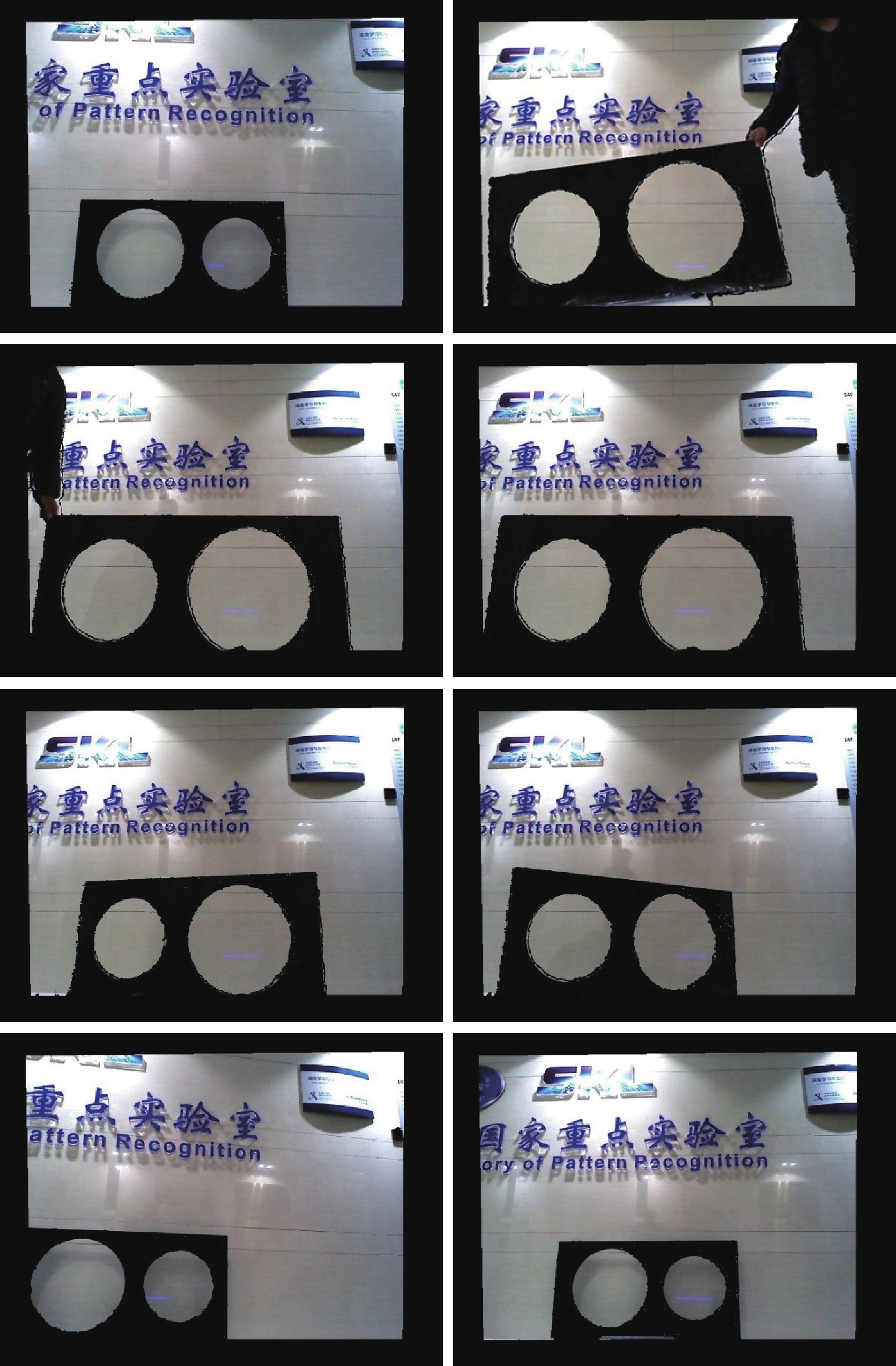
Relative Pose Calibration Between a Range Sensor and a Camera Using Two Coplanar Circles
-
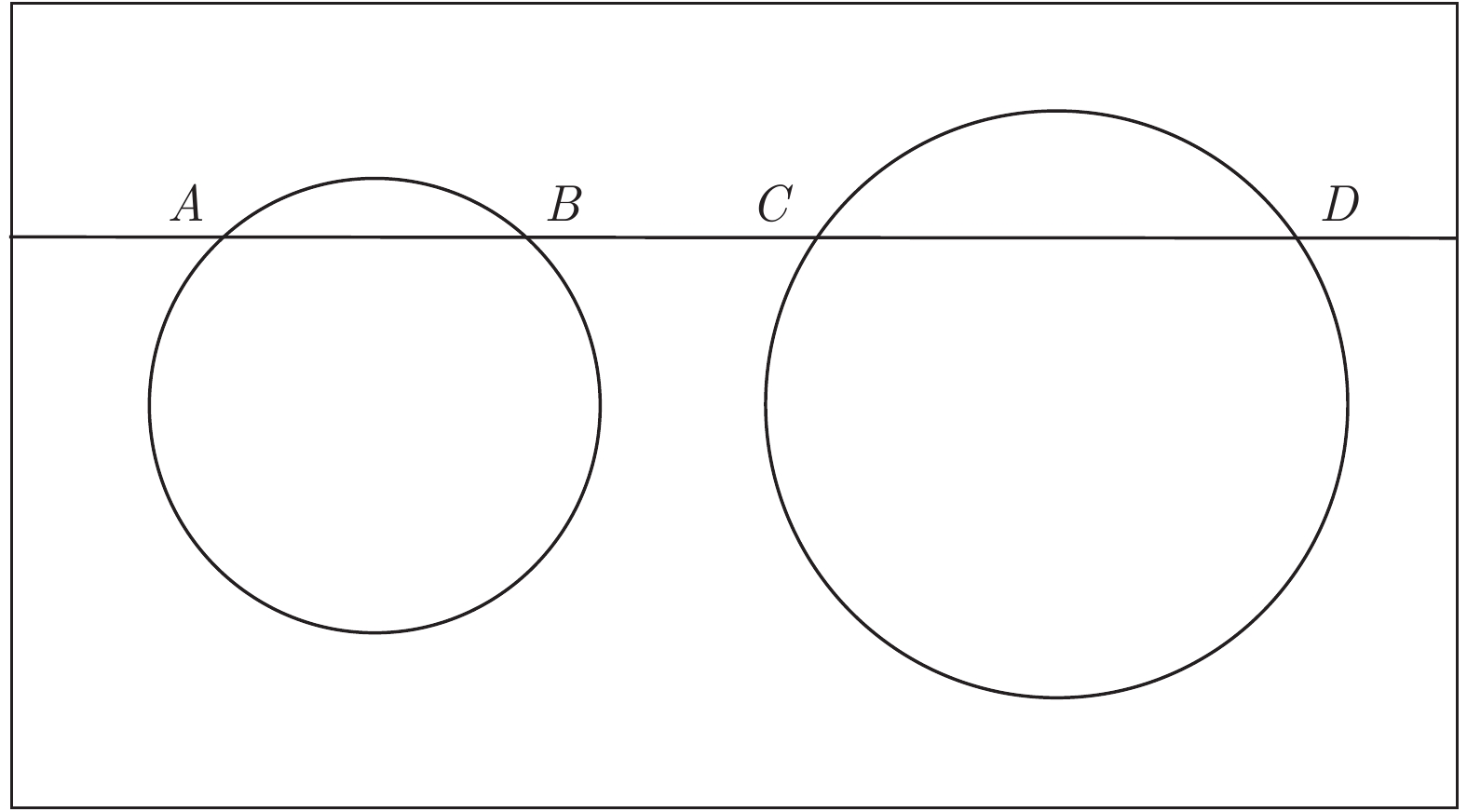
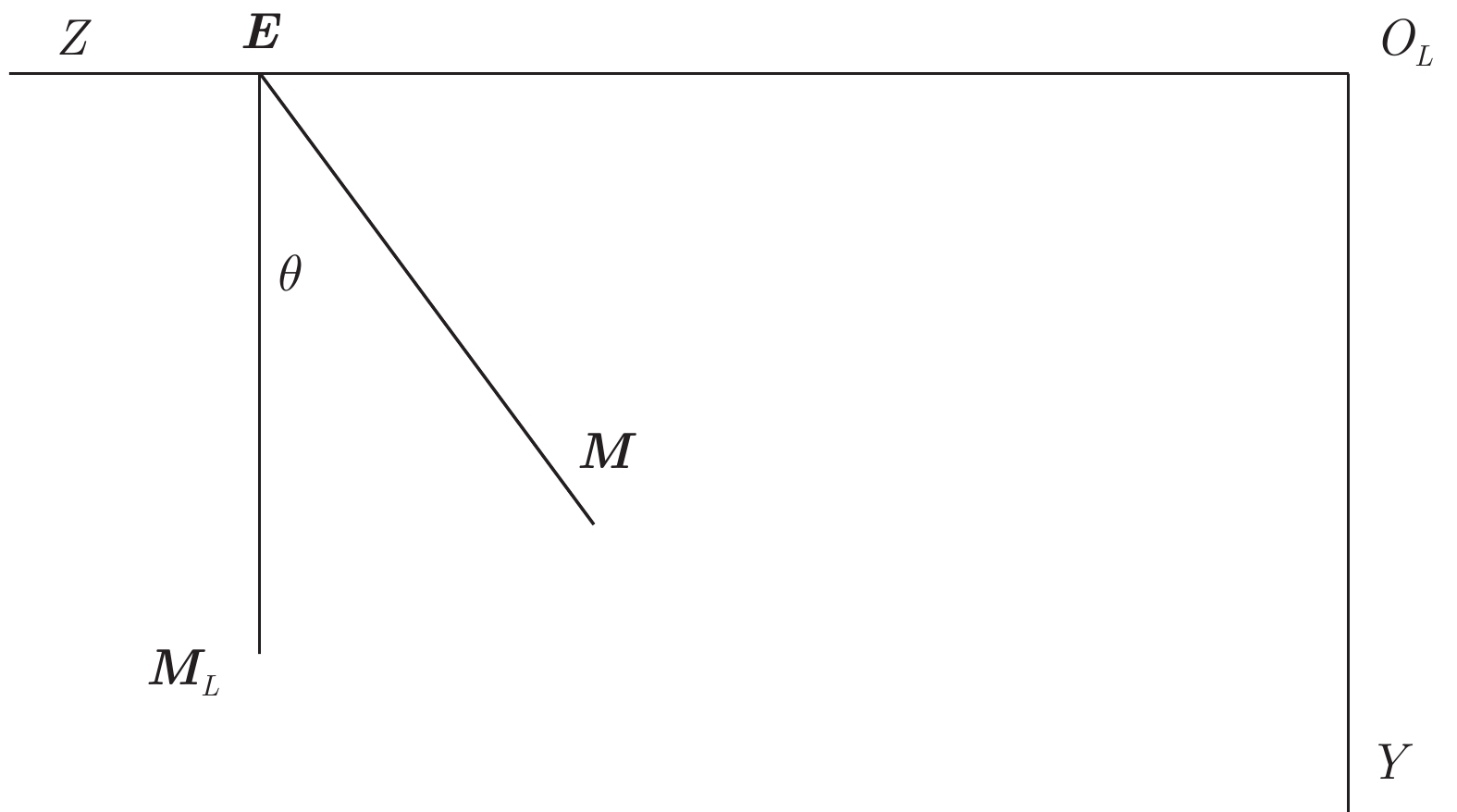
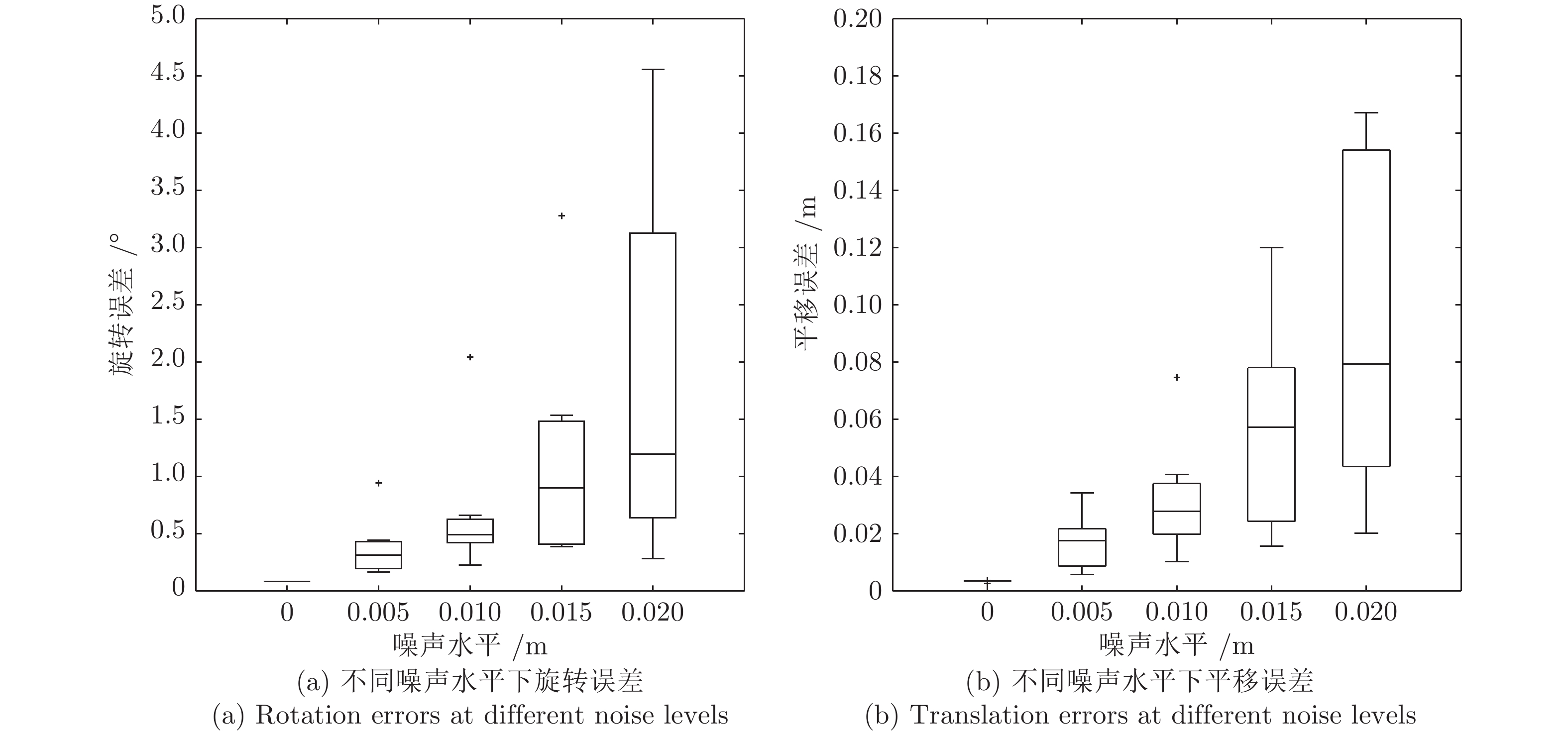
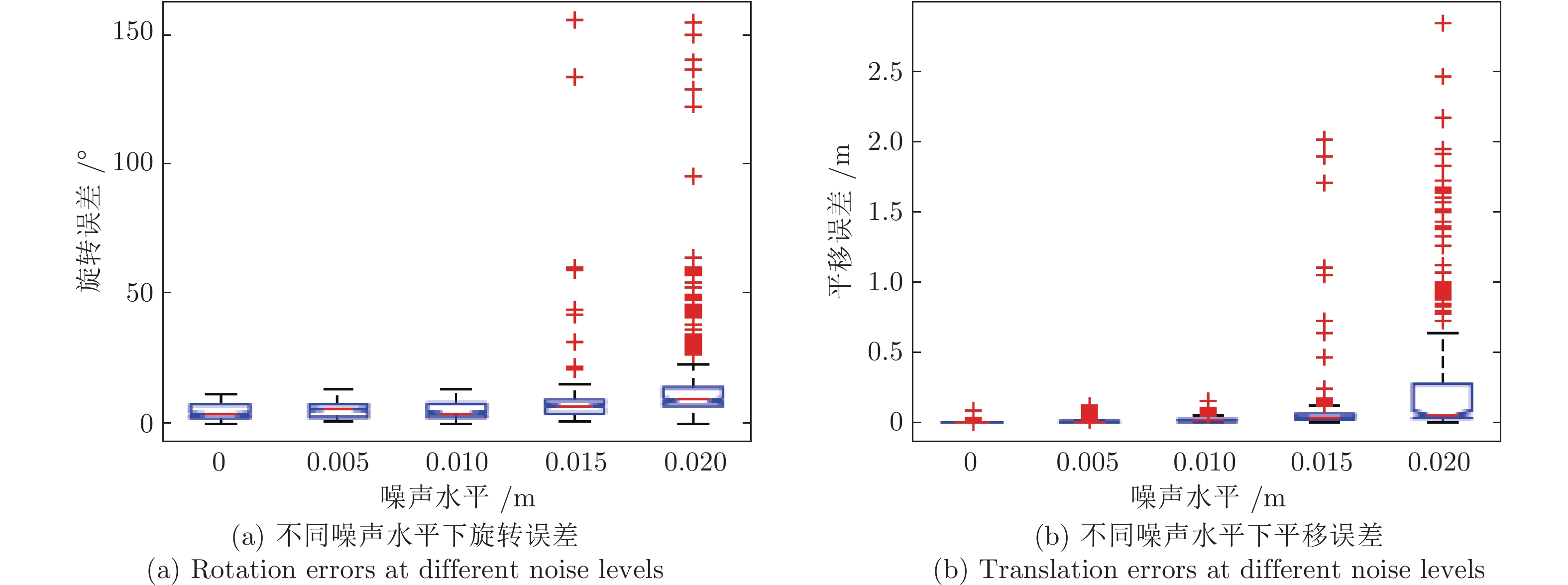
摘要: 近年来, 距离传感器与摄像机的组合系统标定在无人车环境感知中得到了广泛的研究与应用, 其中基于平面特征的方法简单易行而被广泛采用. 然而, 目前多数方法基于点匹配进行, 易错且鲁棒性较低. 本文提出了一种基于共面圆的距离传感器与相机的组合系统相对位姿估计方法. 该方法使用含有两个共面圆的标定板, 可以获取相机与标定板间的位姿, 以及距离传感器与标定板间的位姿. 此外, 移动标定板获取多组数据, 根据计算得到两个共面圆的圆心在距离传感器和相机下的坐标, 优化重投影误差与3D对应点之间的误差, 得到距离传感器与相机之间的位姿关系. 该方法不需要进行特征点的匹配, 利用射影不变性来获取相机与三维距离传感器的位姿. 仿真实验与真实数据实验结果表明, 本方法对噪声有较强的鲁棒性, 得到了精确的结果.
-
关键词:
- 多传感器标定 /
- 距离传感器与相机标定 /
- 深度相机与相机标定 /
- 激光与相机标定
Abstract: Relative pose calibration between a range sensor and a camera has been widely studied and applied in the environment perception of unmanned vehicles, of which the methods based on the planar features are greatly easy to be implemented. However, most of the current methods are based on point matching, which is easy to have errors and low robustness. In this paper, a relative pose calibration method between a range sensor and a camera from two coplanar circles is proposed. Using such a calibration object including two coplanar circles, the pose between the camera and the calibration object can be determined as well as the pose between the range sensor and the calibration object. Moreover, moving the calibration object to obtain more data, the center coordinates of two circles in the range sensor and camera coordinate system can be computed to refine the reprojection errors and 3D-3D correspondence point errors. Then, the pose between a range sensor and a camera can be estimated. The advantages of this method are as follows: matching among multiple points are not needed by using projective invariance. The simulation and real data experiments proved that this method has high accuracy and robustness. -
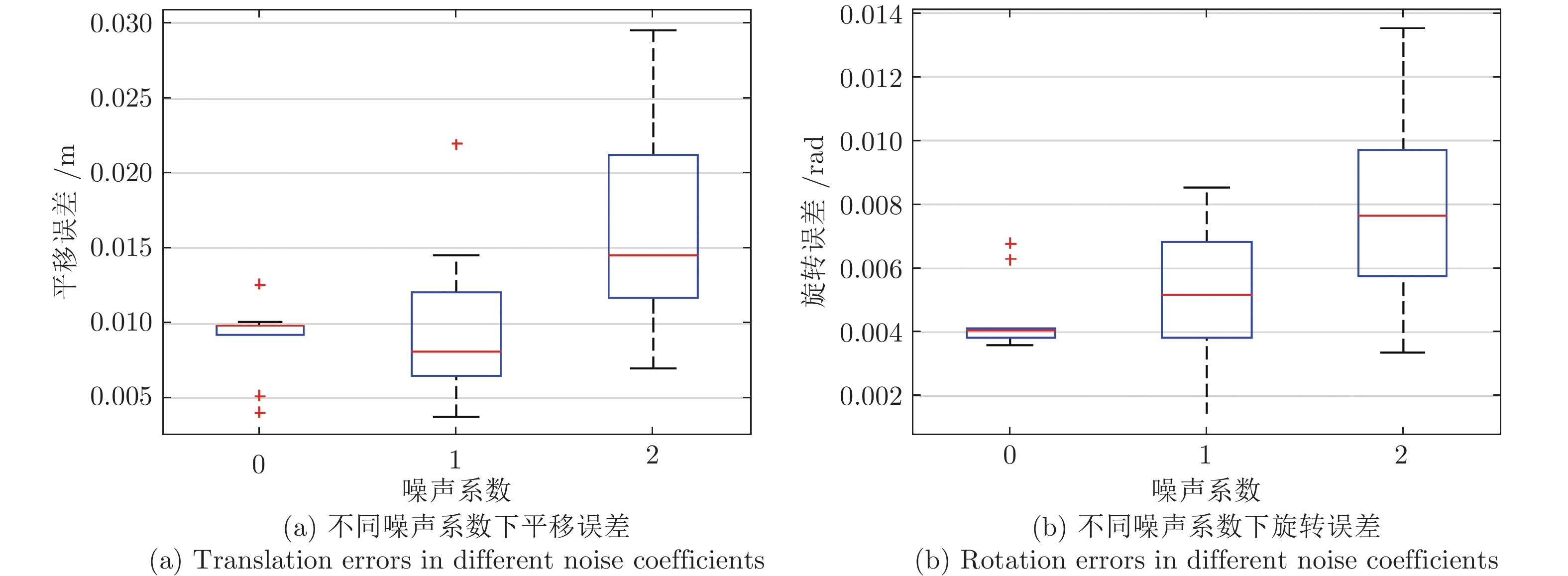
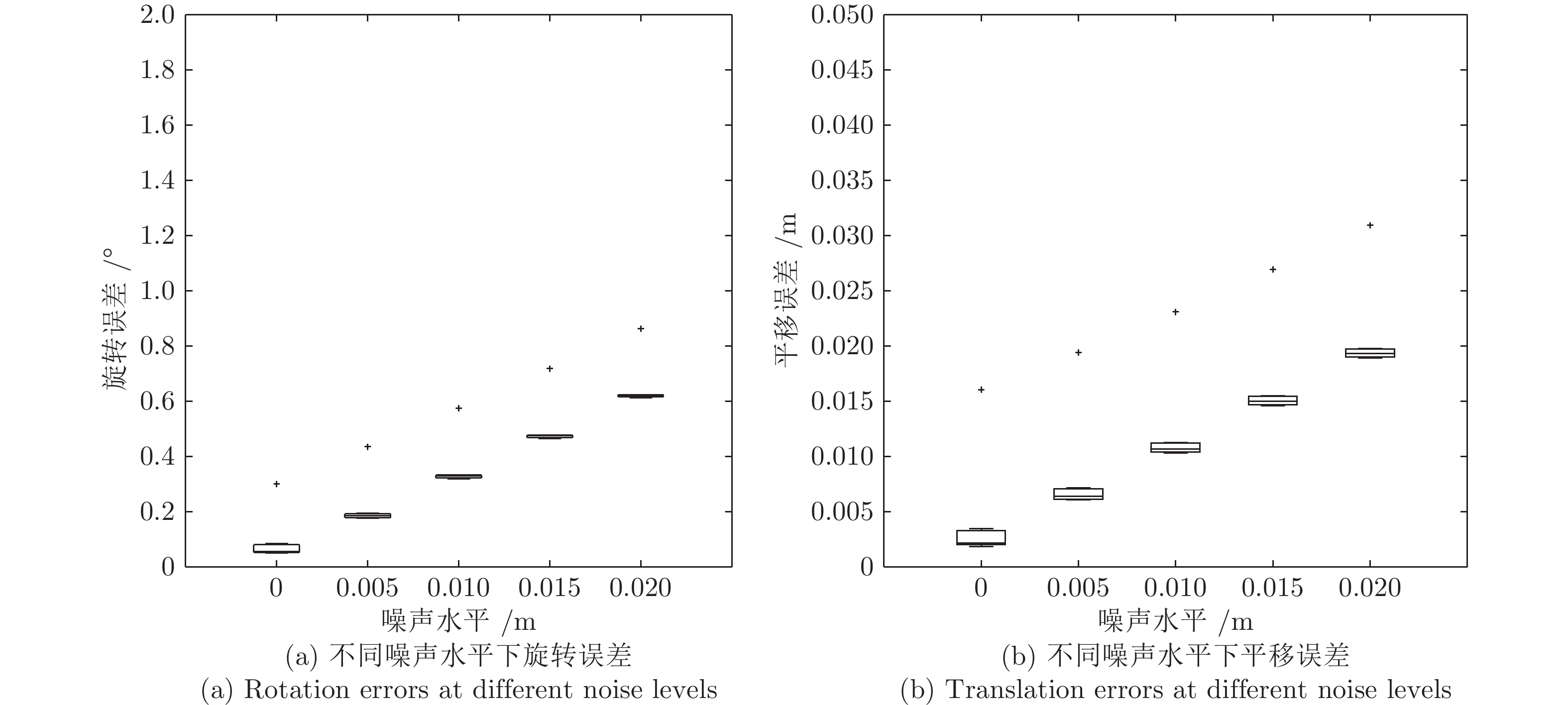
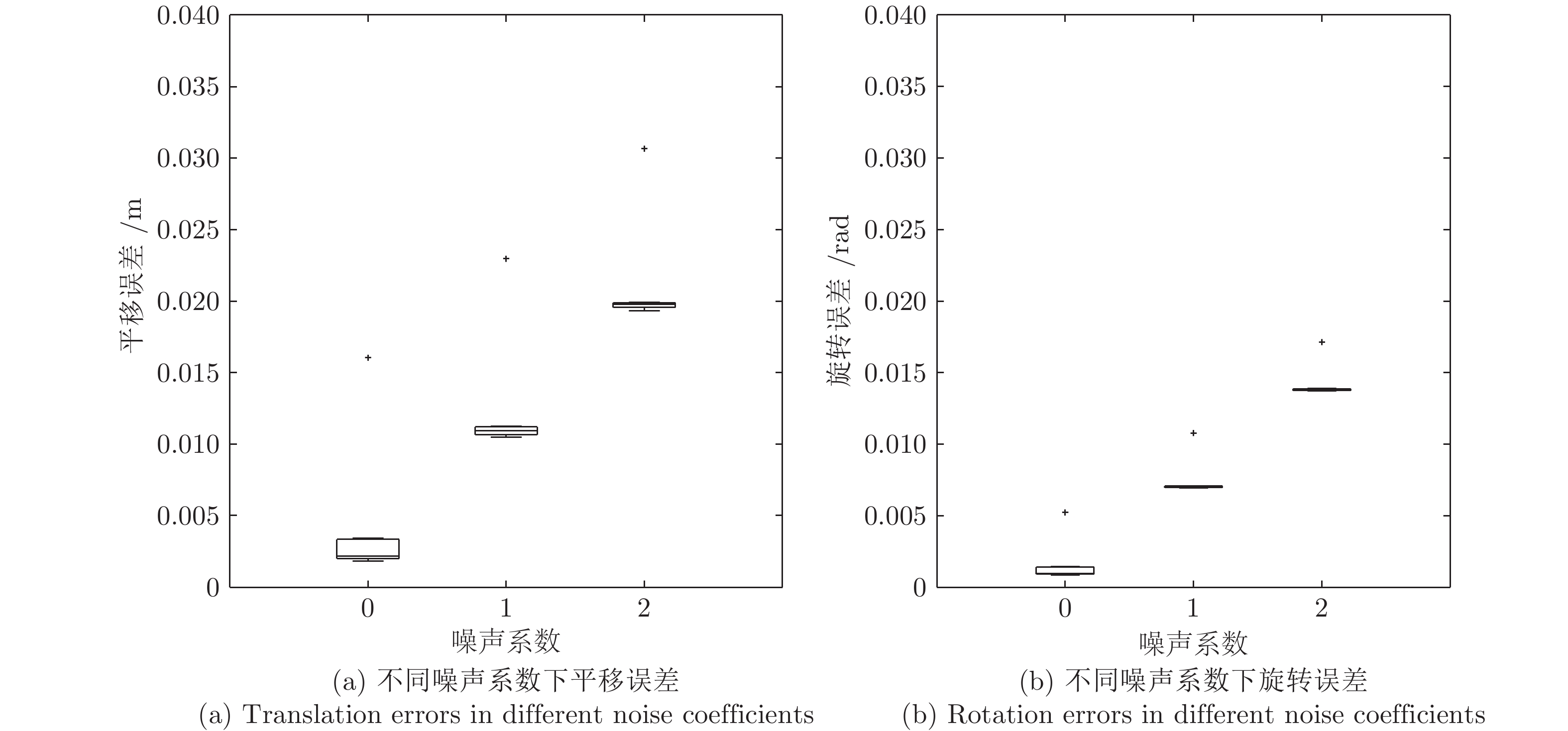
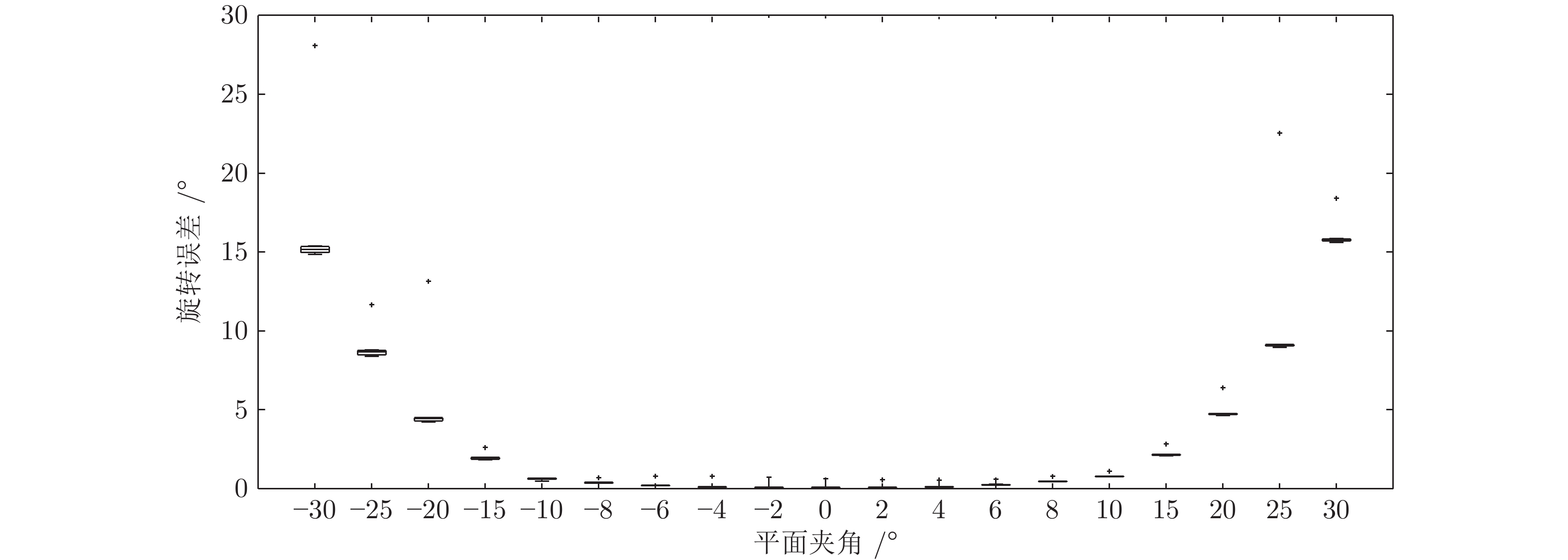
表 1 仿真实验中所用的激光相机位姿参数
Table 1 Camera-Lidar transformation parameters in the simulator settings used for the experiments
设定 $t_x\;(\rm m)$ $t_y\;(\rm m)$ $t_z\;(\rm m)$ $\psi\;(\rm rad)$ $\theta\;(\rm rad)$ $\phi\;(\rm rad)$ 1 −0.8 −0.1 0.4 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0.5 0 0 3 0 0 0 0.3 0.1 0.2 4 −0.3 0.2 −0.2 0.3 −0.1 0.2 5 0 0 0 0 0.1 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0.4 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 -
[1] Ha J H. Extrinsic calibration of a camera and laser range finder using a new calibration structure of a plane with a triangular hole. International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, 2012, 10(6): 1240−1244 doi: 10.1007/s12555-012-0619-7 [2] Hoang V D, Cáceres Hernández D, Jo K H. Simple and efficient method for calibration of a camera and 2D laser rangefinder. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Asian conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems (ACIIDS 2014). Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Bangkok, Thailand: Springer, Cham, 2014. 561−570 [3] Zhang Q, Pless R. Extrinsic calibration of a camera and laser range finder (improves camera calibration). In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Sendai, Japan: IEEE, 2004. 2301−2306 [4] Bok Y, Jeong Y, Choi D G, Kweon I S. Capturing village-level heritages with a hand-held camera-laser fusion sensor. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2011, 94(1): 36−53 doi: 10.1007/s11263-010-0397-8 [5] Bok Y, Choi D G, Vasseur P, Kweon I S. Extrinsic calibration of non-overlapping camera-laser system using structured environment. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2014). Chicago, IL, USA: IEEE, 2014. 436−443 [6] Vasconcelos F, Barreto J P, Nunes U. A minimal solution for the extrinsic calibration of a camera and a laser-rangefinder. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2097−2107 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.18 [7] 胡钊政, 赵斌, 李娜, 夏克文. 基于虚拟三面体的摄像机与二维激光测距仪外参数最小解标定新算法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(11): 1951−1960Hu Zhao-Zheng, Zhao Bin, Li Na, Xia Ke-Wen. Minimal solution to extrinsic calibration of camera and 2D laser rangefinder based on virtual trihedron. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(11): 1951−1960 [8] Li G H, Liu Y H, Dong L, Cai X P, Zhou D X. An algorithm for extrinsic parameters calibration of a camera and a laser range finder using line features. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2007. 3854−3859 [9] Lee G M, Lee J H, Park S Y. Calibration of VLP-16 lidar and multi-view cameras using a ball for 360 degree 3D color map acquisition. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI 2017). Daegu, Korea: IEEE, 2017. 64−69 [10] Dhall A, Chelani K, Radhakrishnan V, Krishna K M. LiDAR-camera calibration using 3D-3D point correspondences [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.09785.pdf, January 9, 2019 [11] Geiger A, Moosmann F, Car O, Schuster B. Automatic camera and range sensor calibration using a single shot. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. RiverCentre, Saint Paul, Minnesota, USA: IEEE, 2012. 3936−3943 [12] Velas M, Španěl M, Materna Z, Herout A. Calibration of RGB camera with Velodyne LiDAR. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision (WSCG). Plzen, Czech: WSCG, 2014. 135−144 [13] Guindel C, Beltrán J, Martín D, García F. Automatic extrinsic calibration for lidar-stereo vehicle sensor setups. In: Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). IEEE, 2017. [14] Wu Y H, Zhu H J, Hu Z Y, Wu F C. Camera calibration from the quasi-affine invariance of two parallel circles. In: Proceedings of the 2004 European Conference on Computer Vision. Prague, Czech. 2004. 190−202 [15] Wu Y H, Li X J, Wu F C. Hu Z Y. Coplanar circles, quasi-affine invariance and calibration. Image and Vision Computing, 2006, 24(4): 319−326 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2005.11.008 [16] 范蓉蓉, 唐付林, 刘青山. 基于两个共面圆的无匹配相机位姿计算. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(5): 993−998Fan Rong-Rong, Tang Fu-Lin, Liu Qing-Shan. Effective camera localization from two coplanar circles without matching. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(5): 993−998 [17] Wu Y H, Wang H R, Tang F L. Conic fitting: New easy geometric method and revisiting sampson distance. In: Proceedings of the 4th IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition. Nanjing, China. 2017. [18] Arun K S, Huang T S, Blostein S D. Least-squares fitting of two 3-d point sets. IEEE Transactions on Patten Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1987, 5: 698−700 [19] Pomerleau F, Colas F, Siegwart R. A review of point cloud registration algorithms for mobile robotics. Foundations and Trends in Robotics (FnTROB), 2015, 4(1): 1−104 doi: 10.1561/2300000035 [20] Kümmerle R, Grisetti G, Strasdat H, Konolige K, Burgard W. G2o: A general framework for graph optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Shanghai, China: IEEE. 2011. -




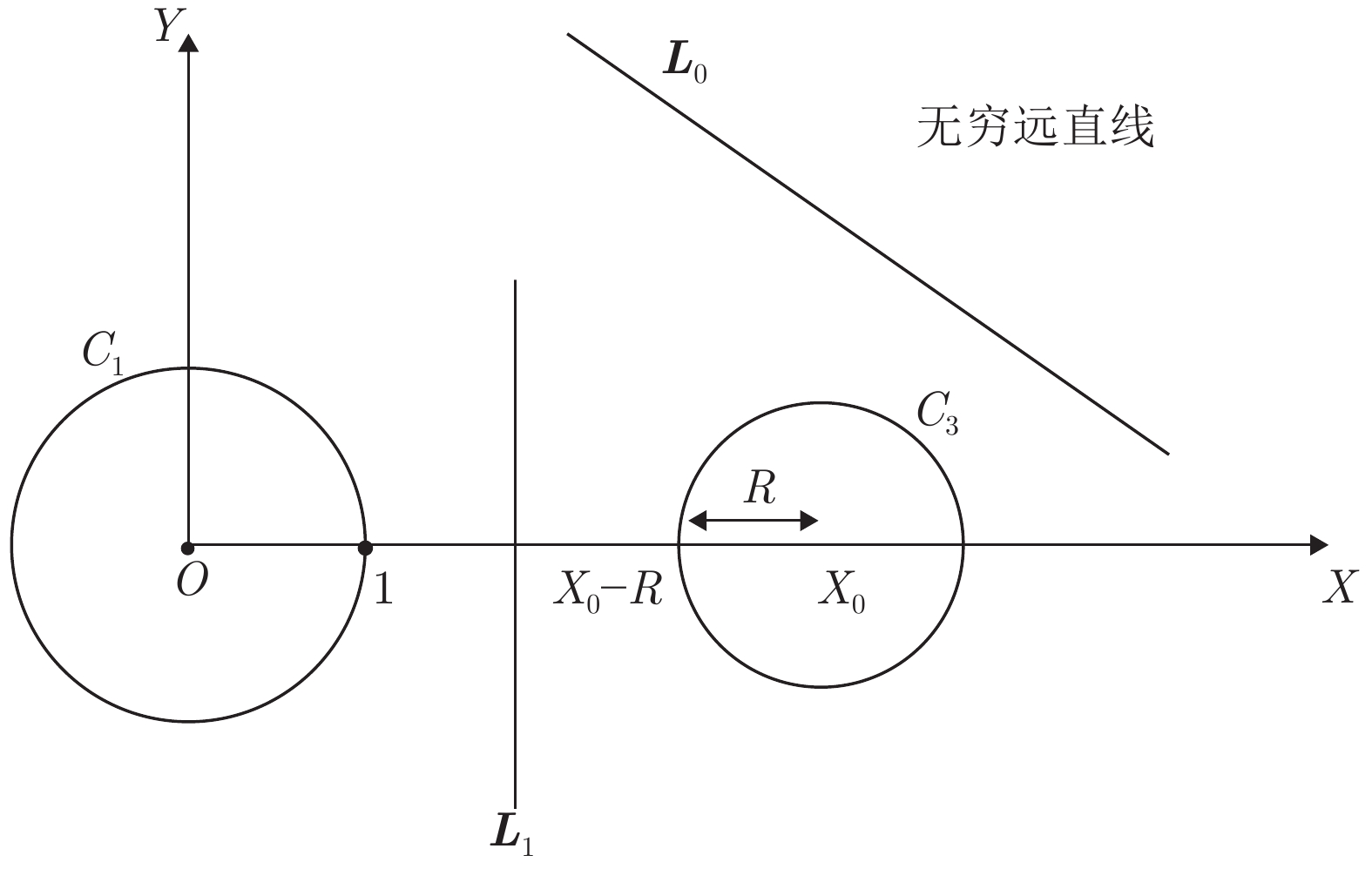
 下载:
下载: