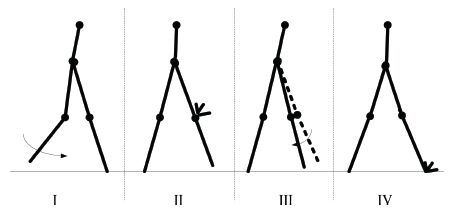
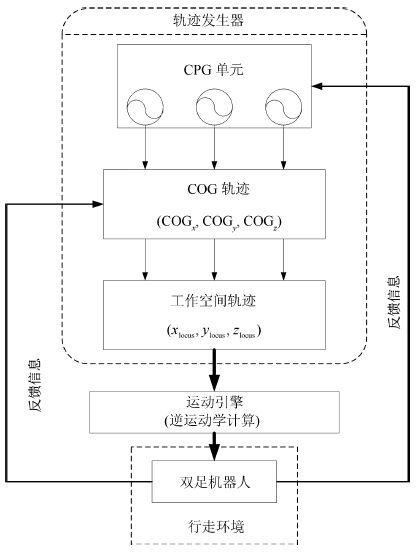
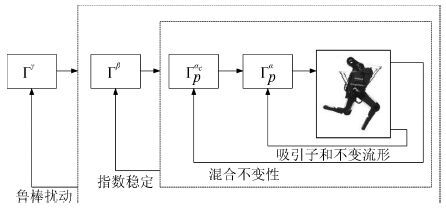
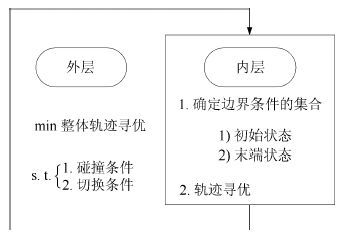
|
[1]
|
Goswami A, Espiau B, Keramane A. Limit cycles in a passive compass gait biped and passivity-mimicking control laws. Autonomous Robots, 1997, 4(3):273-286 doi: 10.1023/A:1008844026298
|
|
[2]
|
Collins S, Ruina A, Tedrake R, Wisse M. Efficient bipedal robots based on passive-dynamic walkers. Science, 2005, 307(5712):1082-1085 doi: 10.1126/science.1107799
|
|
[3]
|
Alexander R M. Walking made simple. Science, 2005, 308(5718):58-59 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1567923375&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
|
[4]
|
Kuo A D. Harvesting energy by improving the economy of human walking. Science, 2005, 309(5714):1686-1687 http://science.sciencemag.org/content/309/5741/1686
|
|
[5]
|
Wisse M, Keliksdal G, van Frankenhyyzen J, Moyer B. Passive-based walking robot. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation Magazine, 2007, 14(2):52-62 doi: 10.1109/MRA.2007.380639
|
|
[6]
|
Hobbelen D, de Boer T, Wisse M. System overview of bipedal robots flame and TUlip:tailor-made for limit cycle walking. In:Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Nice, France:IEEE, 2008.2486-2491
|
|
[7]
|
Karssen J D, Wisse M. Running with improved disturbance rejection by using non-linear leg springs. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(13):1585-1595 doi: 10.1177/0278364911408631
|
|
[8]
|
Bhounsule P A, Cortell J, Ruina A. Design and control of ranger:an energy-efficient, dynamic walking robot. In:Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Climbing and Walking Robots and the Support Technologies for Mobile Machines. Baltimore, Maryland, USA:World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte Ltd., 2012.441-448
|
|
[9]
|
Park H W, Sreenath K, Jonathan W H, Grizzle J W. Identification of a bipedal robot with a compliant drivetrain. IEEE Control Systems, 2011, 31(2):63-88 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2010.939963
|
|
[10]
|
Buss B G, Ramezani A, Hamed K A, Grffin B A, Galloway K S, Grizzle J W. Preliminary walking experiments with underactuated 3D bipedal robot MARLO. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Chicago, IL:IEEE, 2014.2529-2536
|
|
[11]
|
Kuindersma S, Deits R, Fallon M, Valenzuela A, Dai H K, Permenter F, Marion P, Tedrake R. Optimization-based locomotion planning, estimation, and control design for the atlas humanoid robot. Autonomous Robots, 2016, 40(3):429-455 doi: 10.1007/s10514-015-9479-3
|
|
[12]
|
宫赤坤, 黄成林, 张智斌, 蓝黎恩. 仿人双足机器人上楼梯仿真研究. 现代制造工程, 2013, (8):108-112 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXGY201308027.htmGong Chi-Kun, Huang Cheng-Lin, Zhang Zhi-Bin, Lan Li-En. Simulation research of humanoid bipedal robot upstairs. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2013, (8):108-112 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXGY201308027.htm
|
|
[13]
|
宋宪玺, 周烽, 梁青, 王永. 双足机器人上楼梯步态的规划与控制. 计算机仿真, 2011, 28(4):176-180 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJZ201104046.htmSong Xian-Xi, Zhou Feng, Liang Qing, Wang Yong. Gait planning and control of a biped robot climbing upstairs. Computer Simulation, 2011, 28(4):176-180 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJZ201104046.htm
|
|
[14]
|
Westervelt E R, Grizzle J W, Chevallereau C, Choi J H, Morris B. Feedback Control of Dynamic Bipedal Robot Locomotion. Boca Raton:CRC Press, 2007.19-20
|
|
[15]
|
Grizzle J W, Abba G, Plestan F. Asymptotically stable walking for biped robots:analysis via systems with impulse effects. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2001, 46(1):51-64 doi: 10.1109/9.898695
|
|
[16]
|
Fu C L, Chen K. Section-map stability criterion for biped robots part Ⅰ:theory. In:Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation. Harbin, China:IEEE, 2007.1529-1534
|
|
[17]
|
Ames A D, Galloway K, Sreenath K, Grizzle J W. Rapidly exponentially stabilizing control Lyapunov functions and hybrid zero dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(4):876-891 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2299335
|
|
[18]
|
Orlov Y, Aoustin Y, Chevallereau C. Finite time stabilization of a perturbed double integrator——part Ⅰ:continuous sliding mode-based output feedback synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(3):614-618 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2090708
|
|
[19]
|
Lamperski A, Ames A D. Lyapunov theory for Zeno stability. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2013, 58(1):100-112 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2012.2208292
|
|
[20]
|
Hürmüzlü Y, Moskowitz G D. Bipedal locomotion stabilized by impact and switching:Ⅰ. Two-and three-dimensional, three-element models Ⅱ. Structural stability analysis of a four element bipedal locomotion model. Dynamics and Stability of Systems, 1987, 2(2):73-112 doi: 10.1007%2Fs11044-009-9185-z
|
|
[21]
|
Westervelt E R, Buche G, Grizzle J W. Experimental validation of a framework for the design of controllers that induce stable walking in planar bipeds. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2004, 23(6):559-582 doi: 10.1177/0278364904044410
|
|
[22]
|
Liu L M, Tian Y T. Switch control between different speeds for a passive dynamic walker. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2012, 9:241 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2142112651&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
|
[23]
|
刘德君, 田彦涛. 双足步行机器人能量成型控制. 控制理论与应用, 2012, 29(10):1301-1308 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201210008.htmLiu De-Jun, Tian Yan-Tao. Energy shaping control of biped walking robot. Control Theory and Applications, 2012, 29(10):1301-1308 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201210008.htm
|
|
[24]
|
Nguyen Q, Sreenath K. L1 adaptive control for bipedal robots with control Lyapunov function based quadratic programs. In:Proceedings of the 2015 American Control Conference. Chicago, IL:IEEE, 2015.862-867
|
|
[25]
|
Orlov Y. Finite time stability and robust control synthesis of uncertain switched systems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2004, 43(4):1253-1271 doi: 10.1137/S0363012903425593
|
|
[26]
|
Aoustin Y, Chevallereau C, Orlov Y. Finite time stabilization of a perturbed double integrator——part Ⅱ:applications to bipedal locomotion. In:Proceedings of the 49th IEEE Conference of Decision and Control. Atlanta, GA:IEEE, 2010.3554-3559
|
|
[27]
|
Oza H B, Orlov Y V, Spurgeon S K, Aoustin Y, Chevallereau C. Finite time tracking of a fully actuated biped robot with pre-specified settling time:a second order sliding mode synthesis. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Hong Kong, China:IEEE, 2014.2570-2575
|
|
[28]
|
Oza H B, Orlov Y V, Spurgeon S K, Aoustin Y, Chevallereau C. Continuous second order sliding mode based robust finite time tracking of a fully actuated biped robot. In:Proceedings of the 2014 European Control Conference. Strasbourg, France:IEEE, 2014.2600-2605
|
|
[29]
|
Or Y, Ames A D. Stability and completion of Zeno equilibria in Lagrangian hybrid systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(6):1322-1336 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2080790
|
|
[30]
|
Or Y, Teel A R. Zeno stability of the set-valued bouncing ball. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(2):447-452 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2090411
|
|
[31]
|
Goebel R, Teel A R. Solutions to hybrid inclusions via set and graphical convergence with stability theory applications. Automatica, 2006, 42(4):573-587 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2005.12.019
|
|
[32]
|
Ames A D. Characterizing knee-bounce in bipedal robotic walking:a Zeno behavior approach. In:Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Hybrid Systems:Computation and Control. New York, USA:ACM, 2011.163-172
|
|
[33]
|
胡峻峰, 曹军, 双足被动步行的全局稳定性分析. 计算机工程, 2015,41(2):173-177 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC201502033.htmHu Jun-Feng, Cao Jun. Analysis for global stability of passive bipeds walking. Computer Engineering, 2015, 41(2):173-177 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC201502033.htm
|
|
[34]
|
MontañO E, Orlov Y, Aoustin Y. Nonlinear state feedback H_∞-control of mechanical systems under unilateral constraints. In:Proceedings of the 19th IFAC World Congress. Cape Town, South Africa:IFAC, 2014.3833-3838
|
|
[35]
|
Dai H K, Tedrake R. Optimizing robust limit cycles for legged locomotion on unknown terrain. In:Proceedings of the 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Maui, HI, USA:IEEE, 2012.1207-1213
|
|
[36]
|
Manchester I R, Mettin U, Iida F, Tedrake R. Stable dynamic walking over uneven terrain. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(3):265-279 doi: 10.1177/0278364910395339
|
|
[37]
|
Dai H K, Tedrake R. L2-gain optimization for robust bipedal walking on unknown terrain. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe, Germany:IEEE, 2013.3116-3123
|
|
[38]
|
Gan C B, Ding C T, Yang S X. Dynamical analysis and performance evaluation of a biped robot under multi-source random disturbances. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2014, 30(6):983-994 doi: 10.1007/s10409-014-0074-1
|
|
[39]
|
Montano O, Orlov Y, Aoustin Y, Chevallereau C. Orbital stabilization of an underactuated bipedal gait via nonlinear H∞ control using measurement feedback. Autonomous Robots, DOI: 10.1007/s1054-015-9543-z
|
|
[40]
|
Hamed K A, Buss B G, Grizzle J W. Exponentially stabilizing continuous time controllers for periodic orbits of hybrid systems:application to bipedal locomotion with ground height variations. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2016, 35(8):977-999 doi: 10.1177/0278364915593400
|
|
[41]
|
Hodgins J K, Raibert M N. Adjusting step length for rough terrain locomotion. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1991, 7(3):289-298 doi: 10.1109/70.88138
|
|
[42]
|
Andrada E, Rode C, Blickhan R. Grounded running in quails:simulations indicate benefits of observed fixed aperture angle between legs before touch-down. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2013, 335:97-107 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2013.06.031
|
|
[43]
|
Maus H M, Seyfarth A. Walking in circles:a modelling approach. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2014, 11(99), doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0594
|
|
[44]
|
李满天, 于海涛, 郭伟, 王鹏飞, 蔡鹤皋. 基于摄动理论的SLIP模型解析化研究及其运动控制. 机器人, 2012, 34(6):689-696 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1218.2012.00689Li Man-Tian, Yu Hai-Tao, Guo Wei, Wang Peng-Fei, Cai He-Gao. Research on the analyticity of SLIP model based on perturbation theory and locomotion control. Robot, 2012, 34(6):689-696 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1218.2012.00689
|
|
[45]
|
Yu H T, Li M T, Cai H G. Analysis on the performance of the SLIP runner with nonlinear spring leg. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 26(5):892-899 doi: 10.3901/CJME.2013.05.892
|
|
[46]
|
Meghdari A, Sohrabpour S, Naderi D, Tamaddoni S H, Jafari F, Salarieh H. A novel method of gait synthesis for bipedal fast locomotion. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 2008, 53(2):101-118 doi: 10.1007/s10846-008-9233-6
|
|
[47]
|
Kwon O, Park J H. Asymmetric trajectory generation and impedance control for running of biped robots. Autonomous Robots, 2009, 26(1):47-78 doi: 10.1007/s10514-008-9106-7
|
|
[48]
|
Celik H, Piazza S J. Simulation of aperiodic bipedal sprinting. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 2013, 135(8):81008 doi: 10.1115/1.4024577
|
|
[49]
|
Tamaddoni S H, Jafari F, Meghdari A, Sohrabpour S. Biped hopping control bazsed on spring loaded inverted pendulum model. International Journal of Humanoid Robotics, 2010, 7(2):263-280 doi: 10.1142/S0219843610002106
|
|
[50]
|
Han B, Luo X, Liu Q Y, Zhou B, Chen X D. Hybrid control for SLIP-based robots running on unknown rough terrain. Robotica, 2014, 32(7):1065-1080 doi: 10.1017/S0263574713001239
|
|
[51]
|
Shen Z H, Seipel J. A piecewise-linear approximation of the canonical spring-loaded inverted pendulum model of legged locomotion. Journal of Computational and Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 11(1):011007 doi: 10.1115/1.4029664
|
|
[52]
|
Geng T, Porr B, Wörgötter F. Fast biped walking with a sensor-driven neuronal controller and real-time online learning. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2006, 25(3):243-259 doi: 10.1177/0278364906063822
|
|
[53]
|
Geng T. Online regulation of the walking speed of a planar limit cycle walker via model predictive control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(5):2326-2333 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2272274
|
|
[54]
|
Endo G, Morimoto J, Matsubara T, Nakanishi J, Cheng G. Learning CPG-based biped locomotion with a policy gradient method:application to a humanoid robot. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2008, 27(2):213-228 doi: 10.1177/0278364907084980
|
|
[55]
|
Fu C L, Tan F, Chen K. A simple walking strategy for biped walking based on an intermittent sinusoidal oscillator. Robotica, 2010, 28(6):869-884 doi: 10.1017/S0263574709990713
|
|
[56]
|
Liu C J, Wang D W, Chen Q J. Central pattern generator inspired control for adaptive walking of biped robots. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2013, 43(5):1206-1215 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2012.2235426
|
|
[57]
|
薛方正, 陈强, 厚之成. 基于CPG的双足机器人多层步行控制器设计. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(3):467-472 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201503013.htmXue Fang-Zheng, Chen Qiang, Hou Zhi-Cheng. Central pattern generator based multi-level walking controller design of biped robot. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(3):467-472 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201503013.htm
|
|
[58]
|
Srinivasan M, Ruina A. Computer optimization of a minimal biped model discovers walking and running. Nature, 2006, 439(7072):72-75 doi: 10.1038/nature04113
|
|
[59]
|
Sinnet R W, Jiang S, Ames A D. A human-inspired framework for bipedal robotic walking design. International Journal of Biomechatronics and Biomedical Robotics, 2014, 3(1):20-41 doi: 10.1504/IJBBR.2014.059275
|
|
[60]
|
Ames A D. Human-inspired control of bipedal walking robots. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(5):1115-1130 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2299342
|
|
[61]
|
Ames A D. First steps toward automatically generating bipedal robotic walking from human data. Robot Motion and Control 2011. London:Springer, 2011.89-116
|
|
[62]
|
Zhao H H, Ma W L, Ames A D, Zeagler M B. Human-inspired multi-contact locomotion with AMBER2. In:Proceedings of the 2014 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems. Berlin, Germany:IEEE, 2014.199-210
|
|
[63]
|
Zhao H H, Powell M J, Ames A D. Human-inspired motion primitives and transitions for bipedal robotic locomotion in diverse terrain. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 2014, 35(6):730-755 doi: 10.1002/oca.v35.6
|
|
[64]
|
Powell M J, Cousineau E A, Ames A D. Model predictive control of underactuated bipedal robotic walking. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Seattle, USA:IEEE, 2015.5121-5126
|
|
[65]
|
Arai H, Tanie K, Shiroma N. Time-scaling control of an underactuated manipulator. Journal of Robotic Systems, 1998, 15(9):525-536 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4563
|
|
[66]
|
Dahl O, Nielsen L. Torque-limited path following by online trajectory time scaling. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1990, 6(5):554-561 doi: 10.1109/70.62044
|
|
[67]
|
Chevallereau C, Grizzle J W, Shih C L. Asymptotically stable walking of a five-link underactuated 3-D bipedal robot. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2009, 25(1):37-50 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2010366
|
|
[68]
|
Shih C L, Grizzle J W, Chevallereau C. From stable walking to steering of a 3D bipedal robot with passive point feet. Robotica, 2012, 30(7):1119-1130 doi: 10.1017/S026357471100138X
|
|
[69]
|
Holm J K, Lee D, Spong M W. Time-scaling trajectories of passive-dynamic bipedal robots. In:Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Roma, Italy:IEEE, 2007.3603-3608 http://www.doc88.com/p-9975360014940.html
|
|
[70]
|
Holm J K. Gait regulation for bipedal locomotion[Ph.D. dissertation], University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA, 2008.
|
|
[71]
|
Hu Y, Yan G F, Lin Z Y. Gait generation and control for biped robots with underactuation degree one. Automatica, 2011, 47(8):1605-1616 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.04.018
|
|
[72]
|
Routh E J. A Treatise on the Stability of a Given State of Motion:Particularly Steady Motion. London:MacMillan, 1877.
|
|
[73]
|
Routh E J. Advanced Rigid Dynamics. London:McMillan, 1884.
|
|
[74]
|
Arnold V I. Dynamical Systems Ⅲ. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 1988.
|
|
[75]
|
Marsden J E, Scheurle J. Lagrangian reduction and the double spherical pendulum. Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik, 1993, 44(1):17-43 doi: 10.1007/BF00914351
|
|
[76]
|
Marsden J E, Scheurle J. The reduced euler-lagrange equations. Fields Institute Communications, 1993, 1:139-164 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1681099931&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
|
[77]
|
Ames A D, Sastry S. Hybrid Routhian reduction of Lagrangian hybrid systems. In:Proceedings of the 2006 American Control Conference. Minneapolis, MN:IEEE, 2006. http://robotics.eecs.berkeley.edu/~sastry/2006Publications.htm
|
|
[78]
|
Ames A D, Sastry S. Hybrid geometric reduction of hybrid systems. In:Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. San Diego, USA:IEEE, 2006.923-929 http://authors.library.caltech.edu/view/year/2006.html
|
|
[79]
|
Gregg R D, Spong M W. Reduction-based control of three-dimensional bipedal walking robots. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2010, 29(6):680-702 doi: 10.1177/0278364909104296
|
|
[80]
|
Ames A D, Gregg R D, Spong M W. A geometric approach to three-dimensional hipped bipedal robotic walking. In:Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. New Orleans, LA, USA:IEEE, 2007.5123-5130
|
|
[81]
|
Sinnet R W, Ames A D. 2D bipedal walking with knees and feet:a hybrid control approach. In:Proceedings of the 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 28th Chinese Control Conference. Shanghai, China:IEEE, 2009.3200-3207 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221043432_2D_Bipedal_Walking_with_Knees_and_Feet_A_Hybrid_Control_Approach
|
|
[82]
|
Ames A D, Tabuada P, Schürmann B, Ma W L, Kolathaya S, Rungger M, Grizzle J W. First steps toward formal controller synthesis for bipedal robots. In:Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Hybrid Systems:Computation and Control. Seattle, WA, USA:ACM, 2015.209-218
|
|
[83]
|
Westervelt E R, Grizzle J W, Koditschek D E. Hybrid zero dynamics of planar biped walkers. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(1):42-56 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2002.806653
|
|
[84]
|
Wang T, Chevallereau C, Tlalolini D. Stable walking control of a 3D biped robot with foot rotation. Robotica, 2014, 32(4), 551-570 doi: 10.1017/S0263574713000866
|
|
[85]
|
Wang T, Chevallereau C, Rengifo C F. Walking and steering control for a 3D biped robot considering ground contact and stability. Robotics & Autonomous Systems, 2012, 60(7):962-977 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chevallereau_Christine/publication/257343871_Walking_and_steering_control_for_a_3D_biped_robot_considering_ground_contact_and_stability/links/561f6c6908aef097132df18e.pdf?inViewer=true&pdfJsDownload=true&disableCoverPage=true&origin=publication_detail
|
|
[86]
|
Sreenath K, Park H W, Poulakakis I, Grizzle J W. Embedding active force control within the compliant hybrid zero dynamics to achieve stable, fast running on MABEL. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(3):324-345 doi: 10.1177/0278364912473344
|
|
[87]
|
Hereid A, Hubicki C M, Cousineau E A, Hurst J W, Ames A D. Hybrid zero dynamics based multiple shooting optimization with applications to robotic walking. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Seattle, WA, USA:IEEE, 2015.5734-5740
|
|
[88]
|
Ober-Blöbaum S. Discrete Mechanics and Optimal Control[Ph.D. dissertation], University of Paderborn, Germany, 2008 doi: 10.1007/s10569-009-9229-y?view=classic
|
|
[89]
|
Pekarek D, Ames A D, Marsden J E. Discrete mechanics and optimal control applied to the compass gait biped. In:Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. New Orleans, USA:IEEE, 2007.5376-5382
|
|
[90]
|
孙中波, 段复建, 许春玲, 田彦涛. 不等式约束优化超线性收敛的信赖域-SQP算法. 应用数学学报, 2014, 37(5):878-890Sun Zhong-Bo, Duan Fu-Jian, Xu Chun-Ling, Tian Yan-Tao. A superlinearly convergent trust region-SQP algorithm for inequality constrained optimization. Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica, 2014, 37(5):878-890
|
|
[91]
|
Kai T, Shintani T. A gait generation method for the compass-type biped robot on slopes via discrete mechanics. In:Proceedings of the 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference. Orlando, USA:IEEE, 2011.675-681
|
|
[92]
|
Kai T, Shintani T. Gait generation on periodically unlevel grounds for the compass-type biped robot via discrete mechanics. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications. Dubrovnik, Croatia:IEEE, 2012.1362-1368 http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/conf/IEEEcca/IEEEcca2012
|
|
[93]
|
Kai T, Shintani T. A discrete mechanics approach to gait generation on periodically unlevel grounds for the compass-type biped robot. International Journal of Advanced Research in Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 2(9):43-51 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2043086838&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
|
[94]
|
Sun Z B, Tian Y T, Li H Y, Wang J. A superlinear convergence feasible sequential quadratic programming algorithm for bipedal dynamic walking robot via discrete mechanics and optimal control. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, DOI: 10.1002/oca.2228
|
|
[95]
|
Sun Z B, Li H Y, Wang J, Tian Y T. A gait optimization smoothing penalty function method for bipedal robot via DMOC. In:Proceedings of the 17th IFAC Symposium on System Identification. Beijing, China:IFAC, 2015.1148-1153
|
|
[96]
|
Aoyama T, Sekiyama K, Lu Z G, Hasegawa Y, Fukuda T. 3-D biped walking using double support phase and swing leg retraction based on the assumption of point-contact. Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 2012, 24(5):866-875 doi: 10.20965/jrm.issn.1883-8049
|
|
[97]
|
谭民, 王硕. 机器人技术研究进展. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(7):963-972 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18124.shtmlTan Min, Wang Shuo. Research progress on robotics. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(7):963-972 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18124.shtml
|
|
[98]
|
Grizzle J W, Chevallereau C, Sinnet R W, Ames A D. Models, feedback control, and open problems of 3D bipedal robotic walking. Automatica, 2014, 50(8):1955-1988 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.04.021
|





 下载:
下载: