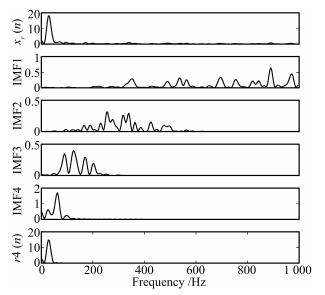
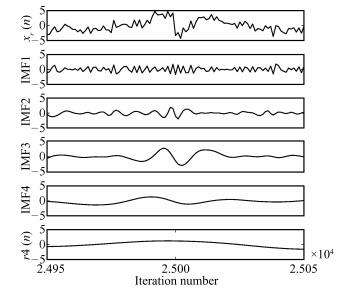
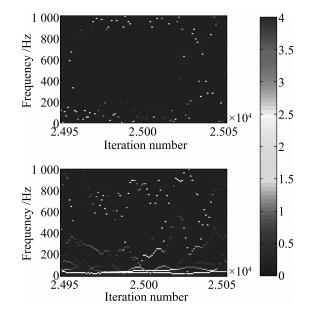
-
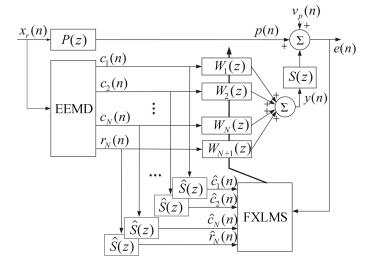
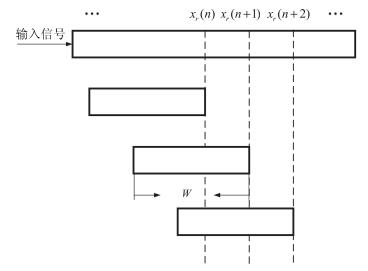
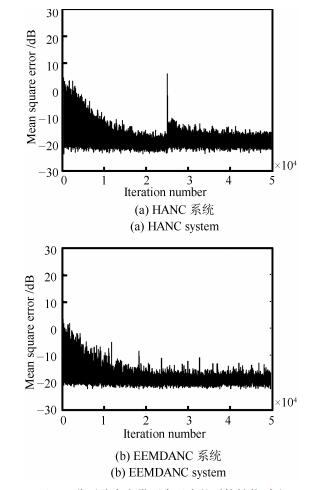
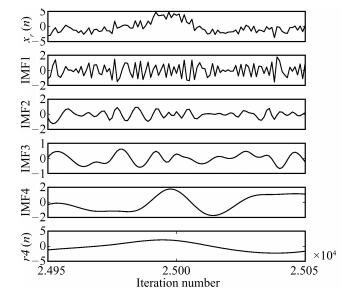
摘要: 为了提高宽窄带混合噪声的消噪效果,本文提出一种基于总体平均经验模态分解(Ensemble empirical mode decomposition,EEMD)的主动噪声控制(Active noise control,ANC)系统,利用实时EEMD算法逐段将混合噪声分解成若干个固有模态函数(Intrinsic mode functions,IMF)分量.因为这些IMF分量的频带各不相同,所以实现了混合噪声中宽带分量和窄带分量的有效分离,独立进行ANC处理后成功解决了处理混合噪声时带来的“火花”现象,而且避免了传统混合ANC(Hybrid ANC,HANC)系统中频率失调的影响. EEMD算法也是对混合噪声的平稳化处理过程,因此当混合噪声中出现非平稳变化时,本文提出的系统也能保持较好的系统稳定性.通过不同噪声环境下进行仿真分析,提出的ANC系统比HANC系统具有更好的系统稳定性和更小的稳态误差.
-
关键词:
- 混合噪声 /
- 主动噪声控制 /
- 总体平均经验模态分解 /
- 固有模态函数 /
- 非平稳变化
Abstract: In order to obtain a better de-noising performance of mixture noise containing both wideband components and narrowband components, a new active noise control (ANC) system based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) is proposed in this paper. Real-time EEMD algorithm is used to decompose the mixture noise into several intrinsic mode functions (IMF) which have a different frequency range each other, so this decomposition can separate wideband components and narrowband components from the mixture noise adaptively. Each component controlled independently can not only process mixture noise without "firework", but also avoid the frequency mismatch occurring in conventional hybrid ANC (HANC) system. The EEMD algorithm can smooth the mixture noise to make sure the proposed system has better stability when non-stationary phenomenon happens in mixture noise. Compared with HANC system, the proposed ANC system has better system stability and smaller steady-state error in processing different noise. -
表 1 次级路径估计参数设置
Table 1 Parameters of secondary path estimation
参数名称 参数值 初级路径$P(z)$的长度 ${\rm{40 (}}L{\rm{ = 41)}}$ 次级路径$S(z)$的长度 ${\rm{20 (}}M{\rm{ = 21)}}$ 次级路径估计${\hat S}(z)$的长度 ${\rm{30 ( }}\hat M{\rm{ = 31)}}$ 计算步长 0.001 训练输入信号的方差 $\sigma _{xs}^2(n)= 1$ 训练观测噪声的方差 $\sigma _{vs}^2(n)= 0.1$ 训练次数 10 000 -
[1] Kuo S M, Morgan D R. Active noise control: a tutorial review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1999, 87(6): 943-973 doi: 10.1109/5.763310 [2] Wu L F, Qiu X J, Guo Y C. A simplified adaptive feedback active noise control system. Applied Acoustics, 2014, 81: 40-46 doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2014.02.006 [3] Xiao Y G, Ikuta A, Ma L Y, Khorasani K. Stochastic analysis of the FXLMS-based narrowband active noise control system. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2008, 16(5): 1000-1014 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2008.921756 [4] Kajikawa K, Gan W S, Kuo S M. Recent applications and challenges on active noise control. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis. Trieste, Italy: IEEE, 2013. 661-666 [5] Xiao Y G, Wang J. A new feedforward hybrid active noise control system. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2011, 18(10): 591-594 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2011.2164067 [6] Kuo S M, Puvvala A B. Effects of frequency separation in periodic active noise control systems. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2006, 14(5): 1857-1866 doi: 10.1109/TSA.2005.858524 [7] Jeon H J, Chang T G, Kuo S M. Analysis of frequency mismatch in narrowband active noise control. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2010, 18(6): 1632-1642 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2009.2038815 [8] Xiao Y G, Ma L Y, Ward R K. Fast RLS Fourier analyzers capable of accommodating frequency mismatch. Signal Processing, 2007, 87(9): 2197-2212 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2007.03.003 [9] Xiao Y G, Ma L Y, Khorasani K, Ikuta A, Xu L. A filtered-X RLS based narrowband active noise control system in the presence of frequency mismatch. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. Kobe, Japan: IEEE, 2005. 260-263 [10] 黄博妍, 常林, 马亚平, 孙金玮, 魏国.一种应对非平稳频率失调的窄带主动噪声控制系统.自动化学报, 2015, 41(1): 186-193 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18597.shtmlHuang Bo-Yan, Chang Lin, Ma Ya-Ping, Sun Jin-Wei, Wei Guo. A new narrowband ANC system against nonstationary frequency mismatch. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(1): 186-193 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18597.shtml [11] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, Wu M C, Shih H H, Zheng Q A, Yen N C, Tung C C, Liu H H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995 doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [12] Flandrin P, Rilling G, Goncalves P. Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(2): 112-114 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2003.821662 [13] 曲从善, 路廷镇, 谭营.一种改进型经验模态分解及其在信号消噪中的应用.自动化学报, 2010, 36(1): 67-73 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00067Qu Cong-Shan, Lu Ting-Zhen, Tan Ying. A modified empirical mode decomposition method with applications to signal de-noising. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(1): 67-73 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00067 [14] 康春玉, 章新华.一种基于EMD和ANC技术的自适应降噪方法.系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(5): 810-812Kang Chun-Yu, Zhang Xin-Hua. Adaptive noise reduction method based on EMD and ANC. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(5): 810-812 [15] Wu Z H, Huang N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41 doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000047 [16] Wang Y H, Yeh C H, Vincent Young H-W, Hu K, Lo M-T. On the computational complexity of the empirical mode decomposition algorithm. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2014, 400: 159-162 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2014.01.020 [17] 汤键, 柴天佑, 丛秋梅, 苑明哲, 赵立杰, 刘卓, 余文.基于EMD和选择性集成学习算法的磨机负荷参数软测量.自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 1853-1866 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18454.shtmlTang Jian, Chai Tian-You, Cong Qiu-Mei, Yuan Ming-Zhe, Zhao Li-Jie, Liu Zhuo, Yu Wen. Soft sensor approach for modeling mill load parameters based on EMD and selective ensemble learning algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 1853-1866 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18454.shtml -




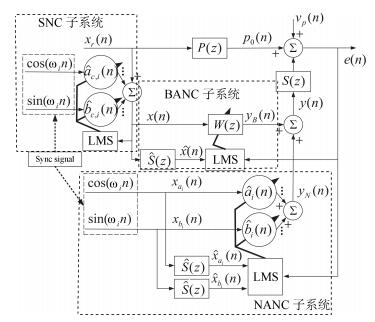
 下载:
下载: