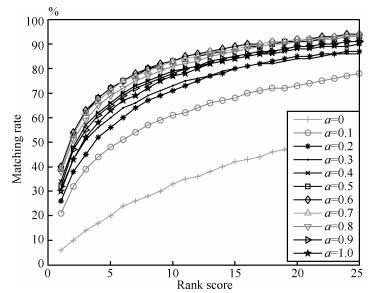
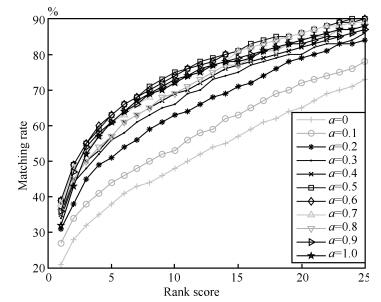
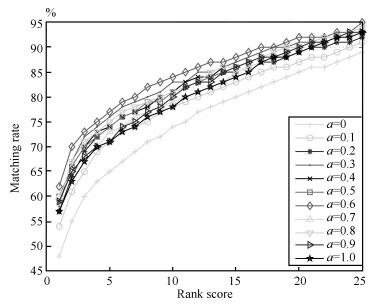
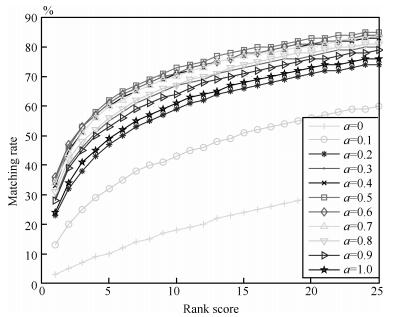
-
摘要: 行人再识别指的是在无重叠视域多摄像机监控系统中, 匹配不同摄像机视域中的行人目标.针对当前基于距离测度学习的行人再识别算法中存在着特征提取复杂、训练过程复杂和识别效果差的问题, 我们提出一种基于多特征子空间与核学习的行人再识别算法.该算法首先在不同特征子空间中基于核学习的方法得到不同特征子空间中的测度矩阵以及相应的相似度函数, 然后通过比较不同特征子空间中的相似度之和来对行人进行识别.实验结果表明, 本文提出的算法具有较高的识别率, 其中在VIPeR数据集上, RANK1达到了40.7%, 且对光照变化、行人姿态变化、视角变化和遮挡都具有很好的鲁棒性.Abstract: Person re-identification is to match pedestrian images observed from different camera views of non-overlapping multi-camera surveillance systems. The current person re-identification based on metric learning is complicated for feature extraction and training process, and has low performance. Therefore, we propose a multi-feature subspace and kernel learning based method for person re-identification. The distance metric and similarity functions can be achieved firstly in different feature subspaces by kernel learning. Then, the object can be recognized by comparing the sum of similarity of different feature subspaces. Experimental results show that the proposed method has a higher accuracy rate, achieving a 40.7% rank-1 recognition rate on the VIPeR benchmark and that it is robust to different viewpoints, illumination changes, varying poses and the effects of occlusion.
-
Key words:
- Person re-identification /
- feature space /
- metric learning /
- kernel learning
-
表 1 本文算法基于不同核函数在VIPeR数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 1 Mathing rates (%) of the proposed algorithm based on different kernel functions on the VIPeR dataset
Kernel Rank1 (%) Rank5 (%) Rank10 (%) Rank20 (%) linear 25.1 53.4 67.3 80.1 $\chi ^{2}$ 38.2 70.0 82.5 91.3 RBF- $\chi ^{2}$ 40.7 72.37 83.95 92.08 表 2 不同算法在VIPeR数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 2 Mathing rates (%) of different methods on the VIPeR dataset
Methods Rank1 (%) Rank5 (%) Rank10 (%) Rank20 (%) PCCA[14] 19.6 51.5 68.2 82.9 LFDA[27] 19.7 46.7 62.1 77.0 SVMML[28] 27.0 60.9 75.4 87.3 KISSME[13] 23.8 54.8 71.0 85.3 文献[12] 29.7 59.8 73.0 84.1 rPCCA[20] 22.0 54.8 71.0 85.3 kLFDA[20] 32.3 65.8 79.7 90.9 MFA[20] 32.2 66.0 79.7 90.6 RDC[29] 15.66 38.42 53.86 70.09 eSDC_knn[10] 26.31 46.61 58.86 72.77 eSDC_ocsvm[10] 26.74 50.70 62.37 76.36 Ours 40.7 72.37 83.95 92.08 表 3 不同算法在VIPeR数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 3 Mathing rates (%) of different methods on the VIPeR dataset
表 4 当 $P=432$ , 不同算法在VIPeR数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 4 Mathing rates (%) of different methods at $P=432$ on the VIPeR dataset
表 5 当 $P=532$ , 不同算法在VIPeR数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 5 Mathing rates (%) of different methods at $P=532$ on the VIPeR dataset
表 6 不同算法在iLIDS数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 6 Mathing rates (%) of different methods on the iLIDS dataset
表 7 不同算法在ETHZ数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 7 Mathing rates (%) of different methods on the ETHZ dataset
表 8 不同算法在CUHK01数据集上的识别率 (%)
Table 8 Mathing rates (%) of different methods on the CUHK01 dataset
Methods Rank1 (%) Rank5 (%) Rank10 (%) Rank20 (%) KISSME[13] 12.5 31.5 42.5 54.9 PCCA[14] 17.8 42.4 55.9 69.1 LFDA[27] 13.3 31.1 42.2 54.3 SVMML[28] 18.0 42.3 55.4 68.8 rPCCA[20] 21.6 47.4 59.8 72.6 kLFDA[20] 29.1 55.2 66.4 77.3 MFA[20] 29.6 55.8 66.4 77.3 MidLevel[26] 34.30 55.74 64.52 74.97 Ours 36.10 62.68 72.61 81.90 表 9 特征核映射前后在VIPeR实验集上的对比效果
Table 9 Performance comparison between before and after the kernel map on the VIPeR dataset
Kernel Rank1 (%) Rank5 (%) Rank10 (%) Rank20 (%) Before 25.66 53.43 67.4 80.5 After 40.7 72.37 83.95 92.08 表 10 特征核映射前后在iLIDS实验集上的对比效果
Table 10 Performance comparison between before and after the kernel map on the iLIDS dataset
Kernel Rank1 (%) Rank5 (%) Rank10 (%) Rank20 (%) Before 30.4 56.4 67.4 78.3 After 38.3 66.5 79.0 88.3 表 11 特征核映射前后在ETHZ实验集上的对比效果
Table 11 Performance comparison between before and after the kernel map on the ETHZ dataset
Kernel Rank1 (%) Rank5 (%) Rank10 (%) Rank20 (%) Before 57.0 72.97 81.5 90.4 After 61.09 74.77 81.96 91.76 表 12 特征核映射前后在CUHK01实验集上的对比效果
Table 12 Performance comparison between before and after the kernel map on the CUHK01 dataset
Kernel Rank1 (%) Rank5 (%) Rank10 (%) Rank20 (%) Before 17.92 38.10 48.0 58.84 After 36.10 62.68 72.61 81.90 -
[1] Swain M J, Ballard D H. Indexing via color histograms. In:Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision. Osaka, Japan:IEEE, 1990. 390-393 [2] Gray D, Brennan S, Tao H. Evaluating appearance models for recognition, reacquisition, and tracking. In:Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil:IEEE, 2007. 41-47 [3] Farenzena M, Bazzani L, Perina A, Murino V, Cristani M. Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In:Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, USA:IEEE, 2010. 2360-2367 [4] Ma B P, Su Y, Jurie F. BiCov:a novel image representation for person re-identification and face verification. In:Proceedings of the 23rd British Machine Vision Conference. Surrey, UK:IEEE, 2012. 1-6 [5] Cheng D S, Cristani M, Stoppa M, Bazzani L, Murino V. Custom pictorial structures for re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 22nd British Machine Vision Conference. Dundee, UK:IEEE, 2011. 749-760 [6] Liu C X, Gong S G, Loy C C, Lin X G. Person re-identification:what features are important? In:Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision. Florence, Italy:IEEE, 2012. 391-401 [7] Wang X G, Doretto G, Sebastian T, Rittscher J, Tu P. Shape and appearance context modeling. In:Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Vision. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil:IEEE, 2007. 1-8 [8] Li W, Zhao R, Xiao T, Wang X G. DeepReID:deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, USA:IEEE, 2014. 152-159 [9] Ahmed E, Jones M, Marks T K. An improved deep learning architecture for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA:IEEE, 2015. 3908-3916 [10] Zhao R, Ouyang W L, Wang X G. Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Portland, USA:IEEE, 2013. 3586-3593 [11] Zheng W S, Gong S G, Xiang T. Person re-identification by probabilistic relative distance comparison. In:Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Colorado Springs, USA:IEEE, 2011. 649-656 [12] 杜宇宁, 艾海舟.基于统计推断的行人再识别算法.电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(7):1612-1618 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201407015.htmDu Yu-Ning, Ai Hai-Zhou. A statistical inference approach for person re-identification. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2014, 36(7):1612-1618 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201407015.htm [13] Kostinger M, Hirzer M, Wohlhart P, Roth P M, Bischof H. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, Rhode island, USA:IEEE, 2012. 2288-2295 [14] Mignon A, Jurie F. Pcca:a new approach for distance learning from sparse pairwise constraints. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, Rhode island, USA:IEEE, 2012. 2666-2672 [15] Dikmen M, Akbas E, Huang T S, Ahuja N. Pedestrian recognition with a learned metric. In:Proceedings of the 10th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Queenstown, New Zealand:Springer-Verlag, 2010, 6495:501-512 [16] Hirzer M, Roth P M, Köstinger M, Bischof H. Relaxed pairwise learned metric for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision. Florence, Italy:Springer-Verlag, 2012, 7577:780-793 [17] Prosser B, Zheng W S, Gong S G, Xiang T. Person re-identification by support vector ranking. In:Proceedings of the 22th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC). Aberystwyth, UK:IEEE, 2010. 1-11 [18] Li W, Zhao R, Wang X G. Human re-identification with transferred metric learning. In:Proceedings of the 11th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Daejeon, Korea:Springer-Verlag, 2012, 7724:31-44 [19] Loy C C, Liu C X, Gong S G. Person re-identification by manifold ranking. In:Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Melbourne, VIC, Australia:IEEE, 2013. 3567-3571 [20] Xiong F, Gou M R, Camps O, Sznaier M. Person re-identification using kernel-based metric learning methods. In:Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland:Springer-Verlag, 2014, 8695:1-16 [21] Gevers T, Smeulders A W M. Color-based object recognition. Pattern Recognition, 1999, 32(3):453-464 doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(98)00036-3 [22] Du Y N, Ai H Z, Lao S H. Evaluation of color spaces for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Tsukuba, Japan:IEEE, 2012. 1371-1374 [23] Gray D, Tao H. Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In:Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision. Marseille, France:Springer-Verlag, 2008, 5302:262-275 [24] Zheng W S, Gong S G, Xiang T. Associating groups of people. In:Proceedings of the 20th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC). London, UK:IEEE, 2009. 1-11 [25] Zhou T F, Qi M B, Jiang J G, Wang X, Hao S J, Jin Y L. Person re-identification based on nonlinear ranking with difference vectors. Information Sciences, 2014, 279:604-614 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.04.014 [26] Zhao R, Ouyang W L, Wang X G. Learning mid-level filters for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, USA:IEEE, 2014. 144-151 [27] Pedagadi S, Orwell J, Velastin S, Boghossian B. Local fisher discriminant analysis for pedestrian re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Portland, USA:IEEE, 2013. 3318-3325 [28] Li Z, Chang S Y, Liang F, Huang T S, Cao L L, Smith J R. Learning locally adaptive decision functions for person verification. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Portland, USA:IEEE, 2013. 3610-3617 [29] Zheng W S, Gong S G, Xiang T. Re-identification by relative distance comparison. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(3):653-668 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.138 [30] Davis J V, Kulis B, Jain P. Information-theoretic metric learning. In:Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning. Corvallis, USA:IEEE, 2007. 209-216 [31] Liu H, Qi M B, Jiang J G. Kernelized relaxed margin components analysis for person re-identification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(7):910-914 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2377204 [32] Weinberger K Q, Saul L K. Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2009, 10(2):207-244 -





 下载:
下载: