-
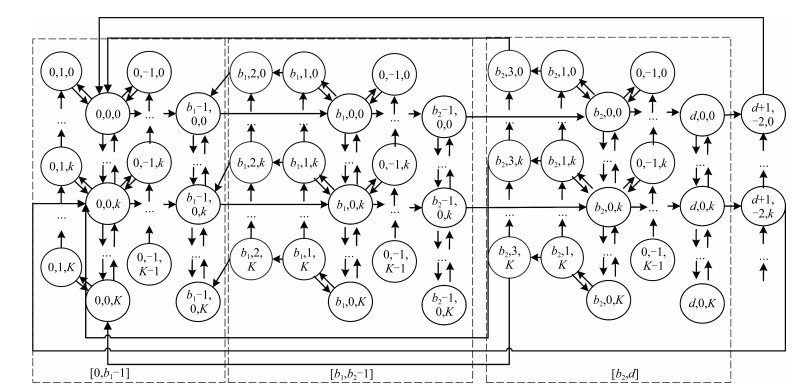
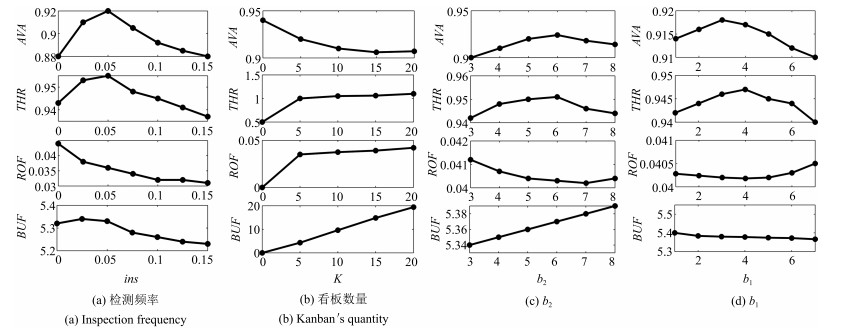
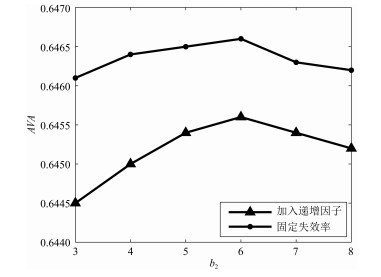
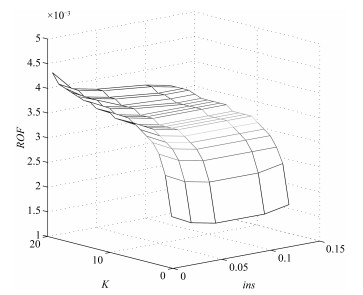
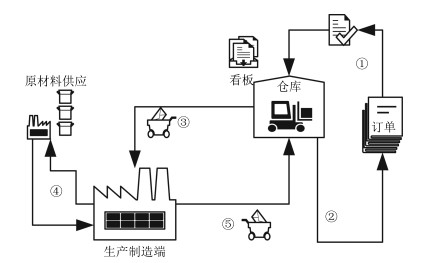
摘要: 为了有效解决同时具有随机失效与退化失效的拉式生产系统的维护问题,提出了基于状态的双阶段预防性维护(Preventive maintenance,PM)策略.首先,根据设备的退化状态、生产端状态以及库存容量构建了系统的状态空间,并利用马尔科夫链描述系统的状态转移.之后,分别以最小化失效率和最大化产出速率为目标,建立了考虑检测周期、看板数量以及预防性维护阈值的综合预防性维护模型.针对设备随役龄增加而故障频发的特点,引入失效率递增因子.最后,给出了最小化失效率和最大化产出速率两种目标下的求解算法,并对决策变量做了敏感性分析.数值实例与现有方案的对比表明了所建模型和算法的有效性.Abstract: To solve the preventive maintenance (PM) problem for a pull production system with both degradation failure and random failure, a two-stage conditional preventive maintenance strategy is proposed. First, the system's state space is built according to the machine's degradation state, the production system's state and the amounts of products in buffers; the state transition matrix is constructed using Markov chain. Then, a joint preventive maintenance and production control optimization model with the goal of minimizing the failure probability and maximizing the throughput rate is built, which takes the inspection period, amounts of Kanban and PM threshold into account simultaneously. Meanwhile, the failure rate increasing factor is introduced into the modeling of the degradation process of machine. Finally, an algorithm for solving the model is proposed, and its sensitivity analysis for key parameters is conducted. Numerical experiments and contrast experiment with the current strategy have verified the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed model.
-
Key words:
- Pull system /
- preventive maintenance (PM) /
- Kanban /
- Markov chain /
- genetic algorithm
1) 本文责任编委 胡昌华 -
表 1 符号及含义
Table 1 Symbols and definitions
符号 定义 $i$ 退化阶段序号 $j$ 生产端状态 $d$ 退化总阶段 $k$ 库存区产品数量 $K$ 看板最优量(决策量) $ins$ 最优检测速率(决策量) $b_1$ & $b_2$ 阈值(决策量) $\lambda_d$ 退化速率 $\lambda_i$ 阶段$i$的失效速率 $\lambda_a$ 订单到达速率 $\lambda_p$ 订单完成速率 $1/{\lambda _{\rm{ins}}}$ 检测平均间隔期 $1/\mu_{ins}$ 检测平均用时 $1/\mu_r$ 小修平均用时 $1/\mu_{upm}$ UPM平均用时 $1/\mu_{ppm}$ PPM平均用时 $1/\mu_{up}$ 更换平均用时 $UB$ & $LB$ 数值上(下)限 表 2 实验参数
Table 2 Experiment parameters
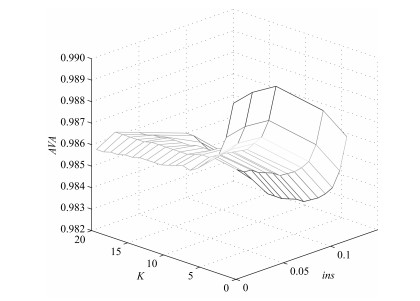
变量 值 实际值 $\lambda_a$ 1.0 接单能力平均100单/天 $\lambda_p$ 1.4 生产能力平均140单/天 $\lambda_d$ 0.02 平均50天退化一个程度 $\lambda_0$ 0.005 初始状态失效间隔期200天 $d$ 8 退化分为8个阶段 $\mu_{ins}$ 0.8 检测平均用时1.25 h $\mu_{r}$ 0.25 小修平均用时4 h $\mu_{upm}$ 1 非完美维护平均用时1 h $\mu_{ppm}$ 0.5 完美维护平均用时2 h $\mu_{up}$ 0.2 更换平均用时5 h 表 3 $\lambda_a=1.0 $时结果对比
Table 3 Comparison of results when $\lambda_a=1.0$
$\lambda_p$ $ROF$ $K, \lambda_{ins}, b_1, b_2$
$K, \lambda_{ins}, b$$THR$ $K, \lambda_{ins}, b_1, b_2$
$K, \lambda_{ins}, b$${\bf 1.0}$ ${\bf 0.0370} $ ${\bf 6, 0.074, 2, 4} $ ${\bf 0.87} $ ${\bf 10, 0.043, 2, 5}$ $0.0393 $ $7, 0.082, 3 $ $0.82 $ $11, 0.103, 5 $ ${\bf 1.2}$ ${\bf 0.0395} $ ${\bf 10, 0.179, 2, 6} $ ${\bf 0.960 } $ ${\bf 11, 0.149, 3, 5} $ $0.0402 $ $10, 0.152, 4 $ $0.94 $ $11, 0.124, 2 $ ${\bf 1.4}$ ${\bf 0.0339} $ ${\bf 6, 0.074, 2, 4} $ ${\bf 1.001} $ ${\bf 20, 0.035, 6, 7}$ $0.0351 $ $7, 0.081, 3 $ $1.201 $ $19, 0.042, 4 $ ${\bf 1.6}$ ${\bf 0.0297} $ ${\bf 5, 0.151, 2, 6} $ ${\bf 1.202} $ ${\bf 20, 0.018, 5, 8} $ $0.0321 $ $6, 0.181, 1 $ $1.187 $ $21, 0.032, 3 $ -
[1] Ji M, He Y, Cheng T C E. Single-machine scheduling with periodic maintenance to minimize makespan. Computers and Operations Research, 2007, 34(6):1764-1770 doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2005.05.034 [2] Lu S S, Tu Y C, Lu H T. Predictive condition-based maintenance for continuously deteriorating systems. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 2007, 23(1):71-81 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1638 [3] Pan E S, Liao W Z, Xi L F. Single-machine-based production scheduling model integrated preventive maintenance planning. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2010, 50(1-4):365-375 doi: 10.1007/s00170-009-2514-9 [4] Fitouhi M C, Nourelfath M. Integrating noncyclical preventive maintenance scheduling and production planning for a single machine. International Journal of Production Economics, 2012, 136(2):344-351 doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.12.021 [5] Nourelfath M, Fitouhi M C, Machani M. An integrated model for production and preventive maintenance planning in multi-state systems. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2010, 59(3):496-506 doi: 10.1109/TR.2010.2056412 [6] Brundage M P, Chang Q, Li Y, Arinez J, Xiao G X. Utilizing energy opportunity windows and energy profit bottlenecks to reduce energy consumption per part for a serial production line. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering. Taipei, China: IEEE, 2014. 461-466 [7] Golmakani H R. Optimal age-based inspection scheme for condition-based maintenance using A* search algorithm. International Journal of Production Research, 2012, 50(23):7068-7080 doi: 10.1080/00207543.2012.664793 [8] Golmakani H R, Pouresmaeeli M. Optimal replacement policy for condition-based maintenance with non-decreasing failure cost and costly inspection. Journal of Quality in Maintenance Engineering, 2014, 20(1):51-64 doi: 10.1108/JQME-12-2012-0044 [9] Karamatsoukis C C, Kyriakidis E G. Optimal maintenance of two stochastically deteriorating machines with an intermediate buffer. European Journal of Operational Research, 2010, 207(1):297-308 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2010.04.022 [10] 陆志强, 张思源, 崔维伟.集成预防性维护和流水线调度的鲁棒性优化研究.自动化学报, 2015, 41(5):906-913 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18665.shtmlLu Zhi-Qiang, Zhang Si-Yuan, Cui Wei-Wei. Integrating production scheduling and maintenance policy for robustness in flow shop problems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5):906-913 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18665.shtml [11] 高文科, 张志胜, 周一帆, 刘飏, 刘祺.存在故障相关及不完备检测的主辅并联系统可靠性建模与维修策略.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12):2100-2114 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18783.shtmlGao Wen-Ke, Zhang Zhi-Sheng, Zhou Yi-Fan, Liu Yang, Liu Qi. Reliability modeling and maintenance policy for main and supplementary parallel system with failure interaction and imperfect detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12):2100-2114 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18783.shtml [12] Lavoie P, Gharbi A, Kenné J P. A comparative study of pull control mechanisms for unreliable homogenous transfer lines. International Journal of Production Economics, 2010, 124(1):241-251 doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2009.11.022 [13] Khojasteh Y, Sato R. Selection of a pull production control system in multi-stage production processes. International Journal of Production Research, 2015, 53(14):4363-4379 doi: 10.1080/00207543.2014.1001530 [14] Thürer M, Stevenson M, Protzman C W. Card-based production control:a review of the control mechanisms underpinning Kanban, ConWIP, POLCA and COBACABANA systems. Production Planning and Control, 2016, 27(14):1143-1157 doi: 10.1080/09537287.2016.1188224 [15] Xanthopoulos A S, Koulouriotis D E, Botsaris P N. Single-stage Kanban system with deterioration failures and condition-based preventive maintenance. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2015, 142:111-122 doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2015.05.008 [16] Ezema C N, Nonum E O, Umezinwa C N, Igwe J I. Optimal performance enhancement using JIT manufacturing system simulation model. International Journal of Technology and Systems, 2016, 1(1):48-71 http://iprjb.org/journals/index.php/IJTS/article/view/60 [17] Batra R, Nanda S, Singhal S, Singari R. Study of Lean Production System Using Value Stream Mapping in Manufacturing Sector and Subsequent Implementation in Tool Room. SAE Technical Papers, Delhi Technological University, India, 2016. [18] 綦法群, 周炳海.基于Markov过程的集束型设备预防维护策略.上海交通大学学报, 2014, 48(10):1461-1467 http://xuebao.sjtu.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8602.shtmlQi Fa-Qun, Zhou Bing-Hai. Preventive maintenance policy of cluster tools based on Markov process. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2014, 48(10):1461-1467 http://xuebao.sjtu.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8602.shtml [19] 夏唐斌, 周晓军, 奚立峰.基于失效率调整因子的多目标动态预防性维护决策建模.上海交通大学学报, 2009, 43(5):821-824 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/SHJT200905030.htmXia Tang-Bin, Zhou Xiao-Jun, Xi Li-Feng. Multi-attribute model for dynamic preventive maintenance decision with hybrid evolution factors. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2009, 43(5):821-824 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/SHJT200905030.htm [20] Zhou B H, Liu Z L. Optimizing preventive maintenance:a deteriorating system with buffers. Industrial Management and Data Systems, 2016, 116(8):1719-1740 doi: 10.1108/IMDS-01-2016-0026 -




 下载:
下载: