-
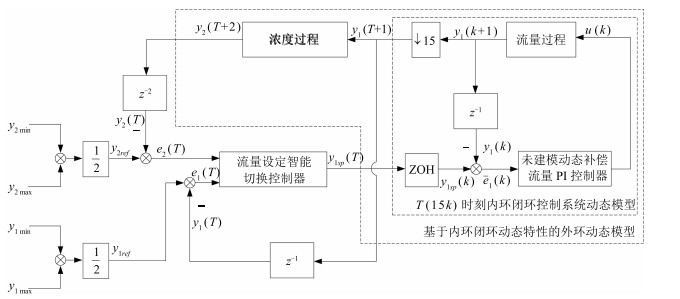
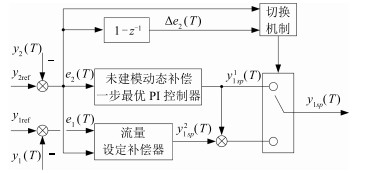
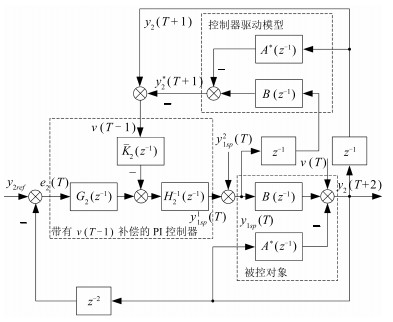
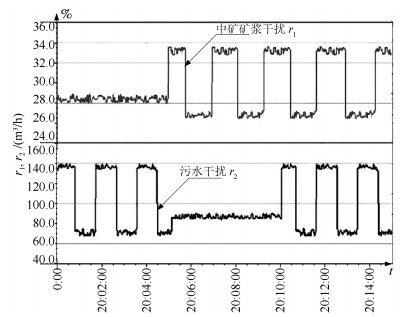
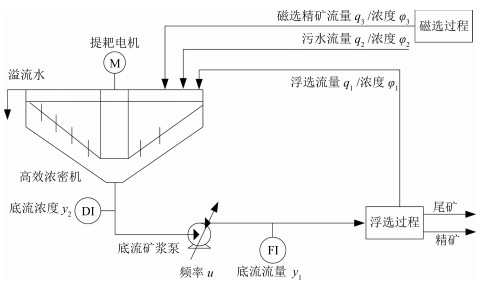
摘要: 赤铁矿混合选别浓密过程是以底流矿浆泵频率为输入,以底流矿浆流量为内环输出,以底流矿浆浓度为外环输出的强非线性串级工业过程.由于受到频繁的浮选过程产生的中矿矿浆和污水的随机干扰,底流矿浆浓度外环和流量内环始终处于动态变化之中,控制器积分作用失效,内外环相互影响,使被控系统的动态性能变坏,底流矿浆浓度与流量超出工艺规定的控制目标的范围,甚至产生谐振.本文针对上述问题利用提升技术建立基于内环流量闭环动态模型的浓度外环动态模型,将基于未建模动态补偿驱动的一步最优PI控制和基于模糊推理与规则推理的切换控制相结合,提出了由浓度外环控制和流量内环控制组成的混合选别浓密过程的双速率智能切换控制算法,建立了由机理主模型和神经网络补偿模型组成的混合选别浓密过程动态模型.所提算法通过混合选别浓密过程的半实物仿真实验结果表明本文所提控制方法的有效性.Abstract: The mixed separation thickening process (MSTP) of hematite beneficiation is a strong nonlinear cascade process with the frequency of underflow slurry pump as the input, the slurry flow-rate as the inner loop output and the concentration as the outer loop output. During its operation, some large and frequent random disturbances generated from the flotation middling and sewage will continuously cause dynamic changes of slurry concentration and slurry flow-rate, which will cause failure of controller integration. The influence between the outer and inner loops will deteriorate the dynamic performance of the controlled system and even cause resonance. To deal with the problem, lifting technique to introduce the dynamic characteristics of the inner closed-loop control system into the outer dynamic model of slurry concentration. We put forward a double-rate intelligent switching control algorithm for MSTP combined with one-step optimal PI control, unmodeled dynamics compensation control and fuzzy switching control. An MSTP dynamic model is established using the master model with mechanism and compensation model with neural network. Simulation experiment on the hardware-in-the-loop simulation system of MSTP proves the effectiveness of our method.1) 本文责任编委 谢永芳
-
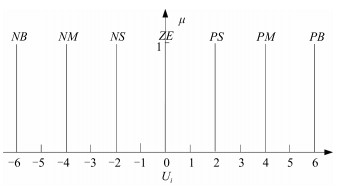
表 1 底流矿浆流量设定补偿量$\bar{U}_i$模糊规则表
Table 1 Pulp flow-rate set compensation $\bar{U}_i$ fuzzy rule table
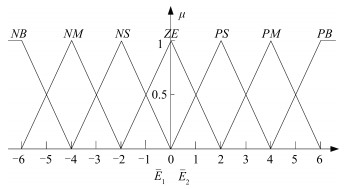
$\bar{U}_i$ $E_{1j}$ $NB$ $NM$ $NS$ $ZE$ $PS$ $PM$ $PB$ $E_{2j}$ $NB$ $ZE$ $PS$ $PS$ $PM$ $PM$ $PB$ $PB$ $NM$ $NS$ $ZE$ $PS$ $PS$ $PM$ $PM$ $PB$ $NS$ $NS$ $NS$ $ZE$ $ZE$ $PS$ $PM$ $PM$ $ZE$ $NM$ $NS$ $NS$ $ZE$ $PS$ $PS$ $PM$ $PS$ $NM$ $NM$ $NS$ $ZE$ $ZE$ $PS$ $PS$ $PM$ $NB$ $NM$ $NM$ $NS$ $NS$ $ZE$ $PS$ $PB$ $NB$ $NB$ $NM$ $NM$ $NS$ $NS$ $ZE$ 表 2 采用本文控制方法与文献[8]控制方法控制时底流矿浆浓度$y_2$的控制器性能评价表(%)
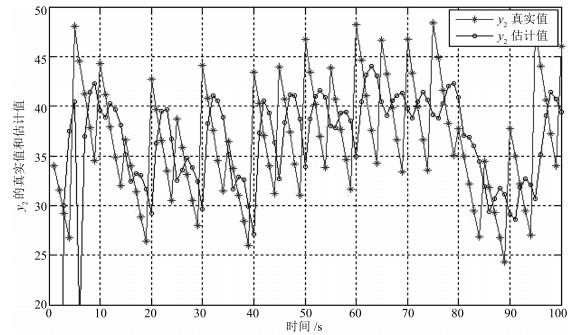
Table 2 Control performance assessment of USD $y_2$ with the proposed method and the method in [8] (%)
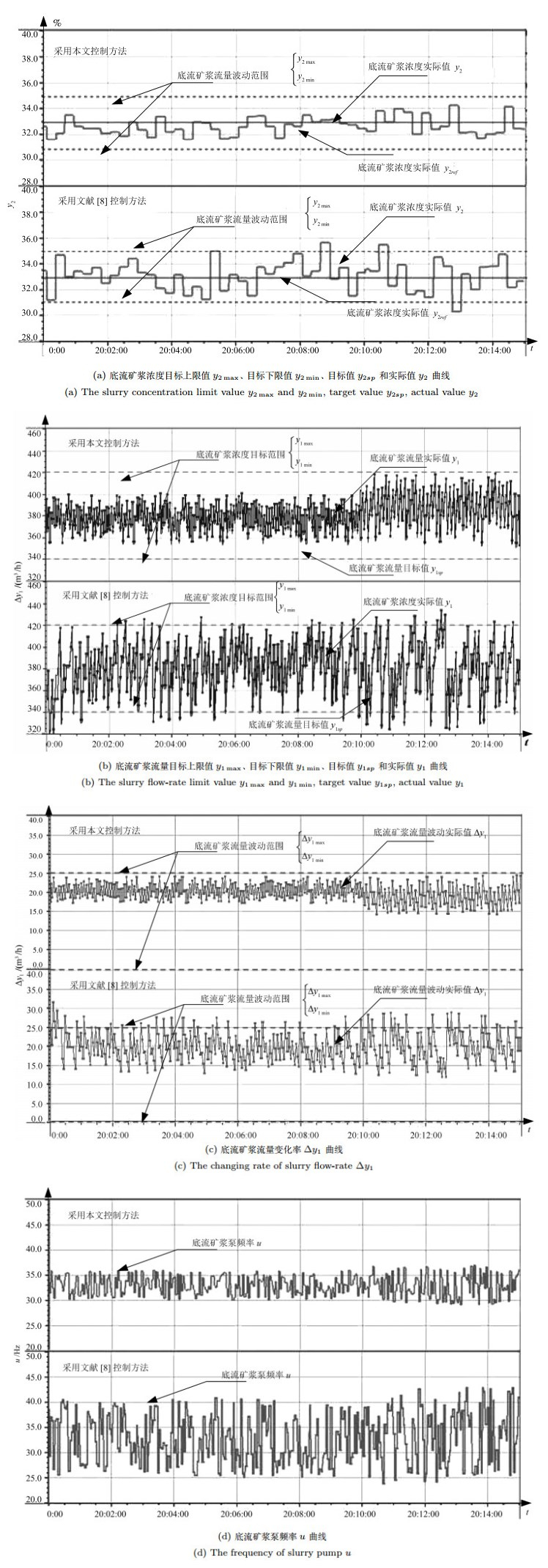
$y_2$ 超过区间最大值 超过区间绝对累积和 本文 0.0 0.0 文献[8] 0.880 2.703 -
[1] Betancourt F, Bürger R, Diehl S, Farås S. Modeling and controlling clarifier-thickeners fed by suspensions with time-dependent properties. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 62:91-101 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2013.12.011 [2] Diehl S. A regulator for continuous sedimentation in ideal clarifier-thickener units. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2008, 60 (3-4):265-291 doi: 10.1007/s10665-007-9149-3 [3] Segovia J P, Concha F, Sbarbaro D. On the control of sludge level and underflow concentration in industrial thickeners. In: Proceedings of the 18th IFAC World Congress. Milano, Italy: IFAC, 2011. 8571-8576 [4] Sidrak Y L. Control of the thickener operation in alumina production. Control Engineering Practice, 1997, 5 (10):1417-1426 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(97)00138-X [5] Shean B J, Cilliers J J. A Review of froth flotation control. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2011, 100 (3-4):57-71 doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2011.05.002 [6] Park H, Wang L G. Experimental studies and modeling of surface bubble behaviour in froth flotation. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 101:98-106 doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2015.04.021 [7] 李海波, 柴天佑, 赵大勇.混合选别浓密机底流矿浆浓度和流量区间智能切换控方法.自动化学报, 2013, 40 (9):1967-1975 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18467.shtmlLi Hai-Bo, Chai Tian-You, Zhao Da-Yong. Intelligent switching control of underflow slurry concentration and flowrate intervals in mixed separation thickener. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40 (9):1967-1975 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18467.shtml [8] Chai T Y, Jia Y, Li H B, Wang H. An intelligent switching control for a mixed separation thickener process. Control Engineering Practice, 2016, 57:61-71 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2016.07.007 [9] 金以慧.过程控制.北京:清华大学出版社, 1993.Jin Yi-Hui. The Process Control. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 1993. [10] Chai T Y, Zhao L, Qiu J B, Liu F Z, Fan J L. Integrated network-based model predictive control for setpoints compensation in industrial processes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9 (1):417-426 doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2217750 [11] 陈敏恒, 丛德滋, 方图南, 齐鸣斋.化工原理.北京:化学工业出版社, 2014.Chen Min-Heng, Cong De-Zi, Fang Tu-Nan, Qi Ming-Zhai. Chemical Engineering. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2014. [12] Kim B H, Klima M S. Development and application of a dynamic model for hindered-settling column separations. Minerals Engineering, 2004, 17 (3):403-410 doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2003.11.013 [13] Zheng Y Y. Mathematical Mode of Anaerobic Processes Applied to the Anaerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor[Ph. D. dissertation], University of Toronto, Canada, 2003 [14] Chai T Y, Zhang Y J, Wang H, Su C Y, Sun J. Data-based virtual unmodeled dynamics driven multivariable nonlinear adaptive switching control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22 (12):2154-2172 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2167685 [15] Fileti A M F, Antunes A J B, Silva F V, Silveira J, Pereira J A F R. Experimental investigations on fuzzy logic for process control. Control Engineering Practice, 2007, 15 (9):1149-1160 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2007.01.009 [16] Zheng J M, Zhao S D, Wei S G. Application of self-tuning fuzzy PID controller for a SRM direct drive volume control hydraulic press. Control Engineering Practice, 2009, 17 (12):1398-1404 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2009.07.001 [17] Precup R E, Hellendoorn H. A survey on industrial applications of fuzzy control. Computers in Industry, 2011, 62 (3):213-226 doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2010.10.001 [18] Hägglund T. A control-loop performance monitor. Control Engineering Practice, 1995, 3 (11):1543-1551 doi: 10.1016/0967-0661(95)00164-P [19] Lin S C, Tseng S S, Teng C W. Dynamic EMCUD for knowledge acquisition. Expert Systems with Applications, 2008, 34 (2):833-844 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2006.10.041 [20] Khargonekar P P, Poolla K, Tannenbaum A. Robust control of linear time-invariant plants using periodic compensation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1985, 30 (11):1088-1096 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1985.1103841 [21] Armstrong J S, Collopy F. Error measures for generalizing about forecasting methods:empirical comparisons. International Journal of Forecasting, 1992, 8 (1):69-80 doi: 10.1016/0169-2070(92)90008-W [22] 唐耀庚, 胡蓉.基于神经网络的矿浆浓度控制系统.控制工程, 2002, 9(5):45-46, 91 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jzdf200205014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQTang Yao-Geng, Hu Rong. Neural network PID control system of the pulp consistency. Control Engineering of China, 2002, 9 (5):45-46, 91 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jzdf200205014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [23] Ogata K. Discrete-Time Control Systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1994. [24] Lequin O, Gevers M, Mossberg M, Bosmans M, Bosmans E, Triest L. Iterative feedback tuning of PID parameters:comparison with classical tuning rules. Control Engineering Practice, 2003, 11 (9):1023-1033 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00303-9 -




 下载:
下载: