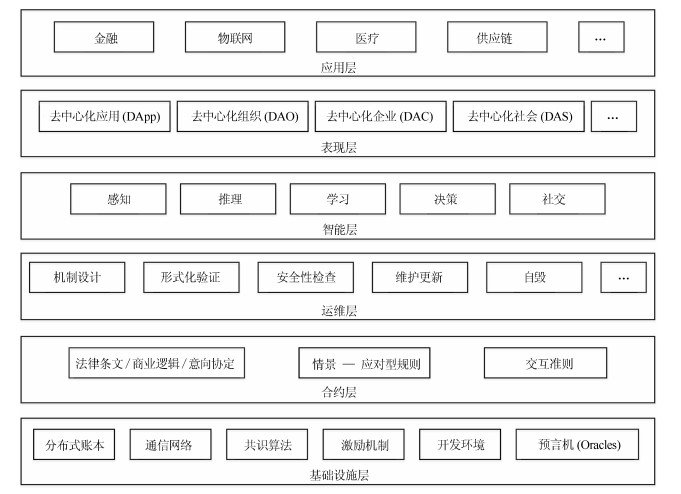
|
[1]
|
Szabo N. Smart contracts[Online], avaliable: http://www.fon.hum.uva.nl/rob/Courses/InformationInSpeech/CDROM/Literature/LOTwinterschool2006/szabo.best.vwh.net/smart.contracts.html, November 5, 2018
|
|
[2]
|
Nakamoto S. Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system[Online], avaliable: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf, January, 2009
|
|
[3]
|
Stark J. Making sense of blockchain smart contracts[Online], available: https://www.coindesk.com/making-sense-smart-contracts/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[4]
|
Bartoletti M, Pompianu L. An empirical analysis of smart contracts:platforms, applications, and design patterns. In:Proceedings of the International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security. Springer, Cham, 2017. 494-509
|
|
[5]
|
Wood G. Ethereum: A secure decentralized generalized transaction ledger (EIP-150 revision)[Online], avaliable: http://gavwood.com/paper.pdf, November 5, 2018
|
|
[6]
|
Wikipedia: The DAO (organization)[Online], available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_DAO_(organization), November 5, 2018
|
|
[7]
|
袁勇, 王飞跃.区块链技术发展现状与展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42(4):481-494 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18837.shtmlYuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Blockchain:the state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):481-494 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18837.shtml
|
|
[8]
|
Hyperledger fabric website[Online], available: https://www.hyperledger.org/projects/fabric, November 5, 2018
|
|
[9]
|
Meiklejohn S, Pomarole M, Jordan G, Levchenko K, McCoy D, Voelker G M, et al. A fistful of bitcoins: characterizing payments among men with no names. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Internet Measurement Conference. New York, USA: ACM, 2013. 127-140
|
|
[10]
|
Ron D, Shamir A. Quantitative analysis of the full bitcoin transaction graph. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013. 6-24
|
|
[11]
|
Kosba A, Miller A, Shi E, Wen Z, Papamanthou C. Hawk: the blockchain model of cryptography and privacy-preserving smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 37th Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York, USA: IEEE, 2016. 839-858
|
|
[12]
|
Zhang F, Cecchetti E, Croman K, Juels A, Shi Elaine. Town crier: an authenticated data feed for smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 270-282
|
|
[13]
|
Ye P J, Wang S, Wang F Y. A general cognitive architecture for agent-based modeling in artificial societies. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2018, 5(1):176-185 doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2017.2777602
|
|
[14]
|
Atzei N, Bartoletti M, Cimoli T. A survey of attacks on ethereum smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Principles of Security and Trust. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2017. 164-186
|
|
[15]
|
Luu L, Chu D H, Olickel H, Saxena P, Hobor A. Making smart contracts smarter. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 254-269
|
|
[16]
|
Chen T, Li X Q, Luo X P, Zhang X S. Under-optimized smart contracts devour your money. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineerin. New York, USA: IEEE, 2017. 442-446
|
|
[17]
|
Juels A, Kosba A, Shi E. The ring of gyges: investigating the future of criminal smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 283-295
|
|
[18]
|
Christin N. Traveling the silk road: a measurement analysis of a large anonymous online marketplace. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web. New York, USA: ACM, 2013. 213-224
|
|
[19]
|
Erdman A G, Sandor G N. Mechanical Design (3rd ed): Analysis and Synthesis (Vol.1). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1997
|
|
[20]
|
曾帅, 袁勇, 倪晓春, 王飞跃.面向比特币的区块链扩容: 关键技术、制约因素与衍生问题.自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180100Zeng Shuai, Yuan Yong, Ni Xiao-Chun, Wang Fei-Yue. Scaling blockchain towards bitcoin: key technologies, constraints and related issues. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180100
|
|
[21]
|
Dickerson T, Gazzillo P, Herlihy M, Koskinen E. Adding concurrency to smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing. New York, USA: ACM, 2017. 303-312
|
|
[22]
|
胡凯, 白晓敏, 高灵超, 董爱强.智能合约的形式化验证方法.信息安全研究, 2016, 2(12):1080-1089 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xxaqyj201612003Hu Kai, Bai Xiao-Min, Gao Ling-Chao, Dong Ai-Qiang. Formal verification method of smart contract. Journal of Information Security Research, 2016, 2(12):1080-1089 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xxaqyj201612003
|
|
[23]
|
Mythril website[Online], available: https://github.com/b-mueller/mythril/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[24]
|
Bhargavan K, Delignat-Lavaud A, Fournet C, Gollamudi A, Gonthier G, Kobeissi N, et al. Short paper: formal verification of smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM Workshop on Programming Languages and 23 Analysis for Security. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 91-96
|
|
[25]
|
Kalra S, Goel S, Dhawan M, Sharma S. Zeus: analyzing safety of smart contracts[Online], available: http://pages.cpsc.ucalgary.ca/joel.reardon/blockchain/readings/ndss2018_09-1_Kalra_paper.pdf, November 5, 2018
|
|
[26]
|
Manticore website[Online], available: https://github.com/trailofbits/manticore, November 5, 2018
|
|
[27]
|
Tsankov P, Dan A, Cohen D D, et al. Securify: practical security analysis of smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York, USA: ACM, 2018. 67-82
|
|
[28]
|
Solgraph website[Online], available: https://github.com/raineorshine/solgraph, November 5, 2018
|
|
[29]
|
乔海曙, 谢姗珊.区块链金融理论研究的最新进展.金融理论与实践, 2017, (3):75-79 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4625.2017.03.014Qiao Hai-Shu, Xie Shan-Shan. The latest development of theoretical research on blockchain finance. Financial Theory and Practice, 2017, (3):75-79 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4625.2017.03.014
|
|
[30]
|
Peters G W, Panayi E. Understanding Modern Banking Ledgers Through Blockchain Technologies: Future of Transaction Processing and Smart Contracts on the Internet of Money. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2016. 5-10
|
|
[31]
|
Corda website[Online], available: https://docs.corda.net/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[32]
|
Gatteschi V, Lamberti F, Demartini C, Pranteda C, Santamaria V. Blockchain and smart contracts for insurance:is the technology mature enough. Future Internet, 2018, 10(2):20
|
|
[33]
|
Bertani T, Butkute K, Canessa F. Smart flight insurance-insureth[Online], available: https://mkvd.s3.amazonaws.com/apps/InsurEth.pdf, November 5, 2018
|
|
[34]
|
ECoinmerce: decentralized marketplace[Online], available: https://www.ecoinmerce.io/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[35]
|
Slock.it: enabling the economy of things[Online], available: https://slock.it/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[36]
|
Beck R, Avital M, Rossi M, Thatcher J B. Blockchain technology in business and information systems research. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 2017, 59(6):381-384 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=WK_MED201804280769
|
|
[37]
|
Weber I, Gramoli V, Ponomarev A, Staples M, Holz R, Tran A B, et al. On availability for blockchain-based systems. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems. New York, USA: IEEE, 2017. 64-73
|
|
[38]
|
Wang S, Ni X C, Yuan Y, Wang X, Ouyang L W, Wang F Y. A preliminary research of prediction markets based on blockchain powered smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain-2018. New York, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1287-1293
|
|
[39]
|
McCorry P, Shahandashti S F, Hao F. A smart contract for boardroom voting with maximum voter privacy. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security. Springer, Cham, 2017. 357-375
|
|
[40]
|
Rosa J L, Gibovic D, Torres-Padrosa V, Maicher L, Miralles F, Fakdi A, et al. On intellectual property in online open innovation for SME by means of blockchain and smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Annual World Open Innovation Conference. Barcelona, Spain, 2016
|
|
[41]
|
IP360 website[Online], available: https://www.ip360.net.cn/index, November 5, 2018
|
|
[42]
|
Xia Q, Sifah E B, Asamoah K O, Gao J B, Du X J, Guizani M. MeDShare:trust-less medical data sharing among cloud service providers via blockchain. IEEE Access, 2017, 5(99):14757-14767 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ021078146/
|
|
[43]
|
Azaria A, Ekblaw A, Vieira T, Lippman A. MedRec: using blockchain for medical data access and permission management. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Open and Big Data. New York, USA: IEEE, 2016. 25-30
|
|
[44]
|
Kuo T T, Ohno-Machado L. ModelChain: decentralized privacy-preserving healthcare predictive modeling framework on private blockchain networks. Computers and Society, arXiv: 1802.01746
|
|
[45]
|
Mediledger website[Online], available: https://www.mediledger.com/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[46]
|
BlockMedx website[Online], available: https://blockmedx.com/en/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[47]
|
Dorri A, Kanhere S S, Jurdak R, Gauravaram P. Blockchain for IoT security and privacy: the case study of a smart home. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops. New York, USA: IEEE, 2017. 618-623
|
|
[48]
|
Dorri A, Kanhere S S, Jurdak R. Towards an optimized blockchain for IoT. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Internet-Of-Things Design and Implementation, Pittsburgh. New York, USA: IEEE, 2017. 173-178
|
|
[49]
|
Zhang Y, Wen J T. An IoT electric business model based on the protocol of bitcoin. In: Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Intelligence in Next Generation Networks. New York, USA: IEEE, 2015. 184-191
|
|
[50]
|
Zhang Y Y, Kasahara S, Shen Y L, Jiang X H, Wan J X. Smart contract-based access control for the Internet of Things. Cryptography and Security, arXiv: 1802.04410
|
|
[51]
|
IoTeX website[Online], available: https://iotex.io/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[52]
|
Byrne R O. How blockchain can transform the supply chain[Online], available: https://www.logisticsbureau.com/how-blockchain-can-transform-the-supply-chain/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[53]
|
Bocek T, Rodrigues B B, Strasser T, Stiller B. Blockchains everywhere——a use-case of blockchains in the pharma supply-chain. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management. New York, USA: IEEE, 2017. 772-777
|
|
[54]
|
Stark J. Making sense of ethereum's layer2 scaling solutions: state channels, plasma, and truebit[Online], available: https://medium.com/l4-media/making-sense-of-ethereums-layer-2-scaling-solutions-state-channels-plasma-and-truebit-22cb40dcc2f4, November 5, 2018
|
|
[55]
|
Taxa Website[Online], available: https://taxa.network/, November 5, 2018
|
|
[56]
|
王飞跃.软件定义的系统与知识自动化:从牛顿到默顿的平行升华.自动化学报, 2015, 41(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2015.01.001Wang Fei-Yue. Software-defined systems and knowledge automation:a parallel paradigm shift from Newton to Merton. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2015.01.001
|
|
[57]
|
王飞跃, 王晓, 袁勇, 王涛, 林懿伦.社会计算与计算社会:智慧社会的基础与必然.科学通报, 2015, 60(5-6):460-469 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fzxtyfzxkx200404002Wang Fei-Yue, Wang Xiao, Yuan Yong, Wang Tao, Lin Yi-Lun. Social computing and computational societies:the fouyndation and consequence of smart societies. China Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(5-6):460-469 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fzxtyfzxkx200404002
|
|
[58]
|
王飞跃.人工社会、计算实验、平行系统——关于复杂社会经济系统计算研究的讨论.复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2004, 1(4):25-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.04.002Wang Fei-Yue. Artificial societies, computational experiments, and parallel systems:a discussion on computational theory of complex social-economic systems. Complex System and Complexity Science, 2004, 1(4):25-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3813.2004.04.002
|
|
[59]
|
Wang F Y, Yuan Y, Wang X, Qin R. Societies 5.0: a new paradigm for computational social systems research. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2018, 5(1): 2-8
|
|
[60]
|
Zhang J J, Wang F Y, Wang Q, Hao D, Yang X. Parallel dispatch:a new paradigm of electrical power system dispatch. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(1):311-319 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510778
|
|
[61]
|
李力, 林懿伦, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃.平行学习——机器学习的一个新型理论框架.自动化学报, 2017, 43(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.01.001Li Li, Lin Yi-Lun, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel learning——a new framework for machine learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.01.001
|
|
[62]
|
袁勇, 王飞跃.平行区块链:概念、方法与内涵辨析.自动化学报, 2017, 43(10):1703-1712 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdhxb201710003Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel blockchain:concept, methods and issues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10):1703-1712 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdhxb201710003
|




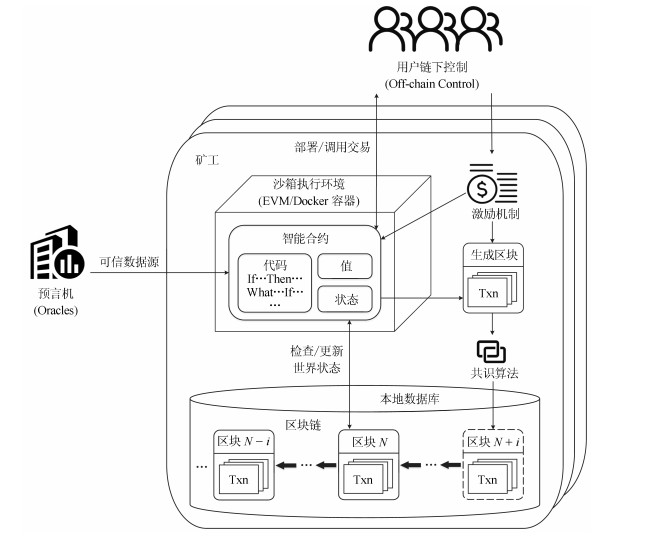
 下载:
下载: