-
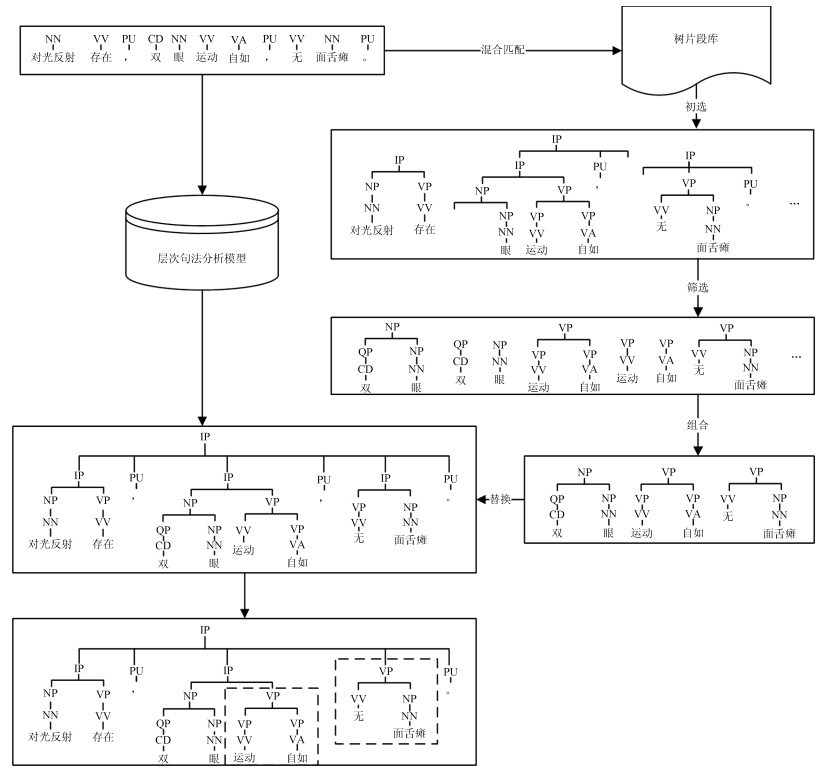
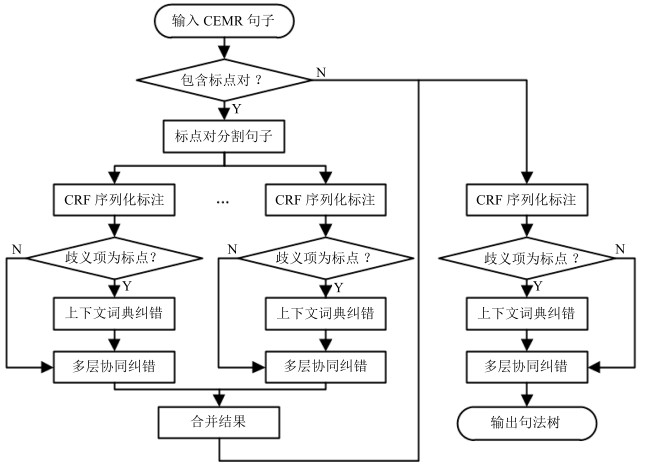
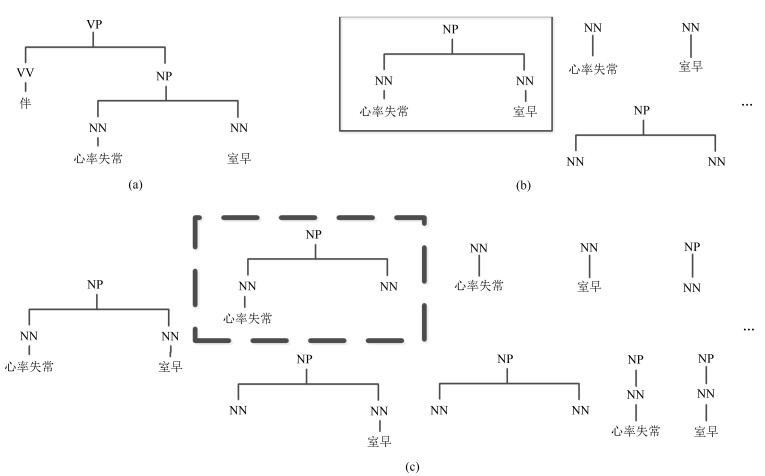
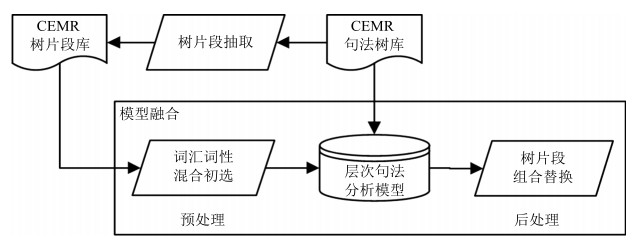
摘要: 完全句法分析是自然语言处理(Natural language processing,NLP)中重要的结构化过程,由于中文电子病历(Chinese electronic medical record,CEMR)句法标注语料匮乏,目前还没有面向中文电子病历的完全句法分析研究.本文针对中文电子病历模式化强的子语言特征,首次以树片段形式化中文电子病历复用的模式,提出了面向数据句法分析(Data-oriented parsing,DOP)和层次句法分析融合模型.在树片段抽取阶段,提出效率更高的标准树片段和局部树片段抽取算法,分别解决了标准树片段的重复比对问题,以及二次树核(Quadratic tree kernel,QTK)的效率低下问题,获得了标准树片段集和局部树片段集.基于上述两个树片段集,提出词汇和词性混合匹配策略和最大化树片段组合算法改进面向数据句法分析模型,缓解了无效树片段带来的噪声.实验结果表明,该融合模型能够有效改善中文电子病历句法分析效果,基于少量标注语料F1值能够达到目前最高的80.87%,并且在跨科室句法分析上超过Stanford parser和Berkeley parser 2%以上.Abstract: Full parsing is an important structuring process of the natural language processing (NLP). However, its research on Chinese electronic medical record (CEMR) is currently a blank because of the lack of syntactical annotated corpus on CEMR. To make the best of the sub-language characteristic of strong pattern in CEMR, patterns reused is first formalized as tree fragment in CEMR, and a model integrating data-oriented parsing (DOP) and hierarchical parsing is proposed. In the extraction stage of tree fragments, we propose a more efficient standard tree fragment algorithm by solving repeated comparison of standard tree fragments, and a partial tree fragment extraction algorithm to substitute for the low-efficient quadratic tree kernel (QTK) algorithm to obtain a standard tree fragment set and a partial tree fragment set. Based on the two extracted tree fragment sets, a strategy matching word and part-of-speech (POS) synchronously and a maximal combination algorithm of tree fragments are proposed to improve DOP, and alleviate the noise caused by invalid tree fragments. Experimental results show that the fusion model based on DOP and hierarchical parsing can effectively improve the parsing effect for CEMR, and the F1 score reaches the highest 80.87% based on a small number of annotated corpora, which is even 2% higher than those of the two state-of-the-art parsers of Stanford and Berkeley in cross-department parsing.1) 本文责任编委 张民
-
表 1 重复模式样例
Table 1 Pattern samples repeated
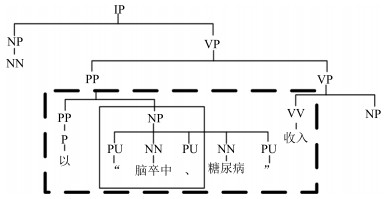
文本类型 重复模式 举例 既往史 疾病史+ (时间) (IP (NP脑梗死病史) (QP 10年)) "承认/否认"+疾病史 (VP否认(NP冠心病病史)) 主观症状 名词+形容词 (IP神志清楚) "伴"+症状(组) (VP伴头晕) 客观检查 检查+ (": ") +结果 (IP钠离子: 129.3 mmol) 无+疾病(组) (VP无中枢性面瘫) 表 2 上下文词典项概括
Table 2 Summary of elements of context dictionary
使用条件 词典项 / $\langle father, lfather, rfather \rangle$ aword = NULL $\langle lgfather, rgfather, lbword, rbword\rangle$ height $>$ 3 $\langle lbbegin, rbend \rangle$ height $<$ 4 $\langle aword\rangle$ 表 3 CEMR句法树库统计信息
Table 3 Corpus statistics of CEMR treebank
科室 份数 句子数 词数 神经内科 70 1 486 28 189 普通外科 68 1 069 19 235 共计 138 2 555 47 424 表 4 树片段抽取结果
Table 4 Results of fragment extraction
树片段类型 句法树数目 树片段种类 抽取速度(秒/句) 局部树片段 958 18 267 7.38 (FTK)/27 (QTK) 标准树片段 958 4 514 4.21 表 5 神经内科CEMR句法分析结果
Table 5 Parsing results on CEMR of neurology department
模型 词性标注准确率(%) 句法分析 解析速度(秒/句) 召回率(%) 准确率(%) F1值(%) Berkeley parser 83.82 85.09 72.29 78.17 0.2 CLPU 89.39 78.88 77.58 78.23 0.4 CLPU + SDOP 89.78 80.16 78.26 79.2 0.4 Berkeley parser (CEMR + PCTB) 92.57 82.18 77.55 79.8 0.3 Stanford parser 93.76 80.1 80.01 80.35 0.1 CLPU + PDOP 89.9 80.52 80.52 80.52 0.9 CLPU + PDOP (TOP 5) 89.92 81.15 80.59 80.87 0.9 表 6 PCTB句法分析结果
Table 6 Parsing results on PCTB
模型 词性标注准确率(%) 句法分析 解析速度(秒/句) 召回率(%) 准确率(%) F1值(%) Stanford parser 86.05 62.94 59.48 61.16 0.1 CLPU 89.98 65.59 61.73 63.6 0.4 CLPU + SDOP (TOP 5) 87.19 65.66 62.46 64.02 1.6 Berkeley parser 82.34 66.67 62.38 64.46 0.2 表 7 跨科室CEMR句法分析结果
Table 7 Parsing results on cross-department CEMR
词性标注准确率(%) 句法分析 解析速度(秒/句) 召回率(%) 准确率(%) F1值(%) 源科室:普通外科 目标科室:神经内科 Berkeley parser 83.85 66.74 66.31 64.52 0.2 Stanford parser 84.69 67.69 65.51 66.58 0.1 CLPU 88.96 69.79 66.04 67.86 0.3 CLPU + SDOP (TOP 5) 79.53 70.6 67.92 69.23 1.2 源科室:普通外科 目标科室:神经内科 Stanford parser 75.23 58.19 57.51 57.85 0.1 Berkeley parser 82.17 67.64 64.63 66.11 0.2 CLPU 89.58 70.78 66.65 68.65 0.3 CLPU + SDOP (TOP 5) 83.75 71.4 67.93 69.62 0.9 -
[1] 中华人民共和国卫生部.电子病历基本规范(试行).[Online], available: http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2010-03/04/content_1547431.htm, March 4, 2010Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. The basic specifications of electronic medical records (trial).[Online], available: http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2010-03/04/con-tent_1547431.htm, March 4, 2010 [2] 杨锦锋, 于秋滨, 关毅, 蒋志鹏.电子病历命名实体识别和实体关系抽取研究综述.自动化学报, 2014, 40 (8):1537-1562 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18425.shtmlYang Jin-Feng, Yu Qiu-Bin, Guan Yi, Jiang Zhi-Peng. An overview of research on electronic medical record oriented named entity recognition and entity relation extraction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(8):1537-1562 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18425.shtml [3] Jiang M, Huang Y, Fan J W, Tang B Z, Denny J C, Xu H. Parsing clinical text:how good are the state-of-the-art parsers? BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 2015, 15(S1):Article No. S2 doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-15-S1-S2 [4] Stubbs A, Kotfila C, Xu H, Uzuner Ö. Identifying risk factors for heart disease over time:overview of 2014 i2b2/UTHealth shared task Track 2. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2015, 58 Suppl:S67-S77 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1532046415001409 [5] Chen Y K, Lask T A, Mei Q Z, Chen Q X, Moon S, Wang J Q, Nguyen K, Dawodu T, Cohen T, Denny J C, Xu H. An active learning-enabled annotation system for clinical named entity recognition. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 2017, 17(S2):Article No. 82 doi: 10.1186/s12911-017-0466-9 [6] 蒋志鹏, 赵芳芳, 关毅, 杨锦锋.面向中文电子病历的词法语料标注研究.高技术通讯, 2014, 24(6):609-615 doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2014.06.009Jiang Zhi-Peng, Zhao Fang-Fang, Guan Yi, Yang Jin-Feng. Research on Chinese electronic medical record oriented lexical corpus annotation. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2014, 24(6):609-615 doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2014.06.009 [7] Petrov S, Klein D. Improved inference for unlexicalized parsing. In: Proceedings of the 2007 Human Language Technologies: the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. New York, USA: ACL, 2007. 404-411 [8] Klein D, Manning C D. Fast exact inference with a factored model for natural language parsing. In: Proceedings of the 2003 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2003. 3-10 [9] Bod R. A computational model of language performance: data oriented parsing. In: Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Computational Linguistics: Volume 3. New York, USA: ACL, 1992. 855-859 [10] 张玥杰, 朱靖波, 张跃, 姚天顺.基于DOP的汉语句法分析技术.中文信息学报, 2000, 14(1):13-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2000.01.003Zhang Yue-Jie, Zhu Jing-Bo, Zhang Yue, Yao Tian-Shun. Implementing Chinese parsing based on DOP technique. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2000, 14(1):13-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2000.01.003 [11] 蒋志鹏, 关毅, 董喜双.基于多层协同纠错的中文层次句法分析.中文信息学报, 2014, 28(4):29-36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2014.04.004Jiang Zhi-Peng, Guan Yi, Dong Xi-Shuang. A Chinese hierarchical parsing approach based on multi-layer collaborative correction. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2014, 28(4):29-36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2014.04.004 [12] Jiang Z P, Zhao F F, Guan Y. Developing a linguistically annotated corpus of Chinese electronic medical record. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). Belfast, UK: IEEE, 2014. 307-310 [13] Jiang Z P, Dai X, Guan Y, Zhao F F. A lexical and syntactic analysis system for Chinese electronic medical record. International Journal of u- and e- Service, Science and Technology, 2016, 9(9):305-318 doi: 10.14257/ijunesst [14] Sangati F, Zuidema W, Bod R. Efficiently extract recurring tree fragments from large treebanks. In:Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation. New York, USA:ELRA, 2010. 219-226 [15] Moschitti A. Making tree kernels practical for natural language learning. In: Proceedings of the 2010 European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Trento, Italy: EACL, 2006. 24 [16] van Cranenburgh A. Extraction of phrase-structure fragments with a linear average time tree-kernel. Computational Linguistics in the Netherlands Journal, 2014, 4:3-16 [17] Yang L E, Sun M S, Cheng Y, Zhang J C, Liu Z H, Luan H B, Liu Y. Neural parse combination. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2017, 32(4):749-757 doi: 10.1007/s11390-017-1756-5 [18] Choe D K, McClosky D, Charniak E. Syntactic parse fusion. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Lisbon, Portugal: ACL, 2015. 1360-1366 [19] Narayan S, Cohen S B. Diversity in spectral learning for natural language parsing. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Lisbon, Portugal: ACL, 2015. 1868-1878 -




 下载:
下载: