Prediction of Malignant and Benign Lung Tumors Using a Quantitative Radiomic Method
-
摘要: 肺癌是世界范围内致死率最高的癌症之一,肺肿瘤的良恶性诊断对于治疗方式选择意义重大.本文借助影像组学(Radiomics)方法利用LIDC(Lung imaging database consortium)肺癌公开数据库中619例病人的肺癌计算机断层(Computed tomography,CT)影像数据,分割出病变区域,并结合肿瘤医学特性和临床认知,提取反映肿瘤形状大小、强度和纹理特性的60个定量影像特征,然后利用支持向量机(Support vector machine,SVM)构建诊断肺肿瘤良恶性的预测模型,筛选出对诊断肺肿瘤良恶性有价值的20个影像组学特征.为肺肿瘤良恶性预测提供了一种非入侵的检测手段.随着CT影像在肺癌临床诊断中的广泛使用,应用样本量的不断增加,本文方法有望成为一种辅助诊断工具,有效提高临床肺肿瘤良恶性诊断准确率.Abstract: Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer mortality around the world. Accurate diagnosis of lung cancer is significant for treatment regimen selection. Radiomics refers to comprehensively quantifying the tumor phenotypes by applying a large number of quantitative image features. Here we analyze a computed tomography (CT) data set of 619 patients with lung cancer on the lung image database consortium (LIDC) by radiomic method. Combining with the medical character and clinical recognition of lung tumor, we present a radiomic analysis of 60 features. Then, we use SVM to build a prediction model and find radiomic features which have predictive value for discrimination of malignant and benign lung tumors. Nowadays, as CT imaging is routinely used in lung cancer clinical diagnosis, there is an increase in data set size. We consider that our radiomic prediction model will be developed a valuable medical software and an auxiliary tool which can provide malignant and benign information of lung tumors efficiently.
-
Key words:
- Radiomics /
- lung cancer /
- image segmentation /
- feature extraction /
- support vector machine (SVM)
1) 本文责任编委 朱朝喆 -
表 1 肺肿瘤良恶性预测模型的诊断准确率
Table 1 Diagnostic accuracy of benign and malignant discrimination model of lung tumor
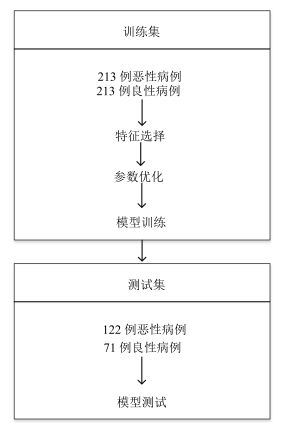
数据集 灵敏度(%) 特异性(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) 准确度(%) 训练集 82.2 82.6 82.5 82.2 82.4 (175/213) (176/213) (175/212) (176/214) (351/426) 测试集 75.4 81.6 87.6 65.9 77.7 (92/122) (58/71) (92/105) (58/88) (150/193) 总计 79.9 82.4 84.2 77.5 80.9 (257/335) (234/284) (267/317) (234/302) (501/619) -
[1] Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout R G P M, Granton P, Zegers C M L, Gillies R, Boellard R, Dekker A, Aerts H J W L. Radiomics:extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. European Journal of Cancer, 2012, 48(4):441-446 doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036 [2] Aerts H J W L, Velazquez E R, Leijenaar R T H, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Carvalho S, Bussink J, Monshouwer R, Haibe-Kains B, Rietveld D, Hoebers F, Rietbergen M M, Leemans C R, Dekker A, Quackenbush J, Gillies R J, Lambin P. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nature Communications, 2014, 5:Article No. 4006 [3] Huang Y Q, Liang C H, He L, Tian J, Liang C S, Chen X, Ma Z L, Liu Z Y. Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2016, 34(18):2157-2164 doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.9128 [4] World Health Organization. Description of the global burden of NCDs, their risk factors and determinants. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010. World Health Organization, 2011. 1-176 [5] Parmar C, Leijenaar R, Grossmann P, Velazquez E R, Bussink J, Rietveld D, Rietbergen M M, Haibe-Kains B, Lambin P, Aerts H J W L. Radiomic feature clusters and prognostic signatures specific for lung and head and neck cancer. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:Article No. 11044 [6] Kumar V, Gu Y H, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich S A, Schabath M B, Forster K, Aerts H J W L, Dekker A, Fenstermacher D, Goldgof D B, Hall L O, Lambin P, Balagurunathan Y, Gatenby R A, Gillies R J. Radiomics:the process and the challenges. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2012, 30(9):1234-1248 doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.010 [7] Gillies B, Kinahan P E, Hricak H. Radiomics:images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology, 2016, 278(2):563-577 doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169 [8] Armato S G, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray M F, Meyer C R, Reeves A P, Zhao B S, Aberle D R, Henschke C I, Hoffman E A, Kazerooni E A, MacMahon H, van Beek E J R, Yankelevitz D, Biancardi A M, Bland P H, Brown M S, Engelmann R M, Laderach G E, Max D, Pais R C, Qing D P Y, Roberts R Y, Smith A R, Starkey A, Batra P, Caligiuri P, Farooqi A, Gladish G W, Jude C M, Munden R F, Petkovska I, Quint L E, Schwartz L H, Sundaram B, Dodd L E, Fenimore C, Gur D, Petrick N, Freymann J, Kirby J, Hughes B, Vande C A, Gupte S, Sallam M, Heath M D, Kuhn M H, Dharaiya E, Burns R, Fryd D S, Salganicoff M, Anand V, Shreter U, Vastagh S, Croft B Y, Clarke L P. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI):a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Medical Physics, 2011, 38(2):915-931 doi: 10.1118/1.3528204 [9] Song J, Yang C, Fan L, Wang K, Yang F, Liu S, Tian J. Lung lesion extraction using a toboggan based growing automatic segmentation approach. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(1):337-353 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2474119 [10] Dougherty E R, Hua J P, Sima C. Performance of feature selection methods. Current Genomics, 2009, 10(6):365-374 doi: 10.2174/138920209789177629 [11] Peng H C, Long F H, Ding C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(8):1226-1238 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159 [12] Vapnik V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. New York:Springer Science and Business Media, 2013. 123-167 [13] 张学工.关于统计学习理论与支持向量机.自动化学报, 2000, 26(1):32-42 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14696.shtmlZhang Xue-Gong. Introduction to statistical learning theory and support vector machines. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2000, 26(1):32-42 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14696.shtml [14] Chang C C, Lin C J. LIBSVM:a library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2011, 2(3):Article No. 27 [15] 张凯军, 梁循.一种改进的显性多核支持向量机.自动化学报, 2014, 40(10):2288-2294 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18503.shtmlZhang Kai-Jun, Liang Xun. An improved domain multiple kernel support vector machine. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(10):2288-2294 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18503.shtml [16] Whitley D, Starkweather T, Bogart C. Genetic algorithms and neural networks:optimizing connections and connectivity. Parallel Computing, 1990, 14(3):347-361 doi: 10.1016/0167-8191(90)90086-O [17] Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:NSGA-Ⅱ. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2):182-197 doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [18] Song J D, Liu Z Y, Zhong W Z, Huang Y Q, Ma Z L, Dong D, Liang C H, Tian J. Non-small cell lung cancer:quantitative phenotypic analysis of CT images as a potential marker of prognosis. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No. 38282 -




 下载:
下载: