3 不同算法获取的结果
Table 3 Results produced by different methods
数据集 PSP SP CP 本文算法 文献[8]算法 文献[9]算法 $M_{\rm 1(Fir)}$ $M_{\rm 1(Fin)}$ $M_2$ $M_1$ $M_2$ $M_1$ $M_2$ Valbonne 21 1 478 147 0.5259 0.7748 9 0.5145 7 0.6631 7 Wadham 53 5 889 421 0.6643 0.8046 11 0.3879 7 0.6492 11 City#1 23 7 110 3 109 0.4608 0.6927 7 0.3390 7 0.4465 6 City#2 28 6 831 2 612 0.5355 0.7081 6 0.3217 5 0.5977 6 注: PSP表示已分配初始可靠平面超像素数量, SP与CP分别表示协同优化后超像素与相应平面数量 -
[1] Çiğla C, Alatan A A. Region-based dense depth extraction from multi-view video. In: Proceedings of IEEE 15th Signal Processing and Communications Applications. Eskisehir, Turkey: IEEE, 2007. 213-216 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/4289275_Region-Based_Dense_Depth_Extraction_from_Multi-View_Video [2] Furukawa Y, Curless B, Seitz S M, Szeliski R. Manhattan-world stereo. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1422-1429 [3] Furukawa Y, Ponce J. Accurate, dense, and robust multiview stereopsis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(8):1362-1376 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.161 [4] Gallup D, Frahm J M, Mordohai P, Yang Q X, Pollefeys M. Real-time plane-sweeping stereo with multiple sweeping directions. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Minneapolis, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1-8 [5] Mičučík B, Košecká J. Multi-view superpixel stereo in urban environments. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 89(1):106-119 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fe96239fdb830da6de10f12dc00568f9 [6] Sinha S N, Steedly D, Szeliski R. Piecewise planar stereo for image-based rendering. In: Proceedings of 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision. Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2009. 1881-1888 [7] Chauve A L, Labatut P, Pons J P. Robust piecewise-planar 3D reconstruction and completion from large-scale unstructured point data. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2010. 1261-1268 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/221364112_Robust_piecewise-planar_3D_reconstruction_and_completion_from_large-scale_unstructured_point_data [8] Bódis-Szomorú A, Riemenschneider H, Van Gool L. Fast, approximate piecewise-planar modeling based on sparse structure-from-motion and superpixels. In: Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE, 2014. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286683959_Fast_Approximate_Piecewise-Planar_Modeling_Based_on_Sparse_Structure-from-Motion_and_Superpixels [9] Verleysen C, De Vleeschouwer C. Piecewise-planar 3D approximation from wide-baseline stereo. In: Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3327-3336 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/311610322_Piecewise-Planar_3D_Approximation_from_Wide-Baseline_Stereo [10] Tola E, Strecha C, Fua P. Efficient large-scale multi-view stereo for ultra high-resolution image sets. Machine Vision and Applications, 2012, 23(5):903-920 doi: 10.1007/s00138-011-0346-8 [11] Antunes M, Barreto J P, Nunes U. Piecewise-planar reconstruction using two views. Image and Vision Computing, 2016, 46:47-63 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2015.11.008 [12] Raposo C, Antunes M, Barreto J P. Piecewise-planar StereoScan:sequential structure and motion using plane primitives. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(8):1918-1931 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2737425 [13] Comaniciu D, Meer P. Mean shift:a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(5):603-619 doi: 10.1109/34.1000236 [14] Pham T T, Chin T J, Yu J, Suter D. The random cluster model for robust geometric fitting. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(8):1658-1671 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.2296310 [15] Hartley R, Zisserman A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision (Second Edition). Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2004. 1-672 [16] Wang Z F, Zheng Z G. A region based stereo matching algorithm using cooperative optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-MOTO200905003.htm [17] Huang X F. Cooperative optimization for energy minimization: a case study of stereo matching[Online], available: http://arxiv.org/pdf/cs.CV/0701057, January 9, 2007. [18] Zhao H S, Shi J P, Qi X J, Wang X G, Jia J Y. Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6230-6239 [19] Zisserman A, Vedaldi A. VGG Multi-view Data[Online], available: http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/mview/, November 7, 2019 [20] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2):91-110 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ025429678/ -




 下载:
下载:










