|
[1]
|
Port F D. Treatment of paralysis. The Decade of Medicine or the Physician of the Rich and the Poorć. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer, 1988. 108-109
|
|
[2]
|
李建军, 周红俊, 洪毅, 季京平, 刘根林, 粟绍强, 赵超男, 董云英, 方玉美, 谭鹏, 周天健, 张爱民, 郑樱. 2002年北京市脊髓损伤发病率调查.中国康复理论与实践, 2004, 10(7):412-413 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKLS200407016.htmLi Jian-Jun, Zhou Hong-Jun, Hong Yi, Ji Jing-Ping, Liu Gen-Lin, Su Shao-Qiang, Zhao Chao-Nan, Dong Yun-Ying, Fang Yu-Mei, Tan Peng, Zhou Tian-Jian, Zhang Ai-Min, Zheng Ying. Spinal cord injuries in Beijing:a municipal epidemiological survey in 2002. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice, 2004, 10(7):412-413 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKLS200407016.htm
|
|
[3]
|
Liu M, Wu B, Wang W Z, Lee L M, Zhang S H, Kong L Z. Stroke in China:epidemiology, prevention, and management strategies. The Lancet Neurology, 2007, 6(5):456-464 doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70004-2
|
|
[4]
|
Zorowitz R D, Gillard P J, Brainin M. Poststroke spasticity:sequelae and burden on stroke survivors and caregivers. Neurology, 2013, 80(Suppl 3):S45-S52 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234155984_Poststroke_spasticity_Sequelae_and_burden_on_stroke_survivors_and_caregivers
|
|
[5]
|
李建军.中国康复医学发展的回顾与展望.中国康复理论与实践, 2011, 17(1):1-4 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKLS201101002.htmLi Jian-Jun. Advance in rehabilitation medicine in China:review and prospects. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice, 2011, 17(1):1-4 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKLS201101002.htm
|
|
[6]
|
Eustis S. Global Robotic Prosthetics, Exoskeletons and Assistive Rehabilitation Technologies Market Assessment & Forecast:2015——2019. Winter Green Research, USA, 2016.
|
|
[7]
|
Kazerooni H. Human augmentation and exoskeleton systems in Berkeley. International Journal of Humanoid Robotics, 2007, 4(3):575-605 doi: 10.1142/S0219843607001187
|
|
[8]
|
Harris S. Exoskeleton stands on its own two feet. Engineer, 2011, 296(7827):1-8 http://nynashamnsnaturskola.se/pdfHtm/MOVEMENT_OF_ANIMALS_1_medbilder.pdf
|
|
[9]
|
Lu R Q, Li Z J, Su C Y, Xue A K. Development and learning control of a human limb with a rehabilitation exoskeleton. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(7):3776-3785 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2275903
|
|
[10]
|
Huang R, Cheng H, Chen Q M, Tran H T, Lin X C. Interactive learning for sensitivity factors of a human-powered augmentation lower exoskeleton. In:Proceeding of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Hamburg, Germany:IEEE, 2015. 6409-6415
|
|
[11]
|
Tsagarakis N G, Caldwell D G. Development and control of a 'soft-actuated' exoskeleton for use in physiotherapy and training. Autonomous Robots, 2003, 15(1):21-33 doi: 10.1023/A:1024484615192
|
|
[12]
|
Wehner M, Quinlivan B, Aubin P M, Martinez-Villalpando E, Baumann M, Stirling L, Holt K, Wood R, Walsh C. A lightweight soft exosuit for gait assistance. In:Proceeding of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe, Germany:IEEE, 2013. 3362-3369
|
|
[13]
|
Müller-Putz G R, Zimmermann D, Graimann B, Nestinger K, Korisek G, Pfurtscheller G. Event-related beta EEG-changes during passive and attempted foot movements in paraplegic patients. Brain Research, 2007, 1137:84-91 doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.12.052
|
|
[14]
|
Qiu S, Yi W B, Xu J P, Qi H P, Du J G, Wang C F, He F, Ming D. Event-related beta EEG changes during active, passive movement and functional electrical stimulation of the lower limb. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2016, 24(2):283-290 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2015.2476481
|
|
[15]
|
del-Ama A J, Gil-Agudo Á, Pons J L, Moreno J C. Hybrid FES-robot cooperative control of ambulatory gait rehabilitation exoskeleton. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 2014, 11:Article No. 27 doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-11-27
|
|
[16]
|
Ha K H, Quintero H A, Farris R J, Goldfarb M. Enhancing stance phase propulsion during level walking by combining FES with a powered exoskeleton for persons with paraplegia. In:Proceeding of the 2012 IEEE Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. San Diego, USA:IEEE, 2012. 344-347
|
|
[17]
|
Baker R. Gait analysis methods in rehabilitation. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 2006, 3:Article No. 4 doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-3-4
|
|
[18]
|
Cappozzo A. Gait analysis methodology. Human Movement Science, 1984, 3(1-2):27-50 doi: 10.1016/0167-9457(84)90004-6
|
|
[19]
|
Bowker P. Gait analysis:an introduction. Physiotherapy, 1991, 77(11):786 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA18631162
|
|
[20]
|
Tao W, Liu T, Zheng R C, Feng H T. Gait analysis using wearable sensors. Sensors, 2012, 12(2):2255-2283 http://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/12/2/2255/pdf
|
|
[21]
|
Bejarano N C, Ambrosini E, Pedrocchi A, Ferrigno G, Monticone M, Ferrante S. A novel adaptive, real-time algorithm to detect gait events from wearable sensors. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2015, 23(3):413-422 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2337914
|
|
[22]
|
Zeilig G, Weingarden H, Zwecker M, Dudkiewicz I, Bloch A, Esquenazi A. Safety and tolerance of the ReWalkm TM exoskeleton suit for ambulation by people with complete spinal cord injury:a pilot study. Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine, 2012, 35(2):96-101 doi: 10.1179/2045772312Y.0000000003
|
|
[23]
|
Esquenazi A, Talaty M, Packel A, Saulino M. The ReWalk powered exoskeleton to restore ambulatory function to individuals with thoracic-level motor-complete spinal cord injury. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 2012, 91(11):911-921 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232532271_The_ReWalk_Powered_Exoskeleton_to_Restore_Ambulatory_Function_to_Individuals_with_Thoracic-Level_Motor-Complete_Spinal_Cord_Injury
|
|
[24]
|
Pappas I P I, Keller T, Mangold S, Popovic M R, Dietz V, Morari M. A reliable gyroscope-based gait-phase detection sensor embedded in a shoe insole. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2004, 4(2):268-274 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2004.823671
|
|
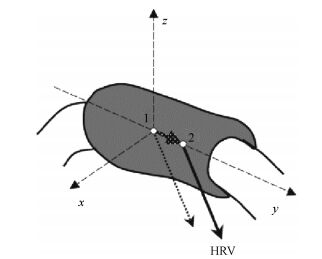
[25]
|
Donaldson N, Yu C H. A study of handle reaction vector (HRV) in walker FES standing. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, 1996, 211(1):81-94 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220715359_Study_on_wireless_dynamometer_walker_system
|
|
[26]
|
Ming D, Wan B K, Hu Y, Wang Y Z, Wu Y H, Liang Z R. Dynamical measurement method of handle reaction vector for FES-assisted paraplegic walking. Transactions of Tianjin University, 2005, 11(5):318-321 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283250125_Dynamical_measurement_method_of_handle_reaction_vector_for_FES-assisted_paraplegic_walking
|
|
[27]
|
Xu R, Qiu S, Zhai T, Xu Q, Qi H, Zhou P, Zhang L, Wan B, Ming D. Step side recognition based on handle reaction forces during functional electrical stimulation. Biomedical Engineering/Biomedizinische Technik, 2013, 58(Suppl 1), DOI: 10.1515/bmt-2013-4023
|
|
[28]
|
Farris R J, Quintero H A, Goldfarb M. Preliminary evaluation of a powered lower limb Orthosis to aid walking in paraplegic individuals. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2011, 19(6):652-659 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2011.2163083
|
|
[29]
|
Suzuki K, Mito G, Kawamoto H, Hasegawa Y, Sankai Y. Intention-based walking support for paraplegia patients with robot suit HAL. Advanced Robotics, 2007, 21(12):1441-1469 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yasuhisa_Hasegawa/publication/220670867_Intention-Based_Walking_Support_for_Paraplegia_Patients_with_Robot_Suit_HAL/links/0deec51bfedc7241c7000000/Intention-Based-Walking-Support-for-Paraplegia-Patients-with-Robot-Suit-HAL.pdf
|
|
[30]
|
Tsukahara A, Hasegawa Y, Eguchi K, Sankai Y. Restoration of gait for spinal cord injury patients using HAL with intention estimator for preferable swing speed. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2015, 23(2):308-318 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2364618
|
|
[31]
|
Yakub F, Md. Khudzari A Z, Mori Y. Recent trends for practical rehabilitation robotics, current challenges and the future. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research, 2014, 37(1):9-21 doi: 10.1097/MRR.0000000000000035
|
|
[32]
|
Gomez-Rodriguez M, Peters J, Hill J, Schölkopf B, Gharabaghi A, Grosse-Wentrup M. Closing the sensorimotor loop:haptic feedback facilitates decoding of motor imagery. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2011, 8(3):Article No. 036005 http://www.ias.tu-darmstadt.de/uploads/Publications/Gomez-RodriguezJNE2011.pdf
|
|
[33]
|
Takahashi M, Takeda K, Otaka Y, Osu R, Hanakawa T, Gouko M, Ito K. Event related desynchronization-modulated functional electrical stimulation system for stroke rehabilitation:a feasibility study. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 2012, 9:Article No. 56 doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-9-56
|
|
[34]
|
Jiang S L, Chen L, Wang Z P, Xu J P, Qi C, Qi H Z, He F, Ming D. Application of BCI-FES system on stroke rehabilitation. In:Proceeding of the 7th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering. Montpellier, France:IEEE, 2015. 1112-1115
|
|
[35]
|
Hara Y, Obayashi S, Tsujiuchi K, Muraoka Y. The effects of electromyography-controlled functional electrical stimulation on upper extremity function and cortical perfusion in stroke patients. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2013, 124(10):2008-2015 doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.03.030
|
|
[36]
|
Young W. Electrical stimulation and motor recovery. Cell Transplantation, 2015, 24(3):429-446 doi: 10.3727/096368915X686904
|
|
[37]
|
Zoss A, Evans J, Sandler R, Harding N, Julin A, Lubin J, Heanue T, Fairbanks D, Stryker J. Reconfigurable Exoskeleton, World Patent 2014093470, June 2014.
|
|
[38]
|
Contreras-Vidal J L, Prasad S, Kilicarslan A, Bhagat N. Methods for Closed-loop Neural-machine Interface Systems for the Control of Wearable Exoskeletons and Prosthetic Devices, U.S. Patent 20150012111, January 2015.
|
|
[39]
|
Fernandez-Leon J A, Acosta G G, Rozenfeld A. How simple autonomous decisions evolve into robust behaviours?:A review from neurorobotics, cognitive, self-organized and artificial immune systems fields. BioSystems, 2014, 124:7-20 doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2014.08.003
|
|
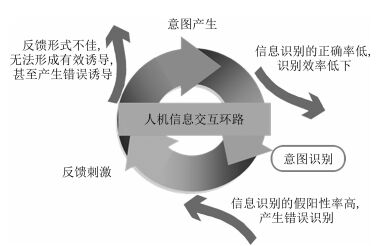
[40]
|
Murphy T H, Corbett D. Plasticity during stroke recovery:from synapse to behaviour. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2009, 10(12):861-872 doi: 10.1038/nrn2735
|
|
[41]
|
Barbero Á, Grosse-Wentrup M. Biased feedback in brain-computer interfaces. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 2010, 7:Article No. 34 doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-7-34
|
|
[42]
|
Grosse-Wentrup M, Liefhold C, Gramann K, Buss M. Beamforming in noninvasive brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 56(4):1209-1219 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2008.2009768
|
|
[43]
|
Grosse-Wentrup M, Mattia D, Oweiss K. Using brain-computer interfaces to induce neural plasticity and restore function. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2011, 8(2):Article No. 025004 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/bookmark?doi=10.1.1.370.8901&title=Using%20brain–computer%20interfaces%20to%20induce%20neural%20plasticity%20and%20restore%20function&site=digg
|
|
[44]
|
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553):436-444 doi: 10.1038/nature14539
|
|
[45]
|
Torres-Oviedo G, Vasudevan E, Malone L, Bastian A J. Locomotor adaptation. Progress in Brain Research, 2011, 191:65-74 doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53752-2.00013-8
|
|
[46]
|
Patla A E. Some characteristics of EMG patterns during locomotion:implications for the locomotor control process. Journal of Motor Behavior, 1985, 17(4):443-461 doi: 10.1080/00222895.1985.10735360
|
|
[47]
|
明东, 王坤, 何峰, 綦宏志, 万柏坤.想象动作诱发生理信息检测及其应用研究:回顾与展望.仪器仪表学报, 2014, 35(9):1921-1931 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201409001.htmMing Dong, Wang Kun, He Feng, Qi Hong-Zhi, Wan Bai-Kun. Study on physiological information detection and application evoked by motor imagery:review and prospect. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(9):1921-1931 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201409001.htm
|
|
[48]
|
Pfurtscheller G, da Silva F H L. Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization:basic principles. Clinical Neurophysiology, 1999, 110(11):1842-1857 doi: 10.1016/S1388-2457(99)00141-8
|
|
[49]
|
Servick K. Kickoff looms for demo of brain-controlled machine. Science, 2014, 344(6188):1069-1070 doi: 10.1126/science.344.6188.1069
|
|
[50]
|
Rajangam S, Tseng P H, Yin A, Lehew G, Schwarz D, Lebedev M A, Nicolelis M A. Wireless cortical brain-machine interface for whole-body navigation in primates. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No. 22170 doi: 10.1038/srep22170
|
|
[51]
|
Gwin J T, Ferris D P. An EEG-based study of discrete isometric and isotonic human lower limb muscle contractions. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 2012, 9:Article No. 35 doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-9-35
|
|
[52]
|
Edelman B J, Baxter B, He B. EEG source imaging enhances the decoding of complex right-hand motor imagery tasks. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 63(1):4-14 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2467312
|
|
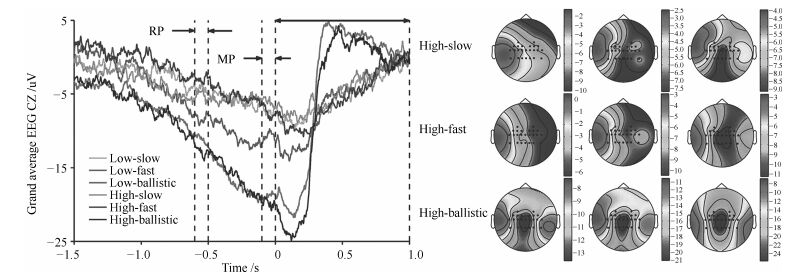
[53]
|
Niazi I K, Jiang N, Tiberghien O, Nielsen J F, Dremstrup K, Farina D. Detection of movement intention from single-trial movement-related cortical potentials. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2011, 8(6):Article No. 066009 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51745583_Detection_of_movement_intention_from_single-trial_movement-related_cortical_potentials
|
|
[54]
|
do Nascimento O F, Nielsen K D, Voigt M. Movement-related parameters modulate cortical activity during imaginary isometric plantar-flexions. Experimental Brain Research, 2006, 171(1):78-90 doi: 10.1007/s00221-005-0247-z
|
|
[55]
|
Jochumsen M, Niazi I K, Mrachacz-Kersting N, Farina D, Dremstrup K. Detection and classification of movement-related cortical potentials associated with task force and speed. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2013, 10(5):Article No. 056015 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256201186_Detection_and_classification_of_movement-related_cortical_potentials_associated_with_task_force_and_speed
|
|
[56]
|
Ibáñez J, Serrano J I, del Castillo M D, Monge-Pereira E, Molina-Rueda F, Alguacil-Diego I, Pons J L. Detection of the onset of upper-limb movements based on the combined analysis of changes in the sensorimotor rhythms and slow cortical potentials. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2014, 11(5):Article No. 056009 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264432388_Detection_of_the_onset_of_upper-limb_movements_based_on_the_combined_analysis_of_changes_in_the_sensorimotor_rhythms_and_slow_cortical_potentials
|
|
[57]
|
Lu J, Xie K, McFarland D J. Adaptive spatio-temporal filtering for movement related potentials in EEG-based brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2014, 22(4):847-857 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2315717
|
|
[58]
|
Yi W B, Qiu S, Wang K, Qi H Z, Zhang L X, Zhou P, He F, Ming D. Evaluation of EEG oscillatory patterns and cognitive process during simple and compound limb motor imagery. PLoS One, 2014, 9(12):e114853 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114853
|
|
[59]
|
Nascimento O F D, Nielsen K D, Voigt M. Relationship between plantar-flexor torque generation and the magnitude of the movement-related potentials. Experimental Brain Research, 2005, 160(2):154-65 doi: 10.1007/s00221-004-1996-9
|
|
[60]
|
彭亮, 侯增广, 王卫群.康复机器人的同步主动交互控制与实现.自动化学报, 2015, 41(11):1837-1846 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18759.shtmlPeng Liang, Hou Zeng-Guang, Wang Wei-Qun. Synchronous active interaction control and its implementation for a rehabilitation robot. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(11):1837-1846 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18759.shtml
|
|
[61]
|
丁其川, 熊安斌, 赵新刚, 韩建达.基于表面肌电的运动意图识别方法研究及应用综述.自动化学报, 2016, 42(1):13-25 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18792.shtmlDing Qi-Chuan, Xiong An-Bin, Zhao Xin-Gang, Han Jian-Da. A review on researches and applications of sEMG-based motion intent recognition methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1):13-25 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18792.shtml
|
|
[62]
|
Amsúss S, Goebel P M, Jiang N, Graimann B, Paredes L, Farina D. Self-correcting pattern recognition system of surface EMG signals for upper limb prosthesis control. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 61(4):1167-1176 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2013.2296274
|
|
[63]
|
Fleischer C, Hommel G. A human-exoskeleton interface utilizing electromyography. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(4):872-882 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.926860
|
|
[64]
|
Han J D, Ding Q C, Xiong A B, Zhao X G. A state-space EMG model for the estimation of continuous joint movements. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(7):4267-4275 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2387337
|
|
[65]
|
Feng W W, Belagaje S R. Recent advances in stroke recovery and rehabilitation. Seminars in Neurology, 2013, 33(5):498-506 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24504613/
|





 下载:
下载: