-
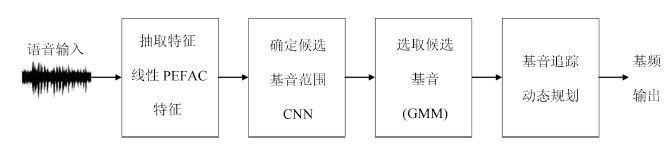
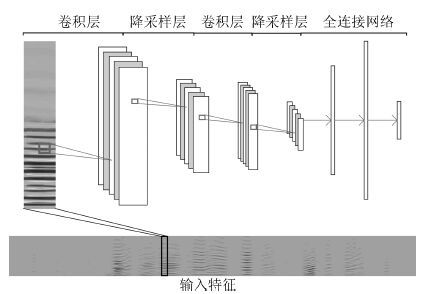
摘要: 在语音信号中, 基音是一个重要参数, 且有重要用途. 然而, 检测噪声环境中语音的基音却是一项难度较大的工作. 由于卷积神经网络(Convolutional neural network, CNN)具有平移不变性, 能够很好地刻画语谱图中的谐波结构, 因此我们提出使用CNN来完成这项工作. 具体地, 我们使用CNN来选取候选基音, 再用动态规划方法(Dynamic programming, DP)进行基音追踪, 生成连续的基音轮廓. 实验表明, 与其他方法相比, 本文的方法具有明显的性能优势, 并且 对新的说话人和噪声有很好的泛化性能, 具有更好的鲁棒性.Abstract: Pitch is an important characteristic of speech and is useful for many applications. However, pitch determination in noisy conditions is difficult. Because shift-invariant property of convolutional neural network (CNN) is suitable to model spectral feature for pitch detection, we propose a supervised learning algorithm to estimate pitch using CNN. Specifically, we use CNN for pitch candidate selection, and dynamic programming (DP) for pitch tracking. Our experimental results show that the proposed method can obtain accurate pitch estimation and that it has a good generalization ability in terms of new speakers and noisy conditions.
-
表 1 本文方法参数设置表
Table 1 Parameters setting of our method
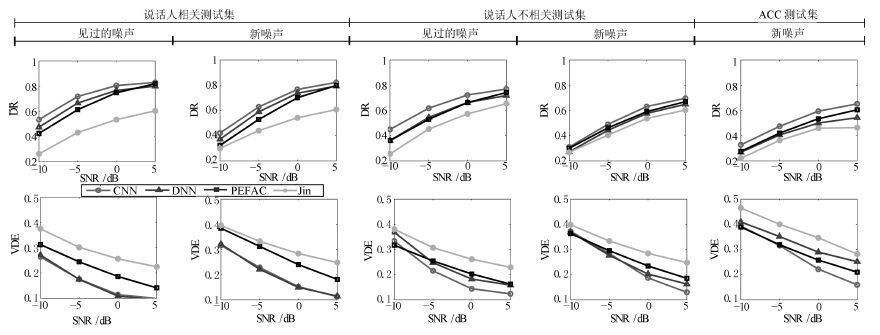
DR VDE SNR -5 0 5 10 -5 0 5 10 说话人相关测试集 见过的噪声 CNN 0.5342 0.7179 0.8049 0.8292 0.264 0.1753 0.114 0.0994 DNN 0.4747 0.6659 0.7664 0.7994 0.2713 0.1746 0.1083 0.0951 PEFAC 0.4248 0.6131 0.7478 0.8187 0.3127 0.2443 0.1862 0.1413 Jin 0.2622 0.4316 0.535 0.6042 0.3751 0.3021 0.2565 0.2244 新噪声 CNN 0.4211 0.6278 0.7671 0.8224 0.3166 0.2287 0.1524 0.1133 DNN 0.372 0.5888 0.7369 0.7934 0.3216 0.2216 0.1499 0.1154 PEFAC 0.3224 0.5291 0.7011 0.7988 0.3844 0.3125 0.2401 0.1815 Jin 0.2998 0.4403 0.542 0.607 0.3954 0.3324 0.2838 0.2484 说话人不相关测试集 见过的噪声 CNN 0.4495 0.6177 0.7228 0.7699 0.3334 0.2156 0.1445 0.1242 DNN 0.3624 0.5449 0.6635 0.7177 0.3685 0.2478 0.1827 0.159 PEFAC 0.3611 0.5302 0.6622 0.7421 0.3172 0.2546 0.203 0.1624 Jin 0.2552 0.4524 0.5731 0.6538 0.3807 0.3074 0.2616 0.2293 新噪声 CNN 0.3097 0.4899 0.6306 0.6961 0.3724 0.284 0.1875 0.1302 DNN 0.2714 0.4427 0.5762 0.6489 0.3689 0.2769 0.2026 0.1633 PEFAC 0.2999 0.4619 0.5902 0.6701 0.3631 0.2953 0.2348 0.1857 Jin 0.268 0.4045 0.5362 0.603 0.3981 0.3339 0.2845 0.2482 ACC测试集 新噪声 CNN 0.3268 0.4739 0.5938 0.6519 0.3931 0.316 0.2222 0.16 DNN 0.2685 0.4053 0.5 0.5425 0.4096 0.3516 0.2896 0.2519 PEFAC 0.2751 0.4201 0.5342 0.6051 0.3893 0.319 0.2583 0.2102 Jin 0.2207 0.3624 0.4592 0.4642 0.4647 0.4002 0.3465 0.2822 -
[1] Kun H, Wang D L. A classification based approach to speech segregation. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2012, 132(5): 3475-3483 [2] Zhao X J, Shao Y, Wang D L. CASA-based robust speaker identification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech,&Language Processing, 2012, 20(5): 1608-1616 [3] Huang F, Lee T. Pitch estimation in noisy speech using accumulated peak spectrum and sparse estimation technique. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech,&Language Processing, 2013, 21(1): 99-109 [4] Rabiner L. On the use of autocorrelation analysis for pitch detection. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech,&Signal Processing, 1977, 25(1): 24-33 [5] Wu M Y, Wang D L, Brown G J. A multipitch tracking algorithm for noisy speech. IEEE Transactions on Speech&Audio Processing, 2003, 11(3): 229-241 [6] Gonzalez S, Brookes M. PEFAC——a pitch estimation algorithm robust to high levels of noise. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech,&Language Processing, 2014, 22(2): 518-530 [7] Zhang H, Zhang X, Nie S, Gao G, Liu W. A pairwise algorithm for pitch estimation and speech separation using deep stacking network. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech&Signal Processing (ICASSP). South Brisbane, QLD: IEEE, 2015. 246-250 [8] Ciresan D, Meier U, Schmidhuber J. Multi-column deep neural networks for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, RI: IEEE, 2012. 3642-3649 [9] Hinton G, Deng L, Yu D, Dahl G E, Mohamed A, Jaitly N, Senior A, Vanhoucke V, Nguyen P, Sainath T N, Kingsbury B. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: the shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82-97 [10] Han K, Wang D L. Neural network based pitch tracking in very noisy speech. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech,&Language Processing, 2014, 22(12): 2158-2168 [11] Kasi K, Zahorian S A. Yet another algorithm for pitch tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Orlando, FL, USA: IEEE, 2002. I-361-I-364 [12] Hu G N. 100 nonspeech sounds[Online], available: http://www.cse.ohio-state.edu/pnl/corpus/HuCorpus.html, April 1, 2006. [13] Giannoulis D, Benetos E, Stowell D, Rossignol M, Lagrange M, Plumbley M D. Detection and classification of acoustic scenes and events: an IEEE AASP challenge. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA). New Paltz, NY: IEEE, 2013. 1-4 [14] Boersma P, Weenink D J M. PRAAT, a system for doing phonetics by computer. Glot International, 2001, 5(9-10): 341-345 [15] Tieleman T, Hinton G. Lecture 6.5——RMSprop. COURSERA: Neural Networks for Machine Learning, 2012. [16] Jin Z Z, Wang D L. Hmm-based multipitch tracking for noisy and reverberant speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech,&Language Processing, 2011, 19(5): 1091-1102 -





 下载:
下载: