Knowledge-based Intelligent Optimal Control for Wastewater Biochemical Treatment Process
-
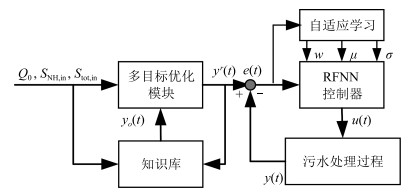
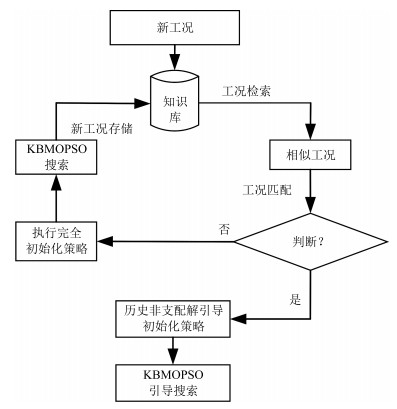
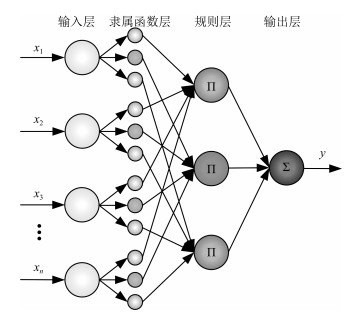
摘要: 针对污水处理过程控制能耗过大和水质超标严重等问题,本文提出一种基于知识的污水生化处理过程智能优化控制方法.该方法通过记忆多目标智能优化算法的动态处理信息,建立环境变量参数与最优解之间的知识模型.优化算法利用知识库中非支配解的引导,结合定向局部区域寻优以及随机全局寻优策略,提高了算法的收敛性,获取了更高质量的解.最后基于国际通用平台BSM1进行实验验证.结果表明,与其他优化算法相比,该方法能够在保证出水水质的前提下产生更少的能量消耗.Abstract: In order to solve the problems of excessive energy consumption and serious water quality in wastewater treatment process, a wastewater treatment process intelligent optimization control method based on knowledge is proposed. Knowledge model of environment variable parameters and optimal solutions are built by memorizing the dynamic processing information of the multi-objective intelligent optimization algorithm. The optimization algorithm is guided by the non-dominated solution in the knowledge base, and combines the oriented local area search and the stochastic global search strategy to improve the convergence of the algorithm and obtains a higher quality solution. Finally, experiment verification is performed on the international common simulation platform BSM1. Results show that the proposed method can reduce energy consumption under the premise of ensuring the quality of the effluent.1) 本文责任编委 郭戈
-
表 1 参数描述
Table 1 Parameters description
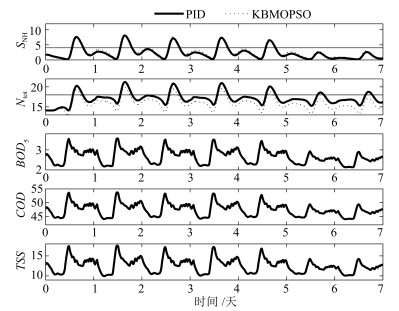
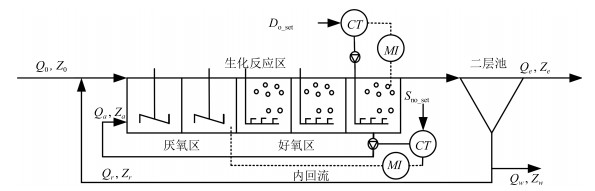
符号 描述 Do_set 溶解氧设定值 Sno_set 硝态氮设定值 CT 控制器 MI 测量设备 Z0 入水组分 Za 内回流组分 Zr 外回流组分 Zw 污泥组分 Ze 出水组分 Q0 入水流量 Qa 内回流 Qr 外回流 Qw 污泥流 Qe 出水流量 表 2 不同算法性能比较
Table 2 Performance comparison for difierent algorithm
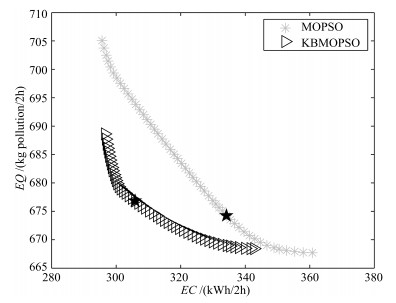
SO, 5 SNO, 2 AE PE Energy Up/Down Fines Up/Down PID[8] 2* 1* 841.1* 86.2* 927.3* - 5129.5 - DDAOC[8] 1.5799* 1.087* 758.2* 89.8* 848.0* ↓8.50%* 5185.6 ↑1.79%* Hopfleld[9] - - 814.8 63.4 878.2 ↓5.30%* - - SOOC[14] - - 852.6 53.8 906.4 ↓2.25%* - - DMOOC[14] - - 849.2 30.4 879.6 ↓5.14%* 5440.9 ↑6.07%* MOPSO 1.5012 1.077 840.4 35.7 876.1 ↓5.52% 5409.1 ↑5.17% KBMOPSO 1.3999 1.294 763.2 102.7 865.9 ↓6.62% 5092.4 ↓0.7% *表示参考了原文给出的结果 -
[1] Shannon M A, Bohn P W, Elimelech M, Georgiadis J G, Mariñas B J, Mayes A M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature, 2008, 452(7185): 301-310 doi: 10.1038/nature06599 [2] Hamitlon R, Braun B, Dare R, Koopman B, Svoronos S A. Control issues and challenges in wastewater treatment plants. IEEE Control Systems, 2006, 26(4): 63-69 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2006.1657877 [3] Åmand L, Carlsson B. Optimal aeration control in a nitrifying activated sludge process. Water Research, 2012, 46(7): 2101-2110 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0043135412000437 [4] Carlsson B, Rehnström A. Control of an activated sludge process with nitrogen removal——a benchmark study. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 45(4-5): 135-142 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11428585_Control_of_an_activated_sludge_process_with_nitrogen_removal_-_A_benchmark_study [5] Wahab N A, Katebi R, Balderud J. Multivariable PID control design for activated sludge process with nitrification and denitrification. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 45(3): 239-248 doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2009.04.016 [6] Harja G, Nascu I, Muresan C, Nascu I. Improvements in dissolved oxygen control of an activated sludge wastewater treatment process. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2016, 35(6): 2259-2281 doi: 10.1007/s00034-016-0282-y [7] Ostace G S, Baeza J A, Guerrero J, Guisasola A, Cristea V M, Agachi P S, Lafuente J. Development and economic assessment of different WWTP control strategies for optimal simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2013, 53: 164-177 doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2013.03.007 [8] Qiao J F, Bo Y C, Chai W, Han H G. Adaptive optimal control for a wastewater treatment plant based on a data-driven method. Water Science and Technology, 2013, 67(10): 2314-2320 doi: 10.2166/wst.2013.087 [9] 韩广, 乔俊飞, 韩红桂, 柴伟.基于Hopfield神经网络的污水处理过程优化控制.控制与决策, 2014, 29(11): 2085-2088 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201411029.htmHan Guang, Qiao Jun-Fei, Han Hong-Gui, Chai Wei. Optimal control for wastewater treatment process based on Hopfield neural network. Control and Decision, 2014, 29(11): 2085-2088 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201411029.htm [10] Santín I, Pedret C, Vilanova R. Applying variable dissolved oxygen set point in a two level hierarchical control structure to a wastewater treatment process. Journal of Process Control, 2015, 28: 40-55 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2015.02.005 [11] Zhang R, Xie W M, Yu H Q, Li W W. Optimizing municipal wastewater treatment plants using an improved multi-objective optimization method. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 157: 161-165 doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.103 [12] Sweetapple C, Fu G T, Butler D. Multi-objective optimisation of wastewater treatment plant control to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Water Research, 2014, 55: 52-62 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.02.018 [13] Hreiz R, Roche N, Benyahia B, Latifi M A. Multi-objective optimal control of small-size wastewater treatment plants. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 102: 345-353 doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2015.06.039 [14] Qiao J F, Zhang W. Dynamic multi-objective optimization control for wastewater treatment process. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016. 1-11, DOI: 10.1007/s00521-016-2642-8 [15] Mendes R, Rocha I, Pinto J P, Ferreira E C, Rocha M. Differential evolution for the offline and online optimization of fed-batch fermentation processes. Advances in Differential Evolution. Berlin: Springer-Heidelberg, 2008. 299-317 [16] Wang Y, Li B. Investigation of memory-based multi-objective optimization evolutionary algorithm in dynamic environment. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Trondheim, Norway: IEEE, 2009. 630-637 [17] 柴天佑.复杂工业过程运行优化与反馈控制.自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1744-1757 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18214.shtmlChai Tian-You. Operational optimization and feedback control for complex industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1744-1757 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18214.shtml [18] Porter B W, Bareiss R, Holte R C. Concept learning and heuristic classification in weak-theory domains. Artificial Intelligence, 1990, 45(1-2): 229-263 doi: 10.1016/0004-3702(90)90041-W [19] Cunningham P. A taxonomy of similarity mechanisms for case-based reasoning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2009, 21(11): 1532-1543 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2008.227 [20] Cover T, Hart P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1967, 13(1): 21-27 doi: 10.1109/TIT.1967.1053964 [21] Zhou P, Chai T Y, Wang H. Intelligent optimal-setting control for grinding circuits of mineral processing process. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2009, 6(4): 730-743 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2008.2011562 [22] Cheng S X, Zhan H, Shu Z X. An innovative hybrid multi-objective particle swarm optimization with or without constraints handling. Applied Soft Computing, 2016, 47: 370-388 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.06.012 -




 下载:
下载: