-
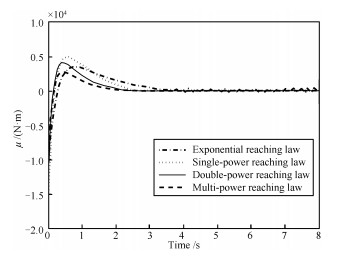
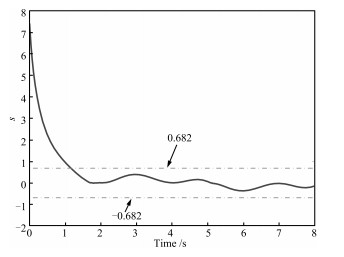
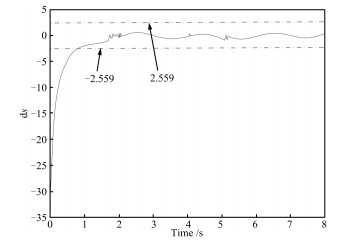
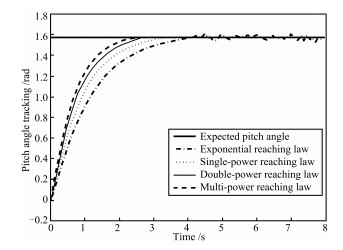
摘要: 针对传统滑模趋近律使系统存在抖振现象、收敛速度较慢及动态响应不平滑等问题, 提出一种多幂次滑模趋近律.该趋近律通过三个幂次项系数在系统趋近过程不同阶段进行针对性地调节, 使系统动态响应过程的收敛速度大幅度提高, 且无抖振现象.理论验证了其存在性、可达性及稳定性, 并详细推导了趋近速率及干扰稳定界.以航天器姿态机动控制系统为例, 对比仿真结果表明该趋近律下, 系统的动态过程有较大改善并消除了抖振, 且在存在模型不确定性及外加干扰作用下, 系统仍可较快地收敛到平衡点附近的邻域内.Abstract: A multi power reaching law of sliding mode control is proposed in this paper, which aims at reducing chattering phenomenon, fastening convergence speed and making dynamic process smoothly. The proposed reaching law has three exponential terms to adjust the convergence process, so that the system has a faster convergence speed obviously and no chattering phenomenon. It is indicated through theoretical analysis that the system under the proposed reaching law has existence, accessibility and stability. The convergence speed and interference stability boundary are deduced in detail. Simulation results show that the dynamic process is improved and the chattering is reduced, as compared with the exponential reaching law, single power reaching law and double power reaching law. Furthermore, when there exists interference or uncertainty, the system can converge to a neighborhood of the origin quickly.
-
表 1 各趋近律仿真参数
Table 1 Simulation parameters of every reaching law
a b c d ka=0.9 kb=0.7 kc1=0.7 k1=0.7 εa=0.5 αb=1.1 kc2=0.9 k2=0.9 αc=1.1 k3=1.1 βc=0.8 k4=1.4 α=1.7 β=0.5 -
[1] Shtessel Y B, Shkolnikov I A, Levant A. Smooth second-order sliding modes:missile guidance application. Automatica, 2007, 43(8):1470-1476 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2007.01.008 [2] Gao W B, Hung J C. Variable structure control of nonlinear systems:a new approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1993, 40(1):45-55 doi: 10.1109/41.184820 [3] 李雪冰, 马莉, 丁世宏.一类新的二阶滑模控制方法及其在倒立摆控制中的应用.自动化学报, 2015, 41(1):193-202 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18598.shtmlLi Xue-Bing, Ma Li, Ding Shi-Hong. A new second-order sliding mode control and its application to inverted pendulum. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(1):193-202 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18598.shtml [4] Moulay E, Perruquetti W. Finite time stability conditions for non-autonomous continuous systems. International Journal of Control, 2008, 81(5):797-803 doi: 10.1080/00207170701650303 [5] Lian R J. Adaptive self-organizing fuzzy sliding-mode radial basis-function neural-network controller for robotic systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(3):1493-1503 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2258299 [6] Tsai C H, Chung H Y, Yu F M. Neuro-sliding mode control with its applications to seesaw systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2004, 15(1):124-134 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2003.811560 [7] Wu J C, Liu T S. A sliding-mode approach to fuzzy control design. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1996, 4(2):141-151 doi: 10.1109/87.486340 [8] 高为炳.变结构控制的理论及设计方法.北京:科学出版社, 1996. 241-254Gao Wei-Bing. Theory and Design Method for Variable Sliding Mode Control. Beijing:Science Press, 1996. 241-254 [9] Yu S H, Yu X H, Shirinzadeh B, Man Z H. Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode. Automatica, 2005, 41(11):1957-1964 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2005.07.001 [10] Bandyopadhyay B, Fulwani D, Park Y J. A robust algorithm against actuator saturation using integral sliding mode and composite nonlinear feedback. In:Proceedings of the 17th IFAC World Congress. COEX, Korea, South:IFAC, 2008. 14174-14179 [11] 梅红, 王勇.快速收敛的机器人滑模变结构控制.信息与控制, 2009, 38(5):552-557 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYK200905008.htmMei Hong, Wang Yong. Fast convergent sliding mode variable structure control of robot. Information and Control, 2009, 38(5):552-557 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYK200905008.htm [12] 张合新, 范金锁, 孟飞, 黄金峰.一种新型滑模控制双幂次趋近律.控制与决策, 2009, 38(5):289-293 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201302024.htmZhang He-Xin, Fan Jin-Suo, Meng Fei, Huang Jin-Feng. A new double power reaching law for sliding mode control. Control and Decision, 2013, 28(2):289-293 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201302024.htm [13] Fallaha C J, Saad M, Kanaan H Y, Al-Haddad K. Sliding-mode robot control with exponential reaching law. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(2):600-610 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2045995 [14] Niu Y, Ho D W C, Wang Z. Improved sliding mode control for discrete-time systems via reaching law. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2010, 4(11):2245-2251 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2009.0296 [15] Jerouane M, Sepehri N, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F. Dynamic analysis of variable structure force control of hydraulic actuators via the reaching law approach. International Journal of Control, 2004, 77(14):1260-1268 doi: 10.1080/00207170412331305579 [16] Utkin V I. Variable structure systems with sliding modes. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1977, 22(2):212-222 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1977.1101446 [17] 刘连福.一类一阶微分方程的通解及应用.黄石理工学院学报, 2011, 27(4):41-42 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSGD201104011.htmLiu Lian-Fu. Application and ordinary solution of a kind of first order differential equation. Journal of Huangshi Institute of Technology, 2011, 27(4):41-42 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSGD201104011.htm [18] Bhat S P, Bernstein D S. Continuous finite-time stabilization of the translational and rotational double integrators. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1998, 43(5):678-682 doi: 10.1109/9.668834 [19] Zhao Y X, Wu T, Li G. A second-order sliding mode controller design for spacecraft tracking control. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2013, 2013:Article ID 429101 -




 下载:
下载: