Feature Fusion Analysis of Simultaneously Recorded EEG-fMRI in Emotion Cognitive Reappraisal
-
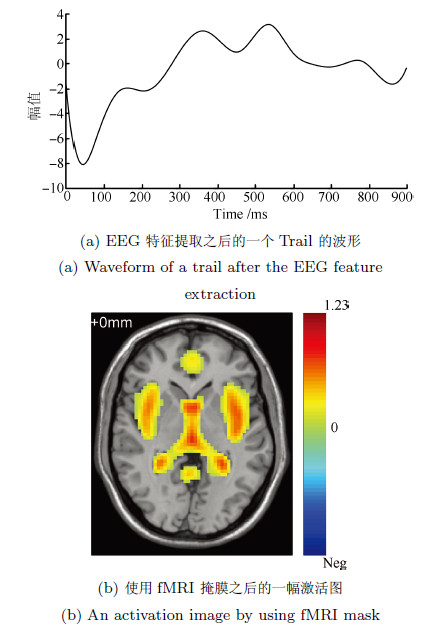
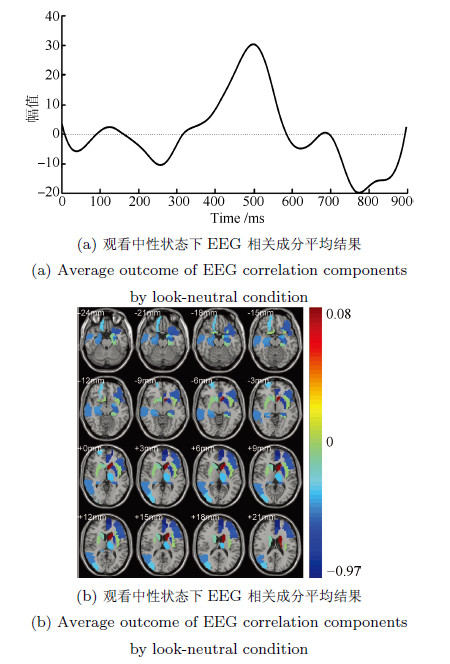
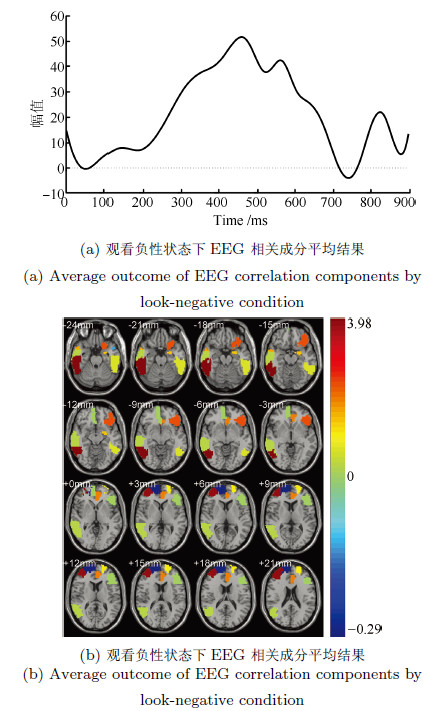
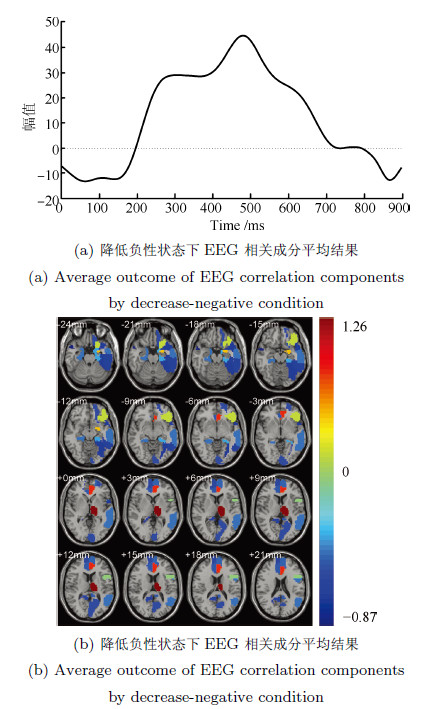
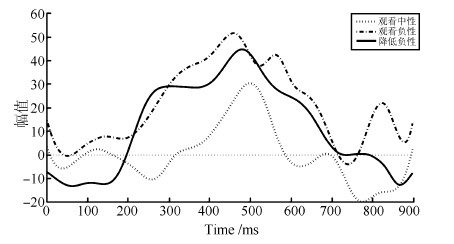
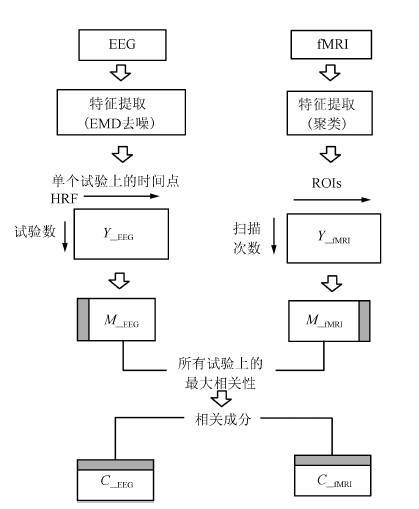
摘要: 脑电(Electroencephalography, EEG)与功能磁共振成像(Functional magnetic resonance imaging, fMRI)为脑科学研究提供了互补的时空信息. 为研究大脑在对情绪图片采取认知重评策略时的神经活动, 基于同步采集的EEG-fMRI数据, 应用典型相关分析、经验模态分解及k-均值聚类等算法对融合情绪数据进行交叉关联和盲源分离, 得到空间上的fMRI图像和与之对应的EEG时间演变信号. 结果表明: 时域上, CCA分离出的脑电成分在认知重评状态下有明显的晚期正电位(Late positive potential, LPP) (潜伏期200ms~900ms)出现, 而且认知重评策略诱发下的LPP 波幅明显小于观看负性诱发的LPP波幅(F(1, 224)= 28.72, P<0.01), 而大于观看中性诱发的LPP波幅(F(1, 224)= 63.32, P<0.01); 与之对应的空域上, 可以明显地看出和情绪调节相关的扣带回, 额叶、颞叶等区域有明显激活区, 采用情绪认知重评策略时的脑区激活强度明显小于观看负性状态, 而大于观看中性, 且观看中性状态下被激活的与情绪相关的区域相对较少. 研究表明, 这种融合数据分析技术通过计算两种模态数据之间潜在的线性相关性, 可以有效地分离出大脑在时空上神经活动情况, 达到了同时描绘出大脑神经活动的时间信息与空间信息的效果.Abstract: Electroencephalography (EEG) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) provide complementary spatio-temporal information for brain function study. In order to study the neural activity during the process of cognitive reappraisal strategy when emotional images are taken, canonical correlation analysis (CCA), empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and k-means clustering algorithms are used to finish the steps of cross-correlation and blinded source separate for simultaneously acquired EEG-fMRI emotion data. Spatial maps for fMRI data and the corresponding temporal evolution features of EEG signals are thus obtained. The results show that EEG components separated by CCA in cognitive reappraisal state have obviously late positive potential (LPP), with latency from 200ms~900ms, meanwhile the amplitudes of LPP evoked by taking cognitive reappraisal strategy are less than that evoked by watching negative images (F(1, 224)= 28.72, P<0.01), but more than that evoked by watching neutral images (F(1, 224)= 63.32, P<0.01). The corresponding spatial regions have apparent activation regions, such as cingulate, frontal, temporal lobe and other regions related to emotion regulation. What is more, the activation intensity evoked by taking cognitive reappraisal strategy is significantly less than that evoked by watching negative images, while it is more than that evoked by watching neutral images. The activated areas related to emotion are small when participants are watching neutral images. This fusion data processing technology computes the potential linear correlation between two modal data, which can effectively separate neural activities of the brain both in spatial and temporal domains, and can achieve the effects of obtaining temporal and spatial information of the brain activity at the same time.
-
表 1 三种情绪状态下具有较大相关性EEG-fMRI相关成分
Table 1 Correlation component of EEG-fMRI which has higher correlation by three emotion conditions
相关成分 相关系数 观看中性 观看负性 降低负性 成分1 0.944 0.966 0.913 成分2 0.888 0.947 0.801 成分3 0.841 0.877 0.731 成分4 0.741 0.816 0.716 成分5 0.681 0.765 0.606 成分6 N/A 0.660 0.537 成分7 N/A 0.584 N/A 表 3 观看负性状态下fMRI相关成分叠加平均激活区域
Table 3 Average ROIs of fMRI correlation components by decrease-negative
观看中性状态fMRI激活区域 ROIs(编号) AAL标签 Z score 颞下回(90) Temporal Inf R 3.980 额中回(8) Frontal Mid R 3.767 眶部额下回(15) Frontal Mid Orb R 2.264 前扣带和旁扣带回(31) Frontal Sup R 1.970 颞极: 颞中回(88) Temporal Pole Mid R 1.674 杏仁核(41) Frontal Mid L 1.492 背外侧额上回(3) Frontal Sup L 1.100 颞下回(89) Temporal Inf L 0.675 颞中回(86) Temporal Mid R 0.297 三角部额下回(13) Frontal Inf Tri L 0.037 眶内额上回(26) Frontal Mid Orb R 0.004 颞极: 颞中回(87) Temporal Pole Mid L -0.12 背外侧额上回(4) Cingulum Ant L -0.284 内侧额上回(24) Frontal Sup Medial R -0.287 表 4 降低负性状态下fMRI相关成分叠加平均激活区域
Table 4 Average ROIs of fMRI correlation components by decrease-negative condition
观看中性状态fMRI激活区域 ROIs(编号) AAL标签 Z score 丘脑(77) Thalamus L 1.260 前扣带和旁扣带脑回(31) Cingulum Ant L 0.824 杏仁核(41) Amygdala L 0.512 眶部额下回(15) Frontal Inf Orb L 0.207 内侧和旁扣带脑回(34) Cingulum Mid R -0.066 岛盖部额下回(11) Frontal Inf Oper L -0.116 内侧和旁扣带脑回(33) Cingulum Mid L -0.327 海马旁回(39) ParaHippocampal L -0.417 颞中回(85) Temporal Mid L -0.476 中央前回(1) Precentral L -0.483 海马旁回(40) ParaHippocampal R -0.487 内侧额上回(23) Frontal Sup Medial L -0.498 后扣带回(35) Cingulum Post L -0.529 前扣带和旁扣带脑回(32) Cingulum Ant R -0.533 眶部额上回(5) Frontal Sup Orb L -0.587 距状裂周围皮层(43) Calcarine L -0.59 内侧额上回(24) Frontal Sup Medial R -0.594 楔前叶(68) Precuneus R -0.664 颞下回(89) Temporal Inf L -0.683 颞极: 颞上回(83) Temporal Pole Sup L -0.694 梭状回(55) Fusiform L -0.709 颞极: 颞中回(88) Temporal Pole Mid R -0.869 表 2 观看中性状态下fMRI相关成分叠加平均激活区域
Table 2 Average ROIs of fMRI correlation components by look-neutral condition
观看中性状态fMRI激活区域 ROIs(编号) AAL标签 Z score 尾状核(71) Caudate L 0.078 嗅皮质(22) Olfactory R -0.027 脑岛(29) Insula L -0.044 豆状壳核(74) Putamen R -0.076 海马旁回(39) ParaHippocampal L -0.111 顶上回(59) Parietal Sup L -0.13 尾状核(72) Caudate R -0.171 枕中回(52) Occipital Mid R -0.333 眶部额上回(6) Frontal Sup Orb R -0.347 丘脑(77) Thalamus L -0.356 杏仁核(41) Amygdala L -0.414 海马(38) Hippocampus R -0.46 颞中回(86) Temporal Mid R -0.471 海马旁回(40) ParaHippocampal R -0.474 海马(37) Hippocampus L -0.536 三角部额下回(13) Frontal Inf Tri L -0.561 眶部额下回(15) Frontal Inf Orb L -0.578 岛盖部额下回(11) Frontal Inf Oper L -0.592 颞极: 颞上回(83) Temporal Pole Sup L -0.609 额中回(7) Frontal Mid L -0.619 顶上回(60) Parietal Inf R -0.677 豆状壳核(73) Putamen L -0.785 前扣带和旁扣带脑回(31) Rectus R -0.789 内侧额上回(23) Frontal Sup Medial L -0.968 -
[1] Logothetis N K. What we can do and what we cannot do with fMRI. Nature, 2007, 453(9197): 869-878 [2] Zou L, Zhang Y, Qian N, Zhou R L. Emotion cognitive reappraisal research based on simultaneous recording of EEG and BOLD responses. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Neural Networks. Dalian, China: Springer, 2013. 52-59 [3] Maloney T C, Tenney J R, Szaflarski J P, Vannest J. Simultaneous electroencephalography and functional magnetic resonance imaging and the identification of epileptic networks in children. Journal of Pediatric Epilepsy, 2015, 4(4): 174-183 [4] 王行愚, 金晶, 张宇, 王蓓. 脑控: 基于脑-机接口的人机融合控制. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(3): 208-221Wang Xing-Yu, Jin Jing, Zhang Yu, Wang Bei. Brain control: human-computer integration control based on brain-computer interface. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(3): 208-221 [5] Vulliemoz S, Rodionov R, Carmichael D W, Thornton R, Guye M, Lhatoo S D, Michel C M, Duncan J S, Lemieux L. Continuous EEG source imaging enhances analysis of EEG-fMRI in focal epilepsy. NeuroImage, 2010, 49(4): 3219-3229 [6] Henson R N, Flandin G, Friston J K, Mattout J. A parametric empirical Bayesian framework for fMRI-constrained MEG/EEG source reconstruction. Human Brain Mapping, 2010, 31(10): 1512-1531 [7] Bridwell A D, Wu L, Eichele T, Calhoun V D. The spatiospectral characterization of brain networks: fusing concurrent EEG spectra and fMRI maps. NeuroImage, 2013, 69: 101-111 [8] Lei X, Qiu C, Xu P, Yao D Z. A parallel framework for simultaneous EEG/fMRI analysis: methodology and simulation. NeuroImage, 2010, 52(3): 1123-1134 [9] Correa N M, Eichele T, Adali T, Li Y-O, Calhoun V D. Multi-set canonical correlation analysis for the fusion of concurrent single trial ERP and functional MRI. NeuroImage, 2010, 50(4): 1438-1445 [10] Wessing I, Rehbein M A, Romer G, Achtergarde S, Dobel C, Zwitserlood P, Fürniss T, Junghöfer M. Cognitive emotion regulation in children: reappraisal of emotional faces modulates neural source activity in a frontoparietal network. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 2015, 13: 1-10 [11] Yuan L, Zhou R L, Hu S Q. Cognitive reappraisal of facial expressions: electrophysiological evidence of social anxiety. Neuroscience Letters, 2014, 577: 45-50 [12] Schindler S, Wegrzyn M, Steppacher I, Kissler J. Perceived communicative context and emotional content amplify visual word processing in the fusiform gyrus. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2015, 35(15): 6010-6019 [13] Mardaga S, Lakimova G. Neurocognitive processing of emotion facial expressions in individuals with self-reported depressive symptoms: the role of personality and anxiety. Neurophysiologie Clinique, 2014, 44(5): 447-455 [14] Sarkheil P, Zilverstand A, Kilian-Hütten N, Schneider F, Goebel R, Mathiak K. fMRI feedback enhances emotion regulation as evidenced by a reduced amygdala response. Behavioural Brain Research, 2015, 281: 326-332 [15] Delorme A, Makeig S. EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2004, 134(1): 9-21 [16] Navarro X, Porée F, Beuchée A, Carrault G. Denoising preterm EEG by signal decomposition and adaptive filtering: a comparative study. Medical Engineering and Physics, 2015, 37(3): 315-320 [17] Scheeringa R, Petersson K M, Oostenveld R, Norris D G, Hagoort P, Bastiaansen M C M. Trial-by-trial coupling between EEG and BOLD identifies networks related to alpha and theta EEG power increases during working memory maintenance. NeuroImage, 2009, 44(3): 1224-1238 [18] Paul S, Simon D, Kniesche R, Kathmann N, Endrass T. Timing effects of antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation strategies. Biological Psychology, 2013, 94(1): 136-142 [19] Liu Y L, Huang H Q, McGinnis-Deweese M, Keil A, Ding M Z. Neural substrate of the late positive potential in emotional processing. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2012, 32(42): 14563-14572 -




 下载:
下载: