H∞ Guaranteed Cost Temperature Tracking Control for Microwave Heating Debye Media Process
-
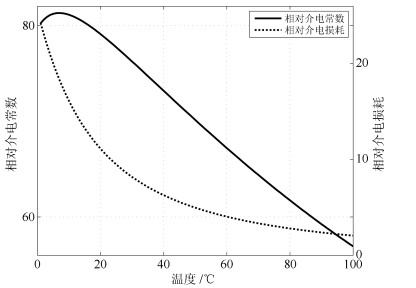
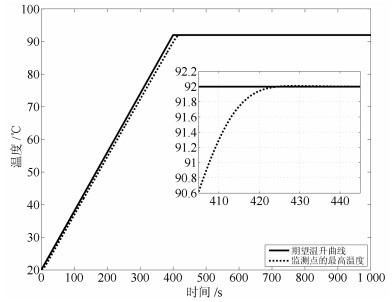
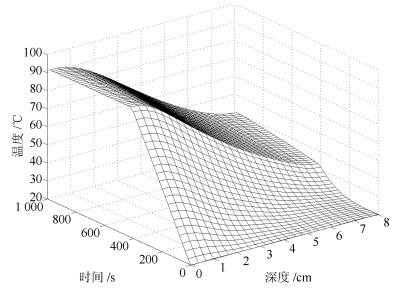
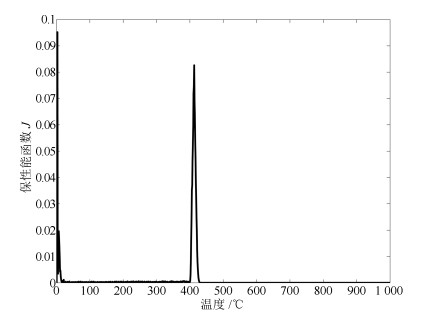
摘要: 德拜媒质微波加热过程中,由于介电常数具有随温度变化的特性,导致电磁场的空间分布将会产生巨大的变化.若缺乏合理的功率调控策略,将导致燃烧、爆炸等一系列热失控现象.针对上述问题,本文提出一种滚动时域H∞保性能温度跟踪控制策略,以实现对监测位置的最高温度进行控制.基于微波加热德拜媒质的机理模型,同时考虑跟踪系统稳定性、动态性能和输入约束,以H∞增益和保性能函数作为性能指标,本文将温度跟踪问题转化为线性矩阵不等式(Linear matrix inequality,LMI)多目标优化问题,使得系统动态性能达到最优.最后以德拜媒质微波加热短波导模型为例,对所提出方法的有效性进行仿真验证.Abstract: For the microwave heating Debye media process, the spatial distribution of electromagnetic field may be changed greatly with the temperature-dependent permittivity. Without any reasonable power regulation strategy, the phenomenon of thermal runaway, such as burning and explosion, may occur. Therefore, this paper proposes a receding horizon H∞ guaranteed cost control strategy. Specifically, the proposed controller has an explicit expression and involves the stability of system, dynamic performance and constrained input. Thereby, the temperature tracking problem can be cast into the linear matrix inequality (LMI) multi-objective optimization problem. The closed-loop control system can not only constrain the intensity of incident electric field, but also satisfy the H∞ norm and guaranteed cost function. The proposed control strategy is implemented on a one-dimensional waveguide heating model and its effectiveness can be evaluated through the simulation.
-
Key words:
- Microwave heating /
- Debye media /
- constrained input /
- H∞ guaranteed cost /
- temperature tracking
1) 本文责任编委 张化光 -
表 1 热力学参数和非齐次Neumann边界条件
Table 1 Thermodynamic parameters and nonhomogeneous Neumann boundary condition
$\rho C_p$ $\kappa $ $ a $ $ b $ $ \rm{ J / \left( cm^3 \cdot {}^\circ C \right)}$ $ \rm{ W / \left( cm \cdot {}^\circ C \right)}$ $ \rm{W / cm} $ $ \rm{W / cm} $ 4.156 0.0068 1 $-1$ -
[1] Chandrasekaran S, Ramanathan S, Basak T. Microwave food processing-a review. Food Research International, 2013, 52(1):243-261 doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.02.033 [2] Wali W A, Al-Shamma'a A I, Hassan K, Cullen J D. Online genetic-ANFIS temperature control for advanced microwave biodiesel reactor. Journal of Process Control, 2012, 22(7):1256-1272 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2012.05.013 [3] Rattanadecho P, Makul N. Microwave-assisted drying:a review of the state-of-the-art. Drying Technology, 2016, 34(1):1-38 doi: 10.1080/07373937.2014.957764 [4] Beale G O, Li M L. Robust temperature control for microwave heating of ceramics. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1997, 44(1):124-131 doi: 10.1109/41.557507 [5] Wu X, Thomas J R Jr, Davis W A. Control of thermal runaway in microwave resonant cavities. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 92(6):3374-3380 doi: 10.1063/1.1501744 [6] 刘长军, 申东雨.微波加热陶瓷中热失控现象的分析与控制.中国科学E辑:技术科学, 2008, 38(7):1097-1105 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200802108332Liu Chang-Jun, Shen Dong-Yu. Analysis and control of the thermal runaway of ceramic slab under microwave heating. Science in China Series E:Technological Sciences, 2008, 51(12):2233-2241 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200802108332 [7] Kappe C O. How to measure reaction temperature in microwave-heated transformations. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(12):4977-4990 doi: 10.1039/c3cs00010a [8] Akkari E, Chevallier S, Boillereaux L. Global linearizing control of MIMO microwave-assisted thawing. Control Engineering Practice, 2009, 17(1):39-47 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2008.05.006 [9] Chandrasekaran S, Ramanathan S, Basak T. Microwave material processing-a review. AIChE Journal, 2012, 58(2):330-363 doi: 10.1002/aic.v58.2 [10] Huang K M, Liao Y H. Transient power loss density of electromagnetic pulse in Debye media. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2015, 63(1):135-140 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2014.2374158 [11] Damour C, Hamdi M, Josset C, Auvity B, Boillereaux L. Energy analysis and optimization of a food defrosting system. Energy, 2012, 37(1):562-570 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0225691512 [12] Yin H M, Wei W. Regularity of weak solution for a coupled system arising from a microwave heating model. European Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2014, 25(1):117-131 doi: 10.1017/S0956792513000326 [13] Zhong J Q, Liang S, Zeng C, Yuan Y P, Xiong Q Y. Approximate finite-dimensional ODE temperature model for microwave heating. Nonlinear Analysis:Modelling and Control, 2016, 21(4):498-514 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316883263_Approximate_finite-dimensional_ODE_temperature_model_for_microwave_heating [14] Zhong J Q, Liang S, Yuan Y P, Xiong Q Y. Coupled electromagnetic and heat transfer ODE model for microwave heating with temperature-dependent permittivity. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2016, 64(8):2467-2477 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2584613 [15] Li Z J, Xiao H Z, Yang C G, Zhao Y W. Model predictive control of nonholonomic chained systems using general projection neural networks optimization. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2015, 45(10):1313-1321 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2015.2398833 [16] 何德峰.约束非线性系统稳定经济模型预测控制.自动化学报, 2016, 42(11):1680-1690 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2016/V42/I11/1680He De-Feng. Stabilizing economic model predictive control of constrained nonlinear systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(11):1680-1690 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2016/V42/I11/1680 [17] Ma J J, Ge S S, Zheng Z Q, Hu D W. Adaptive NN control of a class of nonlinear systems with asymmetric saturation actuators. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(7):1532-1538 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2344019 [18] 彭秀艳, 贾书丽, 张彪.一类具有执行器饱和的非线性系统抗饱和方法研究.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):798-804 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18869.shtmlPeng Xiu-Yan, Jia Shu-Li, Zhang Biao. An anti-saturation method for a class of nonlinear systems with actuator saturation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):798-804 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18869.shtml [19] Chen H, Scherer C W. Moving horizon H∞ control with performance adaptation for constrained linear systems. Automatica, 2006, 42(6):1033-1040 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.03.001 [20] Zhang D, Su H, Chu J, Wang Z. Satisfactory reliable H∞ guaranteed cost control with D-stability and control input constraints. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2008, 2(8):643-653 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta:20070332 [21] Zhao H Y, Chen Q W, Xu S Y. H∞ guaranteed cost control for uncertain Markovian jump systems with mode-dependent distributed delays and input delays. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2009, 346(10):945-957 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2009.05.007 [22] Ding S B, Wang Z S, Wang J D, Zhang H G. H∞ state estimation for memristive neural networks with time-varying delays:the discrete-time case. Neural Networks, 2016, 84:47-56 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2016.08.002 [23] Zhang H G, Luo Y H, Liu D R. Neural-network-based near-optimal control for a class of discrete-time affine nonlinear systems with control constraints. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(9):1490-1503 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2009.2027233 [24] Torres F, Jecko B. Complete FDTD analysis of microwave heating processes in frequency-dependent and temperature-dependent media. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1997, 45(1):108-117 doi: 10.1109/22.552039 [25] 陈虹, 韩光信, 刘志远.基于LMI的约束系统H∞控制及其滚动优化实现.控制理论与应用, 2005, 22(2):189-195 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzllyyy200502005Chen Hong, Han Guang-Xin, Liu Zhi-Yuan. LMI-based H∞ control scheme for constrained systems and its moving horizon implementation. Control Theory and Applications, 2005, 22(2):189-195 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzllyyy200502005 [26] Yu L, Chu J. An LMI approach to guaranteed cost control of linear uncertain time-delay systems. Automatica, 1999, 35(6):1155-1159 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00007-2 [27] Khargonekar P P, Petersen I R, Zhou K. Robust stabilization of uncertain linear systems:quadratic stabilizability and H∞ control theory. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1990, 35(3):356-361 doi: 10.1109/9.50357 [28] 陈宁, 张小峰, 桂卫华, 李金洲.一类多通道不确定时滞大系统分散鲁棒H∞控制:LMI方法.控制理论与应用, 2008, 25(2):247-252 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzllyyy200802013Chen Ning, Zhang Xiao-Feng, Gui Wei-Hua, Li Jin-Zhou. Robust decentralized H∞ control of multi-channel uncertain time-delay systems:an LMI approach. Control Theory and Applications, 2008, 25(2):247-252 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzllyyy200802013 [29] 罗毅平, 周笔锋.时滞扩散性复杂网络同步保性能控制.自动化学报, 2015, 41(1):147-156 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18592.shtmlLuo Yi-Ping, Zhou Bi-Feng. Guaranteed cost synchronization control of diffusible complex network systems with time delay. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(1):147-156 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18592.shtml [30] Kothare M V, Balakrishnan V, Morari M. Robust constrained model predictive control using linear matrix inequalities. Automatica, 1996, 32(10):1361-1379 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(96)00063-5 [31] Michalski K A, Jabs H S. One-dimensional analysis of microwave batch sterilization of water with continuous impedance matching. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2000, 26(2):83-89 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1098-2760 -





 下载:
下载: