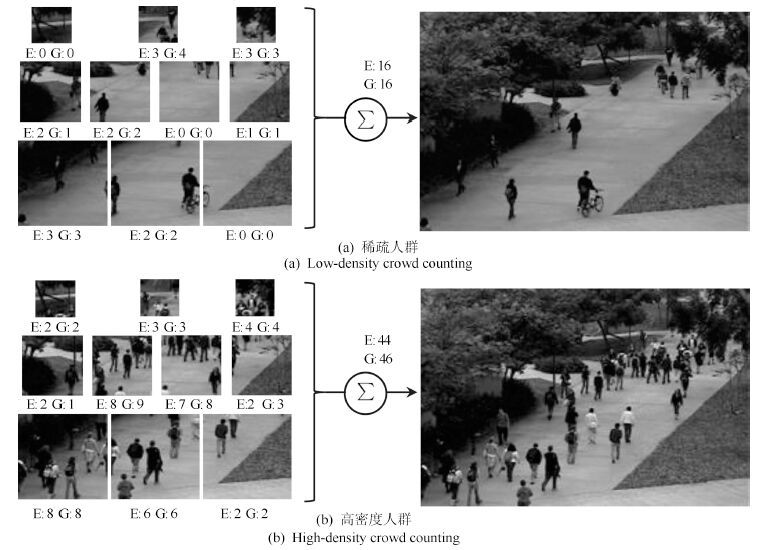
-
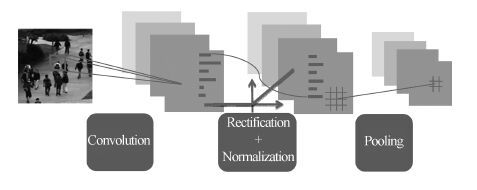
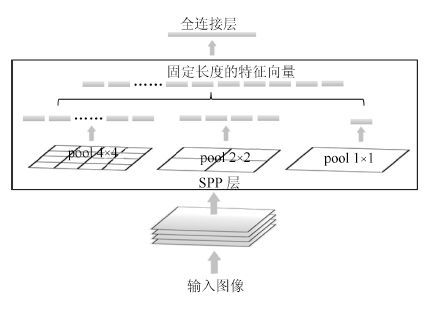
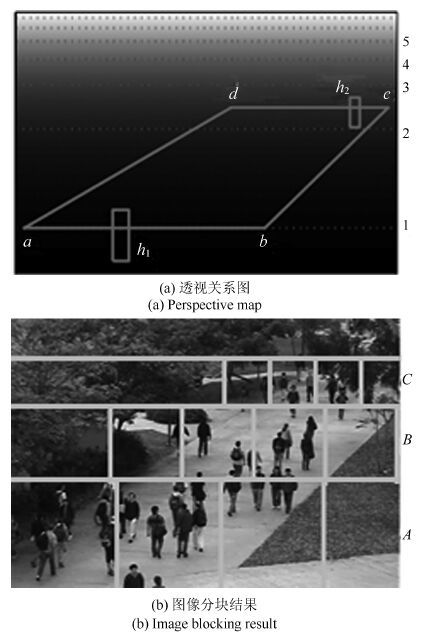
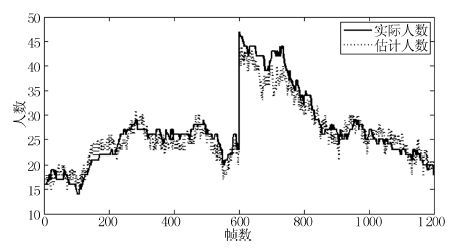
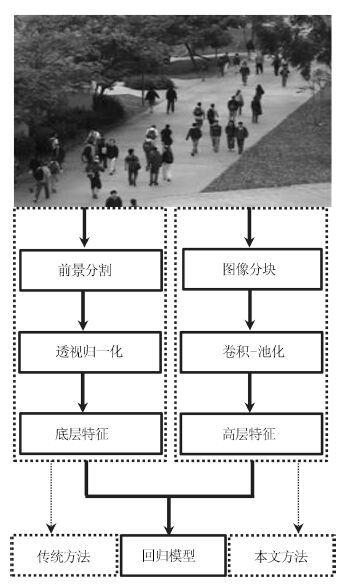
摘要: 视频中的人群计数在智能监控领域具有重要价值. 由于摄像机透视效果、图像背景、人群密度分布不均匀和行人遮挡等干扰因素的制约, 基于底层特征的传统计数方法准确率较低. 本文提出一种基于序的空间金字塔池化(Rank-based spatial pyramid pooling, RSPP)网络的人群计数方法. 该方法将原图像分成多个具有相同透视范围的子区域并在各个子区域分别取不同尺度的子图像块, 采用基于序的空间金字塔池化网络估计子图像块人数, 然后相加所有子图像块人数得出原图像人数. 提出的图像分块方法有效地消除了摄像机透视效果和人群密度分布不均匀对计数的影响. 提出的基于序的空间金字塔池化不仅能够处理多种尺度的子图像块, 而且解决了传统池化方法易损失大量重要信息和易过拟合的问题. 实验结果表明, 本文方法相比于传统方法具有准确率高和鲁棒性好的优点.Abstract: Crowd counting in videos has an important value in the field of intelligent surveillance. Due to the constraints resulting from camera perspective, uneven distribution of crowd density, background clutter, and occlusions, traditional low-level features-based methods suffer from low counting accuracy. In this paper, a new crowd counting method is proposed based on rank-based spatial pyramid pooling (RSPP) network. In the proposed method, the original image is divided into several sub-regions with the same scope of perspective, and then multi-scale sub-image blocks are respectively taken from different sub-regions. Rank-based spatial pyramid pooling network is used to get the numbers of pedestrians in sub-image blocks. Then summing the numbers of persons of all sub-image blocks gives the total number of people on the image. The proposed image blocking method eliminates the effect of camera perspective and uneven distribution of crowd density on crowd counting. The proposed rank-based spatial pyramid pooling can not only handle multi-scale sub-image blocks, but also solve the problem of huge important information loss and over-fitting encountered by traditional pooling methods. Experimental results show that the proposed method has the advantages of high accuracy and good robustness compared with traditional methods.
-
表 1 人群CNN 模型的详细结构
Table 1 Architecture specics for crowd CNN model
层数 1 2 3 4 5(输出) 操作 conv+relu+rsp+rn conv+relu+rsp+rn conv+relu+rspp full full 通道数 64 64 64 512 1 卷积大小 5×5 5×5 5×5 - - 卷积步长 1×1 1×1 1×1 - - 池化大小 3×3 3×3 {4×4, 2×2, 1×1} - - 池化步长 2×2 2×2 - - - 填充大小2 ×2×2×2 2×2×2×2 2×2×2×2 - - 表 2 实验数据
Table 2 Experimental data
图像块尺度 训练集 测试集 64×64 104 000 3 600 44×44 104 000 4 800 28×28 44 000 3 600 表 3 多种池化方法在尺度为64 的子图像块上的测试结果
Table 3 Testing results for sub-image blocks with the scale of 64 of various pooling methods
池化方法 训练集 测试集 MAE MSE MAE MSE 平均池化 1.12 2.29 1.52 3.13 最大池化 0.27 0.13 0.84 1.15 随机池化 1.29 2.27 1.42 3.18 基于序的随机池化 0.43 0.32 0.64 0.81 表 4 子图像块上的测试结果
Table 4 The testing results in sub-image blocks
图像块尺度 联合训练 单独训练 MAE MSE MAE MSE 64×64 0.64 0.81 0.64 0.81 44×44 0.84 1.08 1.98 5.7 28×28 0.72 1.06 1.68 4.16 -
[1] Wu B, Nevatia R. Detection of multiple, partially occluded humans in a single image by Bayesian combination of edgelet part detectors. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005. 90-97 [2] Zhao T, Nevatia R, Wu B. Segmentation and tracking of multiple humans in crowded environments. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(7) : 1198-1211 [3] Chan A B, Liang Z S J, Vasconcelos N. Privacy preserving crowd monitoring: counting people without people models or tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, AK: IEEE, 2008. 1-7 [4] Chan A B, Vasconcelos N. Counting people with low-level features and Bayesian regression. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4) : 2160-2177 [5] Idrees H, Saleemi I, Seibert C, Shah M. Multi-source multi-scale counting in extremely dense crowd images. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 2547-2554 [6] Lempitsky V, Zisserman A. Learning to count objects in images. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NIPS, 2010. 1324-1332 [7] Ma W, Huang L, Liu C. Crowd density analysis using co-occurrence texture features. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Computer Sciences and Convergence Information Technology. Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2010. 170-175 [8] Kong D, Gray D, Tao H. A viewpoint invariant approach for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2006. 1187-1190 [9] Chen K, Loy C C, Gong S G, Xiang T. Feature mining for localised crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the 23rd British Machine Vision Conference. Surrey, British: BMVA Press, 2012. 1-3 [10] Ryan D, Denman S, Sridharan S, Fookes C. An evaluation of crowd counting methods, features and regression models. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2015, 130: 1-17 [11] Rosten E, Porter R, Drummond T. Faster and better: a machine learning approach to corner detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(1) : 105-119 [12] Wu X Y, Liang G Y, Lee K K, Xu Y. Crowd density estimation using texture analysis and learning. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Kunming, China: IEEE, 2006. 214-219 [13] Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786) : 504-507 [14] Zeiler M D, Fergus R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 818-833 [15] Nair V, Hinton G E. Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning. Haifa, Israel: JMLR, 2010. 807-814 [16] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Nevada, USA: NIPS, 2012. 1097-1105 [17] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 346-361 [18] Zeiler M D, Fergus R. Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Learning Representation. Arizona, USA: ICLR, 2013. 1-9 [19] Sainath T N, Kingsbury B, Saon G, Soltau H, Mohamed A R, Dahl G, Ramabhadran B. Deep convolutional neural networks for large-scale speech tasks. Neural Networks, 2015, 64: 39-48 [20] Michalewicz Z. Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures=Evolution Programs. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. 59-61 [21] Saunders C, Gammerman A, Vovk V. Ridge regression learning algorithm in dual variables. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Machine Learning. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1998. 515-521 [22] Jia Y Q, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, Karayev S, Long J, Girshick R, Guadarrama S, Darrell T. Caffe: convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Florida, USA: ACM, 2014. 675-678 [23] Zhang Z X, Wang M, Geng X. Crowd counting in public video surveillance by label distribution learning. Neurocomputing, 2015, 166: 151-163 -




 下载:
下载: