Batch Scheduling Problem of Oil Well Considering Ramping Constraints in Oilfield Production
-
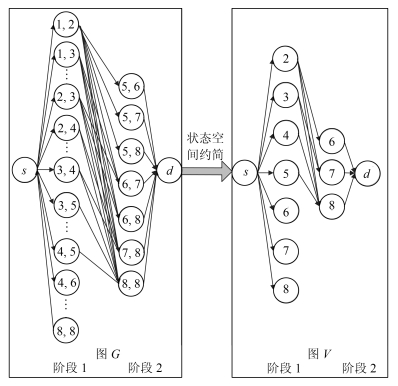
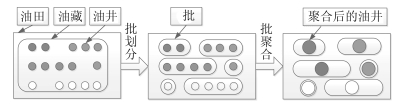
摘要: 油井间抽批调度问题是确定未来给定计划期内油田井场间抽工作方式的油井各时间段的启停状态及采油量,在满足采油需求的情况下,考虑油井底部压力变化特征对油井开启的影响以及油井最小开关机时间和爬坡约束等生产工艺要求,使总的油井采油运行成本最小.针对油井数量多而导致大规模常规数学规划模型难以求解的困难,建立了基于批的混合整数规划模型.根据模型特点设计了基于变量分离的拉格朗日松弛算法(Lagrangian relaxation,LR)进行求解.针对常规动态规划方法求解分解后的带有爬坡约束的单机组子问题效率低的缺点,提出了用特征点代表同一阶段具有相同性质节点群的状态空间约简策略,使动态规划搜索节点的复杂度从O(n4)降到O(n2),显著提高了算法的搜索效率.通过大量随机产生的数值实验表明,提出的基于变量分离的LR算法,小规模问题与CPLEX获得的最优解接近,中大规模问题能够在合理的计算时间内获得高质量的解.Abstract: Batch scheduling of oil wells in oilfield production is to determine the optimum work ways of oil well in oilfield production during a given planning horizon, which includes the start-up and shut-down status in each time period and the yield of production so that the total production operation cost of oil wells is minimized while satisfying the demand of oil recovery and considering the impact of the bottom pressure variation of the oil well on its start-up/shut-down status, ramping constraints and minimum start up and start down time of oil well and so on. Because a large number of oil wells leading to large-scale conventional mathematical programming model is difficult to solve, the nonlinear integer programming model based on batch modeling strategies and parameter aggregation methods is established. According to the characteristics of model, a variable splitting-based Lagrangian relaxation (LR) algorithm is proposed to solve the problem. Due to the inefficiency of ordinary dynamic programming method in solving the decomposed single unit sub-problems with ramping constraints, the state space reduction strategy is put forward by taking the feature states as the representatives of all states which have the same stage, thus the complexity of the proposed dynamic programming can be reduced from O(n4) to O(n2), so the algorithm's efficiency can be significantly improved. Compared with the commercial solver CPLEX, the variable splitting-based LR algorithm can obtain the near-optimal solutions for small scale problems, and the algorithm can obtain high-quality solutions in a reasonable computing time for the medium and large scale problems.
-
Key words:
- Oil well scheduling /
- batching /
- Lagrangian relaxation (LR) /
- variable splitting
1) 本文责任编委 宋士吉 -
表 1 与油井相关的参数的生成范围
Table 1 Range of values for parameters corresponding to oil wells
参数(单位) 下限 上限 $x_{i}^{\min }$ (barrel) 30 100 $x_{i}^{\max }$ (barrel) 800 1 200 $p_{i}^{\max } $ (psia) 6 000 7 000 $p_{i}^{\min }$ (psia) 2 500 3 500 $p^{\rm given}$ (psia) 6 000 700 $T_{i}^{\rm off}$ (h) 1 6 $T_{i}^{\rm on}$ (h) 1 6 $T_{i0}^{{}}$ (h) $-$8 8 ${{S}_{i}}$ ($) 70 150 ${{c}_{1i}}$ 0.10 0.20 ${{c}_{2i}}$ 0.02 0.65 ${{\alpha }_{1i}}$ 40 70 ${{a}_{2i}}$ 0.02 0.30 ${{\gamma }_{i}}$ 9.00 9.30 $D_{1t}^{{}}$ (barrel) 500 1 500 $D_{2t}^{{}}$ (barrel) 500 1 500 表 2 模型与算法的性能比较结果
Table 2 Computational results of the LR algorithm and the CPLEX solver
规模 CPLEX LR-CPLEX LD-CPLEX LD $T \times N$ $AR_1$ (单机) $AR_2$ (批) $AR_3$ (单机) $AR_4$ (批) $AR_5$ (单机) $AR_6$ (批) $AR_7$ (单机) $AR_8$ (批) $24 \times 10$ 1.00000 1.01340 1.00442 1.01340 1.00440 1.01339 1.00467 1.01340 $24 \times 30$ 1.00000 1.00463 1.01224 1.00885 1.01201 1.00885 1.01224 1.00885 $24 \times 50$ 1.00000 1.00224 1.01004 1.01388 1.01004 1.01258 1.00999 1.01388 $24 \times 70$ 1.00000 1.00113 1.01075 1.00761 1.01049 1.00762 1.01124 1.00762 $24 \times 90$ 1.00000 1.00078 1.01140 1.01146 1.01089 1.01119 1.01107 1.01160 $24 \times 100$ 1.00000 1.00037 1.01330 1.01016 1.01178 1.01020 1.01196 1.01016 $24 \times 300$ 1.02071 1.00000 1.01223 1.01016 1.01195 1.01008 1.01209 1.01059 $24 \times 500$ 1.08078 1.00000 1.01254 1.01145 1.01243 1.01131 1.01249 1.01156 $24 \times 700$ 1.12516 1.00000 1.01278 1.01191 1.01256 1.01152 1.01257 1.01154 $24 \times 900$ 1.15323 1.00000 1.01217 1.01129 1.01477 1.01133 1.01181 1.01124 AVE 1.03799 1.00225 1.01119 1.01102 1.01113 1.01081 1.01101 1.01104 表 3 模型与算法的计算时间比较
Table 3 Computational time of the proposed model and algorithm
规模 CPLEX LR-CPLEX LD-CPLEX LD $T\times N$ 单机 批 单机 批 单机 批 单机 批 $24 \times 10$ 120.44 0.03 9.62 1.19 14.37 2.59 0.15 0.05 $24 \times 30$ 247.45 1.25 27.64 2.50 36.82 3.77 0.17 0.03 $24 \times 50$ 3 600 26.65 48.07 4.23 68.40 105.18 0.34 0.05 $24 \times 70$ 3 600 359.45 72.52 6.06 96.70 11.65 0.42 0.05 $24 \times 90$ 3 600 788.54 97.53 7.70 287.47 216.25 0.49 0.05 $24 \times 100$ 3 600 342.16 116.42 8.75 1 074.90 866.45 0.51 0.06 $24 \times 300$ 3 600 3 600 557.95 28.69 789.05 241.23 1.70 0.17 $24 \times 500$ 3 600 3 600 1 273.16 53.08 1 810.21 183.56 2.80 0.28 $24 \times 700$ 3 600 3 600 2 329.22 78.07 3 250.06 307.01 3.93 0.39 $24 \times 900$ 3 600 3 600 3 597 105.56 3 600 734.70 5.07 0.50 AVE 2 916.79 1 591.81 812.91 29.58 1 102.8 267.24 1.56 0.16 -
[1] 邹艳霞.采油工艺技术.北京:石油工业出版社, 2006.Zou Yan-Xia. Oil Recovery Technology. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press, 2006. [2] Aronofsky J S, Williams A C. The use of linear programming and mathematical models in under-ground oil production. Management Science, 1962, 102(9):394-407 http://www.jstor.org/stable/2627243 [3] Ortíz-Gómez A, Rico-Ramirez V, Hernández-Castro S. Mixed-integer multiperiod model for the planning of oilfield production. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2002, 26 (4-5):703-714 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098135401007785 [4] Carvalho M C A, Pinto J M. A bilevel decomposition technique for the optimal planning of offshore platforms. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, , 2006, 23:1-11 doi: 10.1590/S0104-66322006000100001 [5] Kosmidis V D, Perkins J D, Pistikopoulos E N. A mixed integer optimization formulation for the well scheduling problem on petroleum fields. Energy Conversion and Management, 2005, 29(7):1523-1541 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=719730687ba4482a43dd2d21505f754f [6] Bohannon M J. A linear programming model for optimum development of multi-reservoir pipeline systems. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1970, 22(11):1429-1436 doi: 10.2118/2626-PA [7] Iyer R R, Grossmann I E. Optimal planning and scheduling of offshore oil field infrastructure investment and operations. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1998, 37(4):1380-1397 doi: 10.1021/ie970532x [8] Ray T, Sarker R. Genetic algorithm for solving a gas lift optimization problem. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007, 59(1):84-89 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=76d3d0022e44918e343c4a29adef1155 [9] Gunnerud V, Foss B. Oil production optimization-a piecewise linear model, solved with two decomposition strategies. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2010, 34:1803-1812 doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2009.10.019 [10] de Souza J N M, de Medeiros J L, Costa A L H, Nunes G C. Modeling, simulation and optimization of continuous gas lift systems for deepwater offshore petroleum production. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2010, 72(3):277-289 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=df7aac76fdbccba507c64edc1ebed4a5 [11] Gunnerud V, Foss B A, McKinnon K I M, Nygreen B. Oil production optimization solved by piecewise linearization in a Branch & Price framework. Computers & Operations Research, 2012, 39:2469-2477 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ff149d047b1a5fb3d0cf4a9e0b1b3517 [12] Tavallali M S, Karimi I A, Teo K M, Baxendale D, Ayatollahi Sh. Optimal producer well placement and production planning in an oil reservoir. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2013, 55:109-125 doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2013.04.002 [13] Knudsen B R, Grossmann I E, Foss B, Conn A R. Lagrangian relaxation based decomposition for well scheduling in shale-gas systems. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2014, 63(17):234-249 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=39d251bbeea01b1723089638e646e93f [14] 刘安枕.基于优化算法的油井间抽控制系统设计与实现.西安航空技术高等专科学校学报, 2008, 26(3):39-41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9233.2008.03.014Liu An-Zhen. Designing and realization of oil drilling interval pump controlling system based on optimization. Journal of Xi'an Aerotechnical College, 2008, 26(3):39-41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9233.2008.03.014 [15] 李军亮, 廖锐全, 陈晓春.抽油井间抽周期的灰色预测.断块油气田, 2012, 19(5):634-637 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkyqt201205022Li Jun-Liang, Liao Rui-Quan, Chen Xiao-Chun. Grey prediction of intermittent cycle for pumping well. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2012, 19(5):634-637 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkyqt201205022 [16] Shapiro J F. Generalized Lagrange multipliers in integer programming. Operations Research, 1971, 19:68-76 doi: 10.1287/opre.19.1.68 [17] Fisher M L. The Lagrangian relaxation method for solving integer programming problems. Management Scienc, 1981, 27:1-18 doi: 10.1287/mnsc.27.1.1 [18] Kaskavelis C A, Caramanis M C. Efficient Lagrangian relaxation algorithms for industry size job-shop scheduling problems. IIE Transactions, 1998, 30:1085-1097 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1080/07408179808966565 -




 下载:
下载: