-
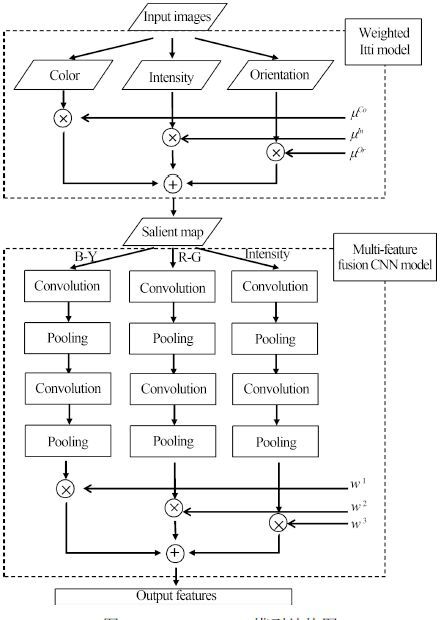
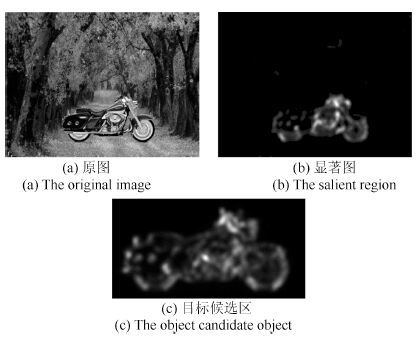
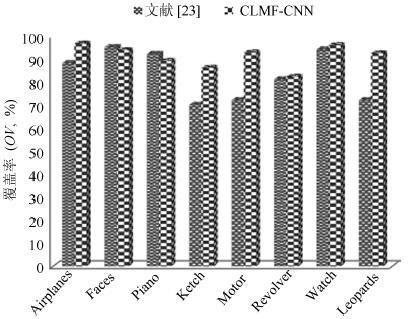
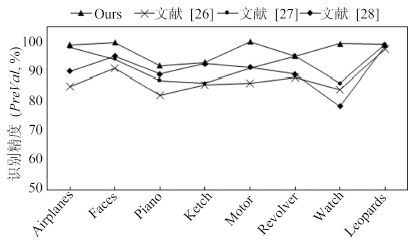
摘要: 针对传统人工特征提取模型难以满足复杂场景下目标识别的需求, 提出了一种基于CLMF的深度卷积神经网络(Convolutional neural networks with candidate location and multi-feature fusion, CLMF-CNN).该模型结合视觉显著性、多特征融合和CNN模型实现目标对象的识别. 首先, 利用加权Itti模型获取目标候选区; 然后, 利用CNN模型从颜色、亮度多特征角度提取目标对象的特征, 经过加权融合供目标识别; 最后, 与单一特征以及目前的流行算法进行对比实验, 结果表明本文模型不仅在同等条件下正确识别率得到了提高, 同时, 达到实时性要求.Abstract: To solve the problem that the traditional manual feature extraction models are unable to satisfy object recognition in complex environment, an object recognition model based on convolutional neural networks with candidate location and multi-feature fusion (CLMF-CNN) model is proposed. The model combines the visual saliency, multi-feature fusion and CNN model to realize the object recognition. Firstly, the candidate objects are conformed via weighted Itti model. Consequently, color and intensity features are obtained via CNN model respectively. After the multi-feature fusion method, the features can be used for object recognition. Finally, the model is tested and compared with the single feature method and current popular algorithms. Experimental result in this paper proves that our method can not only get good performance in improving the accuracy of object recognition, but also satisfy real-time requirements.
-
表 1 本文方法参数设置表
Table 1 Parameters setting of our method
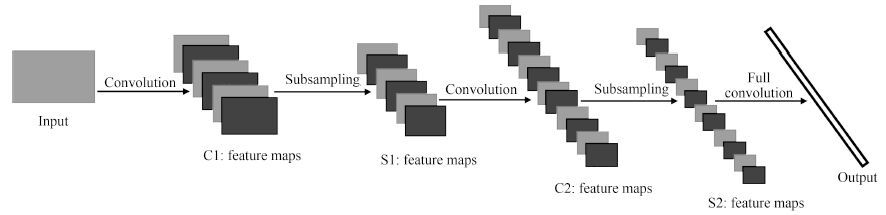
层数 种类 特征图个数 卷积核大小 1 卷积层 100 7£7 2 下采样层 100 2£2 3 卷积层 150 4£4 4 下采样层 150 2£2 5 卷积层 250 4£4 6 下采样层 250 2£2 7 全连接层 300 1£1 8 全连接层 8 1£1 激活函数 Sigmoid 损失函数 Mean square error 表 2 CLMF-CNN模型的图像标注效果
Table 2 The image annotation performance of CLMF-CNN
标识图像 标注信息 
-
[1] Sarikaya R, Hinton G E, Deoras A. Application of deep belief networks for natural language understanding. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, & Language Processing, 2014, 22(4): 778-784 [2] Graves A, Mohamed A R, Hinton G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 38th IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Vancouver, BC: IEEE, 2013. 6645-6649 [3] 刘建伟, 刘媛, 罗雄麟. 深度学习研究进展. 计算机应用研究, 2014, 31(7): 1921-1930Liu Jian-Wei, Liu Yuan, Luo Xiong-Lin. Research and development on deep learning. Application Research of Computers, 2014, 31(7): 1921-1930 [4] Najafabadi M M, Villanustre F, Khoshgoftaar T M, Seliya N, Wald R, Muharemagic E. Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics. Journal of Big Data, 2015, 2: 1 [5] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324 [6] LeCun Y, Boser B, Denker J S, Henderson D, Howard R E, Hubbard W, Jackel L D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(4): 541-551 [7] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25. Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA: Curran Associates, Inc., 2012. 2012-2020 [8] 王欣, 唐俊, 王年. 基于双层卷积神经网络的步态识别算法. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(1): 32-36Wang Xin, Tang Jun, Wang Nian. Gait recognition based on double-layer convolutional neural networks. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 39(1): 32-36 [9] Ouyang W, Wang X. Joint deep learning for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 2056-2063 [10] Ji S W, Xu W, Yang M, Yu K. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 221-231 [11] 徐姗姗, 刘应安, 徐昇. 基于卷积神经网络的木材缺陷识别. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(2): 23-28Xu Shan-Shan, Liu Ying-An, Xu Sheng. Wood defects recognition based on the convolutional neural network. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2013, 43(2): 23-28 [12] 贾世杰, 杨东坡, 刘金环. 基于卷积神经网络的商品图像精细分类. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 33(6): 91-96Jia Shi-Jie, Yang Dong-Po, Liu Jin-Huan. Product image fine-grained classification based on convolutional neural network. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2014, 33(6): 91-96 [13] Unuma H, Hasegawa H. Visual attention and object perception: levels of visual features and perceptual representation. Journal of Kawamura Gakuen Womans University, 2007, 18: 47-60 [14] Serre T, Wolf L, Poggio T. Object recognition with features inspired by visual cortex. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Diego, CA: IEEE, 2005. 994-1000 [15] Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254-1259 [16] 姚原青, 李峰, 周书仁. 基于颜色——纹理特征的目标跟踪. 计算机工程与科学, 2014, 36(8): 1581-1587Yao Yuan-Qing, Li Feng, Zhou Shu-Ren. Target tracking based on color and the texture feature. Computer Engineering & Science, 2014, 36(8): 1581-1587 [17] LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-44 [18] Huang F J, LeCun Y. Large-scale learning with SVM and convolutional for generic object categorization. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 284-291 [19] Scherer D, Müller A, Behnke S. Evaluation of pooling operations in convolutional architectures for object recognition. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Thessaloniki, Greece: Springer, 2010. 92-101 [20] Serences J T, Yantis S. Selective visual attention and perceptual coherence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2006, 10(1): 38-45 [21] 黎万义, 王鹏, 乔红. 引入视觉注意机制的目标跟踪方法综述. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(4): 561-576Li Wan-Yi, Wang Peng, Qiao Hong. A survey of visual attention based methods for object tracking. Acta Automatica Siinica, 2014, 40(4): 561-576 [22] Maljkovic V, Nakayama K. Priming of pop-out: I. role of features. Memory & Cognition, 1994, 22(6): 657-672 [23] Roos M J, Wolmetz M, Chevillet M A. A hierarchical model of vision (HMAX) can also recognize speech. BMC Neuroscience, 2014, 15(Suppl 1): 187 [24] Li P H, Chaumette F. Image cues fusion for object tracking based on particle filter. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects. Palma de Mallorca, Spain: Springer, 2004. 99-110 [25] Wang X, Tang Z M. Modified particle filter-based infrared pedestrian tracking. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2010, 53(4): 280-287 [26] 朱庆生, 张敏, 柳锋. 基于HMAX特征的层次式柑桔溃疡病识别方法. 计算机科学, 2008, 35(4): 231-232Zhu Qing-Sheng, Zhang Min, Liu Feng. Hierarchical citrus canker recognition based on HMAX features. Computer Science, 2008, 35(4): 231-232 [27] 汤毓婧. 基于人脑视觉感知机理的分类与识别研究[硕士学位论文], 南京理工大学, 中国, 2009.Tang Yu-Jing. Classification and Recognition Research based on Human Visual Perception Mechanism[Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China, 2009. [28] Wang J, Yang J, Yu K, Lv F, Huang T, Gong Y. Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, CA: IEEE, 2010. 3360-3367 [29] 张小利, 李雄飞, 李军. 融合图像质量评价指标的相关性分析及性能评估. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(2): 306-315Zhang Xiao-Li, Li Xiong-Fei, Li Jun. Validation and correlation analysis of metrics for evaluating performance of image fusion. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(2): 306-315 [30] 杨波, 敬忠良. 梅花形采样离散小波框架图像融合算法. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(1): 12-22Yang Bo, Jing Zhong-Liang. Image fusion algorithm based on the quincunx-sampled discrete wavelet frame. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(1): 12-22 -




 下载:
下载: