Wafer Defect Detection and Recognition Based on Local and Nonlocal Linear Discriminant Analysis and Dynamic Ensemble of Gaussian Mixture Models
-
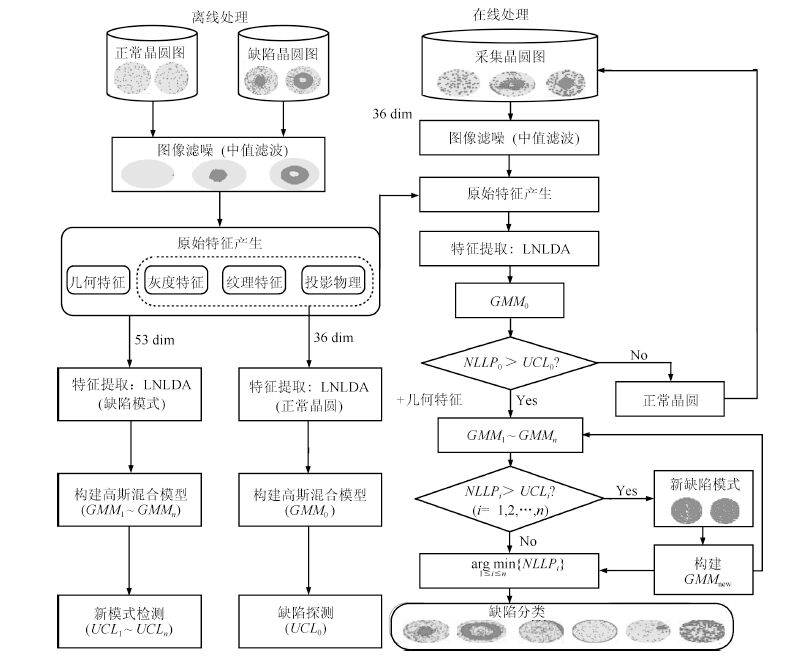
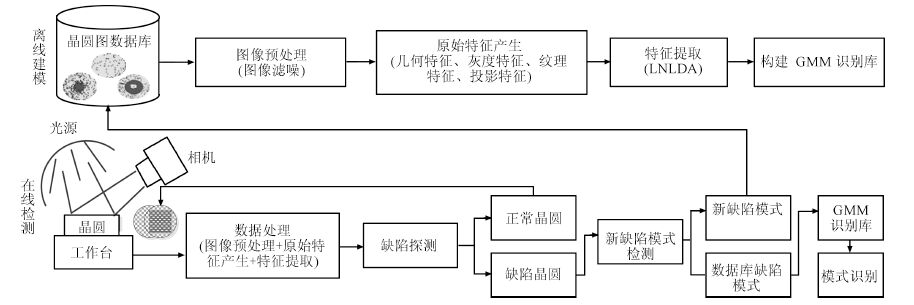
摘要: 在复杂的半导体制造过程中,晶圆生产经过薄膜沉积、蚀刻、抛光等多项复杂的工序,制造过程中的异常波动都可能导致晶圆缺陷产生.晶圆表面的缺陷模式通常反映了半导体制造过程的各种异常问题,生产线上通过探测和识别晶圆表面缺陷,可及时判断制造过程故障源并进行在线调整,降低晶圆成品率损失.本文提出了基于一种流形学习算法与高斯混合模型动态集成的晶圆表面缺陷在线探测与识别模型.首先该模型开发了一种新型流形学习算法——局部与非局部线性判别分析法(Local and nonlocal linear discriminant analysis, LNLDA),通过融合数据局部/非局部信息以及局部/非局部惩罚信息,有效地提取高维晶圆特征数据的内在流形结构信息,以最大化数据不同簇样本的低维映射距离,保持特征数据中相同簇的低维几何结构.针对线上晶圆缺陷产生的随机性和复杂性,该模型对每种晶圆缺陷模式构建相应的高斯混合模型(Gaussian mixture model, GMM),提出了基于高斯混合模型动态集成的晶圆缺陷在线探测与识别方法.本文提出的模型成功地应用到实际半导体制造过程的晶圆表面缺陷在线探测与识别,在WM-811K晶圆数据库的实验结果验证了该模型的有效性与实用性.Abstract: The manufacturing process of wafers is very complicated, which involves thin film deposition, chemical mechanical polishing, etching, etc. Abnormal variation in the manufacturing processes could result in the generation of defect patterns on wafers. On the other hand, the defect patterns on the wafer usually indicate the abnormal sources existing in the manufacturing process. Therefore, wafer defect recognition plays a key role in finding the root causes of the out-of-control process and improving yield. This paper develops a model for wafer defect detection and recognition based on manifold learning and dynamic ensemble of Gaussian mixture models(GMMs). A new manifold learning algorithm called local and nonlocal linear discriminant analysis(LNLDA) is developed, which aims to preserve the geometric structure of samples that belong to the identical cluster in the low dimensional space while maximizing the distance of the projected samples from different clusters. Due to the randomness and complexity of wafer defect generation, a dynamic ensemble scheme for GMMs is proposed to detect and recognize various defect patterns occurring in wafers. The proposed model is applied to a real-world semiconductor manufacturing process. Experimental results on WM-811K wafer bin map database approve the effectiveness of the proposed model.
-
表 1 晶圆缺陷特征集
Table 1 Features of defect wafer pattern
特征类别 特征集 几何特征 区域特征、线性特征、Hu不变矩 灰度特征 平均值、方差、歪斜度、峰值、能量、熵 纹理特征 能量、对比度、相关性、均匀度、熵 投影特征 峰值、平均幅值、均方根幅值、投影波形特征
投影峰值、投影脉冲表 2 基于各种投影算法的1NN最佳识别率(%)及相应输入维度
Table 2 Best recognition rate(%) of 1NN and subspace dimensionality based on the five data projection algorithms
Algorithm train:test=2:1 train:test=1:1 train:test=1:2 Baseline 66.60 (53) 63.71 (53) 62.38 (53) PCA 66.81 (11) 63.71 (14) 62.49 (12) LDA 56.75 (3) 57.57 (21) 64.20 (3) LPP 80.51 (24) 77.71 (30) 77.06 (29) LFDA 77.94 (6) 80.29 (5) 79.42 (5) LNLDA 85.44 (6) 84.71 (10) 84.46 (10) 表 3 晶圆缺陷探测率(%)
Table 3 The defect detection rate (%)
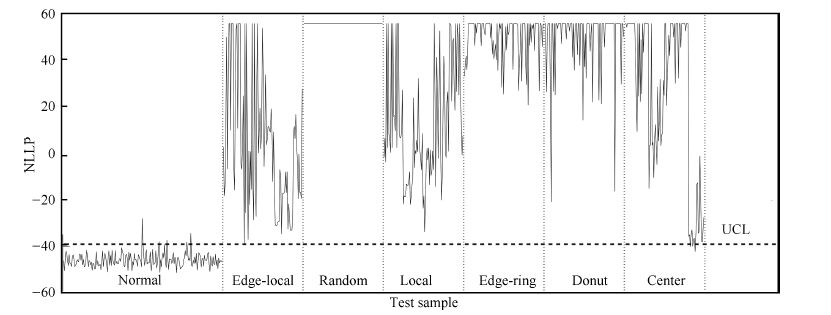
缺陷模式 Center Donut Edge-ring Edge-local Random Local 缺陷探测率 97.0 100 100 99.0 100 100 表 4 两套特征集对应的晶圆缺陷识别率(%)
Table 4 The recognition rate based on two different feature sets (%)
缺陷模式 特征集A 特征集B Center 86 87 Donut 86 87 Edge-ring 100 100 Local 65 76 Random 92 93 Edge-local 67 75 Average 84.0 87.5 表 5 晶圆缺陷模式识别率(%)
Table 5 The recognition rate of different defect patterns (%)
缺陷模式 Center Donut Edge-ring Local Random Edge-local Center 87 0 0 12 0 1 Donut 0 94 0 6 0 0 Edge-ring 0 0 100 0 0 0 Local 8 3 0 76 0 13 Random 0 2 0 2 93 3 Edge-local 67 75 9 14 1 75 表 6 各种分类器的晶圆缺陷识别率比较(%)
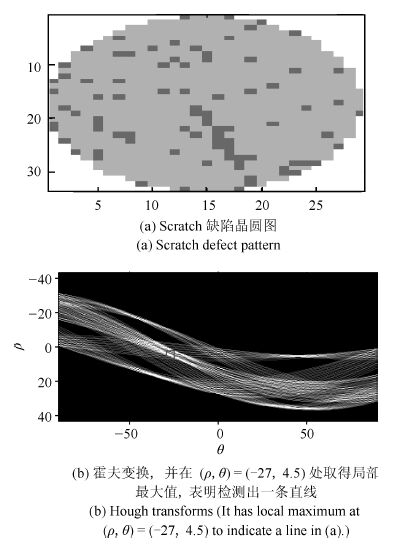
Table 6 Comparison of recognition rates of the five classifiers (%)
分类器 GMM KNN SVM BPN C4.5 Center 87 92 97 95 93 Donut 94 98 100 98 96 Edge-ring 100 100 100 100 100 Local 76 69 68 56 65 Random 93 93 92 94 94 Edge-local 75 66 66 78 56 Average 87.50 86.33 87.17 86.83 84.0 -
[1] Wang C H. Recognition of semiconductor defect patterns using spatial filtering and spectral clustering. Expert Systems with Applications, 2008, 34(3):1914-1923 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2007.02.014 [2] Hess C, Weiland L H. Extraction of wafer-level defect density distributions to improve yield prediction. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 1999, 12(2):175-183 doi: 10.1109/66.762875 [3] Friedman D J, Hansen M H, Nair V N, James D A. Model-free estimation of defect clustering in integrated circuit fabrication. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 1997, 10(3):344-359 doi: 10.1109/66.618208 [4] Chen F L, Liu S F. A neural-network approach to recognize defect spatial pattern in semiconductor fabrication. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 2000, 13(3):366-373 doi: 10.1109/66.857947 [5] Baly R, Hajj H. Wafer classification using support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 2012, 25(3):373-383 doi: 10.1109/TSM.2012.2196058 [6] Wu M J, Jang J S R, Chen J L. Wafer map failure pattern recognition and similarity ranking for large-scale data sets. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 2015, 28(1):1-12 doi: 10.1109/TSM.2014.2364237 [7] Chen S H, Perng D B. Directional textures auto-inspection using principal component analysis. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2011, 55(9-12):1099-1110 doi: 10.1007/s00170-010-3141-1 [8] Tsai D M, Lai S C. Defect detection in periodically patterned surfaces using independent component analysis. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(9):2812-2832 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2008.02.011 [9] 闫德勤, 刘胜蓝, 李燕燕. 一种基于稀疏嵌入分析的降维方法. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(11):1306-1312 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17622.shtmlYan De-Qin, Liu Sheng-Lan, Li Yan-Yan. An embedding dimension reduction algorithm based on sparse analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(11):1306-1312 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17622.shtml [10] Tenenbaum J B, de Silva V, Langford J C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science, 2000, 290(5500):2319-2323 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2319 [11] Roweis S T, Saul L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science, 2000, 290(5500):2323-2326 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2323 [12] He X F, Niyogi X. Locality preserving projections. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2004, 16:153-160 http://www.docin.com/p-779500788.html [13] Yu J B. Local and nonlocal preserving projection for bearing defect classification and performance assessment. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(5):2363-2376 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2167893 [14] Wang C H, Kuo W, Bensmail H. Detection and classification of defect patterns on semiconductor wafers. IIE Transactions, 2006, 38(12):1059-1068 doi: 10.1080/07408170600733236 [15] Byers S, Raftery A E. Nearest-neighbor clutter removal for estimating features in spatial point processes. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1998, 93(442):577-584 doi: 10.1080/01621459.1998.10473711 [16] White Jr K P, Kundu B, Mastrangelo C M. Classification of defect clusters on semiconductor wafers via the Hough transformation. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 2008, 21(2):272-278 doi: 10.1109/TSM.2008.2000269 [17] Schwarz G. Estimating the dimension of a model. The Annals of Statistics, 1978, 6(2):461-464 doi: 10.1214/aos/1176344136 [18] Dempster A P, Laird N M, Rubin D B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 1977, 39(1):1-38 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.133.4884 [19] 郑建炜, 王万良, 姚晓敏, 石海燕. 张量局部 Fisher 判别分析的人脸识别. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(9):1485-1495 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01485Zhang Jian-Wei, Wang Wan-Liang, Yao Xiao-Ming, Shi Hai-Yan. Face recognition using tensor local Fisher discriminant analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(9):1485-1495 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01485 [20] Chang C C, Lin C J. LIBSVM:a library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology(TIST), 2011, 2(3):27 https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/ -




 下载:
下载: