Analog Circuit Diagnostic Method Based on Multi-kernel Learning Multiclass Relevance Vector Machine
-
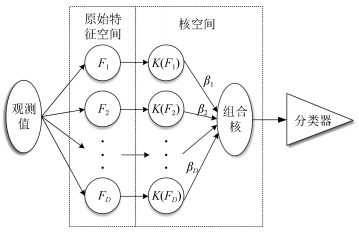
摘要: 针对模拟电路实际存在的多类故障问题,本文提出一种基于多核多分类相关向量机(Multi-kernel learning multiclass relevance vector machine,MKL-mRVM)的模拟电路故障诊断方法.所提方法能够在故障数据所在的原始特征空间上建立多个非线性核,在构建分类器的同时实现故障特征的约简;同时,基于贝叶斯框架的分类模型还能够给出诊断结果的后验概率.通过两个电路的诊断实验证明了所提方法的优越性和实用性.Abstract: Aimed at the problem of multi-class fault diagnosis in practical analog circuits, a new diagnostic method based on multi-kernel learning multiclass relevance vector machine (MKL-mRVM) is proposed. The proposed method can build multi-kernels in the feature space where fault data are originally represented, which can realize the reduction of fault features during the modeling of classifier. In addition, the classifier based on Bayesian framework is able to output the posterior probability of diagnostic results. The fault diagnostic results of two circuits demonstrate the advantage and practicability of the proposed method.1) 本文责任编委 钟麦英
-
表 1 变异操作
Table 1 Mutation operators
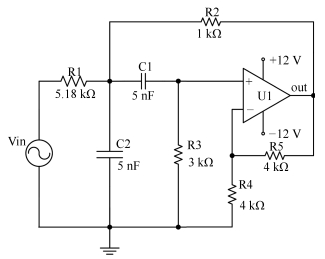
操作 名称 描述 PCH 参数改变(Parameter change) 将元件的指定参数偏离其容差范围 ROP 电阻开路(Resistive open) 在元件的端口间接入一个阻值极大的电阻以表示开路 LRB 局部电阻桥接(Local resistive bridging) 在同一元件的两个端口间接入一个阻值极小的电阻 GRB 全局电阻桥接(Global resistive bridging) 在不同元件的两个节点间接入一个阻值极小的电阻 NSP 节点分裂(Node splitting) 将一个节点分为两个, 并在分出的节点上接入一个阻值极大的电阻 表 2 Sallen-Key带通滤波电路故障描述
Table 2 Faults in Sallen-Key band-pass fllter
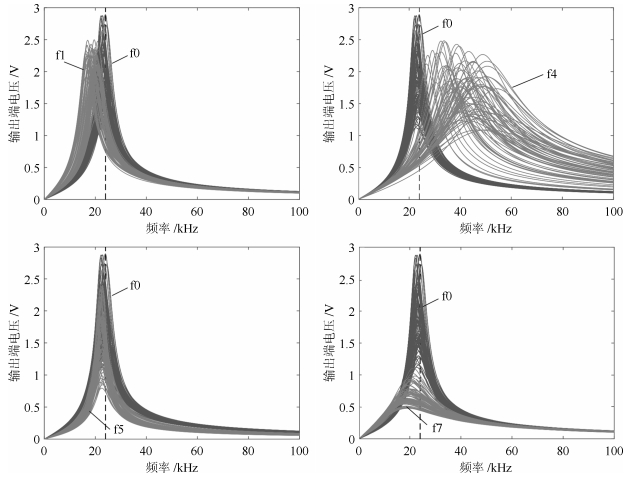
编号 故障描述 标称值 故障值 f0 无故障 — — f1 C1↑ 5 nF [6 ~ 10] nF f2 C1↓ 5 nF [0.5 ~ 4] nF f3 C2↑ 5 nF [6 ~ 10] nF f4 C2↓ 5 nF [0.5 ~ 4] nF f5 R1↑ 5.18 k$\Omega$ [6.22 ~ 10.36] k$\Omega$ f6 R1↓ 5.18 k$\Omega$ [0.52 ~ 4.14] k$\Omega$ f7 R2↑ 1 k$\Omega$ [1.2 ~ 2] k$\Omega$ f8 R2↓ 1 k$\Omega$ [0.1 ~ 0.8] k$\Omega$ f9 R3↑ 2 k$\Omega$ [2.4 ~ 4] k$\Omega$ f10 R3↓ 2 k$\Omega$ [0.2 ~ 1.6] k$\Omega$ f11 R4↑ 4 k$\Omega$ [4.8 ~ 8] k$\Omega$ f12 R4↓ 4 k$\Omega$ [0.4 ~ 3.2] k$\Omega$ f13 R5↑ 4 k$\Omega$ [4.8 ~ 8] k$\Omega$ f14 R5↓ 4 k$\Omega$ [0.4 ~ 3.2] k$\Omega$ 表 3 三种方法的诊断性能对比
Table 3 Diagnostic performance comparison of 3 methods
方法 漏判率 误判率 检测率 隔离率 准确率 训练时间/s 测试时间/s MKL-mRVM 0.0107 0.0200 0.9986 0.9893 0.9640 381.43 3.007E$-$04 OAO-SVM 0.0071 0.0600 0.9957 0.9928 0.9160 2.2103 1.781E$-$04 kELM 0.0114 0.0900 0.9935 0.9886 0.9020 0.1287 3.607E$-$05 表 4 Biquad低通滤波电路故障描述
Table 4 Faults in Biquad low-pass fllter
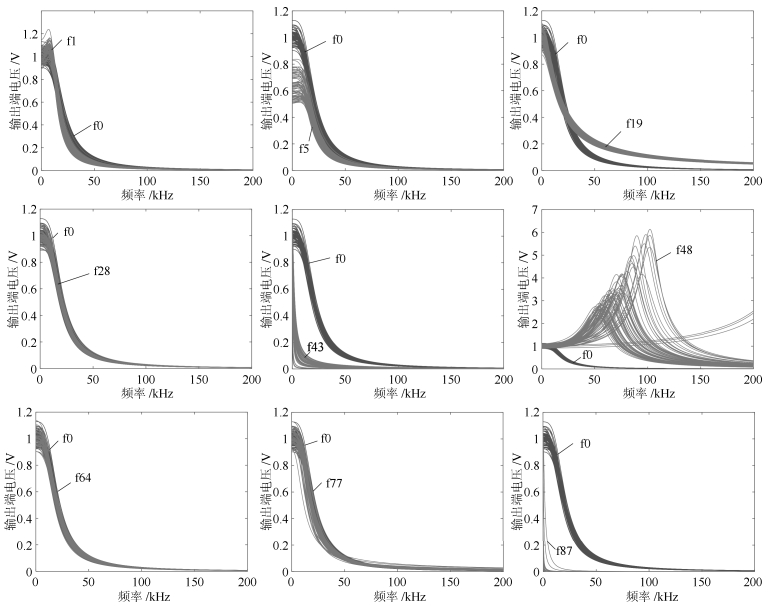
编号 故障描述 编号 故障描述 编号 故障描述 编号 故障描述 f0 无故障 f24 ROP (R4, +) f48 LRB (R4, +, $-$) f72 GRB (n2, in) f1 PCH (C1↑) f25 ROP (R5, +) f49 LRB (R5, +, $-$) f73 GRB (n2, n4) f2 PCH (C1↓) f26 ROP (R6, +) f50 LRB (R6, +, $-$) f74 GRB (n2, n5) f3 PCH (C2↑) f27 ROP (R7, +) f51 LRB (R7, +, $-$) f75 GRB (n2, out) f4 PCH (C2↓) f28 ROP (U1, 1) f52 LRB (U1, 1, 2) f76 GRB (n3, in) f5 PCH (R1↑) f29 ROP (U1, 2) f53 LRB (U1, 2, 3) f77 GRB (n3, n5) f6 PCH (R1↓) f30 ROP (U1, 3) f54 LRB (U1, 3, 4) f78 GRB (n3, out) f7 PCH (R2↑) f31 ROP (U1, 4) f55 LRB (U1, 4, 5) f79 GRB (n4, in) f8 PCH (R2↓) f32 ROP (U1, 5) f56 LRB (U1, 5, 1) f80 GRB (n4, out) f9 PCH (R3↑) f33 ROP (U2, 1) f57 LRB (U2, 1, 2) f81 GRB (n5, in) f10 PCH (R3↓) f34 ROP (U2, 2) f58 LRB (U2, 2, 3) f82 GRB (n6, in) f11 PCH (R4↑) f35 ROP (U2, 3) f59 LRB (U2, 3, 4) f83 GRB (n6, n3) f12 PCH (R4↓) f36 ROP (U2, 4) f60 LRB (U2, 4, 5) f84 GRB (n6, n5) f13 PCH (R5↑) f37 ROP (U2, 5) f61 LRB (U2, 5, 1) f85 GRB (n6, out) f14 PCH (R5↓) f38 ROP (U3, 1) f62 LRB (U3, 1, 2) f86 GRB (in, out) f15 PCH (R6↑) f39 ROP (U3, 2) f63 LRB (U3, 2, 3) f87 NSP (n1, [2, 3] [1, 4]) f16 PCH (R6↓) f40 ROP (U3, 3) f64 LRB (U3, 3, 4) f88 NSP (n1, [2, 4] [1, 3]) f17 PCH (R7↑) f41 ROP (U3, 4) f65 LRB (U3, 4, 5) f89 NSP (n1, [3, 4] [1, 2]) f18 PCH (R7↓) f42 ROP (U3, 5) f66 LRB (U3, 5, 1) f90 NSP (n4, [2, 3] [1, 4]) f19 ROP (C1, +) f43 LRB (C1, +, $-$) f67 GRB (n1, 0) f91 NSP (n4, [2, 4] [1, 3]) f20 ROP (C2, +) f44 LRB (C2, +, $-$) f68 GRB (n1, n3) f92 NSP (n4, [3, 4] [1, 2]) f21 ROP (R1, +) f45 LRB (R1, +, $-$) f69 GRB (n1, n4) f22 ROP (R2, +) f46 LRB (R2, +, $-$) f70 GRB (n1, n5) f23 ROP (R3, +) f47 LRB (R3, +, $-$) f71 GRB (n2, 0) 表 5 三种方法的诊断性能对比
Table 5 Diagnostic performance comparison of 3 methods
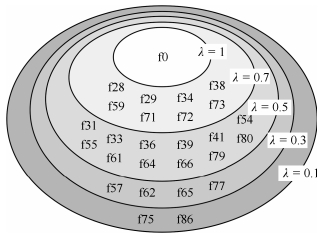
方法 $\lambda$ 漏判率 误判率 检测率 隔离率 准确率 训练时间(s) 测试时间(s) 1 0.0165 0.9200 0.9899 0.9834 0.6069 0.7 0.0235 0.3400 0.9962 0.9765 0.7796 MKL-mRVM 0.5 0.0215 0.0600 0.9993 0.9893 0.8602 2.0436E$-$05 1.7472 0.3 0.0132 0.0200 0.9997 0.9867 0.9202 0.1 0.0132 0.0200 0.9997 0.9867 0.9406 1 0.0254 0.9600 09894 0.9746 0.5303 0.7 0.0608 0.4400 0.9950 0.9656 0.6905 OAO-SVM 0.5 0.0196 0.0400 0.9996 0.9804 0.8009 4.6002E$-$02 0.1628 0.3 0.0167 0.0400 0.9996 0.9833 0.8598 0.1 0.0167 0.0400 0.9996 0.9833 0.9191 1 0.0402 0.9800 0.9890 0.9598 0.5006 0.7 0.0437 0.4800 0.9941 0.9563 0.6301 kELM 0.5 0.0243 0.0800 0.9991 0.9757 0.7623 1.9524 1.4584E$-$04 0.3 0.0191 0.0600 0.9996 0.9809 0.8271 0.1 0.0191 0.0400 0.9996 0.9809 0.9013 表 6 其他特征的诊断性能
Table 6 Diagnostic performance of other features
故障特征 分类算法 训练时间(s) 分类准确率 高阶统计量 mRVM 6.1434E$-$03 0.2046 电路规格参数 mRVM 5.6213E$-$03 0.3871 MAF mRVM 1.7324E$-$04 0.5113 MAF MKL-mRVM 2.0436E$-$05 0.6069 -
[1] Sarathi Vasan A S, Long B, Pecht M. Diagnostics and prognostics method for analog electronic circuits. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 60(11):5277-5291 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2012.2224074 [2] Ao Y C, Shi Y B, Zhang W, Li Y J. An approximate calculation of ratio of normal variables and its application in analog circuit fault diagnosis. Journal of Electronic Testing Theory & Applications, 2013, 29(4):555-565 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b9d32259512026ad9aacb8d8bfed98ac [3] Tadeusiewicz M, Halgas S. A new approach to multiple soft fault diagnosis of analog BJT and CMOS Circuits. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation & Measurement, 2015, 64(10):2688-2695 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=24a338b94522b8a5d797fae90983bd1e [4] Tang X F, Xu A Q. Practical analog circuit diagnosis based on fault features with minimum ambiguities. Journal of Electronic Testing, 2016, 32(1):83-95 doi: 10.1007/s10836-015-5561-1 [5] Liu Z B, Liu T M, Han J W, Bu S H, Tang X J, Pecht M. Signal Model-based fault coding for diagnostics and prognostics of analog electronic circuits. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 64(1):605-614 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=64ef90618081629f53f3e48784a63595 [6] Jing Y P, Yuan L F, He Y G. An analog circuit diagnosis method based on Adaptive-Kernel ICA. International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 2016, 4(2):116-120 [7] Luo H, Wang Y R, Lin H, Jiang Y Y. A new optimal test node selection method for analog circuit. Journal of Electronic Testing, 2012, 28(3):279-290 doi: 10.1007/s10836-011-5274-z [8] Tan H, Peng M F. Minimization of ambiguity in parametric fault diagnosis of analog circuits:a complex network approach. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 2012, 219(1):408-415 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0096300312006327 [9] Kumar A, Singh A P. Fuzzy classifier for fault diagnosis in analog electronic circuits. ISA Transactions, 2013, 52(6):816-824 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2013.06.006 [10] Litovski V, Andrejević M, Zwolinski M. Analogue electronic circuit diagnosis based on ANNs. Microelectronics Reliability, 2006, 46(8):1382-1391 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2005.11.008 [11] Lin H J, Han J R, Zhang X H, Xu J B, Liu Y F. The research on fusion and diagnosis method of multi soft fault of nonlinear analog circuit. International Journal of U & E Service, Science and Technology, 2015, 8(11):191-198 [12] Cui J, Wang Y R. A novel approach of analog circuit fault diagnosis using support vector machines classifier. Measurement, 2011, 44(1):281-289 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2010.10.004 [13] Xie T, He Y G. Fault diagnosis of analog circuit based on high-order cumulants and information fusion. Journal of Electronic Testing, 2014, 30(5):505-514 doi: 10.1007/s10836-014-5478-0 [14] Yuan L F, He Y G, Huang J Y, Sun Y C. A new neural-network-based fault diagnosis approach for analog circuits by using kurtosis and entropy as a preprocessor. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation & Measurement, 2010, 59(3):586-595 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5256198 [15] Kowalewski M. Two-center radial basis function network for classification of soft faults in electronic analog circuits. In:Proceedings of the Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference. Warsaw, Poland:IEEE, 2007. 1-6 [16] Stratigopoulos H G, Mir S, Hora C, Kruseman B. Diagnosis of local spot defects in analog circuits. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation & Measurement, 2012, 61(10):2701-2712 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6197714/ [17] Zhang C L, He Y G, Yuan L F, He W, Xiang S, Li Z G. A novel approach for diagnosis of analog circuit fault by using GMKL-SVM and PSO. Journal of Electronic Testing, 2016, 32(5):531-540 doi: 10.1007/s10836-016-5616-y [18] Yu W X, Sui Y B, Wang J N. The faults diagnostic analysis for analog circuit based on FA-TM-ELM. Journal of Electronic Testing, 2016, 32(4):459-465 doi: 10.1007/s10836-016-5597-x [19] Han H, Wang H J, Tian S L, Zhang N. A new analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on improved mahalanobis distance. Journal of Electronic Testing, 2013, 29(1):95-102 doi: 10.1007/s10836-012-5342-z [20] 徐丹蕾, 杜兰, 刘宏伟, 洪灵, 李彦兵.一种基于变分相关向量机的特征选择和分类结合方法.自动化学报, 2011, 37(8):932-943 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17512.shtmlXu Dan-Lei, Du Lan, Liu Hong-Wei, Hong Ling, Li Yan-Bing. Joint feature selection and classification design based on variational relevance vector machine. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(8):932-943 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17512.shtml [21] Tipping M E. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1(3):211-244 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjs201802008 [22] Psorakis I, Damoulas T, Girolami M A. Multiclass relevance vector machines:sparsity and accuracy. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(10):1588-1598 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2064787 [23] Carin L, Dobeck G J. Relevance vector machine feature selection and classification for underwater targets. In:Proceedings of the OCEANS. San Diego, USA:IEEE, 2003. 1110-1110 [24] Li D F, Hu W C. Feature selection with RVM and its application to prediction modeling. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2006. 1140-1144 [25] Girolami M, Rogers S. Variational Bayesian multinomial probit regression with Gaussian process priors. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(8):1790-1817 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.8.1790 [26] Tipping M E, Faul A C. Fast marginal likelihood maximisation for sparse bayesian models. In:Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Key West, Florida, USA:Miketipping, 2003. 3-6 [27] Yang Z R. A fast algorithm for relevance vector machine. In:Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning. Burgos, Spain:Springer, 2006. 33-39 -




 下载:
下载: