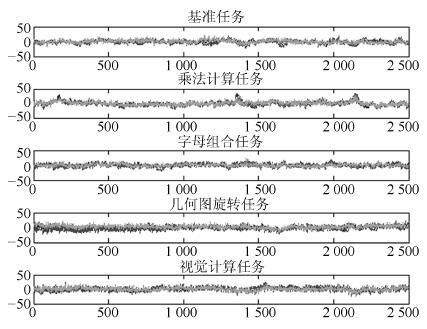
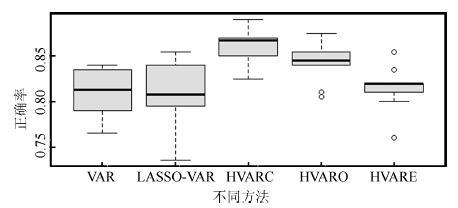
-
摘要: 有效的特征提取方法能提高脑机接口(Brain-computer interface,BCI)系统对脑电(Electroencephalogram,EEG)信号的识别率.因脑电信号都是多通道的,本文将分层向量自回归(Hierarchical vector autoregression,HVAR)模型用于脑电信号的特征提取,并结合传统的线性支持向量机(Support vector machine,SVM)用于脑电信号识别.该模型不仅克服了自回归(Autoregression,AR)模型只能用来提取单通道特征的局限性,而且不再采用传统VAR(Vector autoregression)模型所有通道共用一个时滞的处理方法.创新之处在于在传统的VAR模型基础上添加正则化思想,有效地压缩参数空间,实现合理的分层结构.本文首次将HVAR模型用于由Keirn等采集并整理的脑电数据中.实验结果证明HVAR模型在阶数较小的情况下(2阶)与阶数较大(6阶)的AR模型效果相当,可见低阶的HVAR能很好地刻画脑电信号的时空关联关系,这说明HVAR可能是刻画EEG信号的一种新颖的方法,这对其他多通道时间序列分析都有借鉴意义.Abstract: Feature extraction and classification of electroencephalogram (EEG) signals is a core part of brain-computer interface (BCI). For multi-channel EEG signal and high dimension of feature vector of BCI system, a novel EEG signal recognition method called hierarchical vector autoregression (HVAR) is presented, which extracts EEG feature using regression coefficient of HVAR model and linear support vector machine (SVM). It overcomes the limitations of the autoregression (AR) model that can be used to extract the single channel EEG only, and effectively avoids the vector autoregression (VAR) model sharing a same delay for all channels. Our contribution is that regularization is added on the traditional VAR model and a reasonable hierarchical structure is adopted. It effectively compresses parameter space of VAR model. In this paper, HVAR model is used for EEG data classification for the first time. Experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of extracted feature of HVAR model using a 2 lag order multi-channel is higher than that of AR model of 6 lag order. So low-level HVAR model can describe the portrayed temporal relationship of EEG well. This shows HVAR may be a novel method to portray EEG signal, which has reference significance to other multi-channel time-series.
-
表 1 受试者的样本数
Table 1 Trails of subjects
受试者 样本数 1 10 2 5 3 10 4 10 5 15 6 10 7 5 表 2 任务组合方式
Table 2 Patterns of task combinations
任务编号 组合方式 任务编号 组合方式 1 基准、乘法计算 6 乘法计算、几何图旋转 2 基准、字母组合 7 乘法计算、视觉计算 3 基准、几何图旋转 8 字母组合、几何图旋转 4 基准、视觉计算 9 字母组合、视觉计算 5 乘法计算、字母组合 10 几何图旋转、视觉计算 表 3 VAR模型不同时滞的平均正确率
Table 3 Average accuracy rate using VAR model with differentorder

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 0.83 0.73 0.85 0.85 0.81 0.91 0.84 0.77 0.74 0.78 3 0.79 0.74 0.81 0.82 0.80 0.88 0.80 0.73 0.73 0.75 4 0.75 0.75 0.80 0.82 0.80 0.86 0.80 0.71 0.71 0.70 5 0.73 0.71 0.78 0.78 0.81 0.86 0.77 0.70 0.65 0.70 6 0.73 0.72 0.75 0.76 0.78 0.84 0.76 0.68 0.68 0.69 7 0.71 0.67 0.71 0.73 0.77 0.81 0.72 0.65 0.65 0.65 表 4 LASSO-VAR模型不同时滞的平均正确率
Table 4 Average accuracy rate using LASSO-VAR model with different order

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 0.79 0.70 0.83 0.79 0.81 0.88 0.83 0.70 0.72 0.67 3 0.80 0.73 0.79 0.80 0.80 0.86 0.78 0.65 0.65 0.65 4 0.79 0.73 0.82 0.79 0.78 0.85 0.76 0.65 0.63 0.64 5 0.77 0.69 0.79 0.76 0.76 0.83 0.71 0.67 0.61 0.64 6 0.76 0.71 0.78 0.73 0.75 0.84 0.75 0.66 0.62 0.63 7 0.76 0.66 0.76 0.73 0.73 0.84 0.75 0.63 0.58 0.61 表 5 HVARC模型不同时滞的平均正确率
Table 5 Average accuracy rate using HVARC model with different order

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 0.82 0.73 0.85 0.80 0.86 0.90 0.84 0.73 0.70 0.70 3 0.81 0.75 0.82 0.84 0.84 0.90 0.84 0.70 0.68 0.69 4 0.80 0.76 0.84 0.82 0.83 0.89 0.82 0.69 0.66 0.68 5 0.78 0.73 0.81 0.79 0.85 0.87 0.78 0.69 0.64 0.64 6 0.80 0.73 0.81 0.79 0.82 0.88 0.81 0.70 0.65 0.66 7 0.78 0.73 0.81 0.79 0.80 0.87 0.81 0.67 0.63 0.66 表 6 HVARO模型不同时滞的平均正确率
Table 6 Average accuracy rate using HVARO model with different order

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 0.81 0.72 0.84 0.81 0.84 0.90 0.86 0.71 0.72 0.72 3 0.82 0.76 0.83 0.82 0.85 0.91 0.83 0.69 0.69 0.69 4 0.82 0.74 0.84 0.80 0.83 0.88 0.82 0.67 0.68 0.67 5 0.81 0.71 0.82 0.81 0.83 0.87 0.82 0.67 0.64 0.65 6 0.81 0.72 0.81 0.79 0.81 0.87 0.82 0.67 0.67 0.66 7 0.79 0.71 0.81 0.80 0.81 0.87 0.82 0.65 0.62 0.64 表 7 HVARE模型不同时滞的平均正确率
Table 7 Average accuracy rate using HVARE model with different order

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 0.79 0.70 0.83 0.80 0.82 0.87 0.83 0.69 0.71 0.68 3 0.77 0.72 0.80 0.82 0.81 0.87 0.79 0.64 0.68 0.69 4 0.78 0.73 0.80 0.80 0.79 0.86 0.77 0.65 0.65 0.64 5 0.78 0.71 0.78 0.79 0.80 0.85 0.75 0.66 0.64 0.64 6 0.78 0.71 0.76 0.79 0.80 0.85 0.77 0.68 0.64 0.66 7 0.78 0.68 0.76 0.80 0.76 0.86 0.77 0.64 0.64 0.65 表 8 不同特征提取方法的结果总结
Table 8 Summary of classification results for all subjects
AR-BG VAR LASSO-VAR HVARC HVARO HVARE 受 平均值 0.78 0.81 0.77 0.79 0.79 0.77 试 最大值 0.83 0.91 0.88 0.91 0.90 0.87 者 最佳任务 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 1 组合方式 几何图旋转 几何图旋转 几何图旋转 几何图旋转 几何图旋转 几何图旋转 受 平均值 0.74 0.73 0.67 0.68 0.69 0.67 试 最大值 0.89 0.82 0.76 0.74 0.77 0.76 者 最佳任务 字母组合、 字母组合、 字母组合、 字母组合、 字母组合、 字母组合、 2 组合方式 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 受 平均值 0.67 0.73 0.68 0.71 0.70 0.68 试 最大值 0.77 0.84 0.78 0.82 0.77 0.81 者 最佳任务 字母组合、 几何图旋转、 几何图旋转、 几何图旋转、 字母组合、 几何图旋转、 3 组合方式 几何图旋转 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 几何图旋转 视觉计算 受 平均值 0.77 0.82 0.75 0.77 0.78 0.75 试 最大值 0.93 0.91 0.86 0.89 0.91 0.86 者 最佳任务 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 乘法计算、 4 组合方式 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 视觉计算 -
[1] 王行愚, 金晶, 张宇, 王蓓. 脑控:基于脑——机接口的人机融合控制. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(3):208-221 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60023-3Wang Xing-Yu, Jin Jing, Zhang Yu, Wang Bei. Brain control:human-computer integration control based on brain-computer interface. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(3):208-221 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60023-3 [2] 伏云发, 王越超, 李洪谊, 徐保磊, 李永程. 直接脑控机器人接口技术. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(8):1229-1246 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01229Fu Yun-Fa, Wang Yue-Chao, Li Hong-Yi, Xu Bao-Lei, Li Yong-Cheng. Direct brain-controlled robot interface technology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(8):1229-1246 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01229 [3] McFarland D J, Wolpaw J R. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Communications of the ACM, 2011, 54(5):60-66 doi: 10.1145/1941487 [4] Yang B H, Yan G Z, Yan R G, Wu T. Adaptive subject-based feature extraction in brain-computer interfaces using wavelet packet best basis decomposition. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2007, 29(1):48-53 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2153925452&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Shannon M, Zen H, Byrne W. Autoregressive models for statistical parametric speech synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2013, 21(3):587-597 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2012.2227740 [6] 孙会文, 伏云发, 熊馨, 杨俊, 刘传伟, 余正涛. 基于HHT运动想象脑电模式识别研究. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(9):1686-1692 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18742.shtmlSun Hui-Wen, Fu Yun-Fa, Xiong Xin, Yang Jun, Liu Chuan-Wei, Yu Zheng-Tao. Identification of EEG induced by motor imagery based on Hilbert-Huang transform. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(9):1686-1692 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18742.shtml [7] 伏云发, 徐保磊, 李永程, 李洪谊, 王越超, 余正涛. 基于运动相关皮层电位握力运动模式识别研究. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(6):1045-1057 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18374.shtmlFu Yun-Fa, Xu Bao-Lei, Li Yong-Cheng, Li Hong-Yi, Wang Yue-Chao, Yu Zheng-Tao. Recognition of actual grip force movement modes based on movement-related cortical potentials. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(6):1045-1057 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18374.shtml [8] Mousavi E A, Maller J J, Fitzferald P B, Lithgow B J. Wavelet common spatial pattern in asynchronous offline brain computer interfaces. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2011, 6(2):121-128 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2010.08.003 [9] Li P Y, Wang X R, Li F L, Zhang R, Ma T, Peng Y H, Lei X, Tian Y, Guo D Q, Liu T J, Yao D Z, Xu P. Autoregressive model in the Lp norm space for EEG analysis. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2015, 240:170-174 doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.11.007 [10] Jain N, Dandapat S. Constrained autoregressive (CAR) model. In:Proceedings of 2005 Annual IEEE India International Conference. Chennai, India:IEEE, 2005.255-257 [11] Huan N J, Palaniappan R. Neural network classification of autoregressive features from electroencephalogram signals for brain-computer interface design. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2004, 1(3):142-150 doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/1/3/003 [12] Lawhern V, Hairston W D, McDowell K, Westerfield M, Robbins K. Detection and classification of subject-generated artifacts in EEG signals using autoregressive models. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2012, 208(2):181-189 doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.05.017 [13] Chen L L, Madhavan R, Rapoport B I, Anderson W S. Real-time brain oscillation detection and phase-locked stimulation using autoregressive spectral estimation and time-series forward prediction. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2013, 60(3):753-762 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2109715 [14] Anderson C W, Stolz E A, Shamsunder S. Multivariate autoregressive models for classification of spontaneous electroencephalographic signals during mental tasks. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1998, 45(3):277-286 doi: 10.1109/10.661153 [15] Pei X M, Zheng C X. Feature extraction and classification of brain motor imagery task based on MVAR model. In:Proceedings of 2004 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics. Shanghai, China:IEEE, 2004.3726-3730 [16] Hu X, Nenov V. Multivariate AR modeling of electromyography for the classification of upper arm movements. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2004, 115(6):1267-1287 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1970693885&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] Wang J, Xu G Z, Wang L, Zhang H Y. Feature extraction of brain-computer interface based on improved multivariate adaptive autoregressive models. In:Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics. Yantai, China:IEEE, 2010.895-898 [18] Zhao C L, Zheng C X, Zhao M, Tu Y L, Liu J P. Multivariate autoregressive models and kernel learning algorithms for classifying driving mental fatigue based on electroencephalographic. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(3):1859-1865 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2010.07.115 [19] Heger D, Terziyska T, Schultz T. Connectivity based feature-level filtering for single-trial EEG BCIS. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Florence, Italy:IEEE, 2014.2064-2068 [20] Faes L, Erla S, Porta A, Nollo G. A framework for assessing frequency domain causality in physiological time series with instantaneous effects. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A-Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2013, 371(1997):20110618 doi: 10.1098/rsta.2011.0618 [21] Varotto G, Fazio P, Rossi Sebastiano D, Duran D, D'Incerti L, Parati E, Sattin D, Leonardi M, Franceschetti S, Panzica F. Altered resting state effective connectivity in long-standing vegetative state patients:an EEG study. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2014, 152(1):63-68 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2032694363&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [22] Panzica F, Camafoglia L, Framceschetti S. EEG-EMG information flow in movement-activated myoclonus in patients with Unverricht-Lundborg disease. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2014, 125(9):1803-1808 doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.01.005 [23] Wang J J, Zhang Y N. A novel method of multi-channel feature extraction combining multivariate autoregression and multiple-linear principal component analysis. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 32(1):19-24 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2403326835&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [24] Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 1996, 58(1):267-288 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2135046866&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [25] Yuan M, Lin Y. Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 2006, 68(1):49-67 doi: 10.1111/rssb.2006.68.issue-1 [26] Zhao P, Rocha G, Yu B. The composite absolute penalties family for grouped and hierarchical variable selection. The Annals of Statistics, 2009, 37(6A):3468-3497 doi: 10.1214/07-AOS584 [27] Beck A, Teboulle M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems.SIAM Journal on Image Sciences, 2009, 2(1):183——202 doi: 10.1137/080716542 [28] Jenatton R, Mairal J, Obozinski G, Obozinski G, Bach F. Proximal methods for hierarchical sparse coding. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12:2297-2334 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1539012881&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [29] Keirn Z A, Aunon J I. A new mode of communication between man and his surroundings. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1990, 37(12):1209-1214 doi: 10.1109/10.64464 -





 下载:
下载: