-
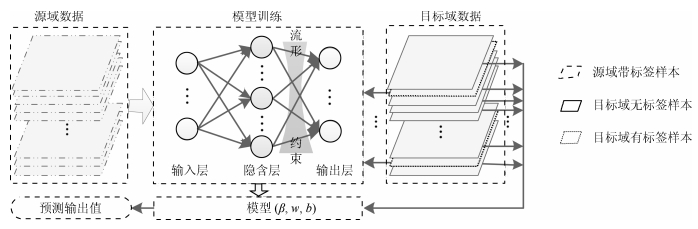
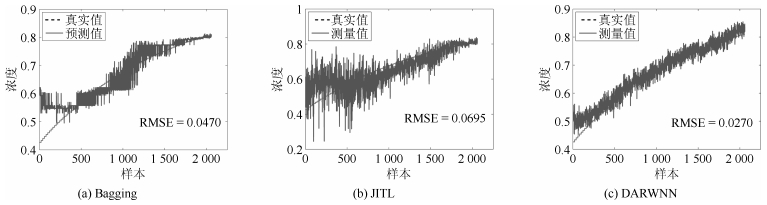
摘要: 针对湿式球磨机多工况运行过程中标签样本难以获取和工况改变导致的原测量模型失准问题,本文引入域适应随机权神经网络(Domain adaptive random weight neural network,DARWNN),实现待测工况中少量标签样本与原工况样本共同进行迁移学习.DARWNN网络解决了不同工况间难以共同进行机器学习的问题,但其只考虑经验风险,而未考虑结构风险,从而泛化性能较差,预测精度较低.在此基础上,本文引入流形正则化,并构建基于流形正则化的域适应随机权神经网络(Domain adaptive manifold regularization random weight neural network,DAMRRWNN),以保持数据几何结构,提高相应模型性能.实验结果表明,所提方法可以有效提高DARWNN的学习精度,解决多工况情况下湿式球磨机负荷参数软测量问题.Abstract: The problem of misalignment of the original measurement model is caused by the difficulty in obtaining the labeled sample and the change of working condition during the operation of the wet-type ball mill. In this paper, we introduce a domain adaptive random weight neural network (DARWNN), thus a small number of labeled samples in the working condition combined with the original working condition samples can be used to implement transfer learning. The DARWNN network can solve the problem of machine learning in different working conditions, however it considers only the empirical risk but not the structural risk. Thus the generalization performance is poor and the prediction accuracy is low. On this basis, we propose a domain adaptive manifold regularization random weight neural network (DAMRRWNN) in terms of manifold regularization to maintain data geometry structure, so as to improve the performance of the corresponding model. Experimental results indicate that the performance of the proposed methods is superior to or at least comparable with the existing benchmarking methods and that the proposed methods can effectively improve the learning accuracy of DARWNN and solve the problem of soft sensor for wet ball mill load parameters under multiple loading conditions.
-
Key words:
- Transfer learning /
- domain adaption /
- mill load /
- manifold regularization /
- soft sensor
1) 本文责任编委 贺威 -
表 1 m5油脂含量预测结果
Table 1 Prediction result of oil content in m5
评价标准 RWNN Bagging JITL RMSE 0.0490 0.1615 0.0803 NRMSE 0.0655 0.2171 0.1079 表 2 m5为源域的不同算法实验结果对比
Table 2 Comparison of experimental results of difierent algorithms for m5 as source domain
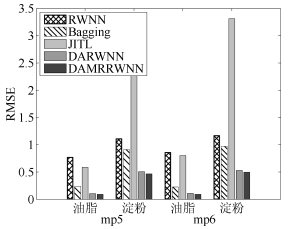
方法 为目标域 为目标域 油脂含量 淀粉含量 油脂含量 淀粉含量 RMSE NRMSE RMSE NRMSE RMSE NRMSE RMSE NRMSE RWNN 0.7723 1.0380 1.1142 0.3056 0.8612 0.1575 1.1701 0.3209 Bagging 0.2346 0.3153 0.9127 0.2503 0.2253 0.3028 0.9707 0.2662 JITL 0.5866 0.7844 2.7080 0.7427 0.8021 1.0781 3.3141 0.9090 DARWNN 0.1047 0.1407 0.5066 0.1389 0.1090 0.1465 0.5294 0.1452 DAMRRWNN 0.0908 0.1220 0.4660 0.1278 0.0911 0.1224 0.4958 0.1360 表 3 不同工况振动信号采集次数
Table 3 Acquisition times of vibration signals under difierent working conditions
MFR 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 次数 139 103 88 95 102 表 4 磨机负荷参数预测结果对比(RMSE)
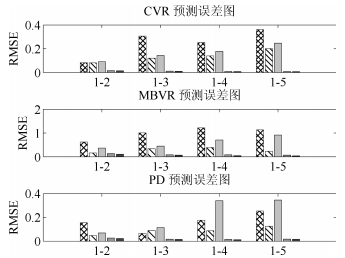
Table 4 Comparison of prediction results of mill load parameters (RMSE)
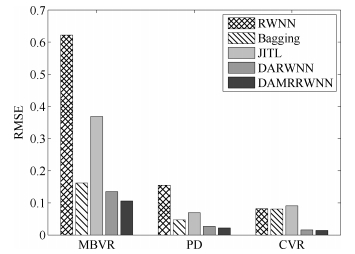
建模算法 负荷参数 1-1 1-2 1-3 1-4 1-5 RWNN MBVR 0.0279 0.6219 1.0044 1.2182 1.1312 PD 0.0040 0.1546 0.0656 0.1763 0.2541 CVR 0.0021 0.0817 0.3063 0.2516 0.3607 Bagging MBVR 0.0923 0.1618 0.3379 0.3919 0.2346 PD 0.0157 0.0470 0.0897 0.0880 0.1263 CVR 0.0086 0.0808 0.1270 0.1395 0.2012 JITL MBVR 0.0829 0.3688 0.4490 0.7043 0.9147 PD 0.0138 0.0695 0.1149 0.3406 0.3467 CVR 0.0094 0.0908 0.1428 0.1777 0.2471 DARWNN MBVR $-$ 0.1349 0.0854 0.0843 0.0709 PD $-$ 0.0270 0.0170 0.0153 0.0178 CVR $-$ 0.0159 0.0114 0.0084 0.0081 DAMRRWNN MBVR $-$ 0.1058 0.0693 0.0457 0.0365 PD $-$ 0.0219 0.0149 0.0120 0.0162 CVR $-$ 0.0141 0.0108 0.0074 0.0072 -
[1] 汤健, 赵立杰, 柴天佑, 岳恒.基于振动频谱的磨机负荷在线软测量建模.信息与控制, 2012, 41(1):123-128 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xxykz201201020Tang Jian, Zhao Li-Jie, Chai Tian-You, Yue Heng. On-line soft-sensing modelling of mill load based on vibration spectrum. Information and Control, 2012, 41(1):123-128 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xxykz201201020 [2] 汤健, 田福庆, 贾美英, 李东.基于频谱数据驱动的旋转机械设备负荷软测量.北京:国防工业出版社, 2015.Tang Jian, Tian Fu-Qing, Jia Mei-Ying, Li Dong. Soft Sensing of Rotating Machinery Equipment Load Based on Spectrum Data Drive. Beijing:National Defense Industry Press, 2015. [3] 汤健, 赵立杰, 岳恒, 柴天佑.湿式球磨机筒体振动信号分析及负荷软测量.东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 31(11):1521-1524 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dbdxxb201011001Tang Jian, Zhao Li-Jie, Yue Heng, Chai Tian-You. Analysis of vibration signal of wet ball mill shell and soft sensoring for mill load. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2010, 31(11):1521-1524 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dbdxxb201011001 [4] Huang G B, Zhu Q Y, Siew C K. Extreme learning machine:theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1-3):489-501 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126 [5] Tang J, Deng C, Huang G B. Extreme learning machine for multilayer perceptron. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 27(4):809-821 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7103337 [6] Maass W. Liquid state machines: motivation, theory, and applications. Computability in Context: Computation and Logic in the Real World. Hackensack, NJ: Imperial College Press, 2009. 275-296 [7] Zhang M, Liu X G, Zhang Z Y. A soft sensor for industrial melt index prediction based on evolutionary extreme learning machine. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 24(8):1013-1019 doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2016.05.030 [8] 汤健, 柴天佑, 余文, 赵立杰.在线KPLS建模方法及在磨机负荷参数集成建模中的应用.自动化学报, 2013, 39(5):471-486 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17934.shtmlTang Jian, Chai Tian-You, Yu Wen, Zhao Li-Jie. On-line KPLS algorithm with application to ensemble modeling parameters of mill load. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(5):471-486 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17934.shtml [9] Shao W M, Tian X M, Wang P. Supervised local and non-local structure preserving projections with application to just-in-time learning for adaptive soft sensor. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2015, 23(12):1925-1934 doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2015.11.012 [10] Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10):1345-1359 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 [11] Zhang L, Zhang D. Domain adaptation extreme learning machines for drift compensation in E-nose systems. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64(7):1790-1801 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2367775 [12] Tenenbaum J B, de Silva V, Langford J C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science, 2000, 290(5000):2319-2323 doi: 10.1126-science.290.5500.2319/ [13] Liu B, Xia S X, Meng F R, Zhou Y. Manifold regularized extreme learning machine. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016, 27(2):255-269 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/txxb201611007 [14] Schmidt W F, Kraaijveld M A, Duin R P W. Feedforward neural networks with random weights. In: Proceedings of the 11th IAPR International Conference on Pattern Recognition Vol.Ⅱ Conference B: Pattern Recognition Methodology & Systems. The Hague, Netherlands: IEEE, 1992. 1-4 [15] Liu X, Lin S B, Fang J, Xu, Z B. Is extreme learning machine feasible? A theoretical assessment (Part Ⅰ). IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 26(1):7-20 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6862852/ [16] 韩敏, 李德才.基于替代函数及贝叶斯框架的1范数ELM算法.自动化学报, 2011, 37(11):1344-1350 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17624.shtmlHan Min, Li De-Cai. A norm 1 regularization term ELM algorithm based on surrogate function and Bayesian framework. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(11):1344-1350 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17624.shtml [17] Deng W Y, Zheng Q H, Chen L. Regularized extreme learning machine. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Data Mining, 2009. CIDM'09. Nashville, TN, USA: IEEE, 2009. 389-395 [18] Tomar V S, Rose R C. Manifold regularized deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 15th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Singapore: ISCA, 2014. 348-352 [19] Guan N Y, Tao D C, Luo Z G, Yuan B. Manifold regularized discriminative nonnegative matrix factorization with fast gradient descent. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(7):2030-2048 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2105496 [20] 徐嘉明, 张卫强, 杨登舟, 刘加, 夏善红.基于流形正则化极限学习机的语种识别系统.自动化学报, 2015, 41 (9):1680-1685 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18741.shtmlXu Jia-Ming, Zhang Wei-Qiang, Yang Deng-Zhou, Liu Jia, Xia Shan-Hong. Manifold regularized extreme learning machine for language recognition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(9):1680-1685 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18741.shtml [21] Amar M, Gondal I, Wilson C. Vibration spectrum imaging:a novel bearing fault classification approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(1):494-502 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2327555 -




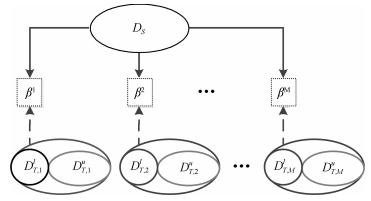
 下载:
下载: